当前位置:网站首页>libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读
libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读
2022-07-07 12:11:00 【凳子花*】
一、前言
最近想实现AD_Census的扫描线优化程序加速,自己将C++的程序改为CUDA程序后,速度还降低了100倍(小菜鸡暴风哭泣),无奈只能网上找一些参考例程看看。直接搜AD_Census又没有,只能曲线救国,找找开源较多的SGM的程序看看。
libSGM是小日子过得不错的日本选手开发的开源程序,源码网址在这里:fixstars/libSGM
这个工程对C++运用非常多,用到了各种模板等等操作,对C++不熟悉的人读起来还挺费劲,而且网上也没有相关的解读。正好我读的时候也做了一些注释,所以在这里分享出来,希望能帮到大家。
如有侵权请联系。(解读开源代码应该不侵权吧hhh)
二、程序解读
由于我只想参考AD_Census的扫描线优化部分,对应到SGM也就是代价聚合部分,所以这里只阅读了horizontal_path_aggregation.cu这个代码,该代码中包含path_aggregation_common.hpp文件,会一并进行解读。
1. horizontal_path_aggregation.cu
代码如下,基本上每行都添加了注释,建议大家把下面代码拷贝一下然后粘贴到文件中通过VSCode进行阅读。
代码中有很多骚操作,真的是佩服作者,把C++和CUDA运用的炉火纯青,这里贴上网址帮助大家理解:
- C++ 模板详解,点进去找C++模板的
非类型参数,仔细阅读一下。其实简单点来说你在读代码的时候把它当做一个常量就可以了。 - 【CUDA 基础】5.6 线程束洗牌指令 | 谭升的博客 (face2ai.com)
- Programming Guide :: CUDA Toolkit Documentation (nvidia.com)
2和3是因为代码中用到了CUDA的洗牌shuffle操作,从这个运用就能看出作者对CUDA的底层了解是多么的深刻,大家可以先看谭升的博客了解__shfl,__shfl_up,__shfl_down, and__shfl_xor这些函数的操作,虽然他们已经被弃用,改成了__shfl_sync,__shfl_up_sync,__shfl_down_sync, and__shfl_xor_sync但是道理都是一样的。 - 关于CUDA中的warp shuffle函数说明这篇文章简单看看,帮助理解
__shfl_sync中的mask是什么作用。 - cuda - Is mask adaptive in __shfl_up_sync call? - Stack Overflow
,在Stack Overflow上面也找到个阅读libSGM代码的老哥hhh,里面其实讲解的知识不多,打开大概看看就可。 - 其他的哪里不懂就百度即可。
/* Copyright 2016 Fixstars Corporation Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http ://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. */
#include <cstdio>
#include "horizontal_path_aggregation.hpp"
#include "path_aggregation_common.hpp"
// 注意:下面的DP实际上是指的视差对应的代价,但是为了省事,我就统一叙述成了视差块,实际上指的是视差对应的代价,不是视差!不是视差!不是视差!
// 一个线程处理
namespace sgm {
namespace path_aggregation {
// DP 表示视差 disparity
// 视差块大小,8个视差一个块
static constexpr unsigned int DP_BLOCK_SIZE = 8u;
// 每个线程处理的视差块,此处处理1块,即每个线程处理8个视差
static constexpr unsigned int DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD = 1u;
// 每个块中的 warp 数量为4
static constexpr unsigned int WARPS_PER_BLOCK = 4u;
// 块大小,即块中线程数量,warp数量 * warp大小
static constexpr unsigned int BLOCK_SIZE = WARP_SIZE * WARPS_PER_BLOCK; // 32 * 4 = 128
// 水平路径聚合
// 这里用的模板,使用了两个非类型参数,就把这两参数看做是个常量即可
// DIRECTION 表示方向,1为从左往右聚合,-1为从右往左聚合
// MAX_DISPARITY 表示最大视差范围,此处以128为例
template <int DIRECTION, unsigned int MAX_DISPARITY>
__global__ void aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel(
uint8_t *dest,
const feature_type *left, // feature_type 是 uint32_t
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp)
{
// 子组大小,即视差范围 MAX_DISPARITY 内需要的视差块数
static const unsigned int SUBGROUP_SIZE = MAX_DISPARITY / DP_BLOCK_SIZE; // 128 / 8 = 16
