当前位置:网站首页>C language custom type enumeration, Union (clever use of enumeration, calculation of union size)
C language custom type enumeration, Union (clever use of enumeration, calculation of union size)
2022-07-02 08:28:00 【Ischanged】

Hold on to the last moment and you will see the dawn of victory .
enumeration
Enumeration, as the name suggests, is to enumerate one by one . List the possible values one by one . For example, in our real life : A week's Monday to Sunday is limited 7 God , You can list them one by one . Gender has : male 、 Woman 、 A secret , You can also list them one by one . Month has 12 Months , You can also list them one by one Here you can use enumeration
Definition of enumeration type
How to define enumeration types ?
In fact, enumeration types and structures are very similar , We can remember by comparison ,** For enumeration, the value in curly braces is the possible value of enumeration , When creating an enumerated variable, the value of the variable is one of the possible values , But if you create a structural variable , The members in curly braces belong to the contents of structural variables ,** We should pay attention to distinguish , The definition of enumeration type is as follows
enum tag
{
member - list;
}ariable - list;
Enumeration label :tag
Enumeration type :eum tag
Possible values of enumeration :member_list
Enumerated variable list :variable_list**
Examples of enumeration type definitions :
enum Day// week
{
Mon,
Tues,
Wed,
Thur,
Fri,
Sat,
sun
};
enum sex// Gender
{
MALE,
FEMALE,
SECRET
};
enum color// Color -- Three primary colors rgb
{
RED,
GREEN,
BLUE
};
As defined above enum Day , enum Sex , enum Color All enumeration types . {} The contents in are possible values of enumeration types , Also called Enumeration constants . Why is it called enumeration constant ? Because these possible values can express some constant values , The type of value is int type .
All these possible values have values , The default from the 0 Start , In turn, increasing 1, Of course, initial values can also be assigned when defining .( Constants can also be assigned initial values , The value of the constant is not changed ) for example :
enum Color
{
RED ,
GREEN ,
BLUE
};
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", RED);
printf("%d\n", GREEN);
printf("%d\n", BLUE);
// Print the results 0,1,2
return 0;
}
By assigning initial values to enumeration members , Change the default size of enumeration constants , The result is 0,2,3
#include<stdio.h>
enum Color
{
RED ,//0
GREEN = 2,//2
BLUE//3
};
int main()
{
enum Color c = BLUE;
//enum Color c = 8;
printf("%d\n", sizeof(c));
return 0;
}
Next, let's look at the following code , We go through enum
Color Type defines an enumeration variable c, The value of the variable is the member of the enumeration type , hold BLUE Assign a value to a variable c,c The value of 3, Can you put 3 Directly assign to c Well ? Can not be , Because the possible values of enumeration variables are those of enumeration types , The type of value is enumeration type , although 3 And the value of enumeration constant is the same , But they belong to different types ( Enumeration types are enumeration types , Plastic surgery is plastic surgery ), about c++ compiler , Run the following code to report an error ,(c++ Compiler detection is more stringent ) about c The compiler will not report errors
#include<stdio.h>
enum Color
{
RED ,//0
GREEN = 2,//2
BLUE//3
};
int main()
{
//CPP Grammar check is more strict
//enum Color c = BLUE;
enum Color c = 3;
printf("%d\n", sizeof(c));
return 0;
}

