当前位置:网站首页>[rust notes] 12 closure
[rust notes] 12 closure
2022-07-03 08:36:00 【phial03】
12 - Closure
Sort integers :
integers.sort();Closure : Anonymous function expression , Can be used to sort composite types :
struct City { name: String, population: i64, country: String, ... } /// Auxiliary function of cities sorted by population // receive City Record , Then extract the key (Key) fn city_population_descending(city: &City) -> i64 { -city.population } // sort_by_key Take the key function as an argument fn sort_cities(cities: &mut Vec<City>) { cities.sort_by_key(city_population_descending); } // The above two functions are abbreviated as follows through closures fn sort_cities(cities: &mut Vec<City>) { cities.sort_by_key(|city| -city.population) // |city| -city.population Receive a parameter city, return -city.polulation. }The feature of accepting closures in the standard library :
IteratorOfmapandfilterMethod , Used to operate sequence data- Start the new system thread
thread::spawnWait for the thread API. The core of concurrency is the exchange between threads , Closures can easily represent units of work . - Some methods calculate default values when necessary , Such as
HashMapOfor_insert_withMethod . The default value is passed in as a closure , Will only be called when a new value must be created .
12.1 - Capture variables
Closures can use data belonging to containing functions :
/// Sort by several different statistical indicators fn sort_by_statisics(citeis: &mut Vec<City>, stat: Statistic) { cities.sort_by_key(|city| -city.get_statistic(stat)); // Closures capture stat }Most languages that support closures , It needs to be closely combined with garbage collection , Like the one below JavaScript Code :
// Start the animation of rearranging city table rows function startSortingAnimation(cities, stat) { // Auxiliary function for sorting tables // Be careful , This function refers to stat function keyfn(city) { return city.get_statistic(stat); } if (pendingSort) pendingSort.cancel(); // Now start the animation , Pass in keyfn // The following sorting algorithm will call keyfn pendingSort = new SortingAnimation(cities, keyfn); }Rust There is no recycling , How to implement this feature ?
12.1.1 - Borrowed value closure
Closures follow borrowing and lifetime rules .
stay 12.1 In the case of , Because closures contain pairs
statReferences to , therefore Rust Don't let closures survive longer than
stat. Closures are only used during sorting .
- here
statWill be saved on the stack . - relative GC Distribution will be faster .
- here
Rust Use lifecycles to ensure code security , Not garbage collection .
12.1.2 - The closure of stolen value
The following example :
use std::thread; fn start_sorting_thread(mut cities: Vec<City>, stat: Statistic) -> thread::JoinHandle<Vec<City>> // The return value of the closure will be wrapped in JoinHandle Return to the calling thread { let key_fn = |city: &City| -> i64 { -city.get_statistic(stat) }; thread::spawn(|| { // `||` Indicates that the closure has no parameters . cities.sort_by_key(key_fn); cities }) }thread::spawnReceive a closure , And call this closure in the new system thread . The new thread runs in parallel with the caller . After the closure returns , The new thread exits .Closure
key_fnContains thestatReferences to . But this time Rust Will reject this program , And prompt the following information :problem 1: `|city: &City| -> i64` // `stat` is borrowed here problem 2: (stat) // may outlive borrowed value `stat`citiesIt belongs to unsafe sharing ,thread::spawnCreating a new thread cannot guarantee that it iscitiesandstatBe destroyed ( End of the function ) Finish the task beforeSolution : Give Way Rust hold
citiesandstatMove to using their closures , Instead of quoting them .fn start_sorting_thread(mut cities: Vec<City>, stat: Statistic) -> thread::JoinHandle<Vec<City>> { let key_fn = move |city: &City| -> i64 { -city.get_statistic(stat) }; // key_fn To obtain the stat The ownership of the thread::spawn(move || { // To obtain the cities and key_fn The ownership of the cities.sort_by_key(key_fn); cities }) }Add
movekeyword : tell Rust, This closure is not borrowing the variables it uses , But to steal it .
Rust There are two ways for closures to get data from containing functions : Transfer and borrowing .—— It is also a way to ensure thread safety
- If the closure transfers a replicable value (
i32), Then it will copy the value . therefore , In the above codeStatisticIt happens to be a replicable type , Then after creating the transfer closure that uses it , You can also usestat Vec<City>In this way, the type cannot be copied , Will really transfer . The above code transfers closures , holdcitiesMove to the new thread . After the code that created this closure ,Rust No more visits from otherscities.- The above code is transferred in closures
citiesafter , No need to usecities了 . If you still need to use , Then you can tell Rust clonecitiesAnd save the copy to another variable . A closure can only steal the copy it refers to .
