当前位置:网站首页>MySQL transaction isolation level
MySQL transaction isolation level
2022-07-06 03:58:00 【ajdhfla】
Business :
A transaction is a logical set of operations , Or both , Either not .
The nature of transactions (ACID)
Atomicity : Transactions are the smallest unit of execution , Division is not allowed . The atomicity of the transaction ensures that the action is either complete , Or it doesn't work at all ;
Uniformity : Before and after the execution of the transaction , Data consistency , For example, in the transfer business , Whether the transaction is successful or not , The total amount of the transferor and payee should be the same ;
Isolation, : When accessing the database concurrently , One user's transaction is not interfered by other transactions , The database between concurrent transactions is independent ;
persistence : After a transaction is committed . Its changes to the data in the database are persistent , Even if the database fails, it should not have any impact .
Problems caused by concurrent transactions
In a typical application , Multiple transactions run concurrently , Often operate the same data to complete their own tasks ( Multiple users operate on unified data ). Concurrency is necessary , But it may cause the following problems .
Dirty reading (Dirty read): When a transaction is accessing data and modifying the data , This modification has not yet been committed to the database , At this time, another transaction also accesses the data , And then I used this data . Because this data is not submitted yet , So the data read by another transaction is “ Dirty data ”, basis “ Dirty data ” The operation may not be correct .
Missing changes (Lost to modify): When a transaction reads a data , Another transaction also accesses the data , After modifying the data in the first transaction , The second transaction also modifies the data . In this way, the modification result in the first transaction will be lost , So it's called lost modification . for example : Business 1 Read data from a table A=20, Business 2 Also read A=20, Business 1 modify A=A-1, Business 2 Also modify A=A-1, final result A=19, Business 1 The modification of is lost .
It can't be read repeatedly (Unrepeatableread): Reading the same data multiple times in a transaction . Before the end of the business , Another transaction also accesses the data . that , Between two reads in the first transaction , Due to the modification of the second transaction, the data read by the first transaction twice may be different . This happens when the data read twice in a transaction is different , So it's called unrepeatable reading .
Fantasy reading (Phantom read): Unreal reading is similar to nonrepeatable reading . It happens in a transaction (T1) Read a few lines of data , Then another concurrent transaction (T2) When some data is inserted . In the subsequent query , The first thing (T1) There will be more records that don't exist , It's like an illusion , So it's called Unreal reading .
The difference between nonrepeatability and unreal reading :
The point of unrepeatable reading is to modify , The point of unreal reading is to add or delete .
example 1( The same conditions , The data you read , Read it again and find that the value is different ): Business 1 Medium A Mr. a read his salary as 1000 The operation of is not finished , Business 2 Medium B Mr. a modified A The salary of is 2000, guide Cause A When I read my salary again, it changed to 2000; This is unrepeatable reading .
example 2( The same conditions , The first 1 Time and number 2 The number of records read is not the same ): The salary in a payroll is greater than 3000 There are 4 people , Business 1 Read all salaries greater than 3000 People who , A total of 4 Bar record , When the transaction 2 Another one is inserted that the salary is greater than 3000 The record of , Business 1 The record found when reading again becomes 5 strip , This leads to unreal reading .
Transaction isolation level
SQL The standard defines four isolation levels :
READ-UNCOMMITTED( Read uncommitted ): Lowest isolation level , Allow read of uncommitted data changes , Can cause dirty reading 、 Phantom or unrepeatable reading .
READ-COMMITTED( Read committed ): Allow to read data submitted by concurrent transactions , Can prevent dirty reading , But phantom or unrepeatable reads can still occur .
REPEATABLE-READ( Repeatable ): Multiple reads of the same field are consistent , Unless the data is modified by the transaction itself , Can prevent dirty and unrepeatable read , But phantom reading can still happen .
