当前位置:网站首页>In depth MySQL transactions, stored procedures and triggers
In depth MySQL transactions, stored procedures and triggers
2022-07-06 04:10:00 【Code Taoist】

stored procedure
One or more stored for future use mysql Collection of statements . Vaguely, it can be regarded as a batch file .
It's a function . Yes , Equivalent to C Functions in language 、c++/java The method in . You can call , Improve SQL Operational efficiency .
In general , Users with normal permissions only have the permission to use stored procedures , Without permission to write , Yes , Stored procedures are also convenient for users to query ( We will talk about “ Create intelligent scenarios ”), It is also user oriented .
Execute stored procedures :mysql The execution of a stored procedure is called , therefore mysql The statement to execute the stored procedure is CALL.CALL Receive the name of the stored procedure and any parameters that need to be passed to it . The following is a stored procedure for a program :
CALL productpricing(@pricelow, @pricehigh, @priceaverage);among , Return the lowest (pricelow)、 The highest (pricehigh)、 And the average price (priceaverage).
Create stored procedure : Direct orders :
create procedure pro()
begin
select avg(prod_price) as priceaverage
from products;
end; This stored procedure is called Pro, use create procedure pro() Definition . If the stored procedure receives parameters , They will be in () To list out .
among ,begin and end Statement is used to define the body of a stored procedure , The process body is just a select sentence .
If you're using mysql Command line utility , Attention should be paid to :mysql Command line utilities and mysql The default is the same , take “;” Treat as separator , They will not eventually be called components of stored procedures , This will make SQL sentence in wrong . terms of settlement : Add a line at the beginning :delimiter // —— Tell the command line utility to use // As a new statement end separator , And then end Situated ; Change it to //, Add another line at the end :delimiter ;—— To reply to the original statement separator
then , How to use ?
CALL pro();Execute the newly created stored procedure ;( Generally, variables are passed in brackets here )
Why? Pro There's going to be ()?—— A stored procedure is actually a function .
Delete stored procedure
drop procedure pro;Please note that , Not using the latter (), Just give the stored procedure name .
but, If the specified procedure does not exist , Then the above statement will be wrong . We can use :drop procedure if exists; ( About if exists, I'll see you later , It is widely used in the establishment of intelligent stored procedures )
Using parameter : commonly , Stored procedures do not display results , Instead, return the result to the variable you specified .
Variable : A specific location in memory , Used to temporarily store data .
Here are Pro Modified version of :
create procedure pro(
out p1 decimal(8,2),
out p2 decimal(8,2),
out p3 decimal(8,2)
)
begin
select min(prod_price)
into p1
from products;
select max(prod_price)
into p2
from products;
select avg(prod_price)
into p3
from products;
end;This process receives three parameters :p1 The lowest price for storage products ,p2 The highest price of storage products ,p3 Average storage price of products . Each parameter must have a specified type . keyword out Point out the corresponding parameters to pass a value from the stored procedure ( Back to the caller ).
mysql Support IN( Pass to stored procedure )、out( From stored procedure )、 and INOUT( Pass in and out of stored procedures ) Parameters of type
IN Input parameters : The value representing the parameter must be specified when the stored procedure is called , Modifying the value of this parameter in a stored procedure cannot be returned , As the default value
OUT Output parameters : This value can be changed within the stored procedure , And can return
INOUT Input/output parameter : When called, specifies , And can be changed and returned
Ⅰ.IN Parameter example
establish :
mysql > DELIMITER //
mysql > CREATE PROCEDURE demo_in_parameter(IN p_in int)
-> BEGIN
-> SELECT p_in;
-> SET p_in=2;
-> SELECT p_in;
-> END;
-> //
mysql > DELIMITER ; Execution results :
mysql > SET @p_in=1;
mysql > CALL demo_in_parameter(@p_in);
+------+
| p_in |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
+------+
| p_in |
+------+
| 2 |
+------+
mysql> SELECT @p_in;
+-------+
| @p_in |
+-------+
| 1 |
+-------+ As can be seen above ,pin Although it is modified in the stored procedure , But it doesn't affect @pid Value
Ⅱ.OUT Parameter example
establish :
mysql > DELIMITER //
mysql > CREATE PROCEDURE demo_out_parameter(OUT p_out int)
-> BEGIN
-> SELECT p_out;
-> SET p_out=2;
-> SELECT p_out;
-> END;
-> //
mysql > DELIMITER ; Execution results :
mysql > SET @p_out=1;
mysql > CALL sp_demo_out_parameter(@p_out);
+-------+
| p_out |
+-------+
| NULL |
+-------+
+-------+
| p_out |
+-------+
| 2 |
+-------+
mysql> SELECT @p_out;
+-------+
| p_out |
+-------+
| 2 |
+-------+
Ⅲ.INOUT Parameter example
establish :
mysql > DELIMITER //
mysql > CREATE PROCEDURE demo_inout_parameter(INOUT p_inout int)
-> BEGIN
-> SELECT p_inout;
-> SET p_inout=2;
-> SELECT p_inout;
-> END;
-> //
mysql > DELIMITER ; Execution results :
mysql > SET @p_inout=1;
mysql > CALL demo_inout_parameter(@p_inout) ;
+---------+
| p_inout |
+---------+
| 1 |
+---------+
+---------+
| p_inout |
+---------+
| 2 |
+---------+
mysql > SELECT @p_inout;
+----------+
| @p_inout |
+----------+
| 2 |
+----------+ As I saw before , Stored procedures are a series select sentence , Used to retrieve values , adopt INTO Save keyword to corresponding variable .
