当前位置:网站首页>Relational database
Relational database
2022-07-04 21:52:00 【Hua Weiyun】
In this article DigitalOcean In the article , We will try to understand some of the most commonly used 、 The most popular relational database management system (RDBMS) Kernel differences . We will explore the bottom differences —— Features and functions , How they work , In which way is better , To help programmers choose the right RDBMS.
Database management system
A database is a space for storing model data in an organized way , Store various types of information ( data ). Every database , Except for modeless , There is a model , Provide a structural description of the data . Database management system is to manage database structure 、 Application of size and sorting ( Or library ).
Relational database management system
The relational database system realizes the relational model , And use it to process data . A relational model associates information with fields in a table ( That is to say schemas), To store data .
This kind of database management system needs structure ( Such as table ) Defined before storing data . With a watch , Each column ( Field ) Store a different type ( data type ) Information about . Every record in the database , All have their own unique key, As a row belonging to a table , Each information in the row corresponds to a column in the table —— All relationships together , Form a relational model .
Relationships and data types
Relationships can be seen as a mathematical set containing a series of attributes that collectively represent the maintained database and related information . This type of identification and collection method allows relational databases to operate in their own way .
When defining a table into which data can be inserted , Every element that forms a record ( for example : attribute ) Must match the defined data type ( for example : One integer, One date wait .). Different relational database management systems realize different data types – They don't always convert directly to each other .
Collaboration with constraints , As we have already introduced , It is very common in the use of relational databases . in fact , Restrictions form the core of the relationship .
Be careful : If you need it, it doesn't really matter , Random data ( For example, a document ), You may use NoSQL Interested in ( Modeless database ).
Important and popular relational databases
In this paper , We will introduce three main and important open source relational database management systems , It is they who have influenced the world of application development .
SQLite:
A powerful embedded relational database management system .
MySQL:
One of the most popular RDBMS.
PostgreSQL:
Most advanced SQL Open source objective-RDBMS.
notes : Open source applications are always free to use . Most of the time , Replication Engineering ( Using code ) Creating new applications is also allowed . If you are right about DBMS Interested in , You can see some branch projects based on these projects , for example MariaDB.
SQLite
SQLite Is an extraordinary database , He can process in the application that uses it . As a self-contained 、 File based database ,SQLite Provides an excellent tool set , Can handle all types of data , There are no restrictions , And it is much easier to use than the process server running on the server .
An application uses SQLite when , Its functions are directly integrated into it , The application will directly access the file containing the data ( namely SQLite database ), Not through some ports (port, socket) To interact . Thanks to this underlying technology , This makes SQLite Become very fast and efficient , And very powerful .
SQLite Supported data types
NULL:
NULL value .
INTEGER:
Signed integers , Use 1、2、3、4、6 or 8 Byte storage .
REAL:
Floating point numbers , Use 8 byte IEEE Floating point storage .
TEXT:
Text string , Use database encoding to store (UTF-8, UTF-16BE or UTF-16LE).
BLOB:
Binary big object , Store as you type .
notes : Want to learn more about SQLite Data type information , You can view the Official documents .
SQLite The advantages of
Based on the file :
The entire database is contained in a file on disk , So it has good mobility .
Standardization :
Although it looks like a “ Simplified edition ” The database of ,SQLite I do support SQL. It omits some functions (RIGHT OUTER JOIN and FOR EACH STATEMENT), however , At the same time, some other functions are added .
Great for development and even testing :
In the development stage of most applications , Most people really need the flexibility of concurrency in the solution .SQLite Rich functional foundation , It can provide more than the development needs , And it's so simple that you only need one file and one C Link library .
SQLite The shortcomings of
No user management :
Advanced databases can support user systems , for example , It can manage the access rights of database connections to databases and tables . But because of SQLite The purpose and nature of the production ( There is no multi-user concurrent high-level design ), It doesn't have this function .
Lack of additional flexibility to optimize performance :
Still from the beginning of design ,SQLite It does not support the use of various techniques for additional performance optimization . This library is easy to configure , Easy to use . Since it is not complicated , Theoretically, it can't be faster than now , In fact, it has been very fast now .
When to use SQLite ?
Embedded applications :
All need mobility , Applications that do not need expansion , for example , Single user local application , Mobile apps and games .
Instead of disk access :
In many cases , Need frequent direct reading / Application of writing disk files , Are very suitable for use SQLite , Can benefit from SQLite Use SQL Bring functionality and simplicity .
test :
It can spike most of the application business logic ( That is, the main purpose of the application : Can complete the function ) Test of .
When not to SQLite ?
Multi user applications :
If the application you are developing needs to be accessed by multiple users , And these users all use the same database , So compared SQLite It is better to choose a relational database with complete functions ( for example MySQL).
