当前位置:网站首页>MIT6.s081-2020 Lab2 System Calls
MIT6.s081-2020 Lab2 System Calls
2022-07-06 05:46:00 【Python's path to immortality】
MIT6.s081-2020 Lab2 System Calls
Get ready
git checkout syscall
make clean
System call trace
introduction
In this task , You will add a system call tracking function , This function may help you when debugging experiments in the future . You will create a new trace The system call that will control the trace . It should take a parameter , An integer “ Mask ”, Its bit specifies the system call to be tracked . for example , Keep track of fork system call , Program call trace(1 << SYS_fork), Where is the SYS_fork Is the system call number from kernel/syscall.h. If the number of the system call is set in the mask , You have to modify xv6 The kernel prints a line when each system call is about to return . This line should contain processes id、 The name and return value of the system call ; You do not need to print system call parameters . this trace A system call should enable tracing of the process that invokes it and any child processes that it subsequently derives , But it should not affect other processes .
Realization
This part requires us to implement a system call trace , according to HINT Just do it step by step .
HINT1: stay Makefile Of UPROGS Add $U/_trace
Open the directory to find that a user/trace.c file , First in Makefile Just add it to .user/trace.c
if (trace(atoi(argv[1])) < 0) {
fprintf(2, "%s: trace failed\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
You can see trace.c It's called in trace() Method ( come from user.h),trace Receive one int Parameters , return int, And if the execution fails, a negative value is returned .
And then this trace() The delta function is going to be , The input parameter is mask , because int yes 32 Bits can represent at most 31 System calls , Be set to 1 The system call bit of will be tracked and printed .
HINT2: stay user/user.h Add the prototype of system call in , stay user/usys.pl Add a placeholder in , And in kernel/syscall.h Add a system call number to .
Makefile call perl Script user/usys.pl To generate user/usys.S,usys.S That is, the actual system call code (stub), It USES RISC-V Of ecall Instruction to enter the kernel state . Run after fixing compilation problems trace 32 grep hello README The execution still fails because you haven't implemented this system call in the kernel .usys.pl The content of
sub entry {
my $name = shift;
print ".global $name\n";
print "${name}:\n";
print " li a7, SYS_${name}\n";
print " ecall\n";
print " ret\n";
}
ecall: xv6 Is based on RISC-V The instruction set , stay RISV-V Command set ecall Represents a system call .
li: Is an instruction that loads an immediate number to a register , The format is li rd, immediate, Express x[rd] = immediate, Load constants into x[rd] in .
SYS_${name} The meaning is in kernel/syscall.h in #define SYS_${name} xxx System call number for , So you can tell ecall What number of system calls to call .
stay user/user.h Add function prototype in .
int trace(int);
stay user/usys.pl Add trace Occupancy of .
entry("trace");
stay syscall.h Add the system call number .
#define SYS_close 21
#define SYS_trace 22 // NEW
HINT3: stay kernel/syspro.c Add sys_trace() function ,sys_trace() By means of proc struct The new system call is implemented by storing parameters in the new variables of . The function that retrieves system call parameters from user space is located at kernel/syscall.c in , Can be in kernel/sysproc.c See the use examples of these functions in .
see kernel/syscall.c You can find :syscall.c Medium argint() The implementation of the function is as follows ,trapframe Yes, the user process fell into (trap) Context information such as registers before the kernel .
// Fetch the nth 32-bit system call argument.
int argint(int n, int *ip) {
*ip = argraw(n);
return 0;
}
static uint64 argraw(int n) {
struct proc *p = myproc();
switch (n) {
case 0:
return p->trapframe->a0;
case 1:
return p->trapframe->a1;
case 2:
return p->trapframe->a2;
case 3:
return p->trapframe->a3;
case 4:
return p->trapframe->a4;
case 5:
return p->trapframe->a5;
}
panic("argraw");
return -1;
}
So you need to proc Structure ( stay kernel/proc.h) Add a new variable to store the tracking number , And then in fork() Copy the newly added variables in the structure , In this way, the purpose of transferring parameters is achieved . Our new variables do not need to be locked , Because it will only be used by its own process , So put it in char name[16] after
modify kernel/proc.h
// Per-process state
struct proc {
// ...
// these are private to the process, so p->lock need not be held.
// ,,
char name[16]; // Process name (debugging)
int trace_mask; // trace mask for debugging
};
open kernel/sysproc.c
The parameters of other system call functions in this file are void, Because the parameters are obtained by argcint() Method ,argint() Used to read in a0-a5 System call parameters passed in registers .
Combined with other functions in this file, we can see that myproc() Function can get the current process struct proc, That is to say PCB. add to sys_trace(void) function .
// add mask to proc's trace_mask
uint64 sys_trace(void) {
int n;
if(argint(0, &n) < 0) {
return -1;
}
myproc()->trace_mask = n;
return 0;
}
HINT4: modify fork() To achieve “ Copy from parent process trace mask To subprocess ” The function of ,fork be located kernel/proc.c.
So you need to kernel/proc.c Of fork() Add a sentence to the function np->trace_mask = p -> trace_mask; that will do .
