Some time ago , In order to optimize a somewhat complex function , I used the shared workers + indexDB, Build a high-performance multi page sharing service . Because it's the first time it's really used workers, I have more experience than before , So share it here !
Various worker Summary
There are three kinds of worker: ordinary worker、shared worker、service worker.( There are very few documents that say there are four kinds of , One more. audio worker, But in fact, the so-called audio worker Namely audio context, Used to build powerful sounds / Video processing system )
- Ordinary worker, It's also called special use worker, Can only be used by the script that generated it , Global object this yes DedicatedWorkerGlobalScope object
- share worker, namely sharedworker, Can be different window page ,iframe, as well as worker visit ( Of course, we have to follow the homology limit ), Global object this yes SharedWorkerGlobalScope object .
- serviceWorker, Specially designed for PWA It was born of application worker, Construct a PWA Must be based on https, And the key signature used must be through CA The certification , Otherwise, your browser will be considered insecure , Instead of loading your service worker. Because of this particularity , I don't know much about service worker!
serviceWorker As a general web Applications 、 Browsers and the web ( If available ) Previous proxy servers . They are designed to ( Among other things ) Create an effective offline experience , Block network requests , And take appropriate actions and update the resources that reside on the server according to the availability of the network . They will also allow access to push notifications and background synchronization API.
As an official standard ,3 Kind of worker The current browser support is very good , Safe to use ! Uh , wait a minute ,shared worker It doesn't seem to be very supportive :
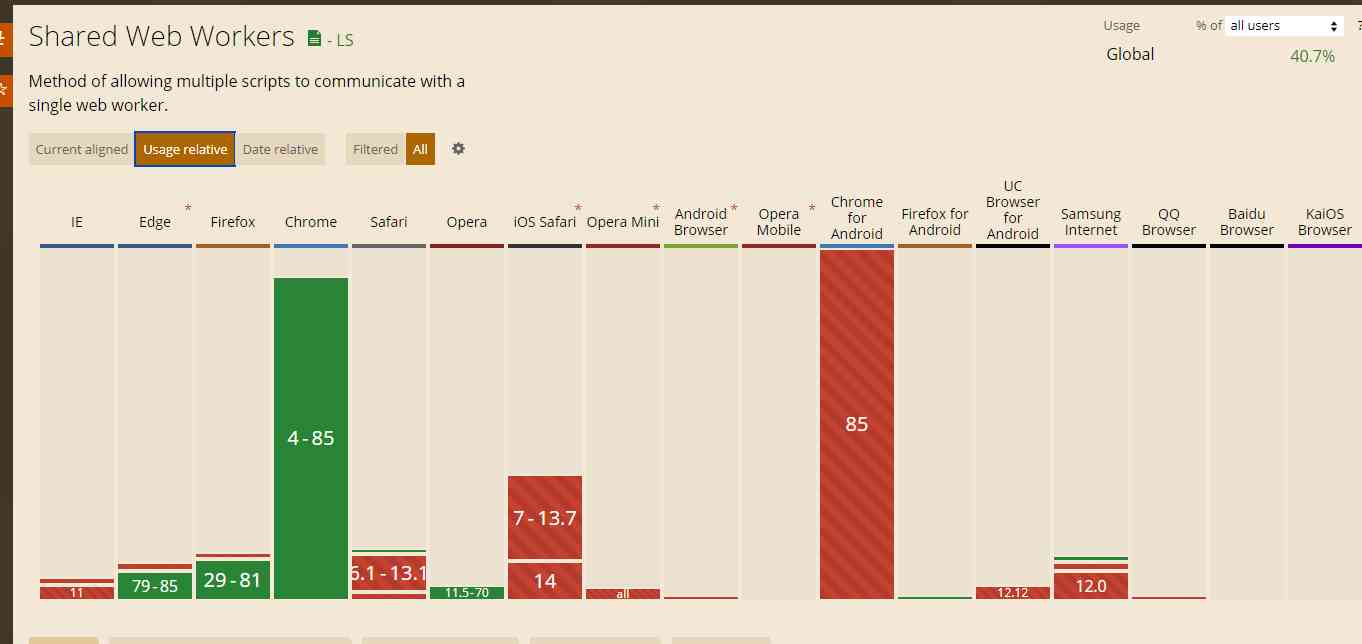
Don't be nervous , What is not supported is mainly mobile terminals with few application scenarios ( Who will open multiple windows for mobile applications ?) and ios 了 , In general, we can ignore ( If you have to think about ios Of web End , Then we have to consider a fallback plan ).
