当前位置:网站首页>Alibaba Tianchi SQL training camp task4 learning notes
Alibaba Tianchi SQL training camp task4 learning notes
2022-07-05 22:57:00 【abbert】
1. Pay attention to distinguish the associated sub queries 、 The union of two tables 、 The table connects the relationship between the three .
2. Use NOT The predicate subtracts the set , Find out product In the table , The price is higher than 2000, But the profit is lower than 30% The goods , The results should be shown in the table below .

Solve this problem , use where+and It can be fixed , But the problem here is to let you use not Predicate resolution , So in and The latter condition cannot be expressed directly , Use not in + The way of subquery , The syntax in this way is equivalent to a comparison conditional statement .
SELECT * FROM product WHERE sale_price > 2000 AND product_id NOT IN (SELECT product_id FROM product WHERE sale_price<1.3*purchase_price)
3. Use not in + union It can achieve the purpose of finding the symmetrical difference between two tables , But because in MySQL 8.0 in , Because the of two tables or query results cannot be obtained directly , Therefore, it is not suitable to use the above idea to calculate the symmetry difference . Fortunately, there are difference set operations that can be used . You can see intuitively , The difference in symmetry between two sets is equal to A-B And go up B-A, Therefore, in practice, we can use this idea to find the symmetry difference .
4. With the help of the Union and symmetric difference of the two tables, the purpose of finding the intersection can be achieved , The intersection of two sets can be regarded as the intersection of two sets, and the symmetry difference between the two sets is removed .
5. Writing order :
SELECT》FROM 》WHERE》GROUP BY》HAVE》ORDER BY
Execution order :
FROM 》WHERE》GROUP BY》HAVE》SELECT》ORDER BY
6. natural SQL The order of statement execution is to execute the subquery first , But the order of associated sub queries is to execute the main query first . The main purpose of this is to solve , The main query queries a row of records each time and the sub query directly outputs the aggregate query results . adopt “ relation ” To subquery , Limit the number of outputs of subqueries each time , So as to achieve the purpose of querying different kinds of aggregation results in a table , Therefore, the associated sub query needs to execute the main query first . It's kind of similar python in for Nesting of loops .

Associated subqueries and table joins can achieve the same effect , But why should there be table connections ?
If you have excel Of vlookup function , You will find that this function can also achieve this function . actually , In the way of thinking , Associated subqueries are more like vlookup function : By table A Main table , Then according to the table A The value of each row of the associated column , Go to the table one by one B Find rows with equal values in the associated columns in .
When the amount of data is small , There is no performance problem with this approach , But when the amount of data is large , This method will lead to large computational overhead : For each row of data returned by the external query , Will pass the value of an associated column to the internal sub query , Then the internal subquery executes a query based on the passed in value and returns its query result . This makes , For example, the returned result of the external main query has 10000 rows , Then the subquery will be executed 10000 times , This will lead to a terrible time consumption .
Why use associated subqueries ?
Sometimes you need to query the extension information in the same table , Do not find a subquery ( View ) As a reference, you cannot directly query , So at this time, you can use the associated sub query , Problems that can be queried with associated subqueries can also be solved with inner connections , Just embed the filter criteria in one of the connection tables in advance .
About within the link , The following three points need to be noted :
Key points : To make a connection, you need to be in FROM Use multiple tables in clause .
Previous FROM There is only one table in the clause , And this time we used shopproduct and product Two tables , Use keywords INNER JOIN You can link the two tables together :
FROMshopproduct AS SP INNER JOINproduct AS Pcombination WHERE Clause uses inner links
The first increase WEHRE The way clause , The above query is used as a sub query , Enclosed in parentheses , Then add filter criteria to the outer query .
SELECT *
FROM (-- Step 1: query results
SELECT SP.shop_id
,SP.shop_name
,SP.product_id
,P.product_name
,P.product_type
,P.sale_price
,SP.quantity
FROMshopproduct AS SP
INNER JOINproduct AS P
ON SP.product_id = P.product_id) AS STEP1
WHERE shop_name = ' Tokyo '
AND product_type = ' clothes ' ; Remember what we learned when we learned sub query ? The result of the subquery is actually a table , It's just a virtual table , It doesn't really exist in the database , Only other tables in the database are filtered , A result of query operations such as aggregation " View ".
This way of writing can clearly distinguish each operation step , We are not very familiar with SQL Querying the execution order of each clause can help us .
