当前位置:网站首页>Cesium learning notes (V) custom geometry and appearance
Cesium learning notes (V) custom geometry and appearance
2022-06-30 08:04:00 【Lafiteeee】
Customize geometry and appearance
of Primitive API Usable Geometry & Appearance System information , This is using a custom grid 、 shape 、 Volume and appearance expansion CesiumJS High level theme of , Not suitable for typical Cesium user .
Geometry overview
Geometry Defines the structure of the element , That is, the triangle that forms the primitive 、 A straight line or point .
Appearance Defines the shading of elements , Including its complete GLSL Vertex and clip shaders and render States .
Use Geometry and Appearance Are the benefits of :
- performance : When drawing a large number of static elements , Use it directly Geometry It allows us to combine them into a geometric figure , Reduce CPU Spend and make better use of GPU. The combination primitive is in web worker The complete , To maintain UI Response speed of .
- flexibility :primitives Combined with the Geometry and Appearance. By decoupling them , We can add new geometries that are compatible with many different appearances , vice versa .
- Low level access : Appearances provide rendering access close to the metal , And don't worry about Renderer Use it directly Direct All the details of .Appearance So that we can easily :
- Write a complete GLSL Vertex and fragment shaders
- Use custom render States
There are also some shortcomings :
- Using geometry and appearance directly requires more code and a deeper understanding of graphics . The entity is at the level of abstraction appropriate for the mapping application ; Geometry and appearance are close to tradition 3D The abstraction level of the engine .
- The combined geometry is valid for static data , For dynamic data, it is not necessarily effective .
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
// original code
//viewer.entities.add({
// rectangle : {
// coordinates : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-100.0, 20.0, -90.0, 30.0),
// material : new Cesium.StripeMaterialProperty({
// evenColor: Cesium.Color.WHITE,
// oddColor: Cesium.Color.BLUE,
// repeat: 5
// })
// }
//});
var instance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-100.0, 20.0, -90.0, 30.0),
vertexFormat : Cesium.EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
})
});
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : instance,
appearance : new Cesium.EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance({
material : Cesium.Material.fromType('Stripe')
})
}));
Not used in the above code entities, But use Primitive Instead of , It is a combination of GeometryInstance and Appearance.
Create rectangular geometry , That is, a triangle that covers a rectangular area and fits the curvature of the earth , We create a RectangleGeometry.
Graphic combination
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
// First rectangle instance
var instance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-100.0, 20.0, -90.0, 30.0),
vertexFormat : Cesium.EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
})
});
// Second rectangle instance
var anotherInstance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-85.0, 20.0, -75.0, 30.0),
vertexFormat : Cesium.EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
})
});
// Graphic combination
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : [instance, anotherInstance],
appearance : new Cesium.EllipsoidSurfaceAppearance({
material : Cesium.Material.fromType('Stripe')
})
}));
We created another instance with another rectangle , Then provide both instances to the element (Primitive). This will draw two instances with the same look .
Some appearances allow each instance to provide unique properties . for example , We can use PerInstanceColorAppearance Different colors shade each instance .
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
var instance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-100.0, 20.0, -90.0, 30.0),
vertexFormat : Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
}),
attributes : {
// Add color attribute
color : new Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.8)
}
});
var anotherInstance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-85.0, 20.0, -75.0, 30.0),
vertexFormat : Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
}),
attributes : {
// Add color attribute
color : new Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.8)
}
});
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : [instance, anotherInstance],
appearance : new Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance()
}));

Each of the above examples has a color attribute , Determine the color of the graphic .
Combining geometry makes CesiumJS Effectively draw a large number of geometric figures . The following example draws 2592 A uniquely colored rectangle .
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
var instances = [];
for (var lon = -180.0; lon < 180.0; lon += 5.0) {
for (var lat = -85.0; lat < 85.0; lat += 5.0) {
instances.push(new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(lon, lat, lon + 5.0, lat + 5.0),
vertexFormat: Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
}),
attributes : {
color : Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(Cesium.Color.fromRandom({
alpha : 0.5}))
}
}));
}
}
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : instances,
appearance : new Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance()
}));

selection
The merged instances can also be accessed separately . Will a id Assign an instance , And use it to determine whether to use Scene.pick Selected this instance .
The following example creates a band id Example , When it is selected, a message is sent to the console .
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
var instance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.RectangleGeometry({
rectangle : Cesium.Rectangle.fromDegrees(-100.0, 30.0, -90.0, 40.0),
vertexFormat: Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
}),
id : 'my rectangle',
attributes : {
color : Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(Cesium.Color.RED)
}
});
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : instance,
appearance : new Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance()
}));
var handler = new Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventHandler(scene.canvas);
handler.setInputAction(function (movement) {
var pick = scene.pick(movement.position);
if (Cesium.defined(pick) && (pick.id === 'my rectangle')) {
console.log('Mouse clicked rectangle.');
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.LEFT_CLICK);

