当前位置:网站首页>2020 CCPC Weihai - A. golden spirit (thinking), D. ABC project (big number decomposition / thinking)
2020 CCPC Weihai - A. golden spirit (thinking), D. ABC project (big number decomposition / thinking)
2022-07-05 20:23:00 【Dimple】
A. Golden Spirit
The question
There is a bridge on a river , The two sides of the Strait have n n n personal .
Now here 2 n 2n 2n Everyone has to go to the opposite bank , Play at least x x x Minutes later, return to the original river bank .
Help this 2 n 2n 2n Crossing the river alone .
Take at most one person when crossing the river , Time is t t t.
ask , How much time does it take to meet everyone's requirements ?
Ideas
In the best case , Helpers don't waste any time , When he transported everyone to the opposite bank , People who are transported from the river bank for the first time can be transported back immediately .
But maybe even the first-time passengers don't have the time to travel , So the helper may need to wait .
Suppose there is a river bank A and B, At first the helper was on the bank A, Then transport everyone to their corresponding river bank , The helper is located on the river bank A.
At this time, there is a problem , The helper is to continue on the river bank A Waiting for the first delivery to the river bank A People who , Or go to the other side by yourself B Go and wait for the first transportation to the river bank B People who ?
The former takes : Time to transport everyone 4nt + Waiting time ( Minimum travel time x - The first person has played time 2nt-2t)
The latter takes : Time to transport everyone 4nt + Time to get to the other side t + Waiting time ( Minimum travel time x - The first person has played time 2nt + t - t)
Because I'm not sure about the size of the two , So we need to choose the two min.
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010, mod = 1e9+7;
int T, n, m;
int a[N];
signed main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
int x, t;
cin >> n >> x >> t;
int ans1 = 4*n*t + t + max(0ll, x - (2*n*t + t - t));
int ans2 = 4*n*t + max(0ll, x - (2*n*t - 2*t));
cout << min(ans1, ans2) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Experience
- When you are not sure which is the best in all cases , You need to minimize the answer in all cases ;
- In some cases, don't write too much if else, Instead, try to abstract it into a big situation .
D. ABC Conjecture
The question
Give a number c, Judge whether it exists a, b Meet the following conditions :
- a + b = c
- abc The product of all prime factors of No more than c
1 ≤ c ≤ 1 0 18 1≤c≤10^{18} 1≤c≤1018
Ideas
I found that : Can satisfy c All the prime factors of decomposition only appear once .
So for a given c, Just judge whether there is a qualitative factor that appears more than once .
however c It's big , The time complexity of the commonly used prime factor decomposition code is O(logn), Will timeout .
So we need to do it in a special way .
Method 1:
- According to the idea of decomposing prime factors c Not more than 1e6 The prime factorization of , Judge whether the number occurs twice or more .
- If 1e6 After screening the internal quality factor, it is found c Not for 1, It means that c There are at most two greater than 1e6 Prime factor of ( Suppose there is 3 individual , Then the multiplication is greater than 1e18, contradiction ).
We are not asking for these two qualitative factors , I just want to judge whether these two qualitative factors are the same . So the last c Take root and round , Judge whether it is square . If it's a square , Then the last two prime factors are the same .
Code1:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1000010, mod = 1e9+7;
int T, n, m;
int a[N];
int f[N];
int prim[N];
int cnt;
int maxa = 1e6;
signed main(){
Ios;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n;
int flag = 0;
for(int i=2; i<=maxa; i++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(n % i == 0) n /= i, cnt++;
if(cnt != 1) flag = 1;
}
}
if(n != 1){
int sq = sqrt(n);
if(sq * sq == n) flag = 1;
}
if(flag) cout << "yes\n";
else cout << "no\n";
}
return 0;
}
Method 2
Directly on the large number prime factorization template , Judge whether there are qualitative factors appearing twice or more .