But actually , If we know WHERE Clause will be FROM Clause is followed by , in other words , Finishing INNER JOIN … ON Get a new table , Will execute WHERE Clause , Then you get the standard writing :
SELECT SP.shop_id
,SP.shop_name
,SP.product_id
,P.product_name
,P.product_type
,P.sale_price
,SP.quantity
FROMshopproduct AS SP
INNER JOINproduct AS P
ON SP.product_id = P.product_id
WHERE SP.shop_name = ' Tokyo '
AND P.product_type = ' clothes ' ;(1) Write where Filter statements (2) After filtering in each query, connect the results
No matter how to solve the problem , It's important to think , Get a question , First analyze whether you need to connect 、 How to determine the screening criteria 、 Need grouping and merging , Consider these problems clearly before , Choose a suitable sentence to write .
Example :
Find out the name and price of clothing goods in each store . The following results are expected :

The problem can be analyzed by sql The execution sequence of statements is substituted into the analysis step by step
1.from: Where are from ,product And shopproduct The two tables , Therefore, internal connection is required
shopproduct as sp inner join product as p on sp.product_id = p.product_id
2.where: What are the screening criteria , According to the meaning of the title, the condition is product_tape = ‘ clothes ’
3.select:SP.shop_id,SP.shop_name,SP.product_id ,P.product_name, P.product_type, P.purchase_price
( For the sentences that do not need to be executed in the topic, you can directly skip )
The final complete statement is :
-- Refer to the answer 1-- Do not use subqueries
SELECT SP.shop_id,SP.shop_name,SP.product_id ,P.product_name, P.product_type, P.purchase_price FROM shopproduct AS SP INNER JOIN product AS P ON SP.product_id = P.product_id WHERE P.product_type = ' clothes ';
-- Refer to the answer 2-- Use subquery
SELECT SP.shop_id, SP.shop_name, SP.product_id ,P.product_name, P.product_type, P.purchase_price FROM shopproduct AS SP INNER JOIN -- from product Table to find out the information of clothing products (SELECT product_id, product_name, product_type, purchase_price FROM product WHERE product_type = ' clothes ')AS P ON SP.product_id = P.product_id;
The second method is to directly perform a subquery on the table used for connection , So the direct connection is the filtered sub query ( View ), There is no need to filter after the connection .
Exercises :
In every store , What are the selling prices of the highest priced goods ?
-- Refer to the answer
SELECT SP.shop_id
,SP.shop_name
,MAX(P.sale_price) AS max_price
FROMshopproduct AS SP
INNER JOINproduct AS P
ON SP.product_id = P.product_id
GROUP BY SP.shop_id,SP.shop_name1.from
2.group by ,group by The next grouping field needs to be filled in according to the actual situation , It is not limited to finding a maximum value and grouping a field
3.select
Inner link and associated subquery
Find out the items in each category that sell at a price higher than the average price of the product .
Associated subquery
SELECT product_type, product_name, sale_price FROM product AS P1 WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price) FROM product AS P2 WHERE P1.product_type = P2.product_type GROUP BY product_type);
Internal connection :
SELECT P1.product_id ,P1.product_name ,P1.product_type ,P1.sale_price ,P2.avg_price FROM product AS P1 INNER JOIN (SELECT product_type,AVG(sale_price) AS avg_price FROM product GROUP BY product_type) AS P2 ON P1.product_type = P2.product_type WHERE P1.sale_price > P2.avg_price;
Ideas :
1.from:product surface , There is no need to connect
2.where: The selling price of each product category sale_price Higher than the average selling price of this kind of goods avg_price Here is an aggregate function , So just use where Pick up group by Definitely not the right number , Therefore, you need to associate sub queries first , Extract the average selling price of each category , Then output the query results , It's a way of thinking .
In addition, we encounter such problems , Self connection can be considered to solve , Is the connection of the same table , Similar to the associated sub query of the same table . First step : First, calculate the average selling price in groups ; The second step : Make internal connection according to the type of goods ; The third step : increase where Clause , Define the screening criteria .
summary : For cases where records need to be compared with aggregate results , Or use sub queries to get aggregate results and compare them with each record ; or : Aggregate first , Then make an internal connection with another table .
