当前位置:网站首页>Application layer of tcp/ip protocol cluster
Application layer of tcp/ip protocol cluster
2022-07-06 20:28:00 【WoLannnnn】
List of articles
application layer
We programmers write one by one to solve our practical problems , A network program that meets our daily needs , All in the application layer .
We can talk “ agreement ”
A protocol is a “ Appointment ”. socket api The interface of , When reading and writing data , All press “ character string ”( The string description is not accurate ) To send and receive . If we want to transmit some " Structured data " What shall I do? ?
Through serialization and deserialization , We send data to the network for serialization , take “ Structured data ” Unite as a whole , When the network sends data to the other end to receive , To deserialize , Turn the overall data into “ Structured data ”. The tools for serialization are json,xml
Online calculator
for example , We need to implement a server version of the adder . We need the client to send the two addends to be calculated , Then the server calculates , Finally, return the result to the client .
Agreed scheme 1 :
- The client sends a message in the form of "1+1" String ;
- There are two operands in this string , It's all plastic ;
- There will be a character between two numbers that is an operator , The operator can only be + ;
- There is no space between numbers and operators ;
- …
Agreed scheme II :
- Define structures to represent the information we need to interact with ;
- When sending data, this structure is converted into a string according to a rule , When receiving the data, convert the string back to the structure according to the same rules ;
- This process is called “ serialize ” and “ Deserialization ”
protocol.hpp
// protocol.hpp Define the structure of communication
#pragma once
typedef struct request{
int x;
int y;
char op;// The operator
}request_t;
typedef struct response{
//code by 0: Normal operation
//code by 1:/ The divisor of is 0
//code by 2:% The divisor of is 0
//code by 3: Illegal operator
int code;// Exit code
int result;// result
}response_t;
// client.hpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include"protocol.hpp"
class client{
private:
std::string _ip;// The server ip
int _port;// Server port number
int _sock;
public:
// Constructors
client(std::string ip = "127.0.0.1", int port = 8080)
:_ip(ip)
,_port(port)
{
}
// initialization
void init_client()
{
// Create socket
_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_sock < 0)
{
std::cerr << "socket error !" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
//connect
// server information
sockaddr_in svr;
svr.sin_family = AF_INET;
svr.sin_port = htons(_port);
svr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
if (connect(_sock, (sockaddr*)&svr, sizeof(svr)) < 0)
{
std::cerr << "connect error !" << std::endl;
exit(2);
}
}
void start()
{
request_t rq;
response_t rsp;
std::cout << " Please enter the first operand : ";
std::cin >> rq.x;
std::cout << " Please enter the operator : ";
std::cin >> rq.op;
std::cout << " Please enter the second operand : ";
std::cin >> rq.y;
// Send it to the server for calculation
send(_sock, &rq, sizeof(rq), 0);
// Receive results
ssize_t s = recv(_sock, &rsp, sizeof(rsp), 0);
if (s > 0)
{
if (rsp.code != 0)
{
std::cout << " Input error !" << std::endl;
