当前位置:网站首页>C language -- structs, unions, enumerations, and custom types
C language -- structs, unions, enumerations, and custom types
2022-07-06 03:44:00 【Les baleines tombent】
List of articles
C Language allows users to construct the same or different basic types into a custom according to their own needs
Special types of , That is, structure and common body .
Structure
Definition of structure type
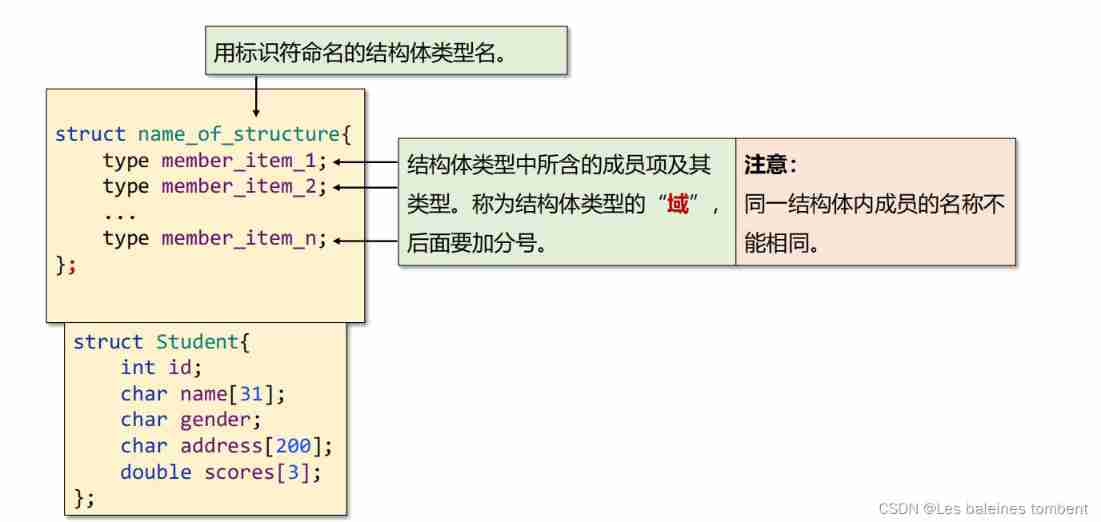
The definition of structure determines the following two points :
- Define the structure type , Determine the name and type of member items in the structure .
- Indicates the organization of variables of this structure type in memory .
That is, defining a structure type only specifies the memory allocation mode of the structure type , Did not open up memory space . Only defined Structure variable or structure array after , Only according to the memory allocation mode of the structure type, can the storage space be opened .
• There are two steps to use the structure type :
- By keyword struct And user-defined structure name ( It is commonly called structure type name ) To define the type .
- Then, the structure type Define the structure variable name
Declaration of structure variables
• Defining a structure only determines the name of the structure type, the composition of its member items, and the class of its member items
type . The structure variable must be specified by the defined structure type , Before opening up the corresponding memory space for
Use . There are three ways to describe structural variables :
- Define variables with the already defined structure type name
- Define structure variables while defining structure types
- Do not define the structure type name , Define structure variables directly
1 Define variables with the already defined structure type name .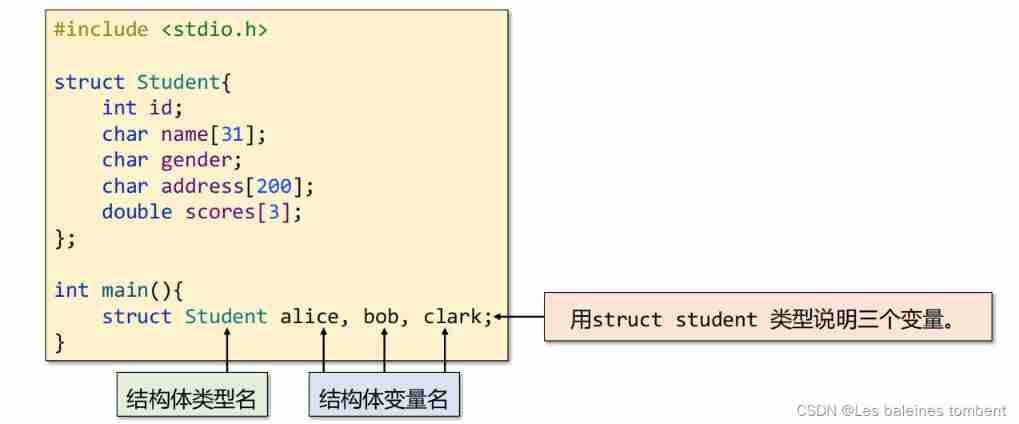
2. Define structure variables while defining structure types 
3. Do not define the structure type name , Define structure variables directly
struct {
int id;
char name[31];
char gender;
char address[200];
double scores[3];
} alice, bob, clark;
explain :
- Pay attention to the difference between types and variables .
