当前位置:网站首页>Attributes of classfile
Attributes of classfile
2022-07-02 09:19:00 【kq1983】
Attributes
Attributes are used in the ClassFile, field_info, method_info, and Code_attribute structures of the class file format ( §4.1, §4.5, §4.6, §4.7.3).
All attributes have the following general format:
attribute_info {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u1 info[attribute_length];
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
For all attributes, the attribute_name_index must be a valid unsigned 16-bit index into the constant pool of the class. The constant_pool entry at attribute_name_index must be a CONSTANT_Utf8_info structure ( §4.4.7) representing the name of the attribute. The value of theattribute_length item indicates the length of the subsequent information in bytes. The length does not include the initial six bytes that contain the attribute_name_index and attribute_length items.
23 attributes are predefined by this specification. They are listed three times, for ease of navigation:
- Table 4.7-A is ordered by the attributes' section numbers in this chapter. Each attribute is accompanied by the first version of the
class file format in which it was defined, and the corresponding version of the Java SE platform. (For old class file versions, the JDK release is used instead of the Java SE platform version). - Table 4.7-B is orderd by the first version of the
class file format in which each attribute was defined. - Table 4.7-C is ordered by the location in a
class file where each attribute is defined to appear.
Within the context of their use in this specification, that is, in the attributes tables of the class file structures in which they appear, the names of these predefined attributes are reserved.
Any conditions on the presence of a predefined attribute in an attributes table are specified explicitly in the section which describes the attribute. If no conditions are specified, then the attribute may appear any number of times in an attributes table.
The predefined attributes are categorized into three groups according to their purpose:
- Five attributes are critical to correct interpretation of the
class file by the Java Virtual Machine: - In a
class file of version V, each of these attributes must be recognized and correctly read by an implementation of the Java Virtual Machine if the implementation recognizes class files of version V, and V is at least the version where the attribute was first defined, and the attribute appears in a location where it is defined to appear.
ConstantValue
Code
StackMapTable
Exceptions
BootstrapMethods
- Twelve attributes are critical to correct interpretation of the
class file by the class libraries of the Java SE platform: - Each of these attributes in a
class file of version V must be recognized and correctly read by an implementation of the class libraries of the Java SE platform if the implementation recognizes class files of version V, and V is at least the version where the attribute was first defined, and the attribute appears in a location where it is defined to appear.
InnerClasses
EnclosingMethod
Synthetic
Signature
RuntimeVisibleAnnotations
RuntimeInvisibleAnnotations
RuntimeVisibleParameterAnnotations
RuntimeInvisibleParameterAnnotations
RuntimeVisibleTypeAnnotations
RuntimeInvisibleTypeAnnotations
AnnotationDefault
MethodParameters
- Six attributes are not critical to correct interpretation of the
class file by either the Java Virtual Machine or the class libraries of the Java SE platform, but are useful for tools: - Use of these attributes by an implementation of the Java Virtual Machine or the class libraries of the Java SE platform is optional. An implementation may use the information that these attributes contain, or otherwise must silently ignore these attributes.
SourceFile
SourceDebugExtension
LineNumberTable
LocalVariableTable
LocalVariableTypeTable
Deprecated
Table 4.7-A. Predefined class file attributes (by section)
Attribute | Section | | Java SE |
| §4.7.2 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.3 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.4 | 50.0 | 6 |
| §4.7.5 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.6 | 45.3 | 1.1 |
| §4.7.7 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.8 | 45.3 | 1.1 |
| §4.7.9 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.10 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.11 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.12 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.13 | 45.3 | 1.0.2 |
| §4.7.14 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.15 | 45.3 | 1.1 |
| §4.7.16 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.17 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.18 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.19 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.20 | 52.0 | 8 |
| §4.7.21 | 52.0 | 8 |
| §4.7.22 | 49.0 | 5.0 |
| §4.7.23 | 51.0 | 7 |
| §4.7.24 | 52.0 | 8 |
Table 4.7-B. Predefined class file attributes (by class file version)
Attribute | | Java SE | Section |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.2 |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.3 |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.5 |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.10 |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.12 |
| 45.3 | 1.0.2 | §4.7.13 |
| 45.3 | 1.1 | §4.7.6 |
| 45.3 | 1.1 | §4.7.8 |
| 45.3 | 1.1 | §4.7.15 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.7 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.9 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.11 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.14 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.16 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.17 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.18 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.19 |
| 49.0 | 5.0 | §4.7.22 |
| 50.0 | 6 | §4.7.4 |
| 51.0 | 7 | §4.7.23 |
| 52.0 | 8 | §4.7.20 |
| 52.0 | 8 | §4.7.21 |
| 52.0 | 8 | §4.7.24 |
Table 4.7-C. Predefined class file attributes (by location)
Attribute | Location | |
| | 45.3 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 51.0 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 52.0 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 49.0 |
| | 50.0 |
| | 52.0 |
4.7.1. Defining and Naming New Attributes
Compilers are permitted to define and emit class files containing new attributes in the attributes tables of class file structures, field_info structures, method_info structures, and Code attributes ( §4.7.3). Java Virtual Machine implementations are permitted to recognize and use new attributes found in these attributes tables. However, any attribute not defined as part of the class file specification must not affect the semantics of the class file. Java Virtual Machine implementations are required to silently ignore attributes they do not recognize.
For instance, defining a new attribute to support vendor-specific debugging is permitted. Because Java Virtual Machine implementations are required to ignore attributes they do not recognize, class files intended for that particular Java Virtual Machine implementation will be usable by other implementations even if those implementations cannot make use of the additional debugging information that the class files contain.
Java Virtual Machine implementations are specifically prohibited from throwing an exception or otherwise refusing to use class files simply because of the presence of some new attribute. Of course, tools operating on class files may not run correctly if given class files that do not contain all the attributes they require.
Two attributes that are intended to be distinct, but that happen to use the same attribute name and are of the same length, will conflict on implementations that recognize either attribute. Attributes defined other than in this specification must have names chosen according to the package naming convention described in The Java Language Specification, Java SE 8 Edition (JLS §6.1).
Future versions of this specification may define additional attributes.
边栏推荐
- 【Go实战基础】gin 如何设置路由
- During MySQL installation, mysqld Exe reports that the application cannot start normally (0xc000007b)`
- 盘点典型错误之TypeError: X() got multiple values for argument ‘Y‘
- Amq6126 problem solving ideas
- Number structure (C language -- code with comments) -- Chapter 2, linear table (updated version)
- Redis installation and deployment (windows/linux)
- Solutions to Chinese garbled code in CMD window
- From concept to method, the statistical learning method -- Chapter 3, k-nearest neighbor method
- 概念到方法,绝了《统计学习方法》——第三章、k近邻法
- Double non undergraduate students enter the factory, while I am still quietly climbing trees at the bottom (Part 1)
猜你喜欢