If you want to implement the function , It is normal for users to operate in multiple windows ; A database ( Such as indexDB)、socket Wait for the link ; A lot of the same common variables …… There is no doubt that you should use shared worker!
I want to optimize the function has these characteristics , This is the adoption of shared worker Why .
worker Interaction with the main thread
It's only for special use worker and sharedWorker Two kinds of (service worker There is no in-depth understanding of ). special worker and sharedWorker The difference is very small , So the next step is to put the special worker Explain clearly , Explain again sharedWorker The difference between .
special worker Interaction with the main thread
Example :
// The main thread : const worker = new Worker('./worker.js') worker.onmessage = (e) => { console.log('[main receive]:',e.data ) } worker.postMessage('Hello ,this is main thread') // worker.js: addEventListener('message', function (e) { console.log('[worker receive]:', e.data ) postMessage('Hi,this is worker thread') });
- Main thread and worker It's all through postMessage Method to send a message to the other party .
- Both sides are monitoring message Events to receive messages ( There are two ways to monitor : addEventListener and onmessage , That's it. DOM Event ).
- Event handler data The value of the field is what is passed when the message is sent .
Running results :

postMessage send out + monitor message Event reception —— The interaction principle is so simple , It's also the only way to interact !
Deep into the data delivery of messages
Data will never be referenced “ share ” In the past , Or be copied , Or be transferred
Copy
Normal data transfer , It's done by copying . In other words, it's a copy, not a quote , If it's an object , So modifying the object's properties doesn't affect each other —— Data can change independently , They don't influence each other .
and indexDB equally , Copy is to use Structured cloning Normative , After testing, it has at least the following side effects :
- Objects cannot contain methods , You can't copy the method
- The object cannot contain symbol, You can't copy symbol, The key is symbol The properties of are ignored
- Class information for most objects is lost . Such as : Pass a obj=new Person() The data received will not be Person This kind of information .
But if it's a built-in object , Such as Number,Boolean Such an object , You don't lose !( Be careful : This and mdn The description is different ) - Properties that cannot be enumerated (enumerable by false) Will be ignored .
- The writability configuration of properties (writable To configure ) Will be lost .
- After testing , All through Object.defineProperties Newly added ( Be careful It's new !) Properties will be ignored .
Transfer
Copy can have performance problems in some cases , For example, make a copy of 500M The file of , It will definitely take more time . In addition to copying, it also provides a way to transfer data .
At present, only 4 Object support transfer :ArrayBuffer, MessagePort, ImageBitmap and OffscreenCanvas.
ArrayBuffer It's the original binary buffer , file File,Blob, Various TypedArray , It's all based on arrayBuffer Of . Next, let's say ArrayBuffer To illustrate the transfer of data :
Data that can be transferred , It can also be delivered by copying :
1 // The main thread : 2 const worker = new Worker('./worker.js') 3 const u8 = new Uint8Array(new ArrayBuffer(1)) // Create a length of 1 Of TypedArray u8 4 u8[0] = 1 5 worker.onmessage = (e) => { 6 const receive = e.data 7 console.log('[main receive]:', receive, 'orginal:', u8) 8 } 9 worker.postMessage(u8) // Through ordinary copies , take u8 Pass to worker 10 11 12 // worker.js : 13 addEventListener('message', function (e) { 14 const receive = e.data 15 receive[0] = 9 // worker received u8 after , Change the content 16 console.log('[worker change]:',receive) 17 postMessage(receive) 18 });
console Print the results :

This example only shows that , Transferable bufferArray It can also be delivered by copy . Pay attention to the second print : As expected , Main thread and worker Thread data changes independently .
Transfer delivery example :
The transfer is simple , Just in postMessage when , Additionally, pass in the second parameter , Indicates the object to be transferred , Modify the above example slightly :
1 // The main thread : 2 const worker = new Worker('./worker.js') 3 const u8 = new Uint8Array(new ArrayBuffer(1)) 4 u8[0] = 1 5 worker.onmessage = (e) => { 6 const receive = e.data 7 console.log('[main receive]:', receive, 'orginal:', u8) 8 worker.postMessage('finish') 9 } 10 worker.postMessage(u8 , [u8.buffer]) // The second parameter represents the object to transfer : Note that this has to be an array ; What's shifting is typedArray Of buffer, instead of typedArray! 11 12 13 14 // worker.js : 15 let receive 16 addEventListener('message', function (e) { 17 if(e.data==='finish'){ 18 console.log('[worker after transfer]',receive) 19 return; 20 } 21 receive = e.data 22 receive[0] = 9 23 console.log('[worker change]:',receive) 24 postMessage(receive,[receive.buffer]) // Transfer typedArray Of buffer,typedArray The length will become 0! 25 26 }, false);
console Print result of ( Pay attention to understand the two empty typedArray, Why an empty array , because buffer Of “ Right to use ” It's been transferred !):

Put binary data directly Transfer To the child thread , Once transferred , The main thread can no longer use the binary data !