mysql There are global variables and local variables :
1. local variable : With keywords DECLARE Statement , Followed by variable name and variable type , Such as :declare a int
You can also use keywords DEFAULT Specify default values for variables , Such as :declare a int default 102. Global variables :mysql The session variables in are global variables , Session variables are valid throughout the process , It takes characters “@” start , Such as :
delimiter //
create procedure p2()
begin
set @t=1;
begin
set @t=2;
select @t;
end;
select @t;
end;
delimiter //To call the modified stored procedure , Must specify 3 Variable names , namely :
CALL productpricing(@pricelow, @pricehigh, @priceaverage);all mysql All variables must be in @ Start .
For reasons of length , Please pay attention to my other blog posts for specific matters , I won't elaborate here ...
Of course , The most important of these is , It supports various conditional statements , Such as :IF sentence ( First judgement IF Whether the post condition is true , When true, execute the following THEN The following sentence , If false, continue to judge )、CASE sentence ( First of all, from the WHEN After value Search for and CASE After value Equal value , If found, execute the contents of the branch )、WHILE Loop statement ( First judgement condition Is the condition true , When true, execute the loop body )、LOOP Loop statement (LOOP Allow some giant specific repetition , Implement a simple loop construct , Exit the cycle with LEAVE sentence )、REPEAT Loop statement ( First execute the loop body , And then determine condition Is the condition true , When true, exit the loop )
Example :
1.LOOP
delimiter //
create procedure edxloop(out sum int)
begin
declare i int default 1;
declare s int default 0;
loop_lable:loop
set s=s+i;
set i=i+1;
if i>100 then
leave loop_lable;
end if;
end loop;
set sum=s;
end
delimiter //call exloop(@s);
.................................
select @s;Storage function : The same routine as stored procedures , It's just ,create hinder procedure Turned into function. as follows :
delimiter //
create function name_of_student(std_id int)
return varchar(15)
begin
return(select name from syidentinfo where std=std_id);
end
delimiter //Two return Be short of one cannot , The first one is the type of the parameter , The second is the query results .
Call stored procedures and stored functions :1. Calling stored procedure : As mentioned earlier call,yes, Through the previous example, it must be unnecessary to say this at all ,OK,To proceed to the next item!
2. Calling the storage function : direct select Function name ( Parameters ); that will do
View the definitions of stored procedures and stored functions :SHOW CREATE sentence
show create procedure/function name ;
Check the status of stored functions and stored procedures : Such as :show procedure status like 'filminstock'; ( Check out the process filminstock Information about )
Delete stored procedures and stored functions :drop procedure/function [IF EXISTS] name ;
trigger
above “ Storage function ” Medium “DELIMITER //” The same as when creating triggers , So here is the trigger .
Let's talk about triggers first , In fact, I have learned java Everyone knows that one of them is “ I've been fascinated for a long time ” Things that are , It's called “ The monitor ”, Common as : Mouse monitor , It can realize mouse operation ; Time monitor 、 Color monitor, etc ...
The trigger in the database is similar to this principle : In the implementation of a “ Operations to be monitored ” Set trigger , Trigger is raised during execution , Let the system complete the established procedures .