std::cout << "code: " << rsp.code << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << rq.x << " " << rq.op << " " << rq.y << " = " << rsp.result << std::endl;
}
}
}
// destructor
~client()
{
close(_sock);
}
};
server.hpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include"protocol.hpp"
class server{
private:
int _port;// Server port number
int _lsock;// Listening socket
public:
// Constructors
server(int port = 8080)
:_port(port)
{
}
// initialization
void init_server()
{
// Create socket
_lsock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_lsock < 0)
{
std::cerr << "socket error !" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// Bind socket
sockaddr_in local;
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(_lsock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
{
std::cerr << "bind error !" << std::endl;
exit(2);
}
// monitor
if (listen(_lsock, 5) != 0)
{
std::cerr << "listen error !" << std::endl;
exit(3);
}
}
void cal(int sock)
{
// Short link completion service
request_t rq;
response_t rsp = {
0, 0};
// Receive calculation information
ssize_t s = recv(sock, &rq, sizeof(rq), 0);
if (s > 0)
{
switch(rq.op)
{
case '+':
rsp.result = rq.x + rq.y;
break;
case '-':
rsp.result = rq.x - rq.y;
break;
case '*':
rsp.result = rq.x * rq.y;
break;
case '/':
if (rq.y == 0)
{
rsp.code = 1;
break;
}
rsp.result = rq.x / rq.y;
break;
case '%':
if (rq.y == 0)
{
rsp.code = 2;
break;
}
rsp.result = rq.x % rq.y;
break;
default:
rsp.code = 3;
}
}
// Return results
send(sock, &rsp, sizeof(rsp), 0);
// Short link processing , So here it is closesock
close(sock);
}
void start()
{
// Connect to the client
struct sockaddr_in end_point;
socklen_t len = sizeof(&end_point);
while (1)
{
int sock = accept(_lsock, (struct sockaddr*)&end_point, &len);
if (sock < 0)
{
std::cerr << "accept error !" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// Create sub processes for calculation
if (fork() == 0)
{
// Subprocesses
close(_lsock);
if (fork() > 0)
{
// Or a subprocess
exit(0);// sign out , Prevent blocking child processes
}
else// Grandson process
{
cal(sock);
exit(0);
}
}
close(sock);
waitpid(-1, nullptr, 0);
}
}
// destructor
~server()
{
close(_lsock);
}
};
Whether we adopt scheme 1 , Or plan two , Or another plan , Just promise , Data constructed when one end sends , It can be parsed correctly at the other end , Namely ok Of , For example, input order . This kind of agreement , Namely Application layer protocol
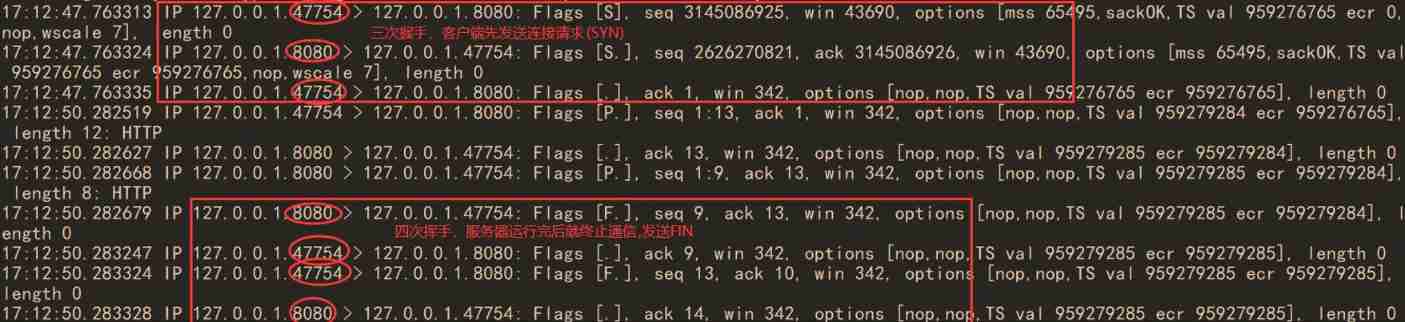
We capture the above calculation :sudo tcpdump -i any -nn tcp port 8080
Three handshakes , Four waves
HTTP agreement
Although we said , The application layer protocol is set by our program .
But actually , Some big guys have defined some ready-made , And very easy to use application layer protocol , For our direct reference . HTTP( Hypertext transfer protocol ) Is one of them .
know URL
We usually call it “ website ” In fact, it means URL

Internet behavior
- Take down the data of the server
- Send your data to the server
urlencode and urldecode
image / ? : Wait for such characters , Has been url Understood as a special meaning . Therefore, these characters cannot appear at will .
such as , These special characters are required in a parameter , You must first escape special characters .