SELECT P1.product_id
,P1.product_name
,P1.product_type
,P1.sale_price
,P2.avg_price
FROM product AS P1
INNER JOIN
(SELECT product_type,AVG(sale_price) AS avg_price
FROM product
GROUP BY product_type) AS P2
ON P1.product_type = P2.product_type
WHERE P1.sale_price > P2.avg_price;
(task4-4.2.1.5) The background is : Find out the items in each category that sell at a price higher than the average price of the product ? Now we use inner connection to solve this problem , I want to ask you something ,P2 The table has passed group by Aggregated product_type, Why can it be combined with those that have not been aggregated P1 Table passing product_type Internal connection , Because “ON P1.product_type = P2.product_type”, I wrote this sentence , Even if the number is different, it can be connected ?
There is a mistake here : Table connection does not require the same number of public fields , There is no need to have the same name , As long as the value of the upper number is right , So here we can directly aggregate the P2 With non aggregated P1 Connected .
Secondly, don't force yourself to find “ or : Aggregate first , Then make an internal connection with another table .” This method is connected with the previous example “ Use subquery ” And “ Do not use subqueries ” There are two ways to find correlation , Because this question is to P1 The records in the table are consistent with P2 Records in which the average value is calculated by grouping aggregation are connected , It is fundamentally different from the two situations mentioned above , So there is no correlation between the two .
-------------------------------------------
This result is not consistent with the result given in the book , Less exercise T T-shirt , This is due to exercise T T-shirt regist_date Field is empty , When making natural connections , From product and product2 The movement of T When comparing this line of data , It's actually equivalent linking field by field , Remember when we were 6.2ISNULL,IS NOT NULL The comparison method of missing values learned in this section can be known , The two missing values are compared with an equal sign , The result is not true . The link will only return those lines that return true to the link condition .
Exercises : Use inner links to find product Table and product2 The intersection of tables .
SELECT P1.*
FROMproduct AS P1
INNER JOINproduct2 AS P2
ON (P1.product_id = P2.product_id
AND P1.product_name = P2.product_name
AND P1.product_type = P2.product_type
AND P1.sale_price = P2.sale_price
AND P1.regist_date = P2.regist_date)
The results are as follows

Note the above results and P230 The results are not consistent – Less product_id='0001' This business , Looking at the source table data, you can find , The less this line of data regist_date Is the missing value , Recall from Chapter 6 IS NULL The predicate , We learned that , This is because missing values cannot be compared with equal signs .
If we just use product_id To connect :
SELECT P1.*
FROMproduct AS P1
INNER JOINproduct2 AS P2
ON P1.product_id = P2.product_id
Query results :

It's the same this time . Internal connections only connect common records .
The inner link will discard the unsatisfied in the two tables ON The conditions are right , The opposite of the inner link is the outer link . The outer link will selectively keep the unmatched rows according to the type of outer link .
According to which table the reserved rows are located , There are three forms of external links : Left link , Right link and all outer link .
The left link will be saved and cannot be followed in the left table ON Clause matches to the line , At this time, the rows corresponding to the right table are all missing values ; The right link will save the right table, which cannot be followed ON Clause matches to the line , At this time, the rows corresponding to the left table are all missing values ; The total external join will save two tables at the same time ON Clause matches to the line , The corresponding row in another table is filled with missing values .
The corresponding grammars of the three external links are :
-- Left link
FROM <tb_1> LEFT OUTER JOIN <tb_2> ON <condition(s)>
-- Right link
FROM <tb_1> RIGHT OUTER JOIN <tb_2> ON <condition(s)>
-- All external links
FROM <tb_1> FULL OUTER JOIN <tb_2> ON <condition(s)>Before, whether it is external connection or internal connection , A common prerequisite is the link condition –ON Clause , Used to specify the conditions of the link . If you have tried a link query without this link condition , You may have found out , There will be many lines . Remove... From the link ON Clause , It's called cross linking (CROSS JOIN), Cross linking is also called Cartesian product , The latter is a mathematical term . Two sets are Cartesian products , It's just using sets A Every element and set in B Each of the elements in makes up an ordered combination . Database table ( Or subquery ) And , Intersection and difference are operations such as expanding or filtering restrictions on the table vertically , This requires the number of columns in the table and the data type of the column in the corresponding position " Compatible with ", Therefore, these operations do not add new columns , And cross connect ( The cartesian product ) Is to expand the table horizontally , That is, add a new column , This is consistent with the function of the link . But because there is no ON Limitation of clause , Each row of the left table and the right table will be combined , This often leads to many meaningless rows appearing in the search results . Of course , In some query requirements , Cross linking also has some uses .