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll pr;
ll pmod(ll a, ll b, ll p) {
return (a * b - (ll)((long double)a / p * b) * p + p) % p; }
ll gmod(ll a, ll b, ll p)
{
ll res = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
res = pmod(res, a, p);
a = pmod(a, a, p);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b)
{
if (!a)
return b;
if (!b)
return a;
int t = __builtin_ctzll(a | b);
a >>= __builtin_ctzll(a);
do
{
b >>= __builtin_ctzll(b);
if (a > b)
{
ll t = b;
b = a, a = t;
}
b -= a;
} while (b);
return a << t;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(ll n)
{
if (n == 46856248255981ll || n < 2)
return false;
if (n == 2 || n == 3 || n == 7 || n == 61 || n == 24251)
return true;
if (!(n & 1) || !(n % 3) || !(n % 61) || !(n % 24251))
return false;
ll m = n - 1, k = 0;
while (!(m & 1))
k++, m >>= 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; ++i)
{
ll a = rand() % (n - 1) + 1, x = gmod(a, m, n), y;
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j)
{
y = pmod(x, x, n);
if (y == 1 && x != 1 && x != n - 1)
return 0;
x = y;
}
if (y != 1)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
ll Pollard_Rho(ll x)
{
ll n = 0, m = 0, t = 1, q = 1, c = rand() % (x - 1) + 1;
for (ll k = 2;; k <<= 1, m = n, q = 1)
{
for (ll i = 1; i <= k; ++i)
{
n = (pmod(n, n, x) + c) % x;
q = pmod(q, abs(m - n), x);
}
t = gcd(x, q);
if (t > 1)
return t;
}
}
map<long long, int> m;
void fid(ll n)
{
if (n == 1)
return;
if (Miller_Rabin(n))
{
pr = max(pr, n);
m[n]++;
return;
}
ll p = n;
while (p >= n)
p = Pollard_Rho(p);
fid(p);
fid(n / p);
}
int main()
{
int T;
ll n;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
m.clear();
scanf("%lld", &n);
pr = 0;
fid(n);
int flag = 0;
for (map<long long, int>::iterator c = m.begin(); c != m.end(); c++)
if(c->second != 1) flag = 1;
if(flag) printf("yes\n");
else printf("no\n");
}
return 0;
}
Tabulation code :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 200010, mod = 1e9+7;
int T, n, m;
int a[N];
vector<int> v, v1, v2;
set<int> st, s;
void div(int x, vector<int> &v)
{
v.clear();
for(int i=2;i<=x/i;i++)
{
if(x%i == 0)
{
while(x%i == 0) x /= i;
v.push_back(i);
}
}
if(x != 1) v.push_back(x);
}
signed main(){
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++)
{
st.clear();
div(i, v);
for(int x : v) st.insert(x);
int flag = 0;
for(int j=1;j<i;j++)
{
s = st;
int x = j, y = i - x;
div(x, v1);
div(y, v2);
for(int x : v1) s.insert(x);
for(int x : v2) s.insert(x);
int sum = 1;
for(int x : s){
sum *= x;
}
if(sum < i){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(!flag){
cout << i << ":";
for(int x : st) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Experience
- When you have no idea, make a list first ;
- Judge whether a number is a square number ,sqrt(n) Round it up and multiply it ;
- Large number prime factorization template .
边栏推荐
- Summer Challenge harmonyos - realize message notification function
- A way to calculate LNX
- Ros2 topic [01]: installing ros2 on win10
- [quick start of Digital IC Verification] 9. Finite state machine (FSM) necessary for Verilog RTL design
- 1. Strengthen learning basic knowledge points
- Practical demonstration: how can the production research team efficiently build the requirements workflow?
- 信息学奥赛一本通 1337:【例3-2】单词查找树 | 洛谷 P5755 [NOI2000] 单词查找树
- Relationship between mongodb documents
- CTF reverse Foundation
- ICTCLAS用的字Lucene4.9捆绑
猜你喜欢

Mysql频繁操作出现锁表问题

leetcode刷题:二叉树14(左叶子之和)
无卷积骨干网络:金字塔Transformer,提升目标检测/分割等任务精度(附源代码)...