The escape rules are as follows :
Convert the characters to be transcoded into 16 Base number , Then from right to left , take 4 position ( Insufficient 4 Bit direct processing ), Every time 2 Be a , prefix %, Code as %XY Format
for example :
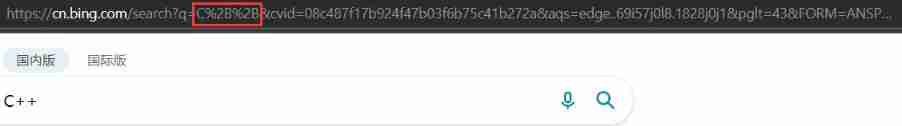
“+” It's translated into “%2B”
urldecode Namely urlencode The inverse process
HTTP Three characteristics
There is no connection . As we know before ,TCP Is to be connected , but TCP Establish connections and http irrelevant ,http Send it directly to the server http request that will do
No state . We use an example to understand statelessness : When we visit a website , Need to log in , If we log in this time , The next time I visit , because http Stateless characteristics of , We need to enter the account and password again to log in . This is it. http stateless . When we actually log in , In fact, you don't need to enter the account password after logging in once , This is from cookie and session Realized
Simple and fast . Short link text (html、img、css、js…) transmission , This is early http/1.0 Transmission mode of
http/1.0 Supports long connections
HTTP Form of agreement
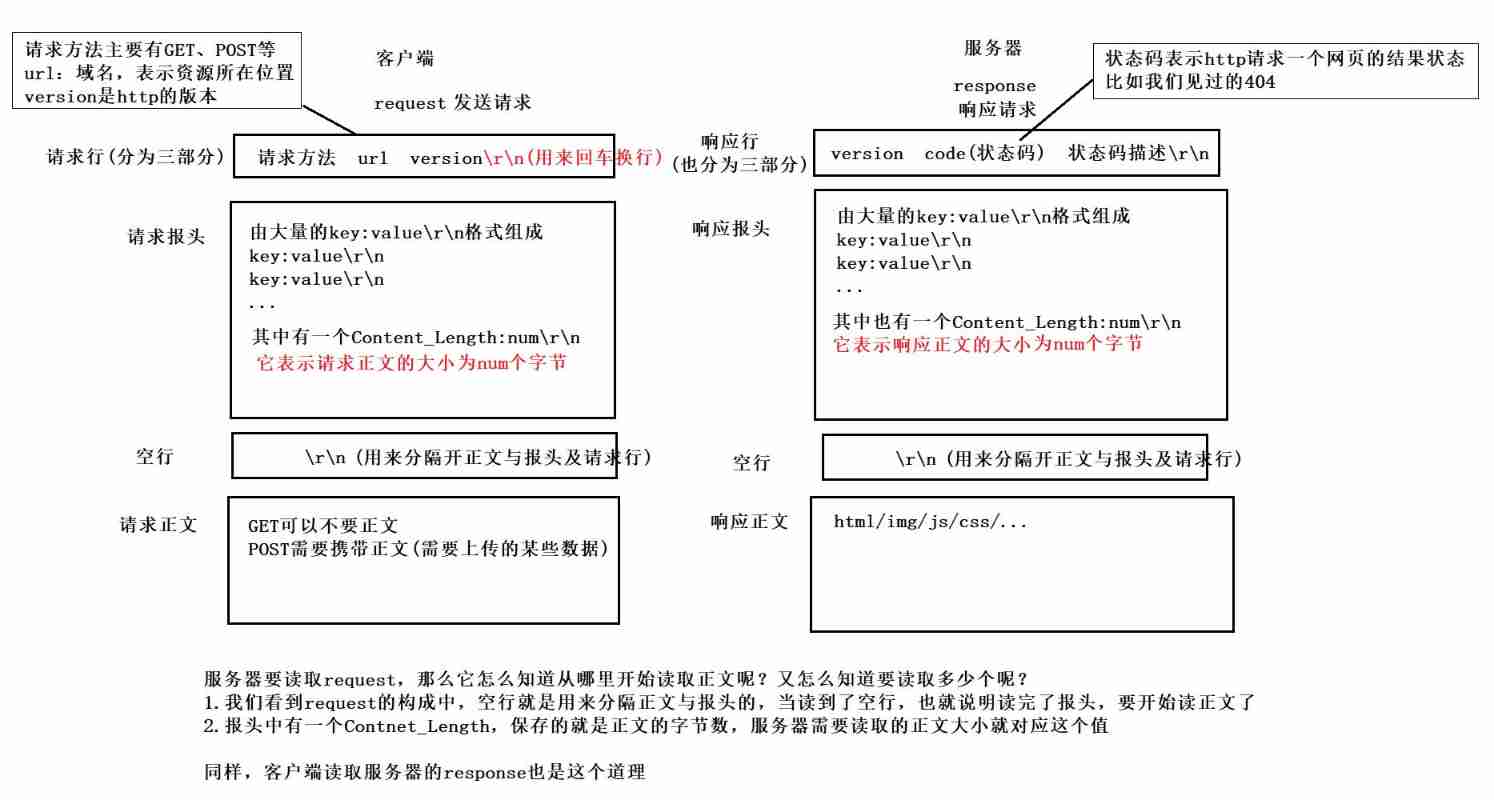
HTTP constitute :
Can pass Fiddler Carry out the bag .