Use id You can avoid keeping the entire instance in memory after the primitive is constructed ( Include Geometry ) References to .
Graphic examples
Instances can be used to locate different parts of the scene 、 Scale and rotate the same geometry . Because multiple instances can reference the same Geometry, Each instance can have a different model matrix . This allows us to calculate geometry only once , And reuse it many times .
The following example creates a EllipsoidGeometry And two examples . Each instance references the same elliptical shape , But by using different modelMatrix Put one oval on top of the other .
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
var ellipsoidGeometry = new Cesium.EllipsoidGeometry({
vertexFormat : Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT,
radii : new Cesium.Cartesian3(300000.0, 200000.0, 150000.0)
});
var cyanEllipsoidInstance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : ellipsoidGeometry,
modelMatrix : Cesium.Matrix4.multiplyByTranslation(
Cesium.Transforms.eastNorthUpToFixedFrame(Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(-100.0, 40.0)),
new Cesium.Cartesian3(0.0, 0.0, 150000.0),
new Cesium.Matrix4()
),
attributes : {
color : Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(Cesium.Color.CYAN)
}
});
var orangeEllipsoidInstance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : ellipsoidGeometry,
modelMatrix : Cesium.Matrix4.multiplyByTranslation(
Cesium.Transforms.eastNorthUpToFixedFrame(Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(-100.0, 40.0)),
new Cesium.Cartesian3(0.0, 0.0, 450000.0),
new Cesium.Matrix4()
),
attributes : {
color : Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(Cesium.Color.ORANGE)
}
});
scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : [cyanEllipsoidInstance, orangeEllipsoidInstance],
appearance : new Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance({
translucent : false,
closed : true
})
}));
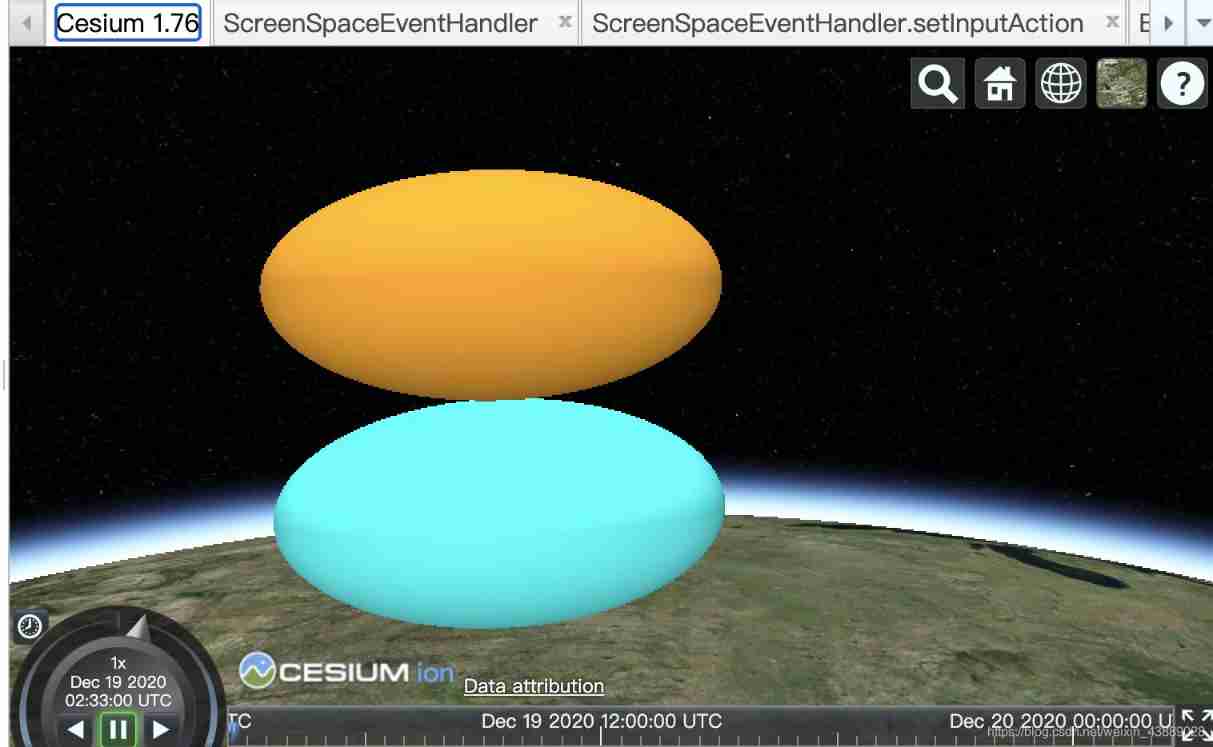
Update the properties of each instance
When a geometric instance is added to the primitive , Update the properties of each instance to change the appearance . These attributes include :
- Color:
ColorGeometryInstanceAttributeDetermines the color of the instance . The primitive must havePerInstanceColorAppearance - Show: Boolean value , Determines whether the instance displays , Any instance has this property .
The following example shows how to change the color of a geometric instance :
var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer');
var scene = viewer.scene;
var circleInstance = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
geometry : new Cesium.CircleGeometry({
center : Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(-95.0, 43.0),
radius : 250000.0,
vertexFormat : Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance.VERTEX_FORMAT
}),
attributes : {
color : Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(new Cesium.Color(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5))
},
id: 'circle'
});
var primitive = new Cesium.Primitive({
geometryInstances : circleInstance,
appearance : new Cesium.PerInstanceColorAppearance({
translucent : false, // translucent
closed : true
})
});
scene.primitives.add(primitive);
setInterval(function() {
var attributes = primitive.getGeometryInstanceAttributes('circle');
attributes.color = Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.toValue(Cesium.Color.fromRandom({