Insight into cloud native | microservices and microservice architecture
Microservice practice | declarative service invocation openfeign practice
![[staff] time sign and note duration (full note | half note | quarter note | eighth note | sixteenth note | thirty second note)](/img/bf/2b0b9c640bdad2c55293f905a22055.jpg)
[staff] time sign and note duration (full note | half note | quarter note | eighth note | sixteenth note | thirty second note)
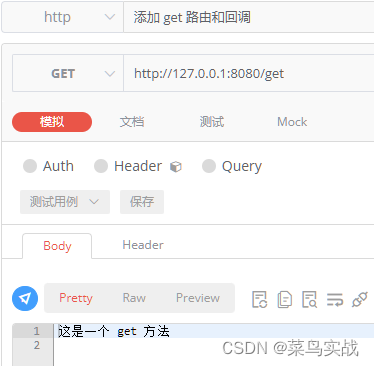
【Go实战基础】gin 如何设置路由

概率还不会的快看过来《统计学习方法》——第四章、朴素贝叶斯法
Redis installation and deployment (windows/linux)
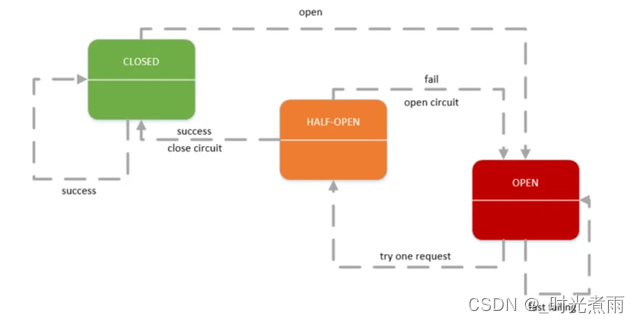
Microservice practice | fuse hytrix initial experience

In depth analysis of how the JVM executes Hello World

Matplotlib剑客行——容纳百川的艺术家教程

【Go实战基础】gin 如何自定义和使用一个中间件
随机推荐
Say goodbye to 996. What are the necessary plug-ins in idea?
"Redis source code series" learning and thinking about source code reading
In depth analysis of how the JVM executes Hello World
Machine learning practice: is Mermaid a love movie or an action movie? KNN announces the answer
Pdf document of distributed service architecture: principle + Design + practice, (collect and see again)
CSDN Q & A_ Evaluation
Microservice practice | load balancing component and source code analysis
Cartoon rendering - average normal stroke
Use of libusb
Matplotlib swordsman - a stylist who can draw without tools and code
使用IBM MQ远程连接时报错AMQ 4043解决思路
1、 QT's core class QObject
Avoid breaking changes caused by modifying constructor input parameters
【Go实战基础】gin 如何设置路由
微服务实战|原生态实现服务的发现与调用
京东面试官问:LEFT JOIN关联表中用ON还是WHERE跟条件有什么区别
Matplotlib剑客行——初相识Matplotlib
AMQ6126问题解决思路
Complete solution of servlet: inheritance relationship, life cycle, container, request forwarding and redirection, etc
微服务实战|微服务网关Zuul入门与实战