sharedWorker And dedicated worker The difference of
Differences in message interaction :
sharedWorker Interact with the main thread and dedicated worker Is essentially the same , Just one more port:
1 // The main thread : 2 const worker = new SharedWorker('worker.js', { name: ' Public service ' }) 3 // establish worker when , Except for the file path , You can also pass in some additional configuration : Such as name. 4 // worker Of name Yes id The function of , Different pages want to share sharedWorker, The same name is necessary ! 5 const key = Math.random().toString(16).substring(2) 6 worker.port.postMessage(key) // adopt worker.port Send a message 7 worker.port.onmessage = e => { // adopt worker.port receive messages 8 console.log(e.data) 9 } 10 11 12 // worker.js: 13 const buf = [] 14 onconnect = function (evt) { // When other threads create sharedWorker In fact, it is to sharedWorker Sent a link ,worker I'll get one connect event 15 const port = evt.ports[0] // connect Event handle evt.ports[0] It's a very important object port, It is used to send and receive messages from the corresponding thread 16 port.onmessage = (m) => { 17 buf.push(m.data) 18 console.log(buf) // I don't see this print ? See the debug differences section ! 19 port.postMessage('worker receive:' + m.data) 20 } 21 }
Pay attention to the note above , Information exchange is through port Conduct ! Usually a sharedWorker It can correspond to multiple main threads , therefore sharedWorker One more. connect event , Get their own port Communicate with their respective main threads !
It should be noted that , stay sharedWorker in , If not through onmessage But through addEventListener monitor message To receive messages , Must explicitly call start Open the connection , Otherwise, you won't be able to receive a message , Only messages can be sent . Example :
// sharedWorker Inside : port.start() port.addEventListener('message',e=>{ // ... }) // Inside the main thread : worker.port.start() worker.port.addEventListener('message',e=>{ // ... })
Debugging differences :
In the example above, there are two prints , The first 8 That's ok Main thread print worker The news came from , The first 18 That's ok worker Internal print cache [ From the main thread ] news . Strangely enough , When you open the developer tool , stay Console I don't see No 18 Line print information !
To see the first 18 Line printed information on sharedWorker debug , The next two steps need to be taken :
Start a new tab , URL input :chrome://inspect/#workers The interface is as follows :
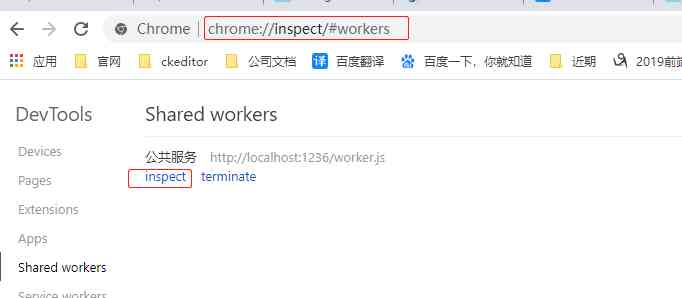
Click on inspect( Never click on terminate, This is the end worker Of ), You'll see that the browser opens a new window , The interface of the new window is the developer tool interface ( done web Mobile terminal development should be very familiar with this interface ):
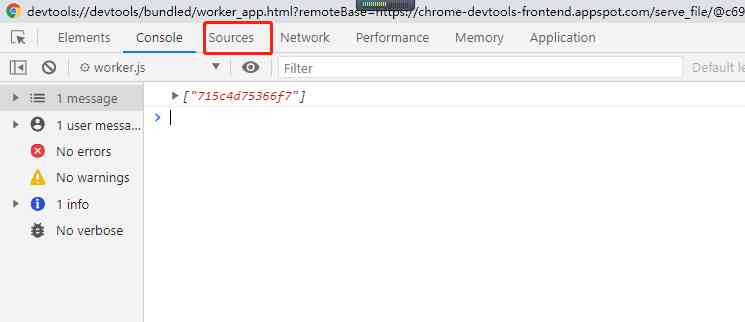
Switch to Sources page , You can do that. SharedWorker The code has been debugged !