// 每个 warp 处理的子组数量
static const unsigned int SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP = WARP_SIZE / SUBGROUP_SIZE; // 32 / 16 = 2
// 每个 warp 的路径数,由于一个线程处理一个视差块,所以一个 warp 处理32个视差块
// 一个子组16个视差块,即一个warp处理2个子组,也即两条路径?不太懂路径是什么意思
static const unsigned int PATHS_PER_WARP =
WARP_SIZE * DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD / SUBGROUP_SIZE; // 32 * 1 / 16 = 2
// 每个块路径数,同上
static const unsigned int PATHS_PER_BLOCK =
BLOCK_SIZE * DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD / SUBGROUP_SIZE; // 128 * 1 / 16 = 8
static_assert(DIRECTION == 1 || DIRECTION == -1, "");
if(width == 0 || height == 0){
return;
}
// 每个线程所需要的缓存,用来存储右图中的值
feature_type right_buffer[DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD][DP_BLOCK_SIZE];
// 这里就是声明一个结构体数组dp,该数组有DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD(此处为1)个元素,每个元素都是一个DynamicProgramming结构体
// 该结构体中有变量last_min和dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE]以及一个函数update()
// dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE]中每一个元素初始值都为0
DynamicProgramming<DP_BLOCK_SIZE, SUBGROUP_SIZE> dp[DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD];
const unsigned int warp_id = threadIdx.x / WARP_SIZE;
// 一个warp里面的组,这里2个组
const unsigned int group_id = threadIdx.x % WARP_SIZE / SUBGROUP_SIZE;
const unsigned int lane_id = threadIdx.x % SUBGROUP_SIZE;
// 这里SUBGROUP_SIZE为16,所以函数返回值为0x0000ffff,每次左移group_id * SUBGROUP_SIZE位
// group_id为0时,左移0位,即0x0000ffff;为1时,左移16位变成0xffff0000。这样每次只有16个线程有效。
// 一个线程即一个lane,处理一个视差块,8个视差
const unsigned int shfl_mask =
generate_mask<SUBGROUP_SIZE>() << (group_id * SUBGROUP_SIZE);
// 行数,group id最先开始变化,其次是warp id,最后是blockIdx.x
// 一个组就是一行,一个组里面有16个视差块,需要16个线程也即lane,1个视差块8个视差
const unsigned int y0 =
PATHS_PER_BLOCK * blockIdx.x +
PATHS_PER_WARP * warp_id +
group_id;
// feature_step用于一个线程处理多个DP块的情况,这里处理多个DP块不是连续的挨着的块,而是
// 下一个warp中的块
// 由于一个子组对应128个视差,即一行,而一个warp有两个子组,所以一个warp能处理两行
// 所以下一个warp要增加SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP * width,表示增加两行
// 如果第一次看这里不明白是什么意思,没有关系,先往后看,等到用到了这个变量再回来仔细品味
const unsigned int feature_step = SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP * width; // 2 * 1920?
// 每一个代价都对应128个视差,所以这里和上面相比要乘以 MAX_DISPARITY
const unsigned int dest_step = SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP * MAX_DISPARITY * width; // 2 * 128 * 1920
// dp 块的步长
const unsigned int dp_offset = lane_id * DP_BLOCK_SIZE;
left += y0 * width;
right += y0 * width;
dest += y0 * MAX_DISPARITY * width;
if(y0 >= height){
return;
}
// 初始化?
