当前位置:网站首页>Distributed transactions - Theoretical Overview
Distributed transactions - Theoretical Overview
2022-06-12 09:09:00 【Eden Garden】
Distributed transactions
1. summary
1.1 What is business
What is business ? Let me give you an example from life : You go to the store to buy something is an example of a business , Shopping is a trade , contain “ Hand in hand , Delivery on one hand ” Two actions , Both payment and delivery must be successful , The deal is successful , Any of these actions failed , The transaction must be cancelled .
Understand the above example , Let's look at the definition of business :
Business can be seen as a big activity , It's made up of different little activities , These small activities are either all successful , All or nothing .
1.2 Local transactions
In software system , Transactions are usually controlled by relational databases , This is achieved by using the transaction characteristics of the database itself , So it's called database transaction , Because the application mainly depends on the relational database to control the transaction , The database is usually on the same server as the application , So transactions based on relational databases are also called local transactions .
Four features of database transaction ACID:
A(Atomic): Atomicity , All operations that make up a transaction , Or they all succeed , Or none at all , Partial success and partial failure are not possible .
C(Consistency): Uniformity , Before and after transaction execution , The consistency constraint of the database is not broken . such as : Yiya turns to Yiqi 13 Billion , The data before and after transfer is in correct status, which is called consistency , If someone turns out 13 Billion , A Qi account has not been increased 13 There is a data error , There is no consistency .
I(Isolation): Isolation, , Transactions in a database are usually concurrent , Isolation means that the execution of two concurrent transactions does not interfere with each other , One transaction cannot see the intermediate state of other transaction running processes . Dirty reading can be avoided by configuring transaction isolation level 、 Repeat reading and so on .
D(Durability): persistence , After the transaction completes , Changes to data from this transaction are persisted to the database , And will not be rolled back .
When database transaction is implemented, all operations involved in a transaction will be incorporated into an indivisible execution unit , All operations in the execution unit are either successful , Or they all failed , As long as any of these operations fail , Will cause the entire transaction to roll back .
1.3 Distributed transactions
With the rapid development of Internet , Software system from the original single application to distributed application , The following figure describes the evolution from a single application to a distributed microservice application :
The distributed system will split an application system into multiple services that can be deployed independently , Therefore, remote cooperation between services is needed to complete transaction operations , This transaction mechanism in distributed system environment is called Distributed transactions .
We know that local transactions rely on the transaction features provided by the database itself to implement , So the following logic works :
begin transaction;
-- 1. Local database operations : A certain amount is reduced
-- 2. Local database operations : Increased amount of a Qi
commit transaction;
But in a distributed environment , It could be like this :
begin transaction;
-- 1.A Microservices operate on local databases : Let someone reduce the amount
-- 2.A Microservice remote call B Microservices : Ask someone to increase the amount
commit transaction;
So on the basis of distributed architecture , Traditional database transactions cannot be used , For example, the above example , The accounts of Ya and Qi are not in the same database or even in the same application system , How to realize transfer transaction ? That is, the same function , It was originally completed by a system , Even if this function contains many operations , You can also use database transactions ( Local transactions ) Get it done , Now, multiple operations contained in this function may be performed by multiple systems ( Microservices ) Participate in the completion of , At this point, the database transaction ( Local transactions ) There's nothing we can do , This requires a new distributed transaction theory to support .
2. Basic theory of distributed transaction
Unlike local transactions , Distributed system is called distributed system , It's because the nodes that provide services are distributed on different machines , Interact with each other through the Internet , Then there must be the risk of network failure , This professional scenario of network disconnection is called network partition , However, this network problem should not cause the whole system to fail to provide services , The network factor has become one of the criteria for distributed transactions . therefore , Distributed transactions need further theoretical support .
2.1 CAP theory
2.1.1 understand CAP
CAP yes Consistency、Availiability、Partition tolerance Abbreviations of three words , They mean consistency 、 Usability 、 Zone tolerance . For the convenience of CAP Theoretical understanding , Let's combine some business scenarios in the e-commerce platform to understand CAP.
Business background :
We know that each database server has its maximum number of connections 、 Load and throughput , If one day we can no longer meet our business needs , You need to expand a few horizontally Slave( From database ) To share Master( Master database ) The pressure of the .
If the service needs a database IO intensive , You may often encounter additions, deletions and changes, which affect the query efficiency . This requires read-write separation , Add, delete and modify a / P in the master database , The query operation is handled from the database , The data of the master-slave database shall be synchronized .
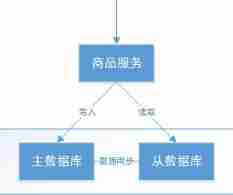
Execute the process :
1、 Commodity service requests the master database to write commodity information ( Add the goods 、 Modify the goods 、 Delete item )
2、 The master database successfully wrote to the goods and services response .
3、 Commodity service requests to read commodity information from the database .
C - Consistency:
Consistency means that the read operation after the write operation can read the latest data status , When data is distributed over multiple nodes , The data read from any node is the latest state .
Above picture , To achieve consistency in reading and writing commodity information is to achieve the following goals :
1、 Goods and services are successfully written into the master database , Then query the new data from the database successfully .
2、 Commodity service failed to write to master database , It also fails to query the new data from the database .
A - Availability :
Availability means that any transaction operation can get response results , And there will be no response timeout or response error .
