当前位置:网站首页>3D激光slam:LeGO-LOAM---地面点提取方法及代码分析
3D激光slam:LeGO-LOAM---地面点提取方法及代码分析
2022-08-02 10:00:00 【华为云】
前言
地面点提取方法
LeGO-LOAM中前端改进中很重要的一点就是充分利用地面点,本片博客主要讲解 如何进行地面点提取
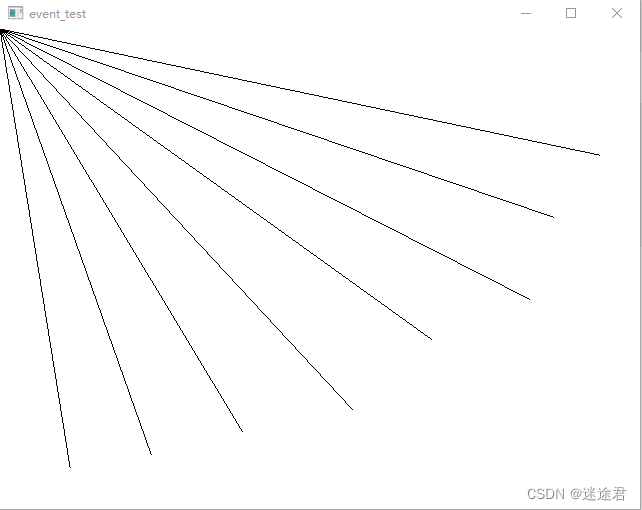
如下图所示,相邻的两个scan的同一列,打在地面上,形成两个点A和B。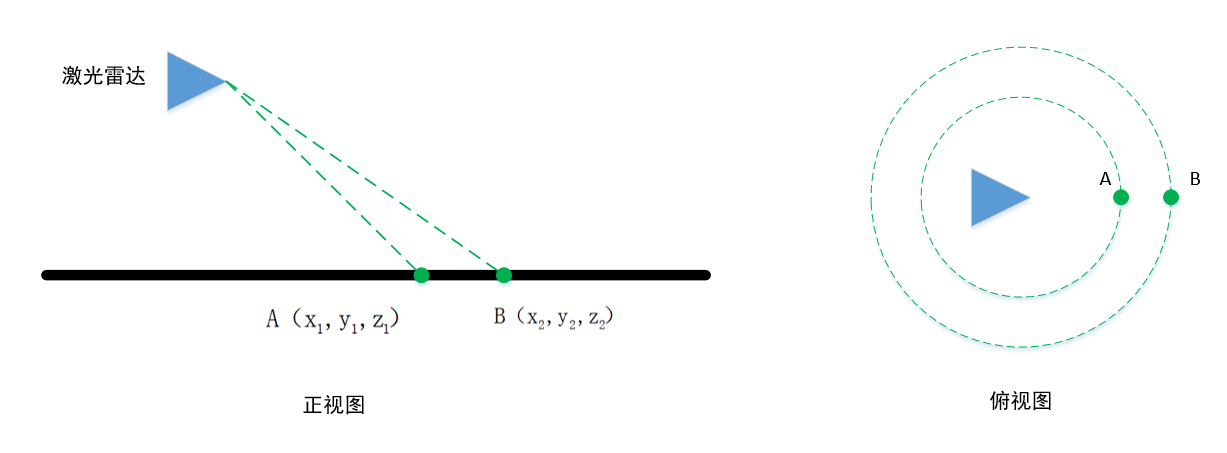
它们的垂直高度差为h,这个值在理想情况(雷达水平安装,地面是水平的)接近于0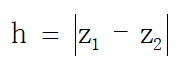
水平距离差d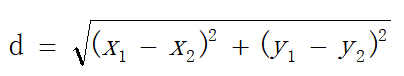
和水平面的夹角为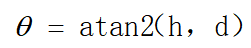
如果为地面点,在理想情况下,这个角点接近0.