So in the associated sub query , Each piece of data in the main query will be combined with the sub query .
exercises :
4.1select *
form product as p1 full outer join product2 as p2
where sale_price > 5000;
intersection : The union of two sets removes the symmetry difference between the two sets
Symmetry difference :A-B And go up B-A, Union of two difference sets
Difference set :
A-B:select * from product where product_id not in (select product_id from product 2);
B-A:select * from product2 where product_id not in (select product_id from product 1);
Symmetry difference :
select * from product where product_id not in (select product_id from product 2)
union
select * from product2 where product_id not in (select product_id from product 1);
4.2.select * from
(select * from product
union
select * from product2) as p1
where product_id not in
(select * from product where product_id not in (select product_id from product 2)
union
select * from product2 where product_id not in (select product_id from product 1);
4.3
select p2.shop_name,p1.product_id,p1.product_type,max(sale_price)
from product as p1 right outer join shopproduct as p2 on product_id
group by product_type;
4.4
select product_type,product_id,sale_price
from product as p1
where sale_price = (select product_type,product_id,max(sale_price)
from product as p2
where p1.product_type = p2.product_type
group by p2.product_type);
select product_type,product_id,sale_price
from product as p1 inner join (select product_type,product_id,max(sale_price)
from product as p2
group by p2.product_type)
on p1.product_type = p2.product_type;
4.5
select product_id, produc_name, slae_price
from product
order by sale_price;
边栏推荐
- 透彻理解JVM类加载子系统
- 终于搞懂什么是动态规划的
- Go language learning tutorial (XV)