Applications that need to write data in a large area :
SQLite One of the defects of is its write operation . This database allows only one write operation at a time , Therefore, the throughput is limited .
MySQL
MySQL The most popular of all large database servers . It has rich characteristics , The open source nature of the product makes it drive a large number of online websites and Applications . To start MySQL Relatively simple , Developers can access a lot of information about this database on the Internet .
Be careful : Because of the popularity of this product , A large number of third-party applications 、 Tools and integration libraries are important for operating this RDBCMS It's very helpful in all aspects .
Mysql No attempt to achieve SQL All of the Standards , Instead, it provides users with many useful functions . As an independent database server , The application is the same as Mysql Interaction of daemons , Tell it to access the database itself – It's not like SQLite.
MySQL Supported data types
TINYINT:
A very small integer .
SMALLINT:
A small integer .
MEDIUMINT:
An integer of intermediate size .
INT or INTEGER:
An integer of normal size .
BIGINT:
A large integer .
FLOAT:
A small ( Single precision ) Floating point numbers , It can't be unsigned .
DOUBLE, DOUBLE PRECISION, REAL:
A normal size ( Double precision ) Floating point number , You can't make the unsigned one .
DECIMAL, NUMERIC:
Floating point numbers that are not wrapped . You can't make the unsigned one .
DATE:
A date .
DATETIME:
A combination of date and time .
TIMESTAMP:
A timestamp .
TIME:
A time .
YEAR:
One with two or 4 The year in digit format ( The default is 4 position ).
CHAR:
A fixed length string , When storing, it is always right aligned in its fixed length space .
VARCHAR:
A variable length string .
TINYBLOB, TINYTEXT:
One BLOB perhaps TEXT Column , Maximum length 255 (2^8 - 1) Characters .
BLOB, TEXT:
One BLOB perhaps TEXT Column , Maximum length 65535 (2^16 - 1) Characters .
MEDIUMBLOB, MEDIUMTEXT:
One BLOB perhaps TEXT Column , Maximum length 16777215 (2^24 - 1) Characters .
LONGBLOB, LONGTEXT:
One BLOB perhaps TEXT Column , Maximum length 4294967295 (2^32 - 1) Characters .
ENUM:
An enumerated type .
SET:
A collection .
MySQL The advantages of
Easy to use :
install MySQL Very easy to . Third party Library , Including visualization ( There is a GUI) The library of makes it very easy to use the database .
Rich in functions :
MySQL Support most relational databases should have SQL function —— Some direct support , Some indirect support .
Security :
MYSQL There are many security features , Some of them are quite advanced .
Flexible and powerful :
MySQL Can handle a lot of data , In addition, if necessary , It can also “ To adapt to ” Data of all sizes .
Fast :
Abandon support for certain standards , Give Way MySQL More efficient and able to use shortcuts , Therefore, the speed is improved .
MySQL The shortcomings of
Known limitations :
From the beginning of design ,MySQL I didn't plan to be omniscient , So it has some functional limitations , Unable to meet the needs of some top-level applications .
Reliability issues :
MySQL For the implementation of some functions ( for example , quote , Business , Data review, etc ) This makes it a little less reliable than some other relational databases .
Development stalled :
Even though MySQL Theoretically, it is still an open source product , Some people complain that it has been updated slowly since its birth . However , It should be noted that some are based on MySQL And a completely integrated database ( Such as MariaDB), In standard MySQL On this basis, it brings additional value .
When to use MySQL?
Distributed operations :
When SQLite When what you provide cannot meet your needs , You can put MySQL Include in your deployment stack , Just like any independent database server , It will bring a lot of freedom of operation and some advanced functions .
High security :
MySQL Safety function of , In a simple way for data access ( And use ) Provides reliable protection .
Web Website and Web application :
Most websites ( and Web Applications ) You can simply work in MySQL On . This flexible and extensible tool is easy to use and easy to manage —— This proved to be very helpful for long-term operation .
Custom solutions :
If you work on a highly customized solution ,MySQL Can easily follow and enforce your rules , Thanks to its rich configuration settings and operation modes .
When not to MySQL?
SQL Obedience :
because MySQL No, [ to want to ] Realization SQL All standards , So this tool is not completely consistent with SQL. If you need to integrate such a relational database management system , from MySQL Switching is not easy .
Concurrent :
Even if MySQL And some storage engines are really good at reading , But there are still problems with concurrent reading and writing .
Lack of characteristics :
Again , According to the selection criteria of database engine ,MySQL Will lack certain characteristics , Such as full-text search .
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL It's an advanced , Open source [ object ]- Relational database management system , Its main goal is to achieve standards and scalability . PostgreSQL, Or rather, Postgres, Try to put right ANSI/ISO SQL The adoption and revision of standards are combined .
