当前位置:网站首页>Distributed cap theory
Distributed cap theory
2022-07-04 06:05:00 【Zhan sir (open source byte)】
CAP The theory is distributed system 、 In particular, the most discussed theory in the field of distributed storage . among C For consistency (Consistency),A For usability (Availability),P Represents partition fault tolerance (Partition tolerance).CAP Theory tells us C、A、P The three cannot be satisfied at the same time , Only two of them can be satisfied at most .
CAP A brief introduction to the theory
CAP The theory is distributed system 、 In particular, the most discussed theory in the field of distributed storage . among C For consistency (Consistency),A For usability (Availability),P Represents partition fault tolerance (Partition tolerance).CAP Theory tells us C、A、P The three cannot be satisfied at the same time , Only two of them can be satisfied at most .

CAP Two out of three
Uniformity (Consistency): A write operation returns success , Then all subsequent read requests must read this new data ; If the return fails , Then all read operations cannot read this data . All nodes access the same latest data .Usability (Availability): High availability for data updates , Requests can be processed in a timely manner , Not always waiting for , Even if a node fails .Partition tolerance (Partition tolerance): Can tolerate network partition , When the network is disconnected , The separated nodes can still provide services to the outside world .
Yes CAP Theoretical understanding
understand CAP The simplest theory is to imagine two replicas on either side of the partition , That is, the network between the two replicas is disconnected , Can't communicate .
- If one copy is allowed to update , It will lead to inconsistent data , That is, to lose C nature .
- If in order to ensure consistency , Set the replica on one side of the partition to unavailable , So lost again A nature .
- Unless two copies can communicate with each other , To guarantee C And promise A, This in turn leads to the loss of P nature .
Generally speaking, distributed systems using network communication , Can't give up P nature , Then we can only make a difficult choice in terms of consistency and availability .
CAP The expression of theory serves its purpose well , It broadens the thinking of distributed system designers , Design a variety of systems under a variety of alternatives . There have been countless new systems in the past decade , As a result, there have been quite a number of debates on the relative relationship between consistency and usability .
CAP In depth theoretical understanding
stay CAP Twelve years after the theory was put forward , The author came out to refute the rumor .“ Two out of three ” There has always been a misleading formula , It oversimplifies the relationship between properties :
- First , Because zoning rarely happens , So there's no reason to sacrifice when there's no partition in the system C or A.
- secondly ,C And A The trade-offs can occur repeatedly in the same system with very small granularity , And every decision may be made because of specific operation , Even because it involves specific data or users .
- Last , All three properties can be measured in degree , It's not black or white with or without . Usability is obviously in 0% To 100% Between successive changes , There are many levels of consistency , Even zoning can be subdivided into different meanings , For example, different parts of the system can have different cognition about whether there is a partition .
So consistency and usability are not incompatible , Either this or that .Paxos、Raft The equally distributed consistency algorithm is the witness of a good balance between consistency and availability .
If you reprint , Please indicate the source : Open source byte https://sourcebyte.cn/article/176.html
边栏推荐
- LayoutManager布局管理器:FlowLayout、BorderLayout、GridLayout、GridBagLayout、CardLayout、BoxLayout
- Accidentally deleted the data file of Clickhouse, can it be restored?
- HMS v1.0 appointment.php editid参数 SQL注入漏洞(CVE-2022-25491)
- How to realize multi account login of video platform members
- How to solve the component conflicts caused by scrollbars in GridView
- [microservice] Nacos cluster building and loading file configuration
- 4G wireless all network solar hydrological equipment power monitoring system bms110
- JS arguments parameter usage and explanation
- 2022.7.3-----leetcode. five hundred and fifty-six
- Excel 比较日器
猜你喜欢
Functions in C language (detailed explanation)
How to solve the component conflicts caused by scrollbars in GridView
接地继电器DD-1/60
gslb(global server load balance)技术的一点理解