Above picture , Product information reading to meet the availability is to achieve the following goals :
1、 Data query requests received from the database can immediately respond to the data query results .
2、 Response timeout or response error is not allowed from database .
To ensure availability , Generally, it needs to be realized by adding slave database nodes .
P - Partition tolerance :
Usually each node of the distributed system is deployed in different subnets , This is network partitioning , Inevitably, the communication between nodes will fail due to network failure . When a distributed system encounters a node or network partition failure , Still able to provide external services to meet the consistency and availability , This is partition tolerance . One or more machines in the distributed system are down , The rest of the machines are still working properly to meet the needs of the system , Or there are network exceptions between machines , Separate the distributed system into separate parts , Each part can also maintain the operation of the distributed system , In this way, it has better partition tolerance .
Above picture , Reading and writing commodity information to meet the tolerance of zoning is to achieve the following goals :
1、 The failure of synchronizing data from the master database to the slave database does not affect the read / write operation .
2、 The failure of one node does not affect the external services provided by the other node .
2.1.2 CAP combination
1、 Does the above example also have CAP Well ?
In all distributed transaction scenarios, there will be no CAP Three characteristics , Because I have P Under the premise of C and A Can't coexist .
On the premise of ensuring partition tolerance , Consistency and availability cannot be balanced , If you want to improve the availability of the system, you need to add multiple nodes , If you want to ensure data consistency, you must achieve data consistency of each node , The more nodes, the better availability , But the data consistency will be worse .
2、CAP What are the combinations ?
1)AP:
Give up consistency , The pursuit of partition tolerance and usability . This is the choice of many distributed systems when they are designed .
for example : Commodity management above , It can be realized AP, The premise is that as long as the user can accept that the queried data is not up-to-date in a certain period of time . Usually achieve AP Will guarantee final consistency , Later on BASE Theory is the basis AP To expand , Some business scenarios such as : Order refund , Today's refund is successful , Tomorrow's account is due , As long as the user can accept the payment within a certain period of time .
2)CP:
Discard availability , Pursue consistency and partition fault tolerance , our zookeeper In fact, the pursuit of strong consistency , Another example is inter-bank transfer , A transfer request is not complete until the banking systems of both parties have completed the whole transaction .
3)CA:
Give up zoning tolerance , That is to say, there is no partition , Do not consider the problem of network impassability or node hang up , You can achieve consistency and availability . Then the system will not be a standard distributed system , Our most commonly used relational database meets CA.
Commodity management above , If we want to achieve CA, The structure is as follows :
2.1.3 summary
We learned from the above CAP Knowledge of theory ,CAP It's a proven theory : A distributed system can only satisfy the consistency at most (Consistency)、 Usability (Availability) And zone tolerance (Partition tolerance) Two of these three . It can be used as our architecture design 、 Consideration criteria for technology selection . For most large Internet application scenarios , There are many nodes 、 Deployment is decentralized , And now the scale of the cluster is growing , So node failure 、 Network failure is the norm , And make sure the service availability reaches N individual 9(99.99…%), And to achieve good response performance to improve the user experience , Therefore, the following choices are generally made : Guarantee P and A, Abandon C Strong consistency , Ensure ultimate consistency .
2.2 BASE theory
1、 Understand strong and final consistency
CAP The theory tells us that a distributed system can only satisfy at most Uniformity (Consistency)、** Usability (Availability) and Zone tolerance (Partition tolerance)** Two of these three , among AP More in practical application ,AP That is, to give up consistency , Ensure availability and partition tolerance , But in actual production, many scenarios need to achieve consistency , Let's take the example above , The master database synchronizes data with the slave database , Even if there is no consistency , But in the end, we also need to synchronize data successfully to ensure data consistency , This consistency and CAP The consistency in is different ,CAP Consistency in requires that each node data must be consistent at any time when queried , It emphasizes strong consistency , But the ultimate consistency is to allow the data of each node to be inconsistent over a period of time , But after a period of time, the data of each node must be consistent , It emphasizes the consistency of the final data .
2、Base A brief introduction to the theory
BASE yes Basically Available( Basic available )、Soft state( Soft state ) and Eventually consistent ( Final consistency ) Abbreviations of three phrases .BASE The theory is right CAP in AP An extension of , Get availability by sacrificing strong consistency , In case of failure, it is allowed that some parts are not available but the core functions shall be available , Allow data to be inconsistent over time , But in the end it's consistent . Satisfy BASE Theoretical business , We call it “ Flexible business ”.
- Basic available : When a distributed system fails , Allow the loss of some available functions , Make sure the core functions are available . Such as , There is something wrong with the payment of e-commerce website transactions , Products can still be viewed normally .
- Soft state : Because don't ask for strong consistency , therefore BASE Allow intermediate states in the system ( Also called Soft state ), This state does not affect system availability , As of the order " In the payment "、“ Data synchronization ” Equal state , After the data is finally consistent, the status changes to “ success ” state .
- Final agreement : Final agreement means after a period of time , All node data will be consistent . As of the order " In the payment " state , In the end, it will become “ Successful payment ” perhaps " Failure to pay ", Agree the order status with the actual transaction result , But it takes a certain delay 、 wait for .
------------- The content of the article comes from hmB Station courses , To use as a study -------------
边栏推荐
- Grab screen and ground glass effect
- 清华大学数据挖掘笔记(一)
- 更改tabledata列名
- 【字符集六】宽字符串和多字节字符互转
- POI library update excel picture
- Introduction to applet cloud development -- questionnaire evaluation applet practice (7)
- On absolute value function in C language
- Binary tree calculation problem
- Exists usage in SQL
- 128. 最長連續序列-哈希錶
猜你喜欢