HINT5: modify kernel/syscall.c Medium syscall() Function to put trace Print out . You need to add an array of storage system call names indexed by the system call number .
stay kernel/syscall.c Realize our printing operation in , The document says that a printed line should include : process id, The name of the system call and the return value of the system call , There is no need to print the parameters of the system call .
In the document, let's make one by ourselves Index the system call name with the system call number Array of , Reference resources static uint64 (*syscalls[])(void) Writing , Let's write something like this .
extern Indicates that this function comes from an external file .
extern uint64 sys_trace(void);
static uint64 (*syscalls[])(void) = {
// ...
[SYS_close] sys_close,
[SYS_trace] sys_trace, // NEW
};
static char* syscall_names[] = {
[SYS_fork] "fork",
[SYS_exit] "exit",
[SYS_wait] "wait",
[SYS_pipe] "pipe",
[SYS_read] "read",
[SYS_kill] "kill",
[SYS_exec] "exec",
[SYS_fstat] "fstat",
[SYS_chdir] "chdir",
[SYS_dup] "dup",
[SYS_getpid] "getpid",
[SYS_sbrk] "sbrk",
[SYS_sleep] "sleep",
[SYS_uptime] "uptime",
[SYS_open] "open",
[SYS_write] "write",
[SYS_mknod] "mknod",
[SYS_unlink] "unlink",
[SYS_link] "link",
[SYS_mkdir] "mkdir",
[SYS_close] "close",
[SYS_trace] "trace",
[SYS_sysinfo] "info",
};
void syscall(void)
{
int num;
struct proc *p = myproc();
char* syscall_name; // NEW
num = p->trapframe->a7;
if(num > 0 && num < NELEM(syscalls) && syscalls[num]) {
p->trapframe->a0 = syscalls[num]();
if ((p->trace_mask & (1 << num)) != 0) {
// NEW
syscall_name = syscall_names[num]; // NEW
printf("%d: syscall %s -> %d", p->pid, syscall_name, p->trapframe->a0); // NEW
} // NEW
} else {
printf("%d %s: unknown sys call %d\n",
p->pid, p->name, num);
p->trapframe->a0 = -1;
}
}
result
Experimental tests :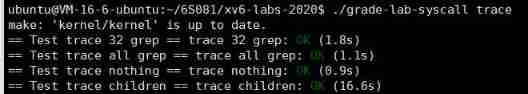
Sysinfo
introduction
In this mission , You will add a system call ,sysinfo, Collect information about the running system . The system call has a parameter : A pointer to a struct sysinfo ( see kernel/sysinfo.h). The kernel should fill in the fields of this structure :freemem The field should be set to the number of bytes of available memory , also nproc The field should be set to the number of its processes state No UNUSED. We provide test procedures sysinfotest; If it prints “sysinfotest:OK”, You passed the task .
Realization
Therefore, the content of this part can also follow the above trace The process is the same , according to HINT Just do it step by step .
HINT1: add to $U/_sysinfotest To Makefile Medium UPROGS
HINT2: function make qemu;user/sysinfotest.c Will not compile . Add system calls sysinfo, The steps are the same as the previous assignment . Statement sysinfo() The prototype of user/user.h You need to declare your existence in advance struct sysinfo:
struct sysinfo;
int sysinfo(struct sysinfo *);
modify user/user.h: Need to be in user.h Once again in struct sysinfo The reason is that : The parameters defined outside this document cannot be seen in the parameter list struct Of .
struct stat;
struct sysinfo;
struct rtcdate;
// system calls
// ...
int sysinfo(struct sysinfo *);
usys.pl
entry("sysinfo");
syscall.h
#define SYS_sysinfo 23
syscall.c
extern uint64 sys_info(void);
static uint64 (*syscalls[])(void) = {
// ...
[SYS_sysinfo] sys_info,
};
static char* syscall_names[] = {
// ...
[SYS_sysinfo] "sys_info",
};
After fixing compilation problems , function sysinfotest; It will fail. , Because you haven't implemented system calls in the kernel yet .
HINT3:sysinfo Need to copy one struct sysinfo Back to user space ; see sys_fstat()(kernel/sysfile.c) and filestat()(kernel/file.c) Examples of how to use copyout().
according to HINT, read sys_fstat() Functions and filestat() function .
// **kernel/sysfile.c**
uint64
sys_fstat(void)
{
struct file *f;
uint64 st; // user pointer to struct stat
if(argfd(0, 0, &f) < 0 || argaddr(1, &st) < 0)
return -1;
return filestat(f, st);
}
// **kernel/file.c**
// Get metadata about file f.
// addr is a user virtual address, pointing to a struct stat.
int
filestat(struct file *f, uint64 addr)
{
struct proc *p = myproc();
struct stat st;
if(f->type == FD_INODE || f->type == FD_DEVICE){
ilock(f->ip);
stati(f->ip, &st);
iunlock(f->ip);
if(copyout(p->pagetable, addr, (char *)&st, sizeof(st)) < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
It can be found from the above , When copying kernel data to user data , Will use copyout The parameters include : Page table of thread , The destination address of the copy object , Copy the address of the object and the space occupied by the object .