principle : When surfing the Internet normally , We can send the request to the server directly through the network . and Fiddler We'll give it to you first Filddler Acting as agent ,Fiddler Then send the request to the server through the network , And receive the response
HTTP request
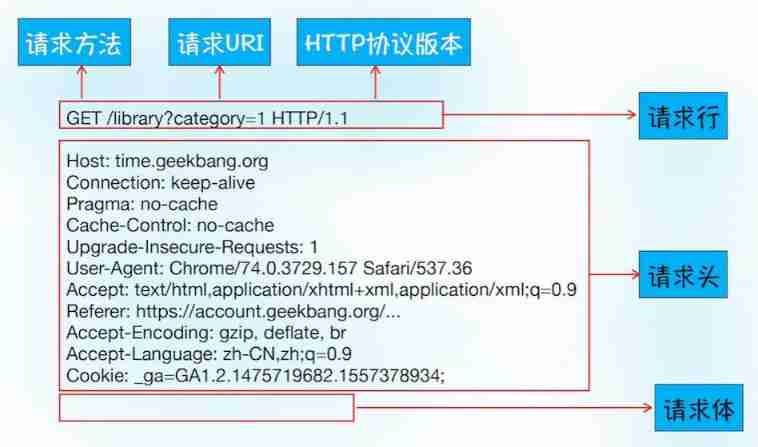
- First line : [ Method ] + [url] + [ edition ]
- Header: Requested properties , Colon divided key value pairs ; Use... Between each set of attributes \n Separate ; When you meet a blank line, it means Header Partial end
- Body: The content behind the blank line is Body. Body Allow empty string . If Body There is , It's in Header There will be one Content-Length Property to identify Body The length of ;
HTTP Respond to
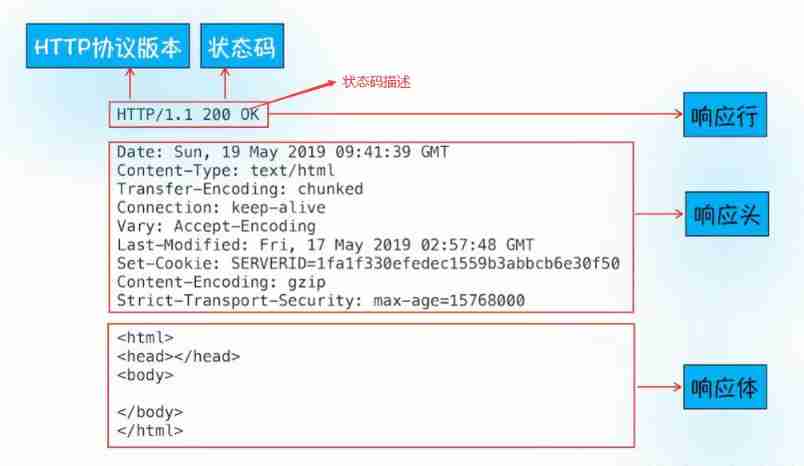
- First line : [ Version number ] + [ Status code ] + [ State code interpretation ]
- Header: Requested properties , Colon divided key value pairs ; Use... Between each set of attributes \n Separate ; When you meet a blank line, it means Header Partial end
- Body: The content behind the blank line is Body. Body Allow empty string . If Body There is , It's in Header There will be one Content-Length Property to identify Body The length of ; If the server returns a html page , that html The content of the page is in body in
HTTP Methods
| Method | explain | Supported by HTTP Protocol version |
|---|---|---|
| GET | Access to resources | 1.0、1.1 |
| POST | Transport entity body | 1.0、1.1 |
| PUT | Transfer files | 1.0、1.1 |
| HEAD | Get the message header | 1.0、1.1 |
| DELETE | Delete file | 1.0、1.1 |
| OPTIONS | Ask for support | 1.1 |
| TRACE | Trace path | 1.1 |
| CONNECT | Require a tunnel protocol to connect to the agent | 1.1 |
| LINK | Build connections with resources | 1.0 |
| UNLINE | Disconnect | 1.0 |
One of the most common is GET Methods and POST Method .