if(DIRECTION > 0){
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD; ++i){
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++j){
right_buffer[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}else{
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD; ++i){
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++j){
const int x = static_cast<int>(width - (min_disp + j + dp_offset));
if(0 <= x && x < static_cast<int>(width)){
// __ldg应该是用来读取只读数据的
right_buffer[i][j] = __ldg(&right[i * feature_step + x]);
}else{
right_buffer[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
// 这里x0就是起始索引,如果是从左往右聚合,起始索引就是0;如果是从右往左,起始索引应该为 width - DP_BLOCK_SIZE
// 只不过此处通过 (width - 1) & ~(DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1) 这个逻辑来实现计算 width - DP_BLOCK_SIZE,结果一样的
// &、~ 都是按位操作,&是按位与,~是按位取反
// 注意这里的x0只是初始值,下面进入到循环后还会增加,每次循环增加DP_BLOCK_SIZE
int x0 = (DIRECTION > 0) ? 0 : static_cast<int>((width - 1) & ~(DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1));
// iter是迭代次数,一共迭代 width / DP_BLOCK_SIZE次,每次迭代内部处理 DP_BLOCK_SIZE 个数据
for(unsigned int iter = 0; iter < width; iter += DP_BLOCK_SIZE){
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++i){
// 在一个视差块中的索引,一共8个数据所以是从0~7,随着x0改变而改变,从右往左也类似
const unsigned int x = x0 + (DIRECTION > 0 ? i : (DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1 - i));
if(x >= width){
continue;
}
// 这里每个线程处理1个DP块,所以只需要迭代1次,如果处理多个,则需迭代多次。每次迭代只需处理1个视差。
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD; ++j){
// y0是行号,一个组一行,一个组16个视差块,也即128个视差。对于此处的j迭代,每次迭代y0都是一样的
const unsigned int y = y0 + j * SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP;
if(y >= height){
continue;
}
// 取出每个视差块的视差对应的左值
const feature_type left_value = __ldg(&left[j * feature_step + x]);
if(DIRECTION > 0){
// 取出视差块最后一个右值,因为一会要右移,怕这个值移没了
const feature_type t = right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1];
// right_buffer每一个值右移一位
// 注意这里每次i循环都会右移一次,等i循环结束,就一共右移了8次。
for(unsigned int k = DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1; k > 0; --k){
right_buffer[j][k] = right_buffer[j][k - 1];
}
#if CUDA_VERSION >= 9000
// 当前子组范围内的所有视差块向上交换t(最后一个视差值)给right_buffer[j][0]
// 比如当前线程为12,则获取线程11的t值给当前线程对应的视差块的第一个视差
// 所以和上面的代码联系起来意思就是:整个子组SUBGROUP中的所有视差块都整体右移一位
// __shfl_up_sync的意思具体请看path_aggregation_common.hpp中的注释
right_buffer[j][0] = __shfl_up_sync(shfl_mask, t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);
#else
right_buffer[j][0] = __shfl_up(t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);
#endif
// 对于线程0,由于第1个视差块的第一个视差已经右移给了第二个视差,但第一个视差前面没有别的视差可以给他值
// 所以这里处理一下没有值的第一个视差
// 注意:right_buffer初始值其实都是0,但是当lane id为0的时候,right_buffer[j][0]会取到right的值,这样在
// 每次i循环结束的时候会取到8个right的值去填充right_buffer。
if(lane_id == 0 && x >= min_disp){
right_buffer[j][0] =
__ldg(&right[j * feature_step + x - min_disp]);
}
}else{
// 艹!!这里这个else不是上面这行if的else,而是if(DIRECTION > 0)的else,第一次看错了!!!我说咋这么迷惑
// 同上,这里因为要左移,所以先存第0个元素
const feature_type t = right_buffer[j][0];
for(unsigned int k = 1; k < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++k){
right_buffer[j][k - 1] = right_buffer[j][k];
}
#if CUDA_VERSION >= 9000
right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1] =
__shfl_down_sync(shfl_mask, t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);
#else
right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1] = __shfl_down(t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);
#endif
// 处理最后一个线程(即最后一个视差块)的最后一个视差值
if(lane_id + 1 == SUBGROUP_SIZE){
if(x >= min_disp + dp_offset + DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1){
right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1] =
__ldg(&right[j * feature_step + x - (min_disp + dp_offset + DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1)]);
}else{
right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1] = 0;
}
}
}
// 存一下每个视差块视差的局部代价值
uint32_t local_costs[DP_BLOCK_SIZE];
