当前位置:网站首页>C language pointer (Part 2)
C language pointer (Part 2)
2022-07-07 09:06:00 【A big cat 1201】
author : A big cat 1201
special column :《C Language learning 》
Maxim : You just try to , Leave the rest to time !
C Language pointer ( medium-length )
stay C Language pointer ( Part 1 ) We have learned what pointers are , How to use the pointer , And some precautions , Now let's have a deeper understanding of pointers .
Pointers and arrays
Ben meow's article The essence of array names As mentioned in , The array name of a one-dimensional array is the address of the first element , Then we can put the array name in the pointer variable to access the array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0 };
int* p = arr; // The pointer holds the address of the first element of the array
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("&arr[%d] = %p <====> p+%d = %p\n", i, &arr[i], i, p + i);
}
return 0;
}
Running results 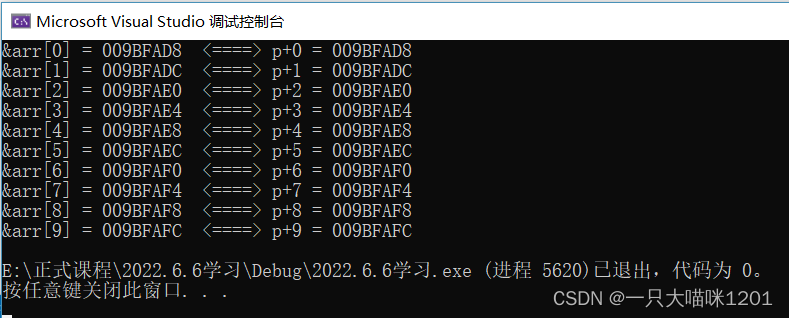
You can see ,p+i The value of is an array arr Subscript is i The address of the element of , Next, we access the array through pointer variables
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int* p = arr; // The pointer holds the address of the first element of the array
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p + i));
}
return 0;
}
p+i Find the address of the element in the array , Then you can access the elements in the array by dereferencing .
The secondary pointer
Pointer variables are also variables , It is also stored in memory , So pointer variables also have addresses , Its address is also placed in the pointer variable .
The pointer variable storing the address of the first level pointer variable is called the second level pointer variable .
There are also three levels of pointers , Four level pointer and so on .
We create a secondary pointer
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
return 0;
}
Secondary pointer creation rules :
int** ppa = &pa; It can be written. int* * ppa = &pa;
The left side of the equal sign can also be written 3 Parts of ,int*, * Number ,ppa
* The sign indicates that this is a pointer ,ppa Indicates that this is the name of the pointer variable ,int * Indicates that the data type stored in this pointer variable is int * Of , That's level one int Pointer variable type data .
therefore ppa It's a secondary pointer .
Take a look at its corresponding relationship :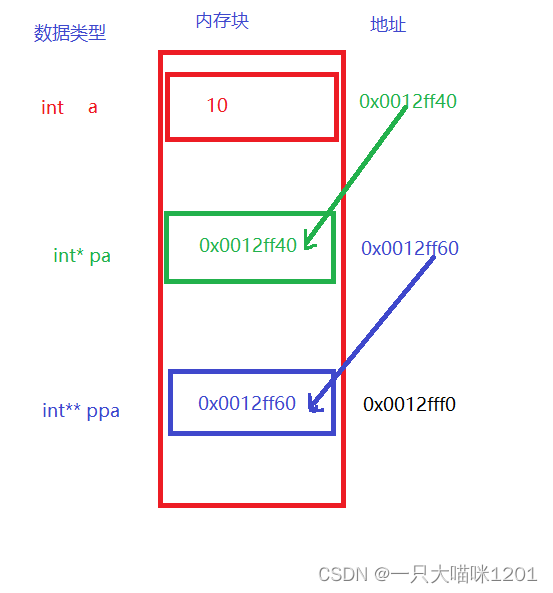
- Let's create a in memory int Variable of type a, Its value is 10, In memory , Suppose its address is 0x0012ff40.
- Then create a first level pointer variable pa, The type is int* Type of , The value in it is the variable a The address of . hypothesis pa The address is 0x0012ff60.
- Create a second level pointer variable ppa, The type is int** Class , The value in it is the first level pointer variable pa The address of , hypothesis ppa The address is 0x0012fff0.
- You can continue to create higher-level pointer variables to store the addresses of lower level pointer variables .
The usage of secondary pointer variables can refer to primary pointer variables , Only the content in it is the address of the first level pointer variable , Dereference to access a specific data requires dereference twice .
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
printf("**ppa = %d\n", **ppa);
printf("*pa = %d\n", *pa);
return 0;
}
Dereference the secondary pointer twice to access the variable a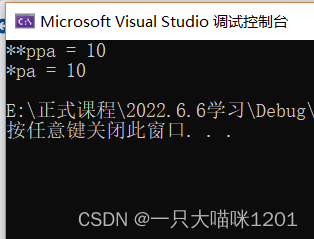
You can see
**ppa and *pa It is equivalent.
Character pointer
The character pointer is char* Pointer to type , The data type it points to is char Type of , There are two uses of character pointers :
- The character array name is stored in the character pointer variable
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
char* p1 = arr;
printf("p1 = %p\n", p1);
return 0;
}
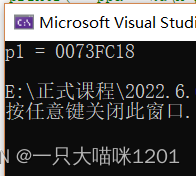
The result of printing is the address of the first element of the array .