Global object differences :
In the main thread , Everything is easy to understand , We created worker To listen or send messages , But in worker Inside , You will find that you call postMessage、onmessage Other methods .
This is because in the worker Inside , There is a global object self, amount to globalThis( If you support it ), It is equivalent to the global scope of this, A direct call is equivalent to self. call :
// special worker Example : globalThis.addEventListener('message', function (e) {}) self.postMessage(msgObj) // serviceWorker Example : // Top level scope : this.onconnect = function(evt){}
above globalThis,self,this Can be omitted , Similar to the main thread window!
As mentioned earlier : special worker Global object this yes DedicatedWorkerGlobalScope object ,sharedWorker It is SharedWorkerGlobalScope object , Both of them are WorkerGlobalScope The derived class , So we can judge :
console.log(this instanceof DedicatedWorkerGlobalScope) // special worker in true, sharedWorker An exception is reported in the main thread console.log(this instanceof SharedWorkerGlobalScope) // sharedWorker in true, special worker An exception is reported in the main thread console.log(this instanceof WorkerGlobalScope) // special worker and sharedWorker All of them are true, Exception error in main thread
Thread life cycle differences :
special worker Well understood. : Create a page for each page you open worker Threads , Close page worker Just destroy it , Refresh the page once worker It went through a process of destruction and creation , Different pages don't interfere with each other .
You can also take the initiative to destroy one as follows worker:
// special worker Inside self.close() // Active shut down worker Connect , Subsequent messages will fail silently // External main thread : worker.terminate() // Or close the connection like this outside , Be careful : Once closed worker,worker Will be destroyed ,worker All ongoing tasks within ( Such as scheduled tasks ) Will be destroyed directly
One sharedWorker It can correspond to multiple main threads , therefore : When opening a page , without sharedWorker Created when , Otherwise, share the existing sharedWorker; When only the current page and sharedWorker When the connection , Close current page sharedWorker Will be destroyed , Refresh current page sharedWorker Will destroy first and then create .
sharedWorker Can also be actively disconnected , But just breaking the link , It will not destroy sharedWorker, Even if it's the only use sharedWorker 's page has broken the link .worker Internal ongoing tasks will work normally , It just can't communicate with the main thread !
// The main thread : worker.port.close() // Just close the connection // worker Inside ( Get port after ): port.close() // Just close the connection
A lot of people like to write code like this , But pay attention to the note ,:
const clients = new Set() // Used to record all and worker Connecting threads this.onconnect = function (c) { let port = c.ports[0] clients.add(port) // There is no way to know port It's disconnected ( If the page is closed ), therefore clients You can only add unlimited port. This can cause a memory leak // Before you have to , In order to achieve such things as “ Send messages to all pages ” When you need it , Pay attention to controlling the extent of memory leaks : // all port Use the same onmessageHandler Instance and onmessageerrorHandler example , It's a good choice ! port.onmessage = onmessageHandler port.onmessageerror = onmessageerrorHandler } function onmessageHandler(evt){} function onmessageerrorHandler(evt){}
The interaction between events and exceptions
In the face of multiple anomalies and event related problems , You have to understand :worker and The main thread is two threads ! So it's easy to understand :
worker In the event , The main thread can't listen , vice versa ;worker The abnormal , The main thread is not aware of , vice versa ! Again , The only way they interact is postMessage And monitoring message event .
// worker.js Inside : // ... other code throw new Error('test error') // This error cannot be retrieved by the main thread , contrary Will you be in worker Of console see “ The error did not catch the hint ” Error prompt for , Not the main thread's console!
The main thread can listen to worker Of error event , But notice what this is error:
worker.onerror = e=>{ // Please note that Here, the main thread is listening to create worker It's abnormal , Instead of worker Create internal exception after successful creation // Exception while creating : Such as download worker Script error , Wrong path ,worker Script parsing error, etc }
Both sides can monitor messageerror event , But after testing, it has not been able to trigger this event , According to the official interpretation : When a message is received , But when the data of the message cannot be parsed successfully , Will trigger this event . Please note that , Here is “ receive ”! I tried to send an object that couldn't be copied ( If it contains function Field ), But it failed when it was sent .
You can see onerror and onmessageerror Events are events that have nothing to do with each other !
Conclusion
This article explains in depth worker and sharedWorker And The interaction of the main thread .
Now you can use two kinds of worker Did some simple work , But the work is more complicated , And in the face of webpack In a project like this , Use worker( or sharedWorker) There will be new problems . Coming soon : thorough web workers ( Next ), I will discuss with you in detail workers Best practices in Engineering .