How to choose the middle-aged crisis of the testing post? Stick to it or find another way out? See below
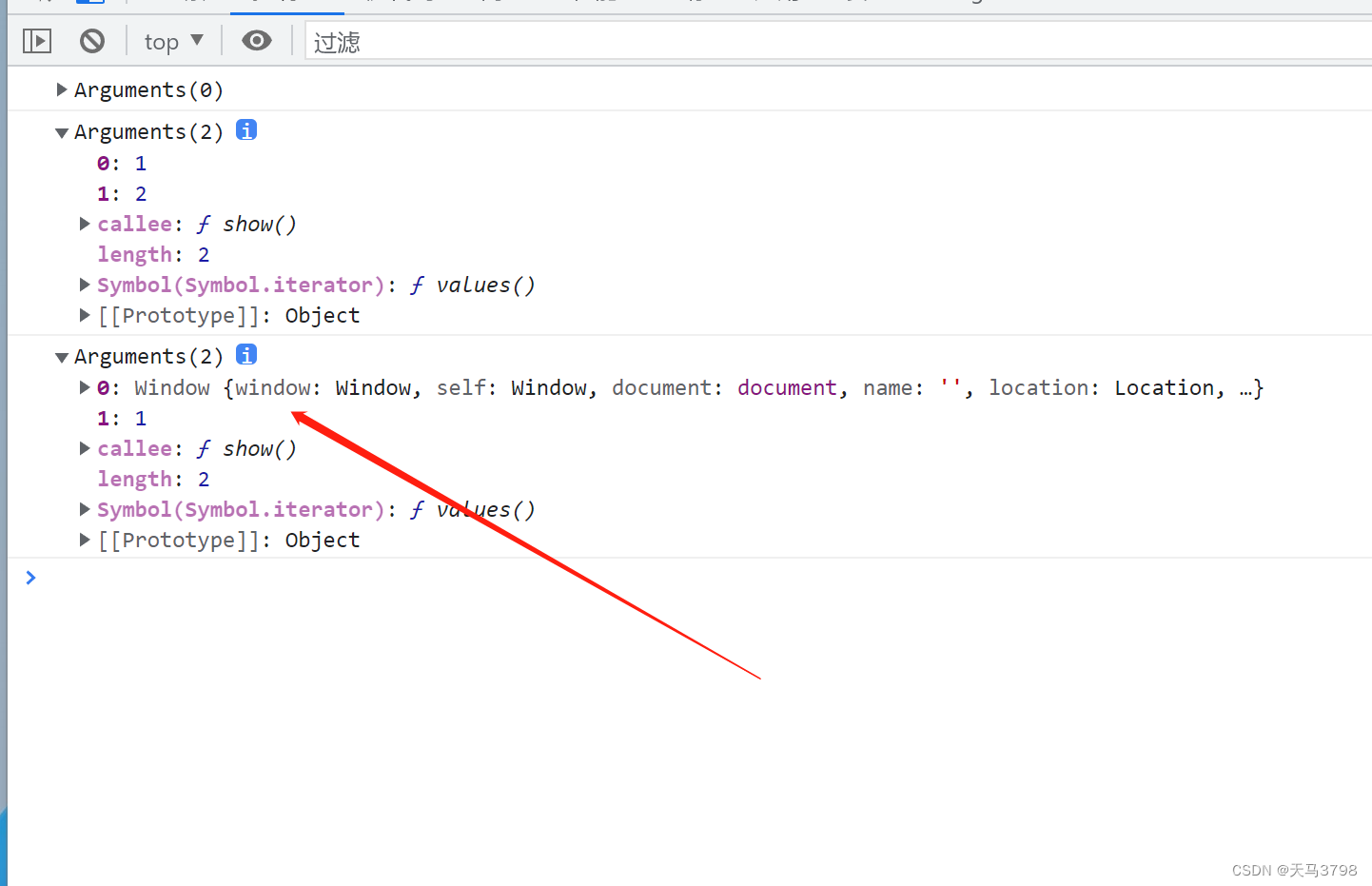
JS arguments parameter usage and explanation
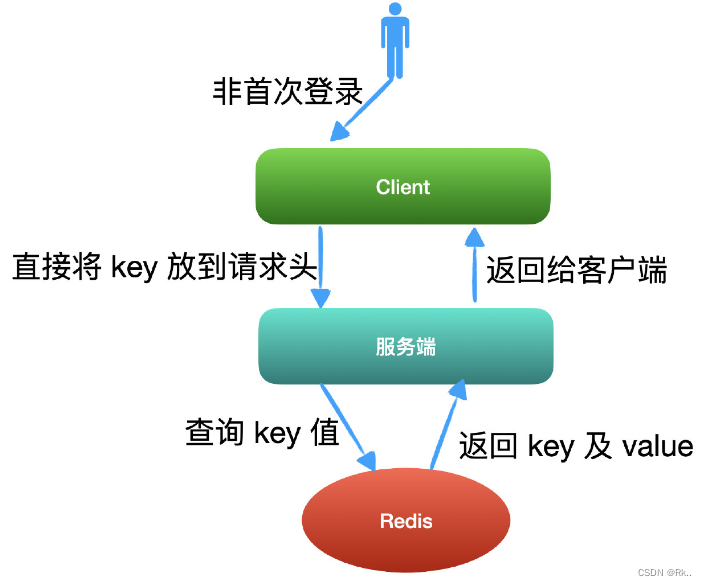
JSON Web Token----JWT和傳統session登錄認證對比

ES6 modularization
![[excel] PivotChart](/img/45/be87e4428a1d8ef66ef34a63d12fd4.png)
[excel] PivotChart
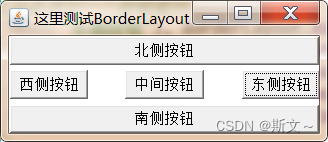
LayoutManager布局管理器:FlowLayout、BorderLayout、GridLayout、GridBagLayout、CardLayout、BoxLayout
随机推荐
Halcon图片标定,使得后续图片处理过后变成与模板图片一样
QT qtablewidget table column top requirements ideas and codes
Wechat applet +php realizes authorized login
js获取对象中嵌套的属性值
如何避免 JVM 内存泄漏?
js如何将秒转换成时分秒显示
QT QTableWidget 表格列置顶需求的思路和代码
Detectron: train your own data set -- convert your own data format to coco format
Review | categories and mechanisms of action of covid-19 neutralizing antibodies and small molecule drugs
Invalid revision: 3.18.1-g262b901-dirty
left_ and_ right_ Net interpretable design
198. House raiding
19. Framebuffer application programming
A little understanding of GSLB (global server load balance) technology
Webrtc quickly set up video call and video conference
fastjson
QT 获取随机颜色值设置label背景色 代码
Learning multi-level structural information for small organ segmentation
Design and implementation of redis 7.0 multi part AOF
测试岗的中年危机该如何选择?是坚守还是另寻出路?且看下文