Head Do not get body information , Only get the first three information ( request / Response line 、 Headlines 、 Blank line )
HTTP The status code
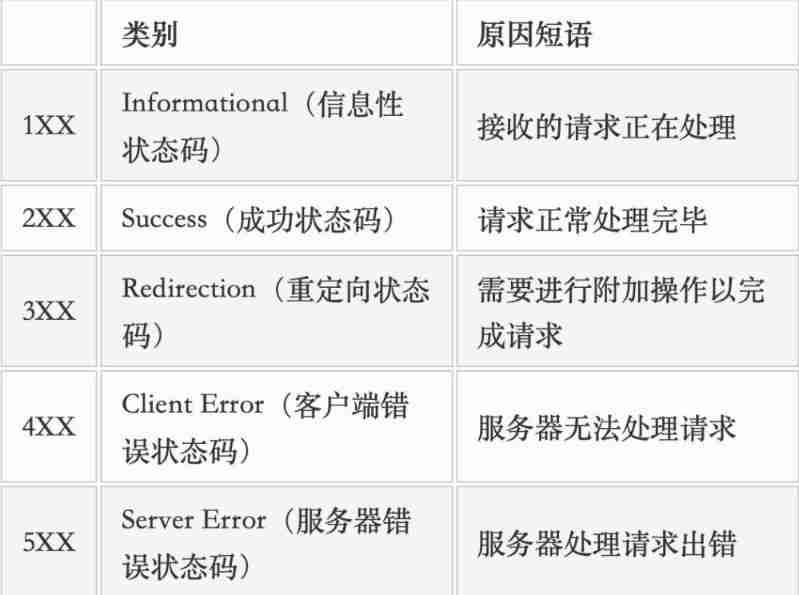
The most common status codes , such as 200(OK), 404(Not Found), 403(Forbidden), 302(Redirect, Redirect ), 504(Bad Gateway)
HTTP common Header
- Content-Type: data type (text/html etc. )
- Content-Length: Body The length of
- Host: Client notification server , The requested resource is on which port of which host ;
- User-Agent: Declare the user's operating system and browser version information ;
- referer: Which page does the current page Jump from ;
- location: collocation 3xx Use of status code , Tell the client where to visit next ;
- Cookie: For storing a small amount of information on the client side . Usually used to implement a session (session) The function of ;
User-Agent The historical story in
Cookie Introduction to : We learned before http Stateless characteristics of , This will bring a bad experience to users , and cookie It's to solve this problem .
principle : Also take the login of the website as an example to understand , When we first logged in on the website , The server saves the user name and password information , When the server responds , Will be in response Contained in the set-cookie: user name 、 password … Information about , When the client receives , The browser is cookie This information is saved in this file . Next time I enter this website , When the browser sends a request to the website , Will carry this cookie File with the request Send it to the server , The server checks , After checking the correctness , We no longer need to enter the password manually .
cookie The essence of the browser is a file , It is divided into memory level and disk level . Memory level cookie Only valid within the current browser opening time , Close the browser and open it next time , We re-enter the website , You still need to enter the account and password to log in . Disk level cookie Is saved locally , In this way, it is not limited by the condition that the browser opens , It can be saved for a long time .
But actually , This is also risky , In case we are hacked , Get the local cookie, He can pass this cookie Access the information we have also visited .
Session Even with Cookie Used together with . After our first login , The server no longer uses user names and passwords response Come back , Instead, use a session Files keep our private information , Then generate a unique sid To mark it , And then again response in , from set-cookie:sid, At this time, the sid return , The local cookie Kept in sid. The next time you visit the website , The browser carries cookie Send a request , Server pass sid Find customer information , Then allow customers to access .