alpha : 1.0}));
},2000);
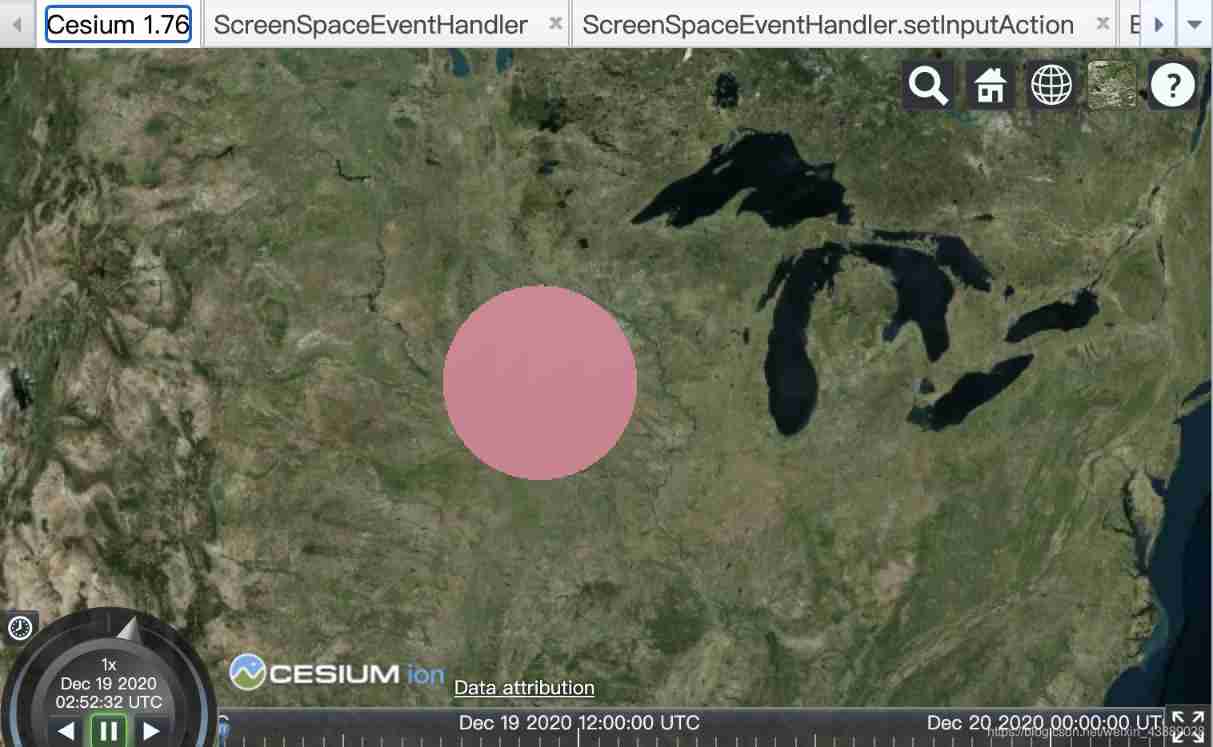
The color of the graph will change constantly .
appearance
Geometry defines the structure . Another key element is appearance , Defines the shading of the element 、 Color, etc. , For example, how a single pixel is colored . An entity can have many geometric instances , But it can only have one appearance . Depending on the type of appearance , The appearance will have a material Property to define the shading body .
The figure above shows the element 、 The relationship between geometric instances and appearances . An entity can correspond to multiple geometric instances , But it can only correspond to one appearance .
CesiumJS Have the following appearance :
MaterialAppearance: A look that applies to all geometric types , And supportmaterialTo describe shadows .EllipsoidSurface:MaterialAppearanceA version of , It assumes that the geometry is parallel to the earth's surface , For example, a polygon , And use this assumption to save memory by programmatically calculating many vertex attributes .PerInstanceColorAppearance: Color each instance with the color of each instance .PolylineMaterialAppearance: Support changing the material of polylinesPolylineColorAppearance: Use per vertex or per segment shading to shade polylines .
Appearance defines when an element is drawn GPU Complete execution on GLSL Vertex and fragment shaders . Appearances also define the full render state , It controls when drawing primitives GPU The state of . We can directly define the presentation state , You can also use more advanced properties , such as closed and translucent, Appearances convert them to render States .
Once the appearance is created , We can't change its renderState attribute , But we can change its material attribute . We can also change the appearance attribute .
Most appearances have flat and faceForward attribute , They indirectly control GLSL Shaders .
flat: Flat shadow , Regardless of the light .faceForward: Consider the effects of light , Keep it always facing the observer , Avoid the black areas on the back , Like the inside of the wall .flat:true
faceForward: false
faceForward: true
Compatibility of geometry and appearance
Not all appearances apply to all geometric shapes . for example , Ellipsoidal surface appearance does not apply to wall geometry , Because the wall is not on the surface of the earth .
To make the appearance compatible with geometry , They must have a matching vertex format , This means that the geometry must have the data expected as input . When creating geometry, you can provide VertexFormat.
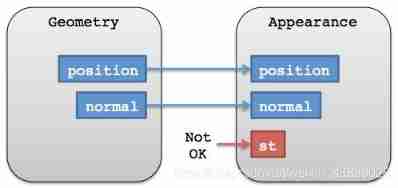
Of a geometric shape vertexFormat Determines whether it can be combined with other geometries . The two geometries do not have to be of the same type , But they must match vertex format.
For convenience , Appearance also has vertexFormat Property or a static constant VERTEX_FORMAT, This constant can be passed in as an option for geometry .
边栏推荐
- 多快好省,低门槛AI部署工具FastDeploy测试版来了!
- Simple application of generating function
- Niuke Xiaobai month race 52
- [notes] polygon mesh processing learning notes (10)
- Deep learning -- Realization of convolution by sliding window
- Cadence innovus physical implementation series (I) Lab 1 preliminary innovus
- JS code case
- Redis 的过期数据如何处理,淘汰机制都有那些?
- 期末複習-PHP學習筆記5-PHP數組
- Deep learning -- language model and sequence generation
猜你喜欢