Advantages of enumeration
Why use enumeration ? We can use #define Define constants , Why do I have to use enumeration ? Advantages of enumeration :
- Increase the readability and maintainability of the code
- and #define The defined identifier comparison enumeration has type checking , More rigorous .(#define The defined macro is just a simple symbol replacement without any type , Enumeration is a type , There is a type check when assigning data )
- Prevent named pollution (#define The macro defined is a global variable , Enumeration constants are defined in enumeration types )
- Easy to debug (#define The defined macro has been replaced before debugging , The back debugging is not good )
- Easy to use , You can define more than one constant at a time
The following code , Suppose we want to implement a simple calculator , We input numbers from the keyboard 0,1,2,3,4 Run and exit separately , Add, subtract, multiply and divide
adopt switch Statements realize the corresponding functions ,case The number after the sentence has only a single meaning , If you don't look at the code and explanation , Don't read the code quickly , If through the definition of enumeration ,ADD Not only means to perform addition , It also means that there is an addition function after the statement , This makes the code readable , And improved maintainability ,
// 0. exit 1. add 2. sub
// 3. mul 4. div
enum Option
{
EXIT,//0
ADD,//1
SUB,//2
MUL,//3
DIV//4
};
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do
{
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1://ADD
break;
case 2://SUB
break;
case 3://MUL
break;
case4://DIV
break;
case 0://EXIT
break;
default:
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Use of enumeration
Implementation of simple calculator
#include<stdio.h>
enum option// Define enumeration types option
{
EXIT,//0
ADD,//1
SUB,//2
MUL,//3
DIV//4
};
void menu()
{
printf("******************************************\n");
printf("****** 1. add 2.sub *****\n");
printf("****** 2.mul 4.div *****\n");
printf("****** 0.exit *****\n");
printf("******************************************\n");
}
int add(int x, int y)// Add
{
return x + y;
}
int sub(int x, int y)// Subtraction
{
return x - y;
}
int mul(int x, int y)// Multiplication
{
return x * y;
}
int div(int x, int y)// division
{
return x / y;
}
int main()
{
enum option input = EXIT;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case ADD:
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", add(x, y));
break;
case SUB:
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", sub(x, y));
break;
case MUL:
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", mul(x, y));
break;
case DIV:
printf(" Please enter two operands :>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", div(x, y));
break;
case EXIT:
printf(" Exit the computer \n");
break;
default:
printf(" Input error , Please re-enter \n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
union ( Shared body )
Definition of consortium type
Federation is also a special custom type Variables defined by this type also contain a series of members , The feature is that these members share the same block Space ( So union is also called community ). such as :
// Declaration of union type
union Un
{
char c;
int i;
};
// The definition of joint variables
union Un un;
// Calculate the size of the variables
printf("%d\n", sizeof(un));
Characteristics of Union
Members of the union share the same memory space , The size of such a joint variable , At least the size of the largest member ( Because the Union has to be able to keep at least the largest member ).
#include<stdio.h>
union Un
{
int i;
char c;
};
int main()
{
union Un un;
// Is the result of the following output the same ?
printf("%d\n", &(un.i));
printf("%d\n", &(un.c));
// What is the output below ?
return 0;
}