Summary of common character sets

Minimum transfer times

Introduction to applet cloud development -- questionnaire evaluation applet practice (7)

【无标题】Task3 多路召回

IP, DNS, domain name, URL, hosts
![(node:22344) [DEP0123] DeprecationWarning: Setting the TLS ServerName to an IP address is not permit](/img/c1/d56ec09663857afa52f20848aeadac.png)
(node:22344) [DEP0123] DeprecationWarning: Setting the TLS ServerName to an IP address is not permit

解压缩zip文件的工具类

ISCSI详解(五)——ISCSI客户端配置实战

Analysis of 43 cases of MATLAB neural network: Chapter 8 prediction of GRNN Network - Freight Volume Prediction Based on generalized regression neural network
Popular understanding of time domain sampling and frequency domain continuation
随机推荐
RuntimeError:Input and parameter tensors are not at the same device, found input tensor at cuda:0 an
128. 最长连续序列-哈希表
torch. logical_ And() method
Popular understanding of time domain sampling and frequency domain continuation
43 cas d'analyse du réseau neuronal MATLAB: chapitre 7 régression du réseau RBF - - réalisation de la régression fonctionnelle non linéaire
Machine learning notes - circular neural network memo list
List < string > sort
(十五) TweenRunner
After receiving the picture, caigou was very happy and played with PDF. The submission format was flag{xxx}, and the decryption characters should be in lowercase
Exists usage in SQL
(13) Text rendering text
Black screen solution for computer boot
Chapter 8 - two basic problems of data processing
2022 melting welding and thermal cutting test questions and answers
Chapter IV - first procedure
重启Kubernetes Pod的几种方式
128. Plus longue séquence continue - table de hachage
CodeCraft-22 and Codeforces Round #795 (Div. 2) 题解
Quick sort
长安链节点证书、角色、权限管理介绍