但是雷达的安装不会完全水平,并且地面也不是平的,因此这个角度会大于0,LeGO-LOAM设置的是10°。
即小于10°被判断为地面点
这种地面点的提取算法有些过于简单,还可以结合激光雷达安装高度,等其它信息进行判断。例如下面这种情况,也会被判断为地面点: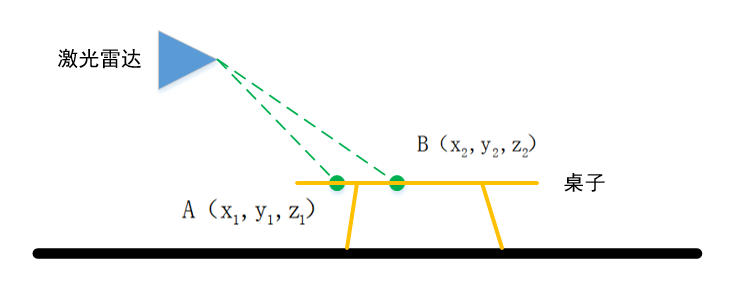
代码分析
LeGO-LOAM的地面提取的代码在 imageProjection.cpp 中 groundRemoval 函数
void groundRemoval(){ size_t lowerInd, upperInd; float diffX, diffY, diffZ, angle;lowerInd, upperInd 是相邻scan上点的索引值
diffX, diffY, diffZ, angle 是 dx dy dz 水平角
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){//遍历水平方向的点 360/0.2 1800个点 for (size_t i = 0; i < groundScanInd; ++i){//groundScanInd 为8 地面点不能在上面嵌套两个for循环, 列要在前面,因为要计算同一列的值
第一行,遍历水平方向的点 360/0.2 1800个点
第二行,groundScanInd 为8 地面点不能在上面
lowerInd = j + ( i )*Horizon_SCAN;//下面的点 upperInd = j + (i+1)*Horizon_SCAN;//上面的点计算的两个点的索引
Horizon_SCAN为1800,
if (fullCloud->points[lowerInd].intensity == -1 || fullCloud->points[upperInd].intensity == -1){ // no info to check, invalid points groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = -1;//标志位 至-1 continue; } 判断两个点是否有效,点无效的话intensity为-1
有一个点无效的话 标志位 至-1
diffX = fullCloud->points[upperInd].x - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].x;//dx diffY = fullCloud->points[upperInd].y - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].y;//dy diffZ = fullCloud->points[upperInd].z - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].z;//dz angle = atan2(diffZ, sqrt(diffX*diffX + diffY*diffY) ) * 180 / M_PI;//计算水平角度计算 dx dy dz 和水平角,就是这个公式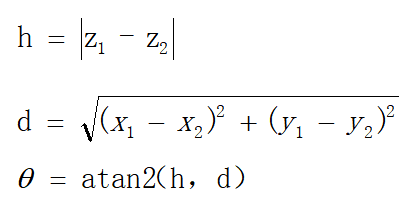
if (abs(angle - sensorMountAngle) <= 10){ groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = 1; groundMat.at<int8_t>(i+1,j) = 1; } } }sensorMountAngle 是 liadr 是和水平面的倾斜角
这里就是把那两个点的水平角,和10°做比较,判断是不是地面点
如何使把标志位 至 1
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){ for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){ if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1 || rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) == FLT_MAX){ labelMat.at<int>(i,j) = -1;//labelMat 至为 -1 ,不参与后续线特征和面特征的提取 } } }判断完地面点后,再遍历每个点,
如过该点是 地面点或者无效点,则把 labelMat 上的该点标志位至-1 .