cookie and session It's relatively safe , But it may still be stolen . At this time, all you steal is sid, Instead of our user name and password . And he doesn't know sid Which website does it correspond to . To change the password, you need the original password , Unless our password is too simple to be seen by others , Otherwise, he can't change our password and let us lose this account forever , Unless the background server is broken , Get the code .
The simplest HTTP The server
To achieve one of the simplest HTTP The server , Output only on Web pages “hello world”; As long as we follow HTTP Construct data according to the requirements of the protocol , It's easy to do ;
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<string>
#define BAGLOG 5
using namespace std;
class httpserver{
private:
int _port;
int _lsock;
public:
// structure
httpserver(int port)
:_port(port)
,_lsock(-1)
{
}
// destructor
~httpserver()
{
if (_lsock != -1)
close(_lsock);
}
void initServer()
{
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
// Create socket
_lsock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_lsock < 0)
{
cerr << "socket error !" << endl;
exit(1);
}
// binding
struct sockaddr_in local;
// take local Clear the contents of
bzero(&local, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if (bind(_lsock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
{
cerr << "bind error !" << endl;
exit(2);
}
// monitor
if (listen(_lsock, BAGLOG) != 0)
{
cerr << "listen error !" << endl;
exit(3);
}
}
void EchoHttp(int sock)
{
// Short link execution
// receive data
char request[1024];
ssize_t s = recv(sock, request, sizeof(request) - 1, 0);
if ( s > 0 )
{
request[s] = 0;
// Print request
cout << request << endl;
// Respond to
// Response line
string response = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n";
// Respond to the headlines
response += "Content-type: text/html\r\n";// The type of sending is html, Page type
// Respond to blank lines
response += "\r\n";
// Response Content
response += "\ <html>\ <head>\ <title>ysj</title>\ </head>\ <body>\ <h1>Welcome</h1>\ <p>Hello World !</p>\ </body>\ </html>\r\n";
send(sock, response.c_str(), response.size(), 0);
}
close(sock);
}
void start()
{
while (1)
{
// Establishing a connection
sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
bzero(&peer, len);
int sock = accept(_lsock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if (sock < 0)
{
cerr << "accept error !" << endl;
continue;
}
cout << "get a link..." << endl;
// Create child processes to handle tasks
pid_t id = fork();
if (id == 0)// Subprocesses
{
// The parent process ignores the SIGCHLD The signal
close(_lsock);
EchoHttp(sock);
exit(0);
}
close(sock);
}
}
};
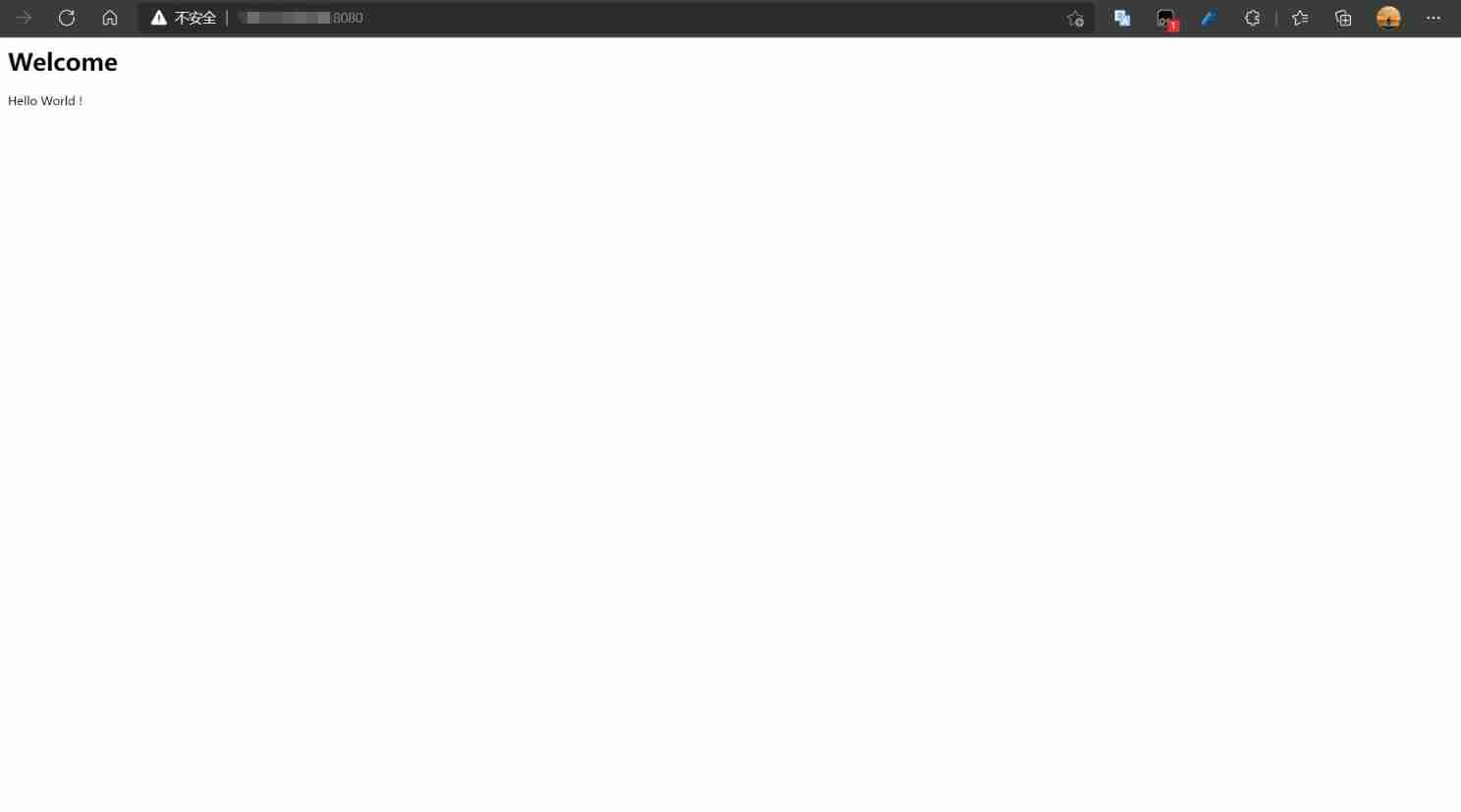
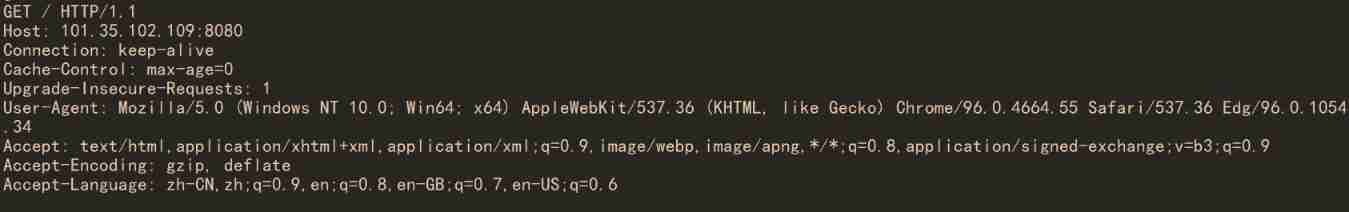
compile , Start the service . Enter... In the browser http://[ip]:[port], You can see the displayed results “Hello World”
remarks :