- Member items can be used alone ,bob.id=140101
- The member items of a structure can also be structural variables .
4. Nested definition of structure type
struct Birthday{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct Student{
int id;
char name[30];
struct Birthday birth;
char gender;
double scores[3];
};
Initialization of structure variables
Structural variables can be assigned initial values when describing , Called initialization . Curly braces can be used to enclose the initial values corresponding to these structural type variables as a whole .
The number of initial values is allowed to be less than the number of members in the structure variable , However, the number of initial values is not allowed to be more than the number of members in the structure variable .
In the former case , When the initialization statement is executed, the initial value symbol in the initial value table is used to assign values to the members in front of the structure variable , The remaining members without corresponding initial value symbols are implicitly initialized . namely : Members of all arithmetic types are assigned 0, Members of all pointer types are given null pointer constants
struct Birthday{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct Student{
int id;
char name[30];
struct Birthday birth;
char gender;
double scores[3];
};
struct Student alice = {
200250,
"Alice",
{
2002, 4},
'm',
{
77, 88, 69.5}
};
struct Student alice = {
200250,
"Alice", {
2002, 4},
'm', {
77}};
that , Structural variables alice Member of the alice.birth.day Is implicitly initialized to 0 ,alice.scores[1] and alice.scores[2] It's also initialized to 0.
References to structure variables
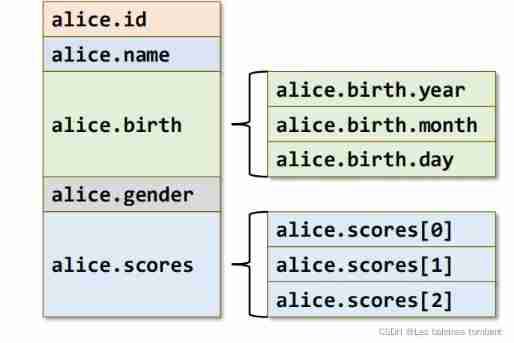
- Reference structure members
• Because the types of each member in the structure variable are different , Generally, you can only reference members of structural variables , Do not reference structural variables as a whole .
• Without nesting , The way to reference structural variable members is :
Structure variable name . Member item name
alice.id;
explain :
“.” be called “ Struct member operator ”, The structure member referenced in this way is equivalent to a common variable , It has the same properties as ordinary variables .
for example :
alice.id = 200250
effect : Reference structure variables alice Members of the id, Equivalent to an integer variable .
lucy.name
effect : Structural variable alice Members of name, Equivalent to one Character array name .C Some library functions of the language can access the character array through the first address , for example :puts(lucy.name);
So it is legal to reference the name of character array .
lucy.score[0]
effect : Reference structure variables alice Members of the score[0], because score yes int Type of the array , Can't quote... As a whole , So you must reference array elements , Equivalent to one Variable of integer type .
- Structural variables can perform various operations , It's fine too The address of the reference member or the address of the structure variable .
for example :scanf("%d",&alice.id);
- Structural variables can be referenced as a whole .
Structural variables of the same type can be assigned as a whole . Structure type members embedded in structure variables are also the same .
struct Student alice = {
200250,
"Alice",
{
2002, 4},
'm',
{
77}};
struct Student bob = alice;
bob.birth = alice.birth;
Example : Define a structure type , The member item includes the student number 、 full name 、 Birthday 、 Gender 、 English 、 mathematics 、 Scores of three Chinese courses , And define the structural variable of this type . Programming the input of structural variable member items 、 Output . And calculate the average score of the three courses
#include <stdio.h>
struct Birthday{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct Student{
int id;
char name[30];
struct Birthday birth;
char gender;
double scores[3];
};
struct Student alice;
scanf("%d", &alice.id);
getchar();
gets(alice.name);
scanf("%d %d %d", &alice.birth.year, &alice.birth.month, &alice.birth.day);
getchar();
alice.gender = getchar();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++){
scanf("%lf", &alice.scores[i]);
}
Output
printf("id: %d\nname: ", alice.id);
puts(alice.name);
printf("birthday: %d-%d-%d\n",
alice.birth.year,
alice.birth.month,
alice.birth.day);
printf("math\tenglish\tliterature\n");
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("%.1f\t", alice.scores[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
Find the average score of the three courses
double average = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++){
average += alice.scores[i];
}
printf("%f", average);
Array of structs
Structural variables can also be constructed into arrays , It's called a structure array . Each array element is a structural variable , Both contain structure member items . Their addresses in memory are continuous .