Create trigger :
CREATE TRIGGER Trigger Name BEFORE|AFTER Triggering event ON Table name FOR EACH ROW Execute statement
before and after: Specify the time when the trigger executes ( Before or after the trigger time );
for each row: Indicates that the trigger event will be triggered if the operation on any record satisfies the trigger event ;
Execute statement : Refers to the program executed after the trigger is triggered
for example : Create a file called timelog Table of
create table timelog(
id int primary key auto_increment,
savetime varchar(50) not null
);Create a save_time The trigger of
delimiter //
create trigger save_time before insert
on studentinfo for each row
insert into timelog(savetime) values(now());
delimiter //insert That sentence is “now()”, So let's return a message : Time to run this operation !
This is the function of trigger .
Above is a single event , What if there are multiple events ?
Created above timelog On the basis of , Create another one named timeinfo Data sheet for
create table timeinfo(
id int primary key,
info varchar(50) not null
);And then create one by DELETE Trigger of multiple statements triggered , as follows :
delimiter //
create trigger delete_time_info after delete
on studentinfo for each row
begin
insert into timelog(savetime) values(now());
insert into timeinfo(info) values(now());
end
delimiter //The code that performs the delete operation ( The command that triggers the trigger ) by :
DELETE FROM studentinfo where name='Chirs';
then , use select Statement to view timelog Data sheets and timeinfo Data sheet , You can see the returned result .
Check triggers : use SHOW TRIGGERS; Check the basic information of trigger ;
Delete trigger : use DROP TRIGGER Trigger Name ;
Take a look at the complete example of a trigger :
One 、 establish MySQL Instance data table :
stay mysql The default test test Under database , Create two tables ta And tb:
/*Table structure for table `t_a` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_a`;
CREATE TABLE `t_a` (
`id` smallint(1) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`groupid` mediumint(8) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=16 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
/*Data for the table `t_a` */
LOCK TABLES `t_a` WRITE;
UNLOCK TABLES;
/*Table structure for table `t_b` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_b`;
CREATE TABLE `t_b` (
`id` smallint(1) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`groupid` mediumint(8) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=57 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
/*Data for the table `t_b` */
LOCK TABLES `t_b` WRITE;
UNLOCK TABLES;stay ta Create one on the table CUD( increase 、 Change 、 Delete )3 Trigger , take ta Table data and t_b Synchronous implementation CUD, Note that each table has only one corresponding trigger for the same event , Why only one trigger , No explanation , see MYSQL Help documentation for instructions .
MySQL Business
First say ,mysql Variables are really a magical thing , It can not only be simulated by stored procedures and stored functions c/c++/java Function of ( Method ),mysql The view of variables is also added in (select @ Variable ).
What does this have to do with what we are going to say ? No, .
stay mysql in , A transaction consists of one or more separate units SQL Sentence composition , In this unit , Every mysql Statements are interdependent .
Let's talk about it first , What are the applications of transaction data ?
online shopping , Users log on to the website , Browse information , Put your favorite items in the shopping cart , Then pay online , When the user finishes paying , Inform the merchant to deliver the goods , Be careful , At this time, the merchant did not receive the payment , When the user receives the goods , Click confirm receipt , The merchant received the payment , The whole deal is done . Imagine when users choose products , Choose to cancel the order during shipment , This is business did not get payment will cancel operation , If transactions are not used , After the user cancels the operation , Merchants still deliver goods to users , It will cause some unhappiness . Therefore, in the whole transaction process , Transaction rollback operation must be taken .
Simply speaking , Transaction is to add a “ insurance ”.
Tips :mysql Transactions are only for InnoDB and BDB Type table , When we create tables, the default is MyISAM Type table .
Atomicity : That is, the integrity and indivisibility of the transaction , All transactions go forward and backward . Or say , The execution of atoms is a whole process of all occurrences or all failures . In an atomic operation , If any statement of the transaction fails , The statements executed earlier will be returned , I. ensure that the integrity of the data is not destroyed .
Uniformity : be based on mysql Journal processing mechanism , Record all changes in the database , Provide trace records for transaction recovery . Such as : user A To the user B Transfer accounts 5000 element , user B But I found that my account only increased 3000 element , Is it very sad ...
persistence : Committed transactions even mysql The system crashed and still kept running . When a transaction is completed , When the database log has been updated , Persistence can play its unique role . and , stay mysql in , If the system crashes or the data storage medium is damaged , By using logs , The system can recover the last successful update before restart .
Isolation
By default ,InnoDB Tables last the longest .
Creation of affairs
The process is a bit cumbersome : Initialize transaction 、 Create transaction 、 application select Statement to query whether the data is entered 、 Commit transaction .
