当前位置:网站首页>Index of MySQL
Index of MySQL
2022-07-07 03:36:00 【Fire eye Dragon】
Introduce :
The index is through some algorithm , Build a data model , Used to quickly find rows with a specific value in a column , No index ,MySQL You must read the entire table from the first entry , Until you find the relevant row , The bigger the watch , The more time it takes to query the data , If the queried column in the table has an index ,MySQL Can quickly reach a location to search data files , Instead of looking at all the data , That would save a lot of time .
classification
An index is a data structure used by a storage engine to quickly find records , According to the way of implementation, it is divided into , There are mainly HASH Index and B+TREE Indexes
Create index
Single index : An index contains only a single column , But you can have multiple single-column indexes in a table
General index :MySQL Basic index type , There are no restrictions , Allows you to insert duplicate values and controls into columns that define indexes , Just to query data faster .
Single index
General index
Create operation
for example :
CREATE DATABASE mydb5;
USE mydb5;
-- Mode one - When creating a table, specify
CREATE TABLE student(
sid INT PRIMARY KEY,
card_id VARCHAR(50),
name VARCHAR(50),
gender VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
birth DATE,
phone_num VARCHAR(20),
score DOUBLE,
INDEX index_name(name) -- to name Column creation index
);
SELECT * FROM student WHERE name=' Zhang San ';
-- The second way - Create directly
CREATE INDEX index_gender ON student(gender);
-- The third way - Modify table structure ( Add index )
ALTER TABLE student ADD INDEX index_age(age);
Check operation
for example :
-- 1. View all indexes of the database
SELECT * FROM mysql.innodb_index_stats a WHERE a.database_name='mydb5';
-- 2. View all indexes in the table
SELECT * FROM mysql.innodb_index_stats a WHERE a.database_name = 'mydb5' AND a.table_name LIKE '%student%';
-- 3. View all indexes in the table
SHOW INDEX FROM student;
Delete index
Method :
DROP INDEX Index name ON Table name
or
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP INDEX Index name
for example :
-- Delete index
DROP INDEX index_gender ON student;
ALTER TABLE student DROP INDEX index_age;
unique index
Concept : The unique index is similar to the previous ordinary index , The difference is that : The value of the index column must be unique , But you can have an empty value . If it's a composite index , The combination of column values must be unique .
Add index
for example :
-- Mode one - When creating a table, specify
CREATE TABLE student2(
sid INT PRIMARY KEY,
card_id VARCHAR(50),
name VARCHAR(50),
gender VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
birth DATE,
phone_num VARCHAR(20),
score DOUBLE,
UNIQUE index_card_id(card_id) -- to card_id Column creation index
);
-- The second way - Create directly
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_gender ON student2(gender);
-- The third way - Modify table structure ( Add index )
ALTER TABLE student ADD UNIQUE INDEX index_age(age);
Delete index
Method :
DROP INDEX Index name ON Table name
or
ALTER TABLE Table name DROP INDEX Index name
for example :
-- Delete index
DROP INDEX index_gender ON student2;
ALTER TABLE student2 DROP INDEX index_age;
primary key
Concept : Each table usually has its own primary key , When we create a table MySQL Will automatically create an index on the primary key column , This is the primary key index . The primary key is unique and cannot be NULL, So it's a special kind of unique index .
for example :
-- primary key
SHOW INDEX FROM student2;
-- At this point, you can see the primary key index , But it cannot be seen in the visual interface , And for automatic creation
Composite index
Concept :
- Composite index is also called composite index , It means that we use multiple fields when building the index , For example, use both ID card and mobile phone number to establish index , Similarly, it is also necessary to establish a common index or a unique index .
- The leftmost principle of composite index
Method :
CREATE INDEX indexname ON table_name (column1(length),column2(length));
for example :
-- Create a normal index
CREATE INDEX index_phone_name ON student(phone_num,name);
-- Delete index
DROP INDEX index_phone_name ON student;
-- Create unique index
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_phone_name ON student(phone_num,name);
Full-text index
Concept :
The keyword of full-text index is fulltext
Full text index is mainly used to find keywords in text , Rather than directly comparing the values in the index , It's more like a search engine , Similarity based query is not simple where The parameters of the statement match .
use like+% Then we can achieve fuzzy matching , But this method is suitable when there is less data , For a large number of text data retrieval , You can't . Full text search in a large amount of data , Than like+% It's much faster , But there is a precision problem in full-text retrieval
MySQL5.6 Before , Only MyISAM The storage engine supports full-text indexing
MySQL5.6 after ,MyISAM and InnoDB Storage engines support full-text indexing
Only the data type of the field is char、varchar、text And its series
When the data is large , First put the data into a table without a global index , And then use craete index establish fulltext Indexes , It's better than building a table first fulltext Then the speed of data writing is much faster
When testing or using full-text indexing , Look at your own first MySQL edition 、 Whether the storage engine and data type support full-text indexing .