- The address of the first character of the string stored in the character pointer variable
int main()
{
char* p2 = "abcdefg";
printf("p2 = %p\n", p2);
return 0;
}
What does this program mean ? Is to put the whole string in the pointer variable p2 Medium ? Let me see the result 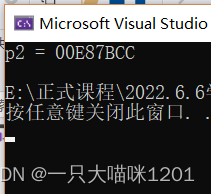
The result of printing is also an address , This address is the address of the first character of the string , That is to say ’a’ The address of .
After understanding the two uses of character pointer variables , Let's look at the following code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello bit.";
char str2[] = "hello bit.";
const char* str3 = "hello bit.";
const char* str4 = "hello bit.";
if (str1 == str2)
printf("str1 be equal to str2\n");
else
printf("str1 It's not equal to str2\n");
if (str3 == str4)
printf("str3 be equal to str4\n");
else
printf("str3 It's not equal to str4\n");
return 0;
}
str1 and str2 Use the first usage ,str3 and str4 Use the second usage .
Let's see the results 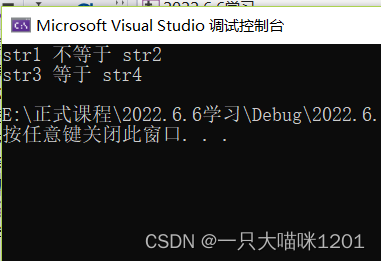
The result is str1 It's not equal to str2,str3 be equal to str4, What's the reason for this ?
First ,srt1 and str2 It's two arrays , Although their contents are the same , But their addresses in memory space are different , So the array names are different .
Look again ,str3 and str4 The value in these two character pointer variables is the address of the first character of the string .
Because this string is a character constant , Stored in the code read-only area , It can't be modified , And only one , therefore str3 and str4 The content in is the same .
Pointer array
We know that there are many types of arrays
int Type array ——int Collection of type elements
char Type array ——char Collection of type elements
float An array of types ——float Collection of type elements
Then we can infer
Pointer array —— A collection of pointer variable elements
Pointer array it is an array , The elements inside are pointer variables .
int main()
{
// establish 3 One dimensional array
int arr1[5] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[5] = {
2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[5] = {
3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[3] = {
arr1,arr2,arr3 };
return 0;
}
We know , The array name of a one-dimensional array is the address of the first element , We created 3 One dimensional array , Put their array names ( Is the pointer variable type ) Stored in a pointer array parr in . Such a pointer array is created .
int main()
{
// establish 3 One dimensional array
int arr1[5] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[5] = {
2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[5] = {
3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[3] = {
arr1,arr2,arr3 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", parr[i][j]);//parr[i] Is the array name of a one-dimensional array
//parr[i][j] Is the specific element in a dimension
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
The above code is using a pointer array 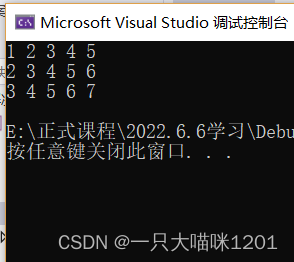
Its result is the same as that printed in two dimensions .
Using pointer array can realize the operation similar to two-dimensional array .
We can also create other types of pointer arrays
char* arr2[4]; // An array of first-order character pointers
You can also create a secondary pointer array
char** arr3[5];// An array of secondary character pointers
The data type stored in the secondary pointer array is char Second level pointer to type , That is, every element is a char* The address of the pointer .
Array pointer
Definition of array pointer
We have learned a lot about pointer types , Yes
char Type a pointer —— Point to char Pointer to type data
int Type a pointer —— Point to int Pointer to type data
float* Type a pointer —— Point to float Pointer to type data
It can be inferred from this that
Array pointer —— Pointer to array type data
An array pointer is a pointer variable , It is used to store the address of the array .
Ben meow's article The essence of array names I've talked about addressing array names (& Array name ) It takes out the address of the entire array , But its expression is the address of the first element of the array .
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
printf("arr = %p\n", arr);
printf("arr+1 = %p\n", arr + 1);
printf("&arr = %p\n", &arr);
printf("&arr+1 = %p\n", &arr + 1);
return 0;
}
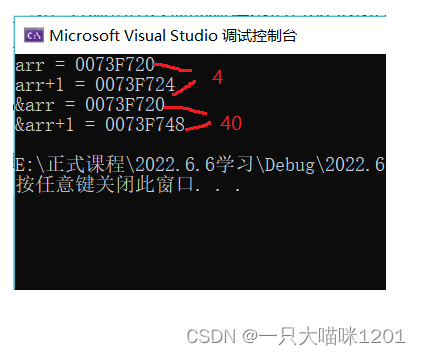
We can see , The result of array name and array name taking address is the same , But the array name plus 1 After that, it added 4 Bytes , That is to say 1 individual int Data of type , and & Array name plus 1 After that, it added 40 Bytes , That is to say 10 individual int Data of type , That is to say, you have escaped an array arr All data for .
int (*p)[10] = &arr;
In this way, we create an array pointer variable ,p The address of the entire array is placed in
Rules for creating array pointers :
int (*p)[10] = &arr; In the sentence
Variable name p The first and * It's a combination of , Combined into * p, explain p Is a pointer variable .