- If the closure transfers a replicable value (
12.2 - Functions and closure types
Functions and closures can be used as values , Naturally, they also have their own types .
Rust The function value of is essentially a pointer :
The types of the following functions are
fn(&City) -> i64: Indicates receiving a parameter (&City), Return to onei64value .fn city_population_descending(city: &City) -> i64 { -city.population }You can use functions like other values . That is, you can save the function in a variable , You can also use commonly used Rust Syntax calculation function value :
let my_key_fn: fn(&City) -> i64 = if user.prefs.by_population { city_population_descending } else { city_monster_attack_risk_descending }; cities.sort_by_key(my_key_fn);The structure can contain fields of function type .
Generic types such as
VecYou can store a batch of functions , As long as theirfnThe same type is ok .The function value is very small , One
fnThe value is the memory address of the function machine code , And C++ The function pointer in is similar to .One function can take another function as an argument :
/// Pass in a group of cities and a test function /// Return to all cities that meet the conditions fn count_selected_cities(cities: &Vec<City>, test_fn: fn(&City) -> bool) -> usize { let mut count = 0; for city in cities { if test_fn(city) { count += 1; } } count } /// Test function example . /// The type of this function is :fn(&City) -> bool /// Follow count_selected_cities The parameters of the function test_fn The same type of fn has_monster_attacks(city: &city) -> bool { city.monster_attack_risk > 0.0 } // Calculate the risk of the city being attacked let n = count_selected_cities(&my_cities, has_monster_attacks);
Closures and functions are not of the same type , Each closure has its own type , In code that uses closures, you usually need to be generic .
The example shown below :
let limit = preferences.acceptable_monster_risk(); let n = count_selected_cities( &my_cities, |city| city.monster_attack_risk > limit // Type error : Type mismatch );For the above type error , The type signature of the function must be modified :
fn count_selected_cities<F>(cities: &Vec<City>, test_fn: F) -> usize where F: Fn(&City) -> bool { let mut count = 0; for city in cities { if test_fn(city) { count += 1; } } count }The new version of the
count_selected_citiesFunction is a generic , Receive any typeFParameters oftest_fn.FSpecial type must be realizedFn(&City) -> bool. All with one&CityFunctions and closures that are arguments and return a blog entry will automatically implement this feature :->And the following return value types are optional .- If omitted , Then the return value type is
().
fn(&City) -> bool // fn type ( Only functions ) Fn(&City) -> bool // Fn Special type ( Including functions and closures )The new version of the
count_selected_citiesCan receive functions , You can also receive closures :count_selected_cities( &my_cities, has_moster_attacks ); count_selected_cities( &my_cities, |city| city.monster_attack_risk > limit );Although closures can call , But it's not
fntype . Closure|city| city.monster_attack_risk > limitHave their own type . This type is usually a temporary type , Big enough to store its data .
Any two closures have different types .
- All closures will be implemented
FnSpecial type . Fn(&City) -> bool
- All closures will be implemented
12.3 - The properties of closures
Closures in most programming languages are usually allocated on the heap , Dynamic dispatch , Then the garbage collection program is responsible for recycling . It is difficult for compilers to internalize closure optimization strategies , To reduce function calls and then reference other optimizations . Such closures usually slow down internal loops (tight inner loop) Performance of .
Rust Closures of are usually not allocated on the heap , Unless the closure is encapsulated in
Box、VecOr other containers . Each closure has a different type ,Rust The compiler only needs to know the type of closure being called , You can internalize the code line of the closure . therefore ,Rust Closures of support for use in internal loops .In the following example , The closure will reference two local variables : character string
foodThe sum is 27 Simple enumeration ofweather.let food = "tacos"; let weather = Weather::Tornadoes; |city| city.eats(food) && city.has(weather) // a、 Use closures for the first time move |city| city.eats(food) && city.has(weather) // b、 Use closures for the second time |city| city.eats("crawfish") // c、 Use closures for the third time- Closure a、 In memory , This closure is similar to a small structure , It contains references to the variables he references .
- Closure b、 Same as above , But it is a transfer closure , Therefore, the actual value will be included , Instead of quoting .
- Closure c、 No variables in the environment are used . At this time, the structure is empty , Therefore, this closure will not occupy memory at all .