- Binary tree (II) -- code implementation of heap
- H5c3 advanced - player
- APK加固技术的演变,APK加固技术和不足之处
- Element positioning of Web Automation
- SPSS analysis of employment problems of college graduates
- Metasploit(msf)利用ms17_010(永恒之蓝)出现Encoding::UndefinedConversionError问题
- Three.js-01 入门
猜你喜欢
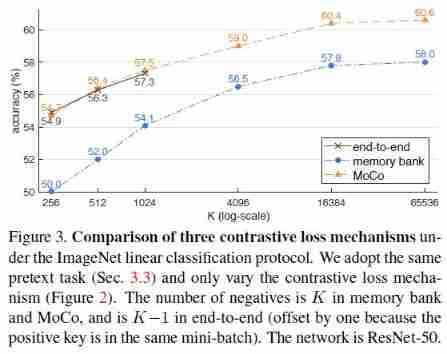
MoCo: Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
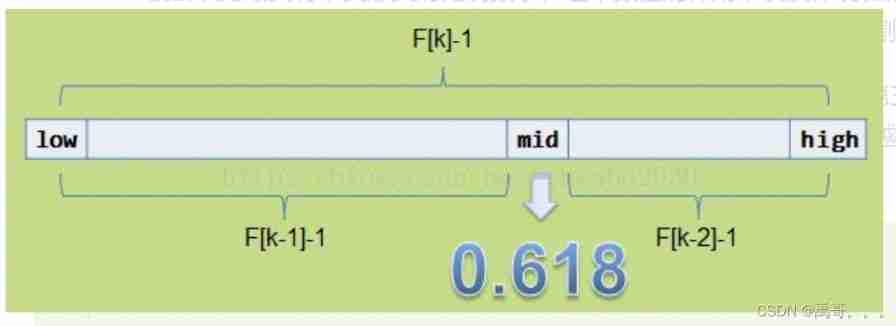
fibonacci search
2022 R2 mobile pressure vessel filling review simulation examination and R2 mobile pressure vessel filling examination questions
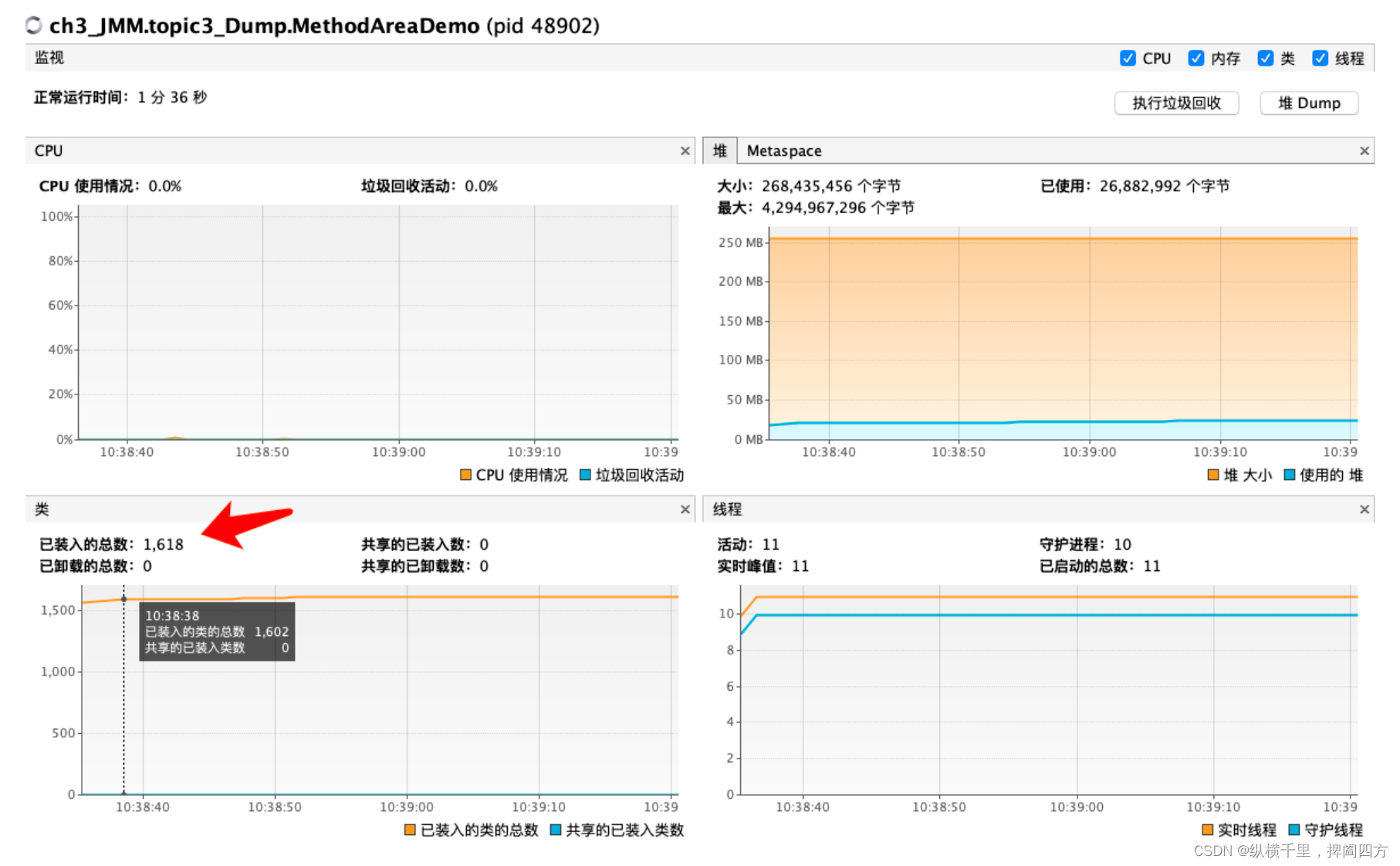
Fix the memory structure of JVM in one article

BFC block level formatting context
终于搞懂什么是动态规划的

Finally understand what dynamic planning is
audiopolicy
Selenium+Pytest自动化测试框架实战

Navigation day answer applet: preliminary competition of navigation knowledge competition
随机推荐
解决thinkphp启动时“No input file specified”的问题
One article deals with the microstructure and instructions of class
Openresty ngx Lua regular expression
分布式解决方案选型
Global and Chinese markets for reciprocating seal compressors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese markets for children's amusement facilities 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
3 find the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple
Event trigger requirements of the function called by the event trigger
谷歌地图案例
Lesson 1: serpentine matrix
终于搞懂什么是动态规划的
Fix the memory structure of JVM in one article
从 1.5 开始搭建一个微服务框架——日志追踪 traceId
一文搞定class的微觀結構和指令
我对新中台模型的一些经验思考总结
2022.02.13 - SX10-30. Home raiding II
Spectrum analysis of ADC sampling sequence based on stm32
d3dx9_ How to repair 31.dll_ d3dx9_ 31. Solution to missing DLL
My experience and summary of the new Zhongtai model
如何快速理解复杂业务,系统思考问题?