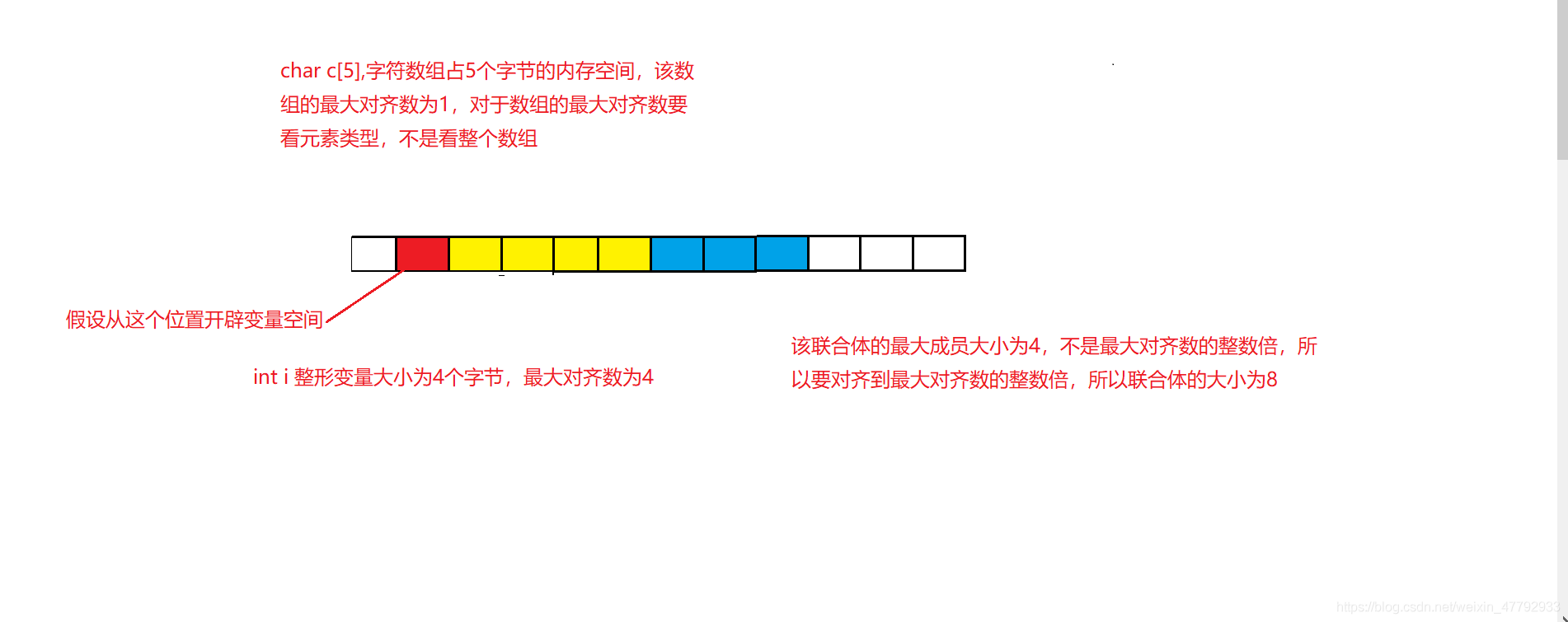
From the execution result of the above code, we can see ,** When creating consortium member variables , They all started from the same starting position , Open up space ,** Therefore, the memory space of consortium member variables overlaps , Covered , Therefore, the calculation of the size of the consortium is different .
Calculation of joint size
- The size of the union is at least the size of the largest member .
- When the maximum member size is not an integral multiple of the maximum number of alignments , It's about aligning to an integer multiple of the maximum number of alignments
As we calculate the following code :
#include<stdio.h>
union Un1
{
char c[5];
int i;
};
union Un2
{
short c[7];
int i;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un1));//8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un2));//16
return 0;
}
Picture understanding :
边栏推荐
- 2022 Heilongjiang's latest eight member (Safety Officer) simulated test question bank and answers
- Carsim-問題Failed to start Solver: PATH_ID_OBJ(X) was set to Y; no corresponding value of XXXXX?
- 旋转链表(图解说明)
- Opencv3 6.3 reduced pixel sampling with filters
- Comparison between setTimeout and requestanimationframe (page refresh)
- 程序猿学英语-Learning C
- Global and Chinese market of medicine cabinet 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- idea中注释代码取消代码的快捷键
- Li Kou daily one question brushing summary: binary tree chapter (continuous update)
- Carsim-路面3D形状文件参数介绍
猜你喜欢
Carsim-問題Failed to start Solver: PATH_ID_OBJ(X) was set to Y; no corresponding value of XXXXX?

Jumping | Blue Bridge Cup

Hcia - Application Layer

Generate database documents with one click, which can be called swagger in the database industry
Use C language to receive JSON strings

Static library and dynamic library
2022 Heilongjiang latest construction eight members (materialman) simulated examination questions and answers

STM32疑难杂症之ST-LINK Connection error INVALID ROM TABLE

Development of digital collection trading website development of metauniverse digital collection
Vs code configuration problem
随机推荐
Global and Chinese markets of tilting feeders 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Force deduction method summary: double pointer
力扣每日一题刷题总结:链表篇(持续更新)
Analysis of the use of comparable, comparator and clonable interfaces
Static library and dynamic library
Carla-ue4editor import Roadrunner map file (nanny level tutorial)
The best blog to explain the basics of compilation (share)
Jz-061-serialized binary tree
Global and Chinese market of medicine cabinet 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
OpenCV常用方法出处链接(持续更新)
OpenCV 6.4 中值滤波器的使用
Use Matplotlib to draw a preliminary chart
【无标题】
Causes of laptop jam
OpenCV3 6.3 用滤波器进行缩减像素采样
Use the kaggle training model and download your own training model
力扣方法总结:滑动窗口
Force deduction method summary: find classes
HCIA—應用層
sqli-labs第2关