1. Create a table :create table table_name(field-defintions) type=INNODB/BDB;
table_name Is the name of the table ,field-defintions It is an in table field
If users want to support transaction processing for existing tables , Applicable ALTER Command to specify :alter table table_name type=INNODB/BDB;2. Initialize transaction :start transaction;
3. Create transaction : After successful initialization , Insert data into table , Such as :
insert into connection(email,cellphone,qq,sid) values('[email protected]',123456789,8975645,3);3. see : Such as :select * from connection where sid=3;
4. Commit transaction : Before the user commits the transaction , When other users connect mysql Server time , use select The query will not show the added transactions .
Commit transaction command :COMMITCancellation of transaction ( Transaction rollback ):ROLLBACK command . If a rollback operation is performed , Then enter start transaction All after the command SQL Statement will execute rollback operation .
If the user commits the transaction , No transaction committed , The transaction defaults to automatic rollback .
How to use transaction rollback ? We need to set up a savepoint Variable , I call it : Rollback label . When rollback is needed , just rollback Just go to the place of this label . Such as :
savepoint test;
...
...
rollback to savepoint test;Transactions do not support nested use , When the user reopens a transaction before ending the first transaction , The previous transaction will be automatically committed , Again mysql Many commands in the command will hide the execution COMMIT command ;
MySQL Behavior
1. About mysql Automatic submission : If the user does not want to control MySQL Auto submit parameters , You can change the submission mode , Such as : Use “SET AUTOCOMMIT=0;” The command turns off auto submit parameters , thereafter , Only when the user enters COMMIT after ,mysql In order to submit the data in the data table to the database .
We can check (select)“@@AUTOCOMMIT” Variable to view the current auto submit status .
mysql Isolated level
1. be based on ANSI/ISO SQL standard ,MySQL Provide 4 Medium isolated level , Namely :SERIALIZABLE( serialize )、REPEATABLE READ( Can be reread )、READ COMMITTED( Submit and read )、READ UNCOMMITTED( Uncommitted read ).
2. Modify the orphan level of the transaction :mysql The default isolation level is “ Can be reread ”, The user can use the command :set global transaction isolation level Isolated level name ; To modify the level ; can use select Command to get the value of the orphan level variable of the current transaction :select @@tx_isolation;
3. If ordinary users want to modify the isolation level of transactions , You have to get SUPER jurisdiction .
Table locking ?——MyISAM Middle simulation InnoDB/BDB Business stuff
abbreviation , Pseudo transaction .
purpose : Avoid interference during user operation of the database .
The basic steps to set table locking instead of transactions are as follows :