SERIALIZABLE( Serializable ): Highest isolation level , Completely obey ACID Isolation level . All transactions are executed one by one , In this way, there is no interference between transactions , in other words , This level prevents dirty reads 、 Unrepeatable reading and phantom reading .
| Isolation level | Dirty reading | It can't be read repeatedly | Phantom reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| READ-UNCOMMITTED | √ | √ | √ |
| READ-COMMITTED | × | √ | √ |
| REPEATABLE-READ | × | × | √ |
| SERIALIZABLE | × | × | × |
MySQL InnoDB The default isolation level supported by the storage engine is REPEATABLE-READ( Can be reread ). We can go through SELECT @@tx_isolation; Order to see ,MySQL 8.0 The order was changed to SELECT @@transaction_isolation;
mysql> SELECT @@tx_isolation; +-----------------+ | @@tx_isolation | +-----------------+ | REPEATABLE-READ | +-----------------+
What needs to be noted here is : And SQL The difference in standards is InnoDB Storage engine in REPEATABLE-READ( Can be reread ) Under transaction isolation level , Allow applications to use Next-Key Lock Lock algorithm to avoid the generation of phantom reads . It works with other database systems ( Such as SQL Server) Is different . So although InnoDB The default isolation level supported by the storage engine is REPEATABLE-READ( Can be reread ) , But it can be read through lock application ( for example select * from table for update sentence ) To guarantee that reading doesn't happen , And the mechanism used for this locking degree is Next-Key Lock Lock algorithm . So as to achieve SQL The standard SERIALIZABLE( Serializable ) Isolation level .
Because the lower the isolation level , The fewer locks the transaction requests , So the isolation level of most database systems is READ-COMMITTED( Read submissions ):, But what you need to know is InnoDB The storage engine uses... By default REPEATABLE-READ( Can be reread ) There will be no loss of performance .
InnoDB Storage engine in Distributed transactions In general, we use SERIALIZABLE( Serializable ) Isolation level .
边栏推荐
- 2.13 weekly report
- 在字节做测试5年,7月无情被辞,想给划水的兄弟提个醒
- math_极限&微分&导数&微商/对数函数的导函数推导(导数定义极限法)/指数函数求导公式推导(反函数求导法则/对数求导法)
- 51nod 1130 n factorial length V2 (Stirling approximation)
- 【可调延时网络】基于FPGA的可调延时网络系统verilog开发
- C mouse event and keyboard event of C (XXVIII)
- 【leetcode】1189. Maximum number of "balloons"
- math_ Derivative function derivation of limit & differential & derivative & derivative / logarithmic function (derivative definition limit method) / derivative formula derivation of exponential functi
- Failure causes and optimization methods of LTE CSFB
- Prime protocol announces cross chain interconnection applications on moonbeam
猜你喜欢
ESP32_ FreeRTOS_ Arduino_ 1_ Create task

Database, relational database and NoSQL non relational database
《2022年中国银行业RPA供应商实力矩阵分析》研究报告正式启动
After five years of testing in byte, I was ruthlessly dismissed in July, hoping to wake up my brother who was paddling
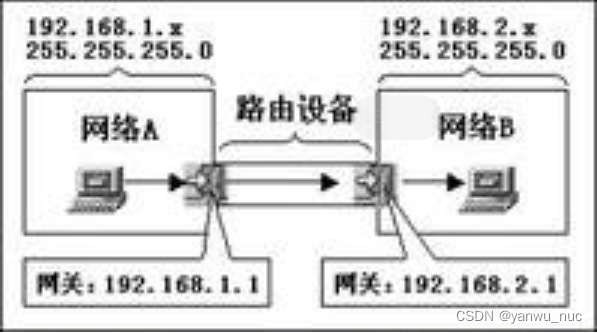
TCP/IP协议里面的网关地址和ip地址有什么区别?