12.4 - Closures and security —— The method of allocating closures on the heap
Closures are mainly created by transferring or borrowing captured variables . The impact is not obvious , Especially when closures clear or modify captured values .
12.4.1 - Value killing closure
Kill value , I.e. clearing (drop) value , The most intuitive way is to call
drop():let my_str = "hello".to_string(); let f = || drop(my_str);If the
ftwo :f(); f();First call
f,my_strWill be cleared , It means that the memory for storing strings will be released , Return it to the system .Second call
f, The same operation is performed on one side . This is it. C++ Classic errors that trigger undefined behavior in : Repeat release (double free).
And in the Rust in , Compile time check can find the above error .
A closure can only be called once .
Closures must strictly follow the life cycle rules , That is, when calling , The value will be exhausted ( Transfer ).
12.4.2-FnOnce
Try to cheat Rust, Let it clear one twice
String. Construct the following generic function :fn call_twice<F>(closure: F) where F: Fn() { closure(); closure() }You can pass any implementation into this function
FnSpecial closures . Such closures do not accept parameters , And will return().hold 12.4.1 The closure of the unsafe closure in is passed in :
let my_str = "hello".to_string(); let f = || drop(my_str); call_twice(f);At compile time ,Rust The following errors will be reported :
error[E0525]: expected a closure that implements the `Fn` trait, but this closure only implements `FnOnce` --> closures_twice.rs:12:13 | 12 | let f = || drop(my_str); | ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | note: the requirement to implement `Fn` derives from here --> closures_twice.rs:13:5 | 13 | call_twice(f); | ^^^^^^^^^^The above error reflects Rust How to deal with “ Kill value closure ” Of . That is, it is completely forbidden from the language level .
image
fSuch a closure cannot beFn, It is a special type that is not universalFnOnce, This special closure can only be called once .First call
FnOnceClosure time , The closure itself will also be used .As shown below , Two special types
FnandFnOnceThe definition of :// Pseudo code , No parameters /// about `Fn` Closure ,`closure()` Method will be extended to `closure().call()`, This method takes its own reference as a parameter , So this closure will not be transferred . trait Fn() -> R { fn call(&self) -R; } /// But if a closure can only be called safely once , That is for `FnOnce` Closure ,`closure()` Method will be extended to `closure().call_once()`, This method will achieve `self` Value , So closures will be used . trait FnOnce() -R { fn call_once(self) -> R; }
The following common errors , You need to pay attention in the real world :
Direct iteration
dict, Cause it to be used . Make the closure becomeFnOncetype .let dict = produce_glossary(); let debug_dump_dict = || { for (key, value) in dict { println!("{:?} - {:?}", key, value); } };Should be changed to
&dict, instead ofdict, That is, the reference of the value to be accessed . Let this closure be calledFntype .let debug_dump_dict = || { for (key, value) in &dict { println!("{:?} - {:?}", key, value); } };
12.4.3-FnMut
Rust Think not
mutValues can be safely shared between threads .- But if the sharing is not
mutThe closure containsmutdata , It's also unsafe . - Call this closure in multiple threads , It will lead to various resource contention problems , It is the same as multiple threads reading and writing the same data at the same time .
- But if the sharing is not
FnMutClosure of type : Contains modifiable data ormutReferenced closures .That is, closures that can write data .
FnMutClosures should usemutReference to call .Definition :
// A feature is defined as a pseudo code implementation /// Fn Are closures and functions that have no limit on the number of calls , It's all fn The highest kind of function . trait Fn() -> R { fn call(&self) -R; } /// FnMut If the closure itself is declared mut, Closures that can also be called multiple times . trait FnMut() -R { fn call_mut(&mut self) -R; } /// FnOnce If the caller has a closure , Can only be called once . trait FnOnce() -R { fn call_once(self) -R; }
Anything that needs to be done with
mutWay to access values , But closures that do not clear any values areFnMutClosure .let mut i = 0; let incr = || { // incr yes FnMut, instead of Fn i += 1; // Borrow right i Modifiable reference of println!("Ding! i is now: {}", i); }; call_twice(incr);Every
FnAll satisfied withFnMutThe requirements of , EveryFnMutAll satisfied withFnOnceThe requirements of .Fn()yesFnMut()Sub type of ;FnMut()yesFnOnce()Sub type of .
call_twice The function should receive all FnMut Closure , That is, it should be revised to :
fn call_twice<F>(mut closure: F) where F: FnMut { closure(); closure(); }Binding by
F: Fn(), It is amended as followsF: FnMut(). In this way, you can still receive allFnClosure .At this point, you can call the new
call_twicefunction .let mut i = 0; call_twice(|| i += 1); assert_eq!(i, 2);
12.5 - Callback
Callback : User provided functions , For the library to call later .