And then with the back [] combination , Explain that it is an array pointer ,[] Medium 10 Indicates that the array pointed to by this pointer has 10 Elements .
The front of int It means 10 The data type of the elements is int type .
The use of array pointers
Code up :
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int(*parr)[10] = &arr;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*parr + i));
}
return 0;
}
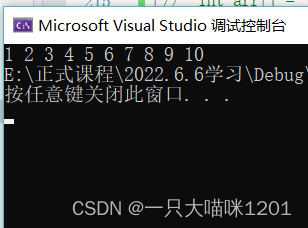
The result is to print the contents of the array , But it is generally not used like this , Because there is a simpler way to simply access the elements in the array .
This code is mainly to tell you :
The dereference of array pointer variable results in the whole array , The whole array is represented by several names , So the array name is obtained by dereferencing the array pointer variable .
Next, let's take a look at the real usage scenario of array pointer variables .
void print(int(*p)[5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j));
//printf("%d ", p[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
1,2,3,4,5,2,3,4,5,6,3,4,5,6,7 };
print(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}
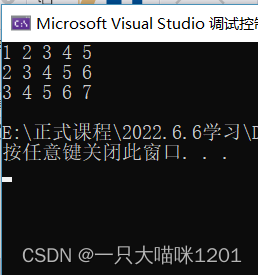
The result is to print out the two-dimensional array .
The real use scenario of array pointer variables is when passing parameters , When the formal parameter is an array pointer variable . For example, two-dimensional array parameters , The argument passes the array name .
Ben meow's article The essence of array names As I mentioned, the essence of the array name of a two-dimensional array is the address of the first element , Is the address of a one-dimensional array .
The above program accesses each element of the two-dimensional array through the array pointer variable .
Be careful
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j));It can be written as
printf("%d ", p[i][j]);*( Pointer to the variable +i) I can write this as : Pointer to the variable [i].
Pointer to the variable +i Result dereference and
Pointer to the variable [i] Add the subscript reference operator , Then remove the dereference operator
It is equivalent. .
At this point, we can easily recognize the meaning of the following codes :
int arr[5];//int An array of types , Yes 5 Elements
int* parr1[10];// Pointer array , Yes 10 Elements , Each element is int* Type of
int(*parr2)[10];// Array pointer ,parr2 Is the array pointer variable name , The array pointed to has 10 Elements , Each element is int Type of
Array pointer array
According to the method we infer above, we can infer , Array pointer array is a set of array pointer variable type elements .
int(*parr3[10])[5];
This is what array pointer array code looks like .
Create rules :
parr3 The first and [] combination , After the combination, it becomes an array ,[] Medium 10 Indicates that the array has 10 Elements .
We know , Array is a custom type , Remove the array name , The rest is its type .
Get rid of parr3[10] The rest is the type of the elements in the array , So the type of elements in this array is int (*)[5], Is an array pointer type , The array pointed to by this pointer has 5 Elements , The type of each element is int type .
Combine pointer array , Array pointer , Array pointer array is not found to feel like a doll , According to this rule, is there still Pointer to array pointer array ?
Yes, indeed , But this type of variable or array is generally not used , Just understand , Know what it is when you meet it .
边栏推荐
- 【ChaosBlade:节点磁盘填充、杀节点上指定进程、挂起节点上指定进程】
- Uniapp wechat applet monitoring network
- How long does the PMP usually need to prepare for the exam in advance?
- RuntimeError: Calculated padded input size per channel: (1 x 1). Kernel size: (5 x 5). Kernel size c
- OpenGL三维图形绘制
- STM32串口寄存器库函数配置方法
- 为不同类型设备构建应用的三大更新 | 2022 I/O 重点回顾
- What is the use of PMP certificate?
- 模拟卷Leetcode【普通】1567. 乘积为正数的最长子数组长度
- 数据在内存中的存储
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
【ChaosBlade:节点 CPU 负载、节点网络延迟、节点网络丢包、节点域名访问异常】
How to count the number of project code lines
C语言指针(特别篇)
Greenplum 6.x version change record common manual
systemd
External interrupt to realize key experiment
LeetCode 736. LISP syntax parsing
串口实验——简单数据收发
Pointer advanced, string function
Synchronized underlying principle, volatile keyword analysis
LED模拟与数字调光
Reading notes of pyramid principle
Output a spiral matrix C language
Uniapp wechat applet monitoring network
[MySQL] detailed explanation of trigger content of database advanced
Two schemes of unit test
OpenGL三维图形绘制
RuntimeError: Calculated padded input size per channel: (1 x 1). Kernel size: (5 x 5). Kernel size c
STM32的时钟系统
Skills that testers must know: Selenium's three waiting ways are interpreted clearly