for(unsigned int k = 0; k < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++k){
// __popc是统计整数中1的个数,这里是一个计算汉明距离的过程(先异或然后计数1的个数)
local_costs[k] = __popc(left_value ^ right_buffer[j][k]);
}
// 更新dp中的dp、last_min
dp[j].update(local_costs, p1, p2, shfl_mask);
// 把dp.dp存到dest中
store_uint8_vector<DP_BLOCK_SIZE>(
&dest[j * dest_step + x * MAX_DISPARITY + dp_offset],
dp[j].dp);
}
}
x0 += static_cast<int>(DP_BLOCK_SIZE) * DIRECTION;
}
}
template <unsigned int MAX_DISPARITY>
void enqueue_aggregate_left2right_path(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream)
{
static const unsigned int SUBGROUP_SIZE = MAX_DISPARITY / DP_BLOCK_SIZE;
static const unsigned int PATHS_PER_BLOCK =
BLOCK_SIZE * DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD / SUBGROUP_SIZE;
const int gdim = (height + PATHS_PER_BLOCK - 1) / PATHS_PER_BLOCK;
const int bdim = BLOCK_SIZE;
aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel<1, MAX_DISPARITY><<<gdim, bdim, 0, stream>>>(
dest, left, right, width, height, p1, p2, min_disp);
}
template <unsigned int MAX_DISPARITY>
void enqueue_aggregate_right2left_path(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream)
{
static const unsigned int SUBGROUP_SIZE = MAX_DISPARITY / DP_BLOCK_SIZE;
static const unsigned int PATHS_PER_BLOCK =
BLOCK_SIZE * DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD / SUBGROUP_SIZE;
const int gdim = (height + PATHS_PER_BLOCK - 1) / PATHS_PER_BLOCK;
const int bdim = BLOCK_SIZE;
aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel<-1, MAX_DISPARITY><<<gdim, bdim, 0, stream>>>(
dest, left, right, width, height, p1, p2, min_disp);
}
template void enqueue_aggregate_left2right_path<64u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
template void enqueue_aggregate_left2right_path<128u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
template void enqueue_aggregate_left2right_path<256u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
template void enqueue_aggregate_right2left_path<64u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
template void enqueue_aggregate_right2left_path<128u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
template void enqueue_aggregate_right2left_path<256u>(
cost_type *dest,
const feature_type *left,
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp,
cudaStream_t stream);
}
}
2. path_aggregation_common.hpp
代码如下,这里主要是用到了update()函数。
/* Copyright 2016 Fixstars Corporation Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http ://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. */
#ifndef SGM_PATH_AGGREGATION_COMMON_HPP
#define SGM_PATH_AGGREGATION_COMMON_HPP
#include <cstdint>
#include <cuda.h>
#include "utility.hpp"
namespace sgm {
namespace path_aggregation {
template <
unsigned int DP_BLOCK_SIZE,
unsigned int SUBGROUP_SIZE>
struct DynamicProgramming {
// 注意此处是一个结构体
// 判断一下传入的参数是否满足要求
static_assert(
DP_BLOCK_SIZE >= 2,
"DP_BLOCK_SIZE must be greater than or equal to 2");
static_assert(
(SUBGROUP_SIZE & (SUBGROUP_SIZE - 1)) == 0,
"SUBGROUP_SIZE must be a power of 2");
uint32_t last_min;
// 看起来是用来存视差值的?一个视差块有多少个视差,dp的大小就为多少
uint32_t dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE];
// 运行在设备上的构造函数,dp 所有值初始化为0
__device__ DynamicProgramming()
: last_min(0)
{
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++i){
dp[i] = 0; }
}
// 设备上的更新函数
// 就是处理每一个视差块dp的每一个值,从k=0开始,一直到k=DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1挨个更新
// 并求当前视差块的最小代价值
// 这段代码看起来很麻烦,其实就三部分,k=0、k=DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1和这两个值中间的k
__device__ void update(
uint32_t *local_costs, uint32_t p1, uint32_t p2, uint32_t mask)
{
// 表示lane的id,lane其实就是thread,正常情况下lane为[0,31],这里一个lane处理一个视差块,即8个视差
const unsigned int lane_id = threadIdx.x % SUBGROUP_SIZE;
//
const auto dp0 = dp[0];
uint32_t lazy_out = 0, local_min = 0;
{
// 下面这里处理的是k=0时的情况,可能是不同情况加上不同惩罚项??