MySQL The full-text index in has two variables , Minimum search length and maximum search length . For words whose length is less than the minimum search length and the maximum search length , Will not be indexed . These two default values can be viewed with the following command :
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘%ft%’
Operation of full-text index
for example :
CREATE table t_article(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
title VARCHAR(255),
content VARCHAR(10000),
writing_date DATE
-- FULLTEXT(content) Create full text index
);
insert into t_article values(null,"Yesterday Once More","When I was young I listen to the radio",'2021-10-01');
insert into t_article values(null,"Right Here Waiting","Oceans apart, day after day,and I slowly go insane",'2021-10-02');
insert into t_article values(null,"My Heart Will Go On","every night in my dreams,i see you, i feel you",'2021-10-03');
insert into t_article values(null,"Everything I Do","eLook into my eyes,You will see what you mean to me",'2021-10-04');
insert into t_article values(null,"Called To Say I Love You","say love you no new year's day, to celebrate",'2021-10-05');
insert into t_article values(null,"Nothing's Gonna Change My Love For You","if i had to live my life without you near me",'2021-10-06');
insert into t_article values(null,"Everybody","We're gonna bring the flavor show U how.",'2021-10-07');
-- Modify table structure to add full-text index
ALTER TABLE t_article ADD FULLTEXT index_context(content);
-- Add full text index ( Choose one from the above modification )
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX index_context ON t_article(content);
-- Use full text indexing
SELECT * FROM t_article WHERE MATCH(content) AGAINST('yo'); -- No results ( The reason is the minimum query value problem )
SELECT * FROM t_article WHERE MATCH(content) AGAINST('you'); -- It turns out
Spatial index
Concept :
- MySQL stay 5.7 Then support spatial index , Support OpenGIS Geometric data model
- A spatial index is an index of a field of a spatial data type ,MySQL Spatial data types in 4 Kind of , Namely GEOMETRY、POINT、LINESTRING、POLYGON..
- MySQL Use SPATIAL Keyword expansion , Yes, it can be used to create a regular index type syntax to create a spatial index .
- A column that creates a spatial index , It must be declared as NOT NULL.
- Spatial index is less used , Understanding can
| type | meaning | explain |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Spatial data | Any type of space |
| Point | spot | Coordinate value |
| LineString | Line | There are a series of points connected |
| Polygon | polygon | Composed of multiple lines |
for example :
create table shop_info (
id int primary key auto_increment comment 'id',
shop_name varchar(64) not null comment ' Store name ',
geom_point geometry not null comment ' Longitude and latitude ',
spatial key geom_index(geom_point)
);
internals
Concept :
- Generally speaking, the index itself is very large , It's impossible to store everything in memory , So indexes are often stored on disk as index files .
- In this case , Disk will be generated during index search I/O Consume , Relative to memory access ,I/O How many orders of magnitude higher is the consumption of access , So the most important index to evaluate a data structure as an index is the disk in the search process I/O Progressive complexity of the number of operations .
- let me put it another way , The structure of index should be organized to minimize the number of disks in the process of searching I/O Access times of .
Hash Algorithm
advantage : Calculated from the value of the field Hash value , Location data is very fast
shortcoming : No range lookup , Because the values in the hash table are unordered , Cannot compare sizes .
Binary tree and binary balanced tree
Binary tree
advantage : It is divided into left subtree 、 Right subtree and root node , The left subtree is smaller than the root node , The right subtree is larger than the root node
shortcoming : It is possible to produce an unbalanced structure similar to a linked list
Balanced binary trees
advantage :
- Its left and right subtrees are balanced binary trees
- The left subtree is smaller than the middle , The right subtree is larger than the middle value
- The absolute value of the difference between the depth of the left subtree and that of the right subtree does not exceed 1
shortcoming : - The insertion operation requires rotation
- Support range query , However, the efficiency of roundabout query is low , For example, the query is larger than 8 Of , Will swing to the parent node 7、10
- If you store hundreds of pieces of data , The higher the tree is , The slower the query efficiency
BTREE Tree model
At present, most data systems and file systems use B-TREE Or its variants B+TREE As an index structure ,BTREE Structure can effectively solve the problems encountered by previous related algorithms .