labelMat 至为 -1 ,不参与后续线特征和面特征的提取
//地面点可视化 if (pubGroundCloud.getNumSubscribers() != 0){//如果有节点要订阅这个地面点的topic 再进行发布 for (size_t i = 0; i <= groundScanInd; ++i){ for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){ if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1) groundCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);//把点加在 地面点点云中 之后会发布出去 } } } }最后进行地面点得可视化
如果有节点要订阅这个地面点的topic 再进行发布
遍历0-groundScanInd 上得每个点,判断如果是地面点,则添加该点到 groundCloud 中
之后会被发布出去
发布得在这个地方
// original dense ground cloud if (pubGroundCloud.getNumSubscribers() != 0){ pcl::toROSMsg(*groundCloud, laserCloudTemp); laserCloudTemp.header.stamp = cloudHeader.stamp; laserCloudTemp.header.frame_id = "base_link"; pubGroundCloud.publish(laserCloudTemp); }topic得名称是/ground_cloud
pubGroundCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("/ground_cloud", 1);gazebo测试
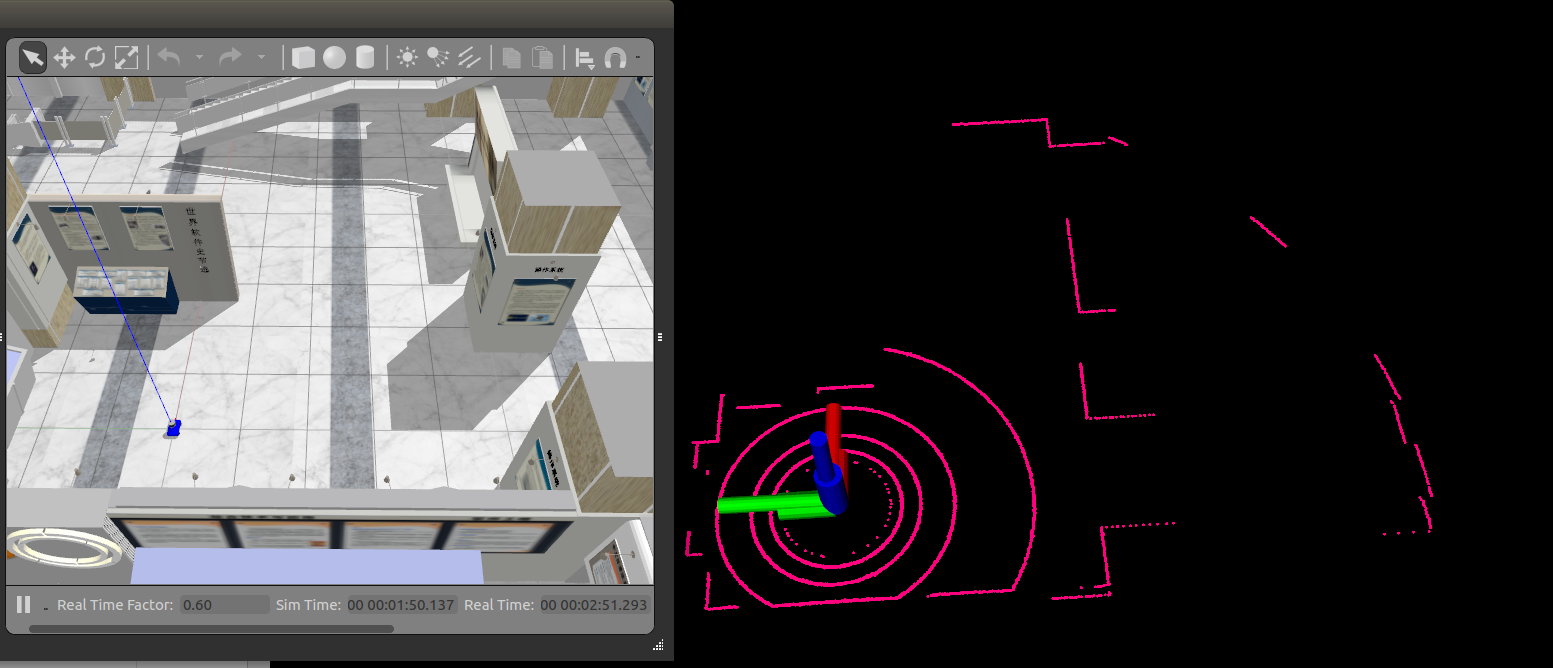

效果还是挺好得,没有出现异常点
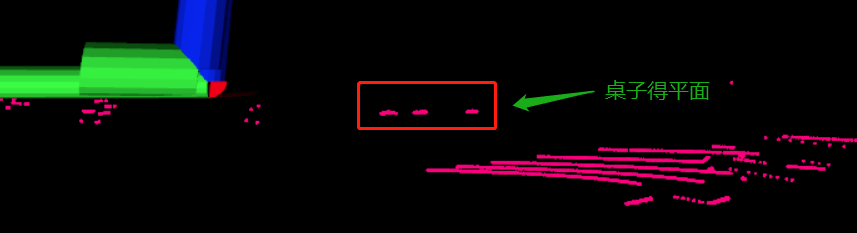
但是由于没有加入高度得判断,在前面里说得这种情况则会出现问题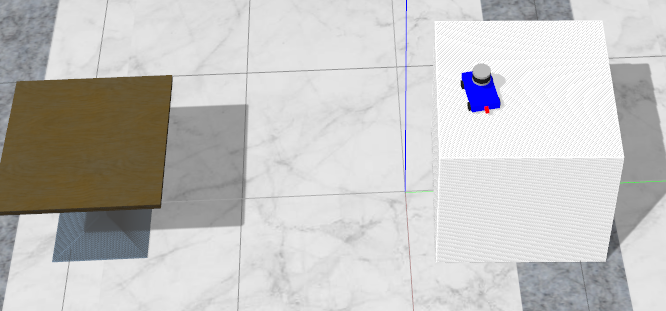
边栏推荐
- R语言时间序列数据算术运算:使用log函数将时间序列数据的数值对数化、使用diff函数计算对数化后的时间序列数据的逐次差分(计算价格的对数差分)
- 日元疲软令游戏机在日本变身“理财产品”:黄牛大赚
- matlab-day02
- armv7与armv8的区别(v8和w12的区别)
- 一款优秀的中文识别库——ocr