const unsigned int k = 0;
#if CUDA_VERSION >= 9000
// 在CC3.0以上,支持了shuffle指令,允许thread直接读其他thread的寄存器值,只要两个thread在同一个warp中,这种比通过shared Memory进行thread间的通讯效果更好,latency更低,同时也不消耗额外的内存资源来执行数据交换。
// 这里介绍warp中的一个概念lane,一个lane就是一个warp中的一个thread,每个lane在同一个warp中由lane索引唯一确定,因此其范围为[0,31]。在一个一维的block中,可以通过下面两个公式计算索引:laneID = threadIdx.x % 32; warpID = threadIdx.x / 32;例如,在同一个block中的thread1和33拥有相同的lane索引1。
// 这句意思应该是把上一个线程(视差块)的最后一个视差值 dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1] 上移到当前线程(视差块)prev(previous)变量处
// __shfl_up_sync具体查看:https://face2ai.com/CUDA-F-5-6-%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B%E6%9D%9F%E6%B4%97%E7%89%8C%E6%8C%87%E4%BB%A4/
// https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#warp-shuffle-functions
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/58869398/is-mask-adaptive-in-shfl-up-sync-call
const uint32_t prev =
__shfl_up_sync(mask, dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1], 1);
#else
const uint32_t prev = __shfl_up(dp[DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1], 1);
#endif
// lane为0时最小值
uint32_t out = min(dp[k] - last_min, p2);
// lane为其他值时最小值
if(lane_id != 0){
out = min(out, prev - last_min + p1); }
out = min(out, dp[k + 1] - last_min + p1);
lazy_out = local_min = out + local_costs[k];
}
// k为其他值的时候(非第一个和最后一个)
// 这里会更新dp[0]~dp[5]
for(unsigned int k = 1; k + 1 < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++k){
uint32_t out = min(dp[k] - last_min, p2);
out = min(out, dp[k - 1] - last_min + p1);
out = min(out, dp[k + 1] - last_min + p1);
dp[k - 1] = lazy_out;
lazy_out = out + local_costs[k];
local_min = min(local_min, lazy_out);
}
{
// 最后一个k
const unsigned int k = DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1;
#if CUDA_VERSION >= 9000
// 取下一个线程的dp0,即下一个视差块的第一个视差
const uint32_t next = __shfl_down_sync(mask, dp0, 1);
#else
const uint32_t next = __shfl_down(dp0, 1);
#endif
uint32_t out = min(dp[k] - last_min, p2);
out = min(out, dp[k - 1] - last_min + p1);
// 不是最后一个lane
if(lane_id + 1 != SUBGROUP_SIZE){
// 这块把上面类似代码中的dp[k+1]用next替代
out = min(out, next - last_min + p1);
}
// 更新dp[6], dp[7]
dp[k - 1] = lazy_out;
dp[k] = out + local_costs[k];
local_min = min(local_min, dp[k]);
}
// 求出子组中的最小代价
last_min = subgroup_min<SUBGROUP_SIZE>(local_min, mask);
}
};
template <unsigned int SIZE>
__device__ unsigned int generate_mask()
{
static_assert(SIZE <= 32, "SIZE must be less than or equal to 32");
return static_cast<unsigned int>((1ull << SIZE) - 1u);
}
}
}
#endif
三、复盘一下整个流程
其实看完上面两个代码,你可能还是不理解这个代码到底怎么工作的hhh,我一开始看完也很疑惑,一直啃到最后才恍然大悟,这里我们在复盘一下整个代码流程:
下面的讲解以DP_BLOCK_SIZE=8,DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD=1,WARPS_PER_BLOCK=4,SUBGROUP_SIZE=16,DIRECTION=1,为例。