With Icon Frame example :
type BoxedCallback = Box<Fn(&Request) -> Response>; struct BasicROuter { routes: HashMap<String, BoxedCallback> }Each box can contain closures of different types .
One
HashMapCan contain all types of callbacks .Adjust the corresponding method :
impl BasicRouter { /// Create an empty router fn new() -> BasicRouter { BasicRouter { routes: HashMap::new() } } /// Add a route to the router fn add_route<C>(&mut self, url: &str, callback: C) where C: Fn(&Request) -> Response + 'static { self.routes.insert(url.to_string(), Box::new(callback)); } }Processing requests :
impl BasicRouter { fn handle_request(&self, request: &Request) -> Response { match self.routes.get(&request.url) { None => not_found_response(), Some(callback) => callback(request) } } }
12.6 - Use closures effectively
stay MVC(Model—View—Controller, Model — View — controller ) In design mode , For every element on the user interface ,MVC Frameworks will be created 3 Objects : Model 、 Views and controllers . Model to represent UI State of element ; Views are responsible for the appearance of elements ; The controller handles user interaction .
- Every object has a reference to another or two objects . It may be a direct reference , It may also be referenced through a callback .
- stay 3 When an event occurs to one of the objects , It will notify the other two objects , So everything will be updated immediately .
- however , Which object has other objects cannot be distinguished .
stay Rust in , Ownership must be clear , Circular references must be eliminated . Models and controllers cannot directly reference each other .
You can let each closure receive the reference it needs as a parameter , Solve the problem through closure ownership and lifecycle .
You can assign a value to everything in the system , Then pass the value instead of the reference .
Can achieve many MVC One of the variants , Ensure that not all objects refer to each other .
You can imitate someone Not MVC System , such as Fackbook Of Flux framework , Implement one-way data flow .
from user input -> Action -> Dispatcher -> Store -> View -> to disblay
Iterators are the subject of closures that really shine .
- You can use Rust The simplicity of closures 、 Write different styles of code quickly and efficiently .
See 《Rust Programming 》( Jim - Brandy 、 Jason, - By orendov , Translated by lisongfeng ) Chapter 14
Original address
边栏推荐
- Advanced OSG collision detection
- Development material set
- Delete the last character of the string in golang
- [redis] redis persistent RDB vs AOF (source code)
- Unity editor expansion - controls, layouts
- Cloudcompare learning (1) - cloudcompare compilation and common plug-in implementation
- Mall management system of database application technology course design
- [rust notes] 05 error handling
- Unity learning notes
- Chocolate installation
猜你喜欢

Jupyter remote server configuration and server startup
![[concurrent programming] Table hopping and blocking queue](/img/b7/023991a00956e469af855e7a81e126.jpg)
[concurrent programming] Table hopping and blocking queue
Advanced OSG collision detection
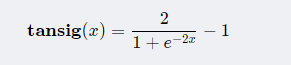
Detailed explanation of all transfer function (activation function) formulas of MATLAB neural network

Base64 and base64url
![[updating] wechat applet learning notes_ three](/img/05/958b8d62d3a42b38ca1a2d8631a7f8.png)
[updating] wechat applet learning notes_ three

Introduction to hexadecimal coding

UE4 source code reading_ Bone model and animation system_ Animation node

数据库原理期末复习

Unity interactive water ripple post-treatment
随机推荐
Thymeleaf 404 reports an error: there was unexpected error (type=not found, status=404)
Visual Studio (VS) shortcut keys
【更新中】微信小程序学习笔记_3
UE4 call DLL
Unity editor expansion - the framework and context of unity imgui
Redis cluster series 4
Ue5 opencv plug-in use
Graphics_ Games101/202 learning notes
Kunlunbase meetup is waiting for you!
Unity4.3.1 engine source code compilation process
Unity multi open script
Development material set
数据分析练习题
Talking about: is the HashSet set ordered or disordered /hashset set unique, why can we store elements with the same content
Why can void * be a general pointer
分配异常的servlet
[RPC] RPC remote procedure call
Huawei interview summary during the epidemic
Get to know unity2 for the first time
[redis] redis persistent RDB vs AOF (source code)