BTREE Trees Index application
MyISAM Engine USES B+TREE As an index structure , Leaf node data The domain stores the address of the data record .
Features of index
advantage
- Greatly speed up the data query speed
- When using grouping and sorting for data query , It can significantly reduce the time of grouping and sorting when querying
- Create unique index , It can ensure the uniqueness of each row of data in the database table
- In terms of reference integrity of real data , Can speed up the connection between tables
shortcoming
- Creating and maintaining indexes takes time , And as the amount of data increases , Time will also increase
- Indexes need to occupy disk space
- When adding, deleting or modifying data in the data table , Indexes should also be maintained dynamically , Reduce the speed of dimension
The principle of index creation
- Columns that update frequently should not be indexed
- Don't use indexes for tables with small amount of data
- Fields with a lot of duplicate data should not be set as indexes
- First of all, we should consider where and order by Index the columns involved
边栏推荐
- VHDL实现单周期CPU设计
- Numpy中排序操作partition,argpartition,sort,argsort
- 21.(arcgis api for js篇)arcgis api for js矩形采集(SketchViewModel)
- When you go to the toilet, you can clearly explain the three Scheduling Strategies of scheduled tasks
- 数学归纳与递归
- Opencv environment, and open a local PC camera.
- SSL certificate deployment
- VHDL implementation of arbitrary size matrix addition operation
- 概率论公式
- MySQL的索引
猜你喜欢
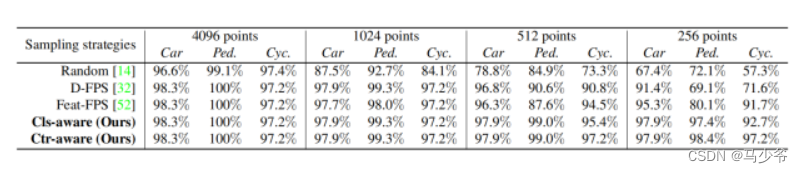
Not All Points Are Equal Learning Highly Efficient Point-based Detectors for 3D LiDAR Point

VHDL implementation of arbitrary size matrix multiplication
图形化工具打包YOLOv5,生成可执行文件EXE
树莓派设置静态ip

Do you know the five most prominent advantages of E-bidding?
Clock in during winter vacation

22. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS Circle Collection (sketchviewmodel)
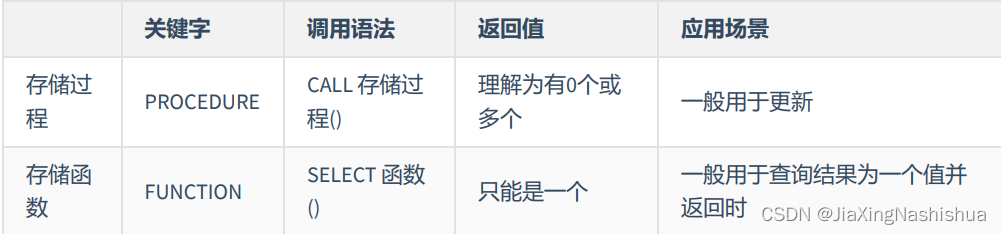
Stored procedures and functions (MySQL)
R data analysis: how to predict Cox model and reproduce high score articles

Experience design details
随机推荐
Jerry's broadcast has built-in flash prompt tone to control playback pause [chapter]
R数据分析:cox模型如何做预测,高分文章复现
【安全攻防】序列化与反序列,你了解多少?
Codeforces round 264 (Div. 2) C gargari and Bishop [violence]
Jerry's RTC clock development [chapter]
海思万能平台搭建:颜色空间转换YUV2RGB
Basic concepts of Huffman tree
About Tolerance Intervals
Domcontentloaded and window onload
input_ delay
Flutter3.0了,小程序不止于移动应用跨端运行
A 股指数成分数据 API 数据接口
【colmap】已知相机位姿情况下进行三维重建
sshd[12282]: fatal: matching cipher is not supported: aes256- [email protected] [preauth]
2022.6.28
First understand the principle of network
leetcode
21. (article ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS rectangular acquisition (sketchviewmodel)
华为小米互“抄作业”
VHDL实现任意大小矩阵乘法运算