The definition of structure array
struct Structure type name Structure array name [( Constant ) expression ] ;
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 50
struct Birthday {
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct Student {
int id;
char name[30];
struct Birthday birth;
char gender;
double scores[3];
};
int main() {
struct Student students[N];
}
Initialization of structure array
struct Student students[3] = {
{
140101, "lucy", {
1991, 1, 2}, 'M', {
78, 89, 91}},
{
140102, "lily", {
1991, 2, 3}, 'F', {
87, 60, 89}},
{
140103, "tom", {
1991, 3, 4}, 'M', {
82, 91, 92}}
};
explain :
- All three structural array elements contain struct Student All member items of .
- Structure array name students, Represents the first address of the structure array .
Use of structure array
Similar to the reference of general array , A reference to a structure array is a reference to a structure array element .
- In addition to initialization , Assign a constant value to the structure array 、 Input and output 、 All operations are performed on the members of the array elements of the structure .
The members of structure array elements are represented as : Structure array name [ Subscript ]. Member name
for example :students[0].id and scanf("%d", &students[0].id);
In the case of nesting :
Structure array name [ Subscript ]. Structure member name … Structure member name . Basic member name
- Structure array elements can be assigned to each other as a whole .
for example :students[0] = students[1];
Define a structure , The member item includes the student number 、 full name 、 Birthday 、 Gender 、 English 、 mathematics 、 Scores of three courses in politics .
Programming to realize 2 Input of student information 、 Output . Find out the average score of each student , And sort .
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 2
struct Birthday {
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
struct Student {
int id;
char name[30];
struct Birthday birth;
char gender;
int scores[3];
double aver;
};
struct Student students[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++){
printf(" Please enter the first %d Student information \n", i + 1);
printf(" Please enter the student number :");
scanf("%d", &students[i].id);
printf(" Please enter a name :");
fflush(stdin);
gets(students[i].name);
printf(" Please enter the date of birth :");
scanf("%d %d %d", &students[i].birth.year, &students[i].birth.month, &students[i].birth.day);
printf(" Please enter gender :");
fflush(stdin);
students[i].gender = getchar();
printf(" Please enter the grades of the three courses :");
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
scanf("%d", &students[i].scores[j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
Calculate the average score
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++){
students[i].aver = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j ++){
students[i].aver += students[i].scores[j];
}
students[i].aver /= 3.0;
}
Sort by average
for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; i ++){
for(int j = 0; j < N - 1 - i; j++){
if(students[j].aver < students[j + 1].aver){
struct Student tmp;
tmp = students[j];
students[j] = students[j + 1];
students[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
printf("***** %d The information of students is as follows *****\n", N);
printf(" Student number \t%-10s\t Year of birth month Japan \t Gender \t English \t mathematics \t Chinese language and literature \t average \n"," full name ");
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
printf("%d\t", students[i].id);
printf("%-10s\t", students[i].name);
printf("%6d%3d%3d\t", students[i].birth.year,
students[i].birth.month, students[i].birth.day);
if (students[i].gender == 'M') printf(" male \t");
else if (students[i].gender == 'F') printf(" Woman \t");
else printf(" nothing \t");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
printf("%d\t", students[i].scores[j]);
}
printf("%6.2f\n", students[i].aver);
}
Structure pointer
The pointer to the structure variable is the first address of the memory unit occupied by the structure variable
Pointer variables to struct variables
struct Student alice;
struct Student *ptr = &alice;
explain :
1. ptr That is to point to structural variables alice Pointer variable for .