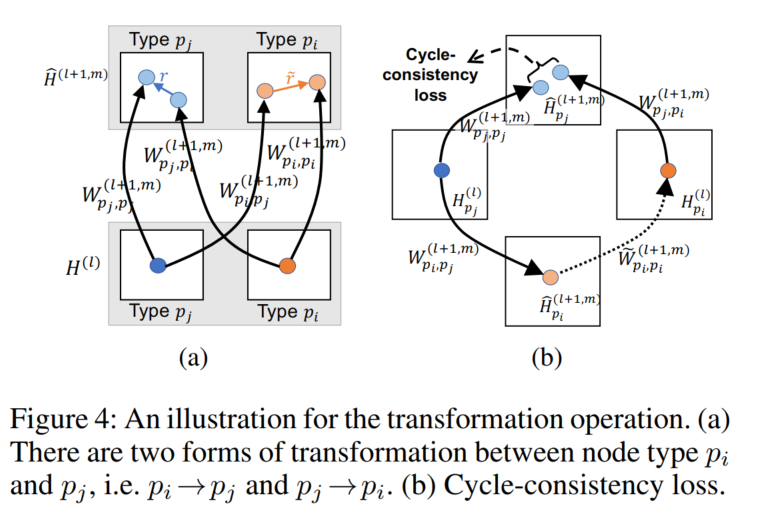
- Re22:读论文 HetSANN An Attention-based Graph Neural Network for Heterogeneous Structural Learning
- Shell script realizes multi-select DNS simultaneous batch resolution of domain name IP addresses (new update)
- The love-hate relationship between C language volatile keyword, inline assembly volatile and compiler
- Rust 从入门到精通03-helloworld
- 读博一年后对机器学习工程的思考
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Use the scrapy to climb to save data to mysql to prevent repetition
行为型模式-模板方法模式
The realization of the list
Re23:读论文 How Does NLP Benefit Legal System: A Summary of Legal Artificial Intelligence
Weak yen turns game consoles into "financial products" in Japan: scalpers make big profits
R语言时间序列数据的平滑:使用KernSmooth包的dpill函数和locpoly函数对时间序列数据进行平滑以消除噪声
List-based queuing and calling system
The love-hate relationship between C language volatile keyword, inline assembly volatile and compiler
leetcode 62. Unique Paths(独特的路径)
新“内卷”席卷科技圈,Google CEO 要求 174000 员工提高工作效率!
c#反射和特性
QT专题:组合会话框和文本编辑器
带你认识40G单纤双向光模块-QSFP+ BiDi光模块
后管实现面包屑功能
练习-17
第十五章 多线程
理解JS的三座大山
神通数据库,批量插入数据的时候失败
yolov7创新点
MySql tens of millions of paging optimization, fast insertion method of tens of millions of data