对于aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel()函数,int x0 = (DIRECTION > 0) ? 0 : static_cast<int>((width - 1) & ~(DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1));这句代码之前都是用来定义一些变量的,我们暂时先不关注太多。只看一下y0这个变量:const unsigned int y0 = PATHS_PER_BLOCK * blockIdx.x + PATHS_PER_WARP * warp_id + group_id;,y0又和3个变量有关:blockIdx.x、warp_id和group_id。group_id是最容易开始变化的,当线程为0~ 15时其为0,线程为16 ~ 31时其为1。然后是根据warp_id进行变化,最后是根据blockIdx.x变化。
以线程0和线程1举例,你会发现它两的blockIdx.x、warp_id和group_id这三个变量都是0,所以y0就是0,也就是这两个线程处理的行数都为第0行。这里很重要,因为下面的代码中:
left += y0 * width;
right += y0 * width;
dest += y0 * MAX_DISPARITY * width;
这三个指针的初始值都和y0有关,0~15线程的这三个指针的初始值都是一样的。
此外,关注一下right_buffer的初始化操作,当DIRECTION=1时,所有的值都初始化为0,不管是哪个线程进来,right_buffer中的值初始都为0,那么right_buffer到底是怎么更新的呢?别急,先往后看。
了解了上述y0和right_buffer之后,从x0之后代码开始理解:
- x0是该线程处理的起始索引,一个warp中的线程都是并发执行的,所以每个线程的起始索引x0都是0。看到这里你可能会很奇怪,每个线程不应该处理不同的视差块吗,为什么起始索引是相同的呢?别急,后面解释。
- 进入到循环,一共三层loop,外层为iter循环,一共循环width / DP_BLOCK_SIZE次;次外层为i循环,一共循环DP_BLOCK_SIZE次,所以外层和次外层合并起来就是图像的一行数据,共width个,也即其实一个线程需要处理一行的数据;内层为j循环,一共循环DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD次,表示每个线程处理的DP块。
- 进入到i循环后定义了一个x变量:
const unsigned int x = x0 + (DIRECTION > 0 ? i : (DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1 - i));,该变量与x0和i有关,每次i循环都会加1,也即x加1;x0在i循环结束时会增加DP_BLOCK_SIZE(i循环一共就循环DP_BLOCK_SIZE次,i最后一次循环值为DP_BLOCK_SIZE-1,x就增加DP_BLOCK_SIZE-1,i循环结束后,x0增加DP_BLOCK_SIZE,也就是x增加DP_BLOCK_SIZE,这样子就使得x的变化连起来了)。 - 然后看j循环。其实这里我们让DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD=1,所以这个j循环相当于没有,为0,就可以不考虑与j相关的操作了。进入到j循环定义了一个y变量,表示行号,其实和y0是相等的,因为j一直为0。
- 下一步就是取出左图像中的值:
const feature_type left_value = __ldg(&left[j * feature_step + x]);请注意,每个线程执行到这里的时候x最先都是0,所以取到的左值也都一样,都是left[0]。 - 由于我们考虑DIRECTION=1的情况,所以程序执行if(DIRECTION > 0)中的代码。首先定义一个变量:
const feature_type t = right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1];,该变量是当前线程处理的DP块的最后一个dp对应的代价值,提前取出来存到t变量中,为啥呢?因为后面的for循环要对right_buffer进行右移操作,如果不保存最后一个值的话,这个值将被前一个移过来的值覆盖掉。 - 当right_buffer右移完成后,骚操作来了:
right_buffer[j][0] = __shfl_up_sync(shfl_mask, t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);作者通过CUDA的洗牌操作,将上一个线程的最后一个值移动到了当前线程的第0个值处,也就完成了线程之间的移动,真是666啊。那么看到这里,大家可能会很疑惑,这是干什么???为什么要右移???别慌,往下看。 - 完成线程之间的数据移动之后,再一个骚操作来了:
if(lane_id == 0 && x >= min_disp){
right_buffer[j][0] =
__ldg(&right[j * feature_step + x - min_disp]);
}
有些同学会说,这不就是处理lane_id为0的时候,也就是线程0吗,有啥稀奇古怪的。没错,这里就是处理一下0线程的第0个数据,但是注意,之前right_buffer其实初始值都是0,但是这里给第0个数据赋的值是right中对应的值。所以right_buffer的值就是在这里更新的。
那么初始值有了,配合上右移操作,你会发现,对于线程0每次循环都会更新一个right_buffer[j][0],而每次循环又会将right_buffer全部右移一位,那么就会将上一次更新的right_buffer[j][0]右移到right_buffer[j][1],进而逐渐右移…一直右移到right_buffer[j][7](此处以DP_BLOCK_SIZE=8为例)。
右移到了right_buffer[j][7]之后,通过第7点讲的骚操作,进行线程之间的数据移动,所以thread0的right_buffer[j][7]就会被移动到thread1的right_buffer[j][0]处,而thread0的right_buffer[j][7]又会被thread0的right_buffer[j][6]所覆盖,这样就完成了所有线程的数据移动…
是不是很神奇,通过右移操作就可以完成所有right_buffer的更新。
if(DIRECTION > 0)对应的else就不看了,操作基本相同。
- 定义一个一维数组local_costs,大小为DP_BLOCK_SIZE,存当前视差对应的局部代价值。局部代价是通过Hamming距离来计算的。将左值与每一个视差对应的右值进行异或,然后计数结果中的1,即得到了Hamming距离。
- 最后通过update() 函数进行更新,然后将更新后的dp值存到dest中。