2. Structure pointer variable plus 1, Address to add 1 The number of bytes occupied by structural variables .
Use the pointer variable pointing to the structure variable to represent the members of the structure variable . Format :
• Mode one :(*p). Member item name
• Mode two : p-> Member item name
• example : If you define a variable that points to a structure alice Pointer variable for ptr,*ptr Express
ptr The structure variable pointed to alice, Its members alice.id Can be expressed as :
(*ptr).id perhaps ptr->id
• The two representations are equivalent , Operator “->” And “.” Operators have the same precedence , Having the highest
priority
Example : Define a structure , The member item includes the student number 、 full name 、 Birthday 、 Gender 、 English 、 mathematics 、 Scores of three courses in politics , Programming the output of structural variable member items , Use a pointer to achieve .
struct Student alice = {
200250, "Alice", {
2002, 2, 3}, 'M', {
78, 89, 75}};
struct Student *ptr = &alice;
printf("%d\n", ptr->id);
puts(ptr->name);
printf("%d-%d-%d\n", ptr->birth.year,ptr->birth.month, ptr->birth.day);
printf("%c\n", ptr->gender);
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++){
printf("%5d", ptr->scores[i]);
}
Structure array and structure pointer variable
The array name of a one-dimensional array represents the first address of the array , One dimensional structure array is the same .
You can assign the array name of one-dimensional structure to the pointer variable pointing to the structure , The pointer variable will point to the subscript
by 0 The elements of , It can move between array elements
Example : Define a structure , The member item includes the student number 、 full name 、 Date of birth 、 Gender 、 English 、 mathematics 、 Scores of three Chinese courses , Programming to realize N A student , The average grade of each student , Then the output .
struct Student students[N] = {
{
140101, "Alice", {
1991, 1, 2}, 'M', {
78, 89, 91}},
{
140102, "Bob", {
1991, 2, 3}, 'F', {
87, 60, 89}},
{
140103, "Clark", {
1991, 3, 4}, 'M', {
82, 91, 92}}
};
struct Student *p;
for(p = students; p < students + N; p++){
p->aver = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j ++){
p->aver += p->scores[j];
}
p->aver /= 3;
printf("%s's average score is %f\n", p->name, p->aver);
}
Structures and functions
Anonymous structure
struct names{
char first[20];
char last[20];
};
Nested structure members
struct person
{
int id;
struct names name;
};
- Anonymous structure
struct person
{
int id;
struct {
char first[20]; char last[20];};
}
Both initialization methods are the same :
struct person jack = {
1000, {
“Jack”, “Zhang”}};
The two access methods are different :
jack.name.first
jack.first omitted name
边栏推荐
- Quartz misfire missed and compensated execution
- The solution of permission denied (750 permissions should be used with caution)
- Remote Sensing Image Super-resolution and Object Detection: Benchmark and State of the Art
- Python implementation of maddpg - (1) openai maddpg environment configuration
- 施努卡:视觉定位系统 视觉定位系统的工作原理
- 2.1 rtthread pin device details
- Pytoch foundation - (1) initialization of tensors
- MySQL 中的数据类型介绍
- 1.16 - 校验码
- Schnuka: what is visual positioning system and how to position it
猜你喜欢
阿里测试师用UI自动化测试实现元素定位
Map sorts according to the key value (ascending plus descending)
![[Massey] Massey font format and typesetting requirements](/img/27/6b641551d6d8699683972f40f3b8e5.jpg)
[Massey] Massey font format and typesetting requirements

指针笔试题~走近大厂

WPF效果第一百九十一篇之框选ListBox
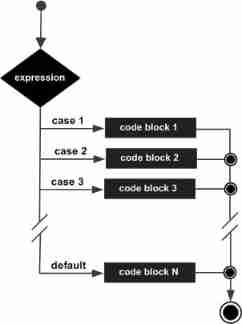
C language judgment, ternary operation and switch statement usage
【SLAM】ORB-SLAM3解析——跟踪Track()(3)
在字节做测试5年,7月无情被辞,想给划水的兄弟提个醒

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower

施努卡:3d视觉检测应用行业 机器视觉3d检测
随机推荐
2.1 rtthread pin设备详解
Pointer written test questions ~ approaching Dachang
3.2 rtthread 串口设备(V2)详解
RT-Thread--Lwip之FTP(2)
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
遥感图像超分辨率论文推荐
Recommended papers on remote sensing image super-resolution
Mysqldump data backup
An article will give you a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external components of "computer"
简述C语言中的符号和链接库
在 .NET 6 中使用 Startup.cs 更简洁的方法
Pytorch基础——(2)张量(tensor)的数学运算
Suggestions for new engineer team members
User experience index system
SWC introduction
简易博客系统
pytorch加载数据
Basic concepts of LTE user experience
Quartz misfire missed and compensated execution
How to write compile scripts compatible with arm and x86 (Makefile, cmakelists.txt, shell script)