Schnuka: visual positioning system working principle of visual positioning system
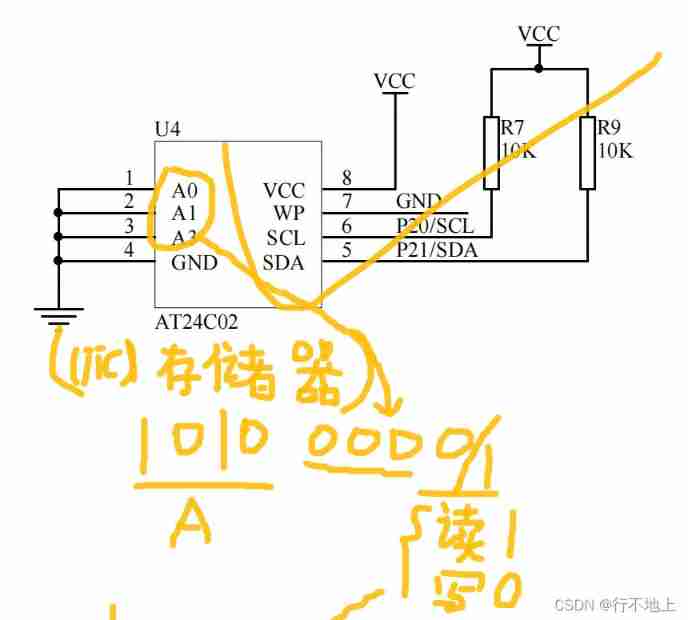
20、 EEPROM memory (AT24C02) (similar to AD)
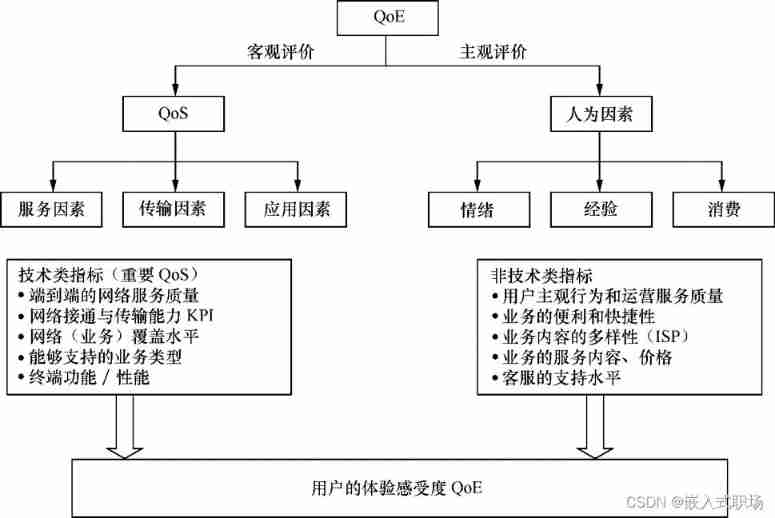
Factors affecting user perception
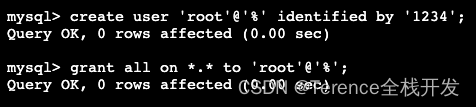
MySql数据库root账户无法远程登陆解决办法
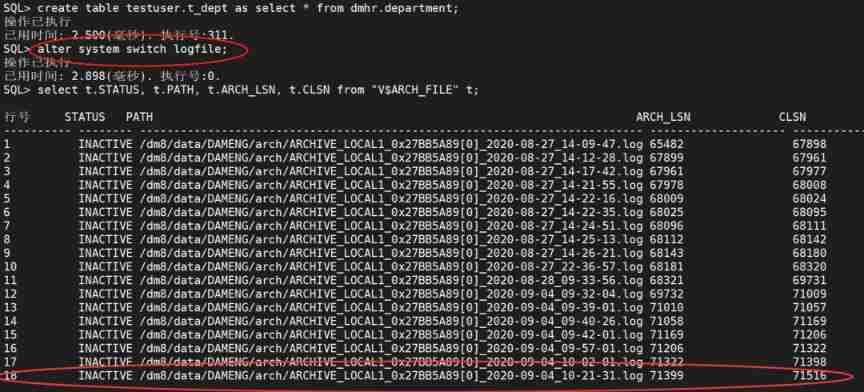
DM8 archive log file manual switching
随机推荐
TCP/IP协议里面的网关地址和ip地址有什么区别?
[analysis of variance] single factor analysis and multi factor analysis
Factors affecting user perception
Detailed explanation of serialization and deserialization
MySQL reads missing data from a table in a continuous period of time
自动化测试的好处
Containerization Foundation
The Research Report "2022 RPA supplier strength matrix analysis of China's banking industry" was officially launched
P7735-[noi2021] heavy and heavy edges [tree chain dissection, line segment tree]
Blue style mall website footer code
RT thread -- FTP of LwIP (2)
Security xxE vulnerability recurrence (XXe Lab)
Python book learning notes - Chapter 09 section 01 create and use classes
User perceived monitoring experience
Data analysis Seaborn visualization (for personal use)
Alibaba testers use UI automated testing to achieve element positioning
Pandora IOT development board learning (HAL Library) - Experiment 9 PWM output experiment (learning notes)
math_极限&微分&导数&微商/对数函数的导函数推导(导数定义极限法)/指数函数求导公式推导(反函数求导法则/对数求导法)
Exchange bottles (graph theory + thinking)
DM8 backup set deletion