OKK!aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel()函数就讲解完了,不禁感叹作者的nb之处。看完之后感觉还是理解的不够透彻,想改成自己的还是有点困难…后面试试能不能一直到自己的算法中去。
接下来讲一下update()函数:
- 该函数其实比较简单,实现的功能就是更新一下dp数组和last_min的值。
- 整个函数就是对一个视差块中的每一个值进行处理和更新,然后计算last_min并进行更新。分为3部分:k = 0, k = 1~6, k = 7。
四、代码阅读技巧
在读代码的过程中总结了一些阅读技巧:
- 读代码的时候有很多宏定义暂时可能不太理解什么意思,没有关系,等你后面具体看它的使用场景的时候可能就明白了。
- 大部分写的很好的这种代码其实会有很多断言语句或者其他无关语句(条件编译、判断是否溢出等等),这些语句对于我们理解代码来说其实有没有都没有太大区别,所以你可以建立一个该代码的副本,然后把这些无关的代码都删掉,这样子代码就看着清爽多了,方便你理解。例如上面的代码其实核心就这么多:
template <int DIRECTION, unsigned int MAX_DISPARITY>
__global__ void aggregate_horizontal_path_kernel(
uint8_t *dest,
const feature_type *left, // feature_type 是 uint32_t
const feature_type *right,
int width,
int height,
unsigned int p1,
unsigned int p2,
int min_disp)
{
const unsigned int y0 =
PATHS_PER_BLOCK * blockIdx.x +
PATHS_PER_WARP * warp_id +
group_id;
left += y0 * width;
right += y0 * width;
dest += y0 * MAX_DISPARITY * width;
// 初始化
if(DIRECTION > 0){
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD; ++i){
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++j){
right_buffer[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int x0 = (DIRECTION > 0) ? 0 : static_cast<int>((width - 1) & ~(DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1));
// iter是迭代次数,一共迭代 width / DP_BLOCK_SIZE次,每次迭代内部处理 DP_BLOCK_SIZE 个数据
for(unsigned int iter = 0; iter < width; iter += DP_BLOCK_SIZE){
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++i){
// 在一个视差块中的索引,一共8个数据所以是从0~7,随着x0改变而改变,从右往左也类似
const unsigned int x = x0 + (DIRECTION > 0 ? i : (DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1 - i));
// 这里每个线程处理1个DP块,所以只需要迭代1次,如果处理多个,则需迭代多次。每次迭代只需处理1个视差。
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < DP_BLOCKS_PER_THREAD; ++j){
// y0是行号,一个组一行,一个组16个视差块,也即128个视差。对于此处的j迭代,每次迭代y0都是一样的
const unsigned int y = y0 + j * SUBGROUPS_PER_WARP;
// 取出每个视差块的视差对应的左值
const feature_type left_value = __ldg(&left[j * feature_step + x]);
if(DIRECTION > 0){
// 取出视差块最后一个右值,因为一会要右移,怕这个值移没了
const feature_type t = right_buffer[j][DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1];
// right_buffer每一个值右移一位
// 注意这里每次i循环都会右移一次,等i循环结束,就一共右移了8次。
for(unsigned int k = DP_BLOCK_SIZE - 1; k > 0; --k){
right_buffer[j][k] = right_buffer[j][k - 1];
}
right_buffer[j][0] = __shfl_up_sync(shfl_mask, t, 1, SUBGROUP_SIZE);
if(lane_id == 0 && x >= min_disp){
right_buffer[j][0] =
__ldg(&right[j * feature_step + x - min_disp]);
}
}
// 存一下每个视差块视差的局部代价值
uint32_t local_costs[DP_BLOCK_SIZE];
for(unsigned int k = 0; k < DP_BLOCK_SIZE; ++k){
// __popc是统计整数中1的个数,这里是一个计算汉明距离的过程(先异或然后计数1的个数)
local_costs[k] = __popc(left_value ^ right_buffer[j][k]);
}
// 更新dp中的dp、last_min
dp[j].update(local_costs, p1, p2, shfl_mask);
// 把dp.dp存到dest中
store_uint8_vector<DP_BLOCK_SIZE>(
&dest[j * dest_step + x * MAX_DISPARITY + dp_offset],
dp[j].dp);
}
}
x0 += static_cast<int>(DP_BLOCK_SIZE) * DIRECTION;
}
}
怎么样是不是看着就爽很多了?