(1) Add a lock to the specified table :LOCK TABLES tablename locktype,......
among ,lock_type Refers to the type of lock , Divided into two : Read (READ) And in writing (WRITE)
One . Read : Lock the user to operate in other ways ( Such as : Delete , Insert , to update )
With studentinfo Table as an example :lock table studentinfo read;
After performing this step , Then insert data into the table , Will report a mistake !
Two . In writing : Set that users can modify the data in the table , However, users in other sessions except themselves cannot perform any read operations .
lock table studentinfo write;
thereafter , Conduct select * from studentinfo when , The results will not be displayed .边栏推荐
- IDEA编译JSP页面生成的class文件路径
- AcWing 243. A simple integer problem 2 (tree array interval modification interval query)
- Global and Chinese markets for otolaryngology devices 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- After five years of testing in byte, I was ruthlessly dismissed in July, hoping to wake up my brother who was paddling
- 【按鍵消抖】基於FPGA的按鍵消抖模塊開發
- Thread sleep, thread sleep application scenarios
- Cf464e the classic problem [shortest path, chairman tree]
- KS008基于SSM的新闻发布系统
- User datagram protocol UDP
- The Research Report "2022 RPA supplier strength matrix analysis of China's banking industry" was officially launched
猜你喜欢

Facebook等大厂超十亿用户数据遭泄露,早该关注DID了
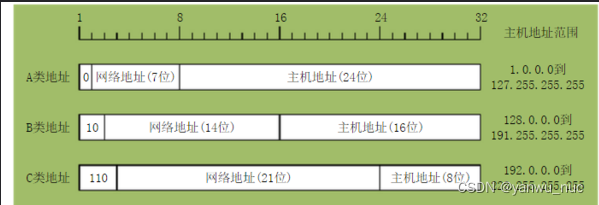
Class A, B, C networks and subnet masks in IPv4
Basic use of MySQL (it is recommended to read and recite the content)
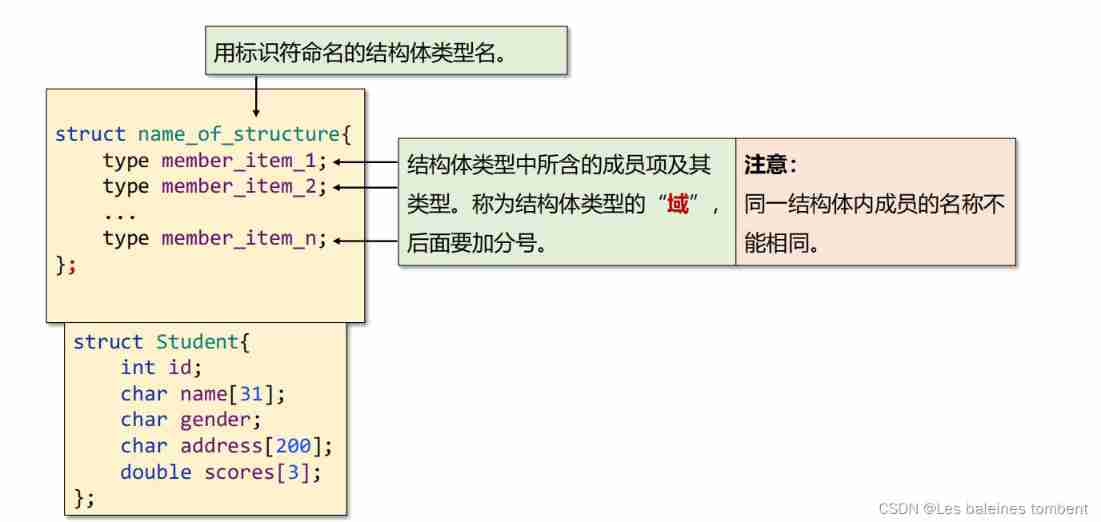
C language -- structs, unions, enumerations, and custom types
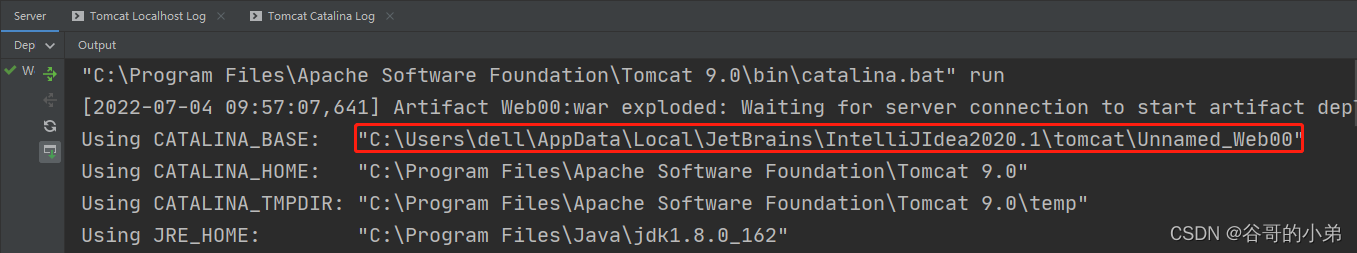
IDEA编译JSP页面生成的class文件路径
KS008基于SSM的新闻发布系统
R note prophet
登录mysql输入密码时报错,ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ (using password: NO/YES
KS003基于JSP和Servlet实现的商城系统
math_极限&微分&导数&微商/对数函数的导函数推导(导数定义极限法)/指数函数求导公式推导(反函数求导法则/对数求导法)
随机推荐
2/13 review Backpack + monotonic queue variant
C (XXIX) C listbox CheckedListBox Imagelist
How to execute an SQL statement in MySQL
How to modify field constraints (type, default, null, etc.) in a table
食品行业仓储条码管理系统解决方案
ESP32(基于Arduino)连接EMQX的Mqtt服务器上传信息与命令控制
登录mysql输入密码时报错,ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ (using password: NO/YES
Record the pit of NETCORE's memory surge
Stack and queue
Brief tutorial for soft exam system architecture designer | general catalog
Python book learning notes - Chapter 09 section 01 create and use classes
Global and Chinese markets for MRI safe implants 2022-2028: technology, participants, trends, market size and share Research Report
10個 Istio 流量管理 最常用的例子,你知道幾個?
C mouse event and keyboard event of C (XXVIII)
Determine which week of the month the day is
SSTI template injection explanation and real problem practice
51nod 1130 n factorial length V2 (Stirling approximation)
Class A, B, C networks and subnet masks in IPv4
mysql关于自增长增长问题
绑定在游戏对象上的脚本的执行顺序