Compared with other RDBMS, PostgreSQL With it for objects - Relationship and \ Or relational database function , For example, for reliable transactions , For example, atomicity , Uniformity , Isolation and persistence (ACID) Full support for , The high demand and collective support of these things , To show its uniqueness .
Due to the powerful underlying technology , Postgres It is good at efficiently completing many processing tasks . Thanks to its multi version concurrency control (MVCC) The implementation of the , Concurrency can be achieved without reading locks , This also ensures ACID Implementation .
PostgreSQL It's highly programmable , Therefore, it can be called “ stored procedure ” The custom program of . These functions can be created to simplify a write repetition 、 The execution of tasks that are complex and often require database operations .
Although the features are powerful , But this DBMS did not MySQL So popular , But there are still many fascinating third-party tools and libraries designed to make PostgreSQL It's easy to operate . Nowadays, it is easy to get through the default package manager of many operating systems PostgreSQL Has become possible .
PostgreSQL Supported data types
bigint:
Signed octet integer
bigserial:
Self increasing octet integer
bit [(n)]:
Fixed length bit string
bit varying [(n)]:
Variable length bit strings
boolean:
Logical Boolean (true/false)
box:
A rectangular box on a plane
bytea:
binary data (“ Digit group ”)
character varying [(n)]:
Variable length string
character [(n)]:
Fixed length string
cidr:
IPv4 perhaps IPv6 network address
circle:
A circle on the plane
date:
Calendar date ( Specific date )
double precision:
Double precision floating point (8 position )
inet:
IPv4 perhaps IPv6 The host address
integer:
Signed four digit integer
interval [fields] [§]:
time span
line:
An infinite straight line on the plane
lseg:
A line segment on the plane
macaddr:
MAC ( Media access control ) Address
money:
The amount of money
numeric [(p, s)]:
Precise numbers with optional precision
path:
Geometric path on a plane
point:
A geometric point on a plane
polygon:
A closed geometric path on a plane
real:
Single-precision floating-point (4 position )
smallint: Signed two digit integer
serial:
Self growth 4 An integer
text:
Variable length character creation
time [§] [without time zone]:
Time of day ( No time zone )
time [§] with time zone:
Time of day , Include time zone
timestamp [§] [without time zone]:
Date and time ( No time zone )
timestamp [§] with time zone:
Date and time , Include time zone
tsquery:
Text search query
tsvector:
Text search documents
txid_snapshot:
User level transactions ID snapshot
uuid:
Universal unique identifier
xml:
XML data
PostgreSQL The advantages of
Standard support SQL Open source relational database :
PostgreSQL It's an open source , free (free) Of , At the same time, a very powerful relational data management system .
A strong community :
PostgreSQL There is a passionate and experienced community behind it , Support can be obtained through knowledge base and Q & a website , Free 24 / 7 .
Strong third-party support :
Even if its own function is very powerful ,PostgreSQL There are still many powerful open source third-party tools to assist the design of the system 、 Management and use .
Extensibility :
You can use pre stored processes to programmatically extend PostgreSQL , An advanced relational database should be like this .
object-oriented :
PostgreSQL Not just a relational database , It is also an object-oriented database —— Support nested , And some other functions .
PostgreSQL The shortcomings of :
performance :
For simple and heavy read operations , PostgreSQL Will make a mountain out of a molehill and may appear better than peers ( Such as MySQL) Lower performance .
Universal :
According to the nature of the tool , In terms of popularity, it still lacks sufficient backstage support , Despite a large number of deployments —— This may affect the ease with which support can be obtained .
trusteeship :
Due to the influence of the above factors , Let the host or service provider propose to use PostgreSQL Examples are difficult .
When to use PostgreSQL?
Data integrity :
When reliability and data integrity are absolutely necessary without reason ,PostgreSQL It's a better choice .
Complex customization process :
If you need your database to perform a custom process , Extensible PostgreSQL It's a better choice .
Integrate :
In the future , If possible, migrate the entire database system to another appropriate solution ( for example Oracle) in ,PostgreSQL For this kind of switching, it will be the most compatible and easy to operate .
Complex design :
Compared with other open source and free RDBMS( Relational database management system ) To achieve , For complex database design ,PostgreSQL Provides most of the functions and possibilities , At the same time, I didn't give up other valuable places .
When not to PostgreSQL?
Speed :
If all you need is a fast read operation , PostgreSQL Not a tool for this .
Simplify the system :
Unless you need absolute data integrity , Atomicity , Uniformity , Isolation, , Durability , Or complex design ,PostgreSQL It is a killer for simplifying the system .
Copy :
Unless you are willing to spend a lot of