深度学习——残差网络ResNets

Construction of energy conservation supervision system for campus buildings of ankery University
![[flower carving experience] 14 line blank board pingpong library test external sensor module (one)](/img/ba/1d1c5b51cdfc4075920a98d64820c2.jpg)
[flower carving experience] 14 line blank board pingpong library test external sensor module (one)
![December 19, 2021 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 5 advanced database search)](/img/e9/8646f3e2da0ece853e7135eb6e30d9.jpg)
December 19, 2021 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 5 advanced database search)

At the age of 25, I started to work in the Tiankeng industry with buckets. After going through a lot of hardships to become a programmer, my spring finally came

More, faster, better and cheaper. Here comes the fastdeploy beta of the low threshold AI deployment tool!

HelloWorld

MySQL cannot connect to the intranet database

Introduction notes to pytorch deep learning (XII) neural network - nonlinear activation
![November 19, 2021 [reading notes] a summary of common problems of sneakemake (Part 2)](/img/f8/ca1874eb999dc2bbb3c1392d0b72bc.jpg)
November 19, 2021 [reading notes] a summary of common problems of sneakemake (Part 2)
随机推荐
期末复习-PHP学习笔记2-PHP语言基础
November 9, 2020 [wgs/gwas] - whole genome analysis (association analysis) process (Part 2)
Halcon12+vs2013 C # configuration
Niuke White Moon race 52
【笔记】Polygon mesh processing 学习笔记(10)
Experiment 6 examination
November 16, 2021 [reading notes] - macro genome analysis process
Do you know the IP protocol?
How to handle the expired data of redis and what are the elimination mechanisms?
1162 Postfix Expression
Use of nested loops and output instances
Experiment 3 remote control
想转行,却又不知道干什么?此文写给正在迷茫的你
Construction of energy conservation supervision system for campus buildings of ankery University
深度学习——GRU单元
Palindrome substring, palindrome subsequence
F12 packet capture is used for the whole process analysis of postman interface test
Implementation of remote monitoring by camera in Experiment 5
Tue Jun 28 2022 15:30:29 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间) 日期格式化
Dlib library blink