Here we use 8080 The port number started HTTP The server . although HTTP Servers generally use 80 port , But it's just a common habit . Is not to say that HTTP The server cannot use other port numbers .
Use chrome When testing our server , You can see that there is another request made by the server GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1 this favicon.ico_ Baidu Encyclopedia (baidu.com)
If we set the status code to 404 Will it show classic Not Found page ?
The answer is : I won't , The display of the page depends on html To set up , It is not determined by the status code
Temporary redirection and permanent redirection
Match status code 3xx Use . When the browser receives a redirect response , The new... Provided by this response will be adopted URL , And load it immediately ; Most of the time , In addition to a small performance loss , Redirection is invisible to the user .
Transform the above server , Set to redirect :
Set in the response header :location: http://baidu.com\r\n
No text is required .
// Response line
string response = "HTTP/1.0 302 Found\r\n";
// Respond to the headlines
response += "Content-type: text/html\r\n";// The type of sending is html, Page type
response += "location: https://www.baidu.com\r\n";// The type of sending is html, Page type
// Respond to blank lines
response += "\r\n";
Enter the ECS public network ip Add slogan , Will jump to Baidu
http And https
https Is in http Directly add another layer to the transport layer SSL/TLS(TLS yes SSL The standardized version of ): Encrypt data / Decrypt .
In most cases, symmetric encryption is used .
Symmetric and asymmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption : Only one key , Encrypt and decrypt with the same key . The client encrypts the data according to the key , The server decrypts the data according to the key . The key is only known by both the client and the server . Send the key to the server , But it may be hijacked by hackers , So simple symmetric encryption is not safe .
So there is asymmetric encryption :
Asymmetric encryption : Encrypt and decrypt through public key and private key . Usually , The public key is used to encrypt , Private key used to decrypt .
The following figure shows the process of sending keys with asymmetric encryption :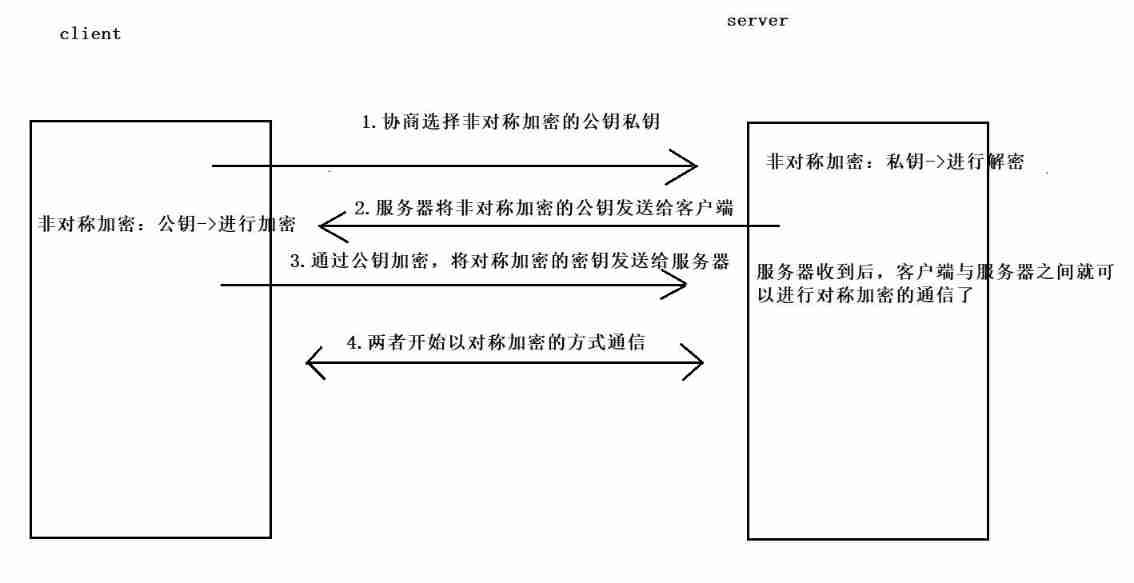
The server has many algorithms for public and private keys , The client and server negotiate which algorithm to use , After negotiation , Each will generate a pair of public and private keys . The server sends its own public key to the client , Keep the private key for yourself , such , The client can encrypt the sent data with the public key of the server , The encrypted data can only be decrypted with the private key of the server . Then the client also sends its public key to the server , After the server gets the public key of the client , The data can be encrypted according to the public key and sent to the client , Again , Only the private key of the client can be decrypted .