3. 很多变量你不知道他是怎么更新的,或者怎么使用的,在VSCode里面可以点一下这个变量,然后就会高亮,然后你就可以大概先去后面的代码浏览一下这个变量用在哪,这样可能更有助于你的理解。
类似这样子: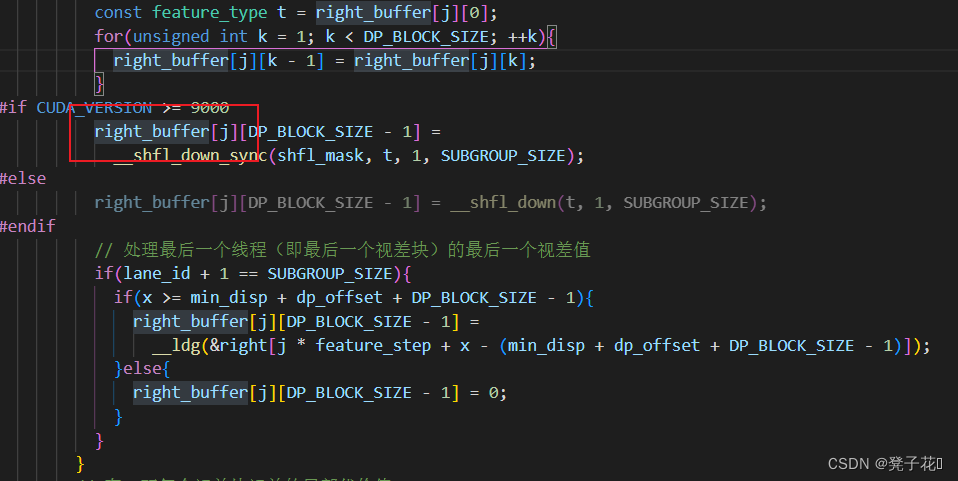
- 建议读代码的时候边读边写注释,写代码的时候最好也是这样,不然读到后面就忘了前面这个变量是啥意思了。
- 待定…
边栏推荐
- Vmware共享主机的有线网络IP地址
- [network security] SQL injection syntax summary
- 请问,在使用flink sql sink数据到kafka的时候出现执行成功,但是kafka里面没有数
- Dry goods | summarize the linkage use of those vulnerability tools
- 作战图鉴:12大场景详述容器安全建设要求
- What are the principles for distinguishing the security objectives and implementation methods that cloud computing security expansion requires to focus on?
- .net core 关于redis的pipeline以及事务
- Laravel form builder uses
- Excusez - moi, l'exécution a été réussie lors de l'utilisation des données de puits SQL Flink à Kafka, mais il n'y a pas de nombre dans Kafka
- SSRF vulnerability file pseudo protocol [netding Cup 2018] fakebook1
猜你喜欢

MySQL error 28 and solution
2022-7-6 Leetcode 977. Square of ordered array
带你掌握三层架构(建议收藏)
118. Yanghui triangle
Enregistrement de la navigation et de la mise en service du robot ROS intérieur (expérience de sélection du rayon de dilatation)
2022-7-6 beginner redis (I) download, install and run redis under Linux
js 获取当前时间 年月日,uniapp定位 小程序打开地图选择地点
2022-7-6 sigurg is used to receive external data. I don't know why it can't be printed out

Leetcode simple question sharing (20)

作战图鉴:12大场景详述容器安全建设要求
随机推荐
Leetcode simple question sharing (20)
Transferring files between VMware and host
[high frequency interview questions] difficulty 2.5/5, simple combination of DFS trie template level application questions
2022-7-6 初学redis(一)在 Linux 下下载安装并运行 redis
118. 杨辉三角
Advanced Mathematics - Chapter 8 differential calculus of multivariate functions 1
Flink | multi stream conversion
请问,我kafka 3个分区,flinksql 任务中 写了 join操作,,我怎么单独给join
高等數學---第八章多元函數微分學1
请问,redis没有消费消息,都在redis里堆着是怎么回事?用的是cerely 。
Solve the cache breakdown problem
手把手教会:XML建模
Beginner XML
Huawei image address
2022-7-7 Leetcode 844. Compare strings with backspace
最长上升子序列模型 AcWing 1012. 友好城市
参数关键字Final,Flags,Internal,映射关键字Internal
PC端页面如何调用QQ进行在线聊天?
PostgreSQL array type, each splice
Social responsibility · value co creation, Zhongguancun network security and Information Industry Alliance dialogue, wechat entrepreneur Haitai Fangyuan, chairman Mr. Jiang Haizhou