HINT4: To collect the amount of available memory , Please add a function kernel/kalloc.c
Read it for a while kernel/kalloc.c Of kfree() and kalloc(), Memory is used for free list freelist Managed in the form of , And freelist Is the head node of the linked list , When free When a piece of memory ,freelist Head into this quilt free Of memory , When applying for a piece of memory ,freelist My head was taken away . And the position of the head will be updated to the next node of the previous head node .
therefore , To get the size of free memory, you only need to traverse freelist Just look at how many free memory blocks there are .
uint64 free_mem(void) {
struct run *r;
uint64 count = 0;
acquire(&kmem.lock);
r = kmem.freelist;
while(r) {
r = r->next;
count++;
}
release(&kmem.lock);
return count * PGSIZE;
}
HINT5: To collect the number of processes , Please add a function kernel/proc.c
from kernel/proc.c Of allocproc() The function shows , The process here uses a process table proc Structure to manage , This schedule is struct proc Make an array of (struct proc proc[NPROC];)
In addition to kernle/proc.h The statement is made. enum procstate { UNUSED, SLEEPING, RUNNABLE, RUNNING, ZOMBIE };
So we copy allocproc() Function to realize our function of counting the number of processes :
uint64 proc_num(void) {
struct proc *p;
uint64 count = 0;
for(p = proc; p < &proc[NPROC]; p++) {
acquire(&p->lock);
if(p->state != UNUSED) {
count++;
}
release(&p->lock);
}
return count;
}
In order to make in kernel/sysproc.c Be able to call the above two methods , You need to add the function declaration to kernel/defs.h
//kalloc.c
//...
void kinit(void);
uint64 free_mem(void);
//proc,c
//...
void procdump(void);
uint64 proc_num(void);
Last , Need to be in kernel/sysproc.c To realize sys_info() function :
uint64 sys_info(void) {
struct sysinfo info;
uint64 addr;
info.freemem = kfreemem();
info.nproc = proc_num();
if(argaddr(0, &addr) < 0) {
return -1;
}
// copy info(kernel space) to addr(user space)
if (copyout(myproc()->pagetable, addr, (char *)&info, sizeof(info)) < 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
Why can you pass argaddr() Function to get the copied address in user space ? Because the form of calling is sysinfo(struct sysinfo *info) In the form of , Pass it on info The address of . also argaddr() The first parameter in the function input parameter refers to the get register a0 Data in the , The second parameter refers to the user space storage address .
result
Experimental tests :
summary
Because of this Lab2 Both parts of are moderate Because of the difficulty , All the way down HINT The tips are very smooth .
finish System call tracing Partially understood xv6 The procedure of system call in . Finishing Sysinfo Part of it is a preliminary peek xv6 Memory management and process management in , Also aware of the need to utilize copyout() Function to transfer a piece of memory from the kernel state copy To user state .
During this process, I also encountered some problems and made notes here :
- The phenomenon : In the test
sysinfoMedium outputpainc:acquire - reason : The request lock is not released
边栏推荐
- [SQL Server Express Way] - authentification et création et gestion de comptes utilisateurs
- Auto. JS learning notes 17: basic listening events and UI simple click event operations
- Garbage collector with serial, throughput priority and response time priority
- 华为路由器如何配置静态路由
- What is independent IP and how about independent IP host?
- Web服务连接器:Servlet
- B站刘二大人-反向传播
- First knowledge database
- A master in the field of software architecture -- Reading Notes of the beauty of Architecture
- 进程和线程
猜你喜欢
Migrate Infones to stm32
Classes and objects (I) detailed explanation of this pointer

js Array 列表 实战使用总结

Embedded interview questions (IV. common algorithms)

26file filter anonymous inner class and lambda optimization
B站刘二大人-反向传播
Installation de la Bibliothèque de processus PDK - csmc

SequoiaDB湖仓一体分布式数据库2022.6月刊
![[Jiudu OJ 08] simple search x](/img/a7/12a00c5d1db2deb064ff5f2e83dc58.jpg)
[Jiudu OJ 08] simple search x
Mysql database master-slave cluster construction
随机推荐
移植InfoNES到STM32
PDK工藝庫安裝-CSMC
[email protected]树莓派
算法-- 爬楼梯(Kotlin)
HAC cluster modifying administrator user password
网站进行服务器迁移前应做好哪些准备?
Garbage collector with serial, throughput priority and response time priority
华为路由器忘记密码怎么恢复
[imgui] unity MenuItem shortcut key
Anti shake and throttling are easy to understand
Auto. JS learning notes 17: basic listening events and UI simple click event operations
嵌入式面试题(四、常见算法)
First acquaintance with CDN
[experience] when ultralso makes a startup disk, there is an error: the disk / image capacity is too small
How can large websites choose better virtual machine service providers?
华为BFD的配置规范
js Array 列表 实战使用总结
29io stream, byte output stream continue write line feed
AUTOSAR from getting started to becoming proficient (10) - embedded S19 file analysis
Station B, Mr. Liu Er - multiple logistic regression, structure 7