Now we can encrypt the data , But we still don't know whether the other party is the object we want to communicate , The server needs to apply SSL Certificate to prove its identity , Must let SSL When the certificate takes effect, it should be submitted to CA(Certificate Authority Certificate Authority Center , Everyone trusts the certificate issued by this institution ) apply , The certificate indicates who the domain name belongs to and so on .
After the client and server complete three handshakes , Both parties will negotiate the encryption method , Then the server will send the certificate to the client to show its identity .
Mixed encryption
Although we can use asymmetric encryption to communicate , But each communication uses asymmetric encryption , It takes a lot of time to encrypt and decrypt , Affect efficiency . So in fact, we use a mixture of the two to encrypt , That is, first obtain the public keys of both parties through asymmetric encryption , The server then sends it through asymmetric encryption Symmetric key , In this way, after the client receives , The two can communicate in the way of symmetric encryption .
Why use symmetric encryption ?
Asymmetric encryption : Low efficiency
Symmetric encryption : More efficient
边栏推荐
- Boder radius has four values, and boder radius exceeds four values
- Zoom with unity mouse wheel: zoom the camera closer or farther
- Unity makes AB package
- 5. 无线体内纳米网:十大“可行吗?”问题
- Le lancement du jupyter ne répond pas après l'installation d'Anaconda
- Crawler (14) - scrape redis distributed crawler (1) | detailed explanation
- 知识图谱构建流程步骤详解
- 微信小程序常用集合
- [Yann Lecun likes the red stone neural network made by minecraft]
- 2022 nurse (primary) examination questions and new nurse (primary) examination questions
猜你喜欢

Why do novices often fail to answer questions in the programming community, and even get ridiculed?
Pytest (3) - Test naming rules

Gui Gui programming (XIII) - event handling
Tencent byte Alibaba Xiaomi jd.com offer got a soft hand, and the teacher said it was great
看过很多教程,却依然写不好一个程序,怎么破?
JMeter server resource indicator monitoring (CPU, memory, etc.)

2022 construction electrician (special type of construction work) free test questions and construction electrician (special type of construction work) certificate examination
设计你的安全架构OKR

【GET-4】
![[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control](/img/df/dd84508dfa2449c31d72c808c50dc0.png)
[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control
随机推荐
使用.Net驱动Jetson Nano的OLED显示屏
[weekly pit] output triangle
[cloud lesson] EI lesson 47 Mrs offline data analysis - processing OBS data through Flink
Core principles of video games
Pytest (3) - Test naming rules
Number of schemes from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the chessboard (2)
Learn to punch in Web
Node.js: express + MySQL实现注册登录,身份认证
JMeter server resource indicator monitoring (CPU, memory, etc.)
js获取浏览器系统语言
2022 construction electrician (special type of construction work) free test questions and construction electrician (special type of construction work) certificate examination
【计网】第三章 数据链路层(3)信道划分介质访问控制
使用.Net分析.Net达人挑战赛参与情况
数字三角形模型 AcWing 1018. 最低通行费
Qinglong panel white screen one key repair
Quel genre de programmation les enfants apprennent - ils?
HMS Core 机器学习服务打造同传翻译新“声”态,AI让国际交流更顺畅
Redisson bug analysis
New generation garbage collector ZGC
Oceanbase Community Edition OBD mode deployment mode stand-alone installation