![[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 6. Quick start of questasim (taking the design and verification of full adder as an example)](/img/6d/110b87747f0a4be52da9fd49a05b82.png)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 6. Quick start of questasim (taking the design and verification of full adder as an example)
![[quick start to digital IC Verification] 8. Typical circuits in digital ICs and their corresponding Verilog description methods](/img/3a/7eaff0bf819c129b4f866388e57b87.png)
[quick start to digital IC Verification] 8. Typical circuits in digital ICs and their corresponding Verilog description methods
【数字IC验证快速入门】1、浅谈数字IC验证,了解专栏内容,明确学习目标
Zero cloud new UI design
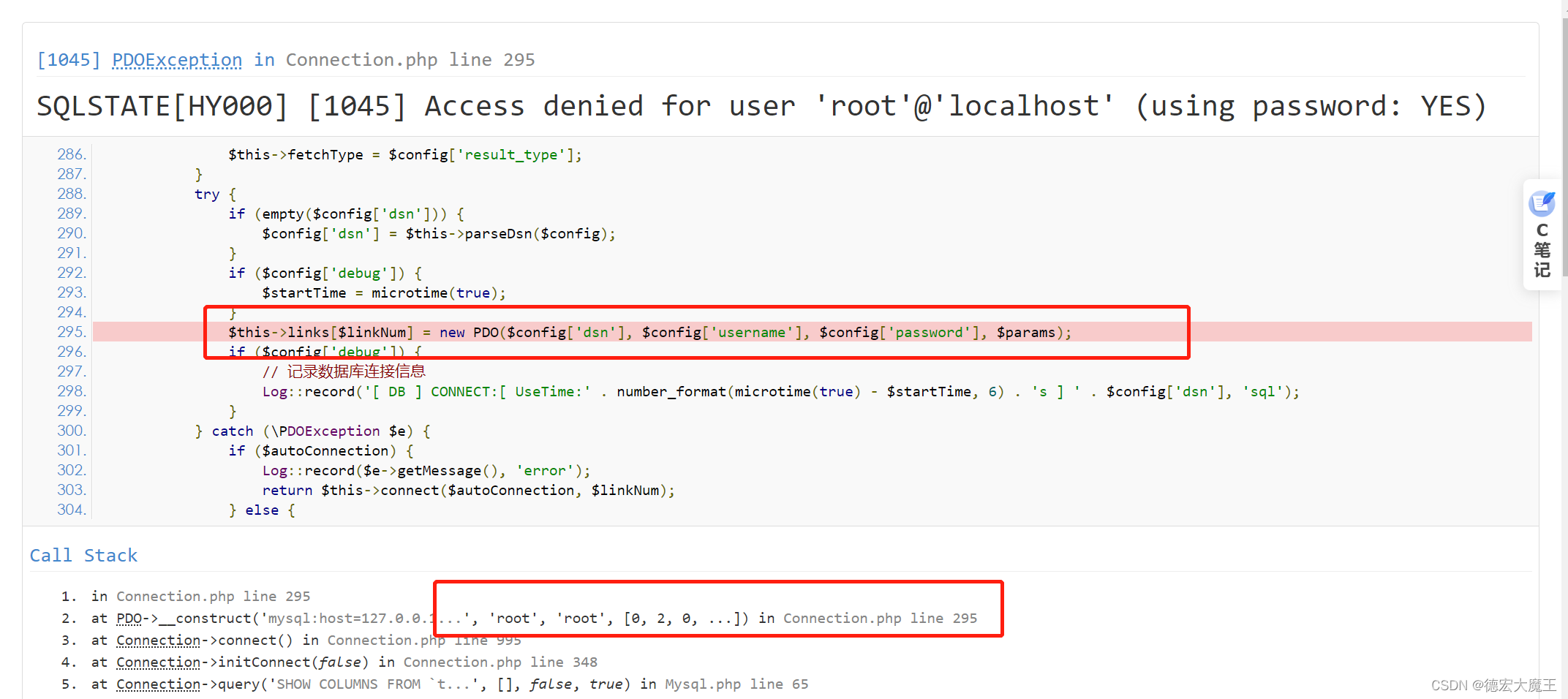
Solve the problem that the database configuration information under the ThinkPHP framework application directory is still connected by default after modification

Guidelines for application of Shenzhen green and low carbon industry support plan in 2023

零道云新UI设计中
随机推荐
Rainbow 5.7.1 supports docking with multiple public clouds and clusters for abnormal alarms
本季度干货导航 | 2022年Q2
C language OJ gets PE, OJ of ACM introduction~
资源道具化
CCPC 2021威海 - G. Shinyruo and KFC(组合数,小技巧)
ffplay文档[通俗易懂]
2020 CCPC 威海 - A. Golden Spirit(思维),D. ABC Conjecture(大数分解 / 思维)
基金网上开户安全吗?去哪里开,可以拿到低佣金?
Station B up builds the world's first pure red stone neural network, pornographic detection based on deep learning action recognition, Chen Tianqi's course progress of machine science compilation MLC,
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 9. Finite state machine (FSM) necessary for Verilog RTL design
【刷题记录】1. 两数之和
鸿蒙os第四次学习
Informatics Olympiad 1337: [example 3-2] word search tree | Luogu p5755 [noi2000] word search tree
【数字IC验证快速入门】3、数字IC设计全流程介绍
Leetcode: binary tree 15 (find the value in the lower left corner of the tree)
小程序页面导航
Leetcode brush questions: binary tree 11 (balanced binary tree)
.Net分布式事务及落地解决方案
Classic implementation of the basic method of intelligent home of Internet of things
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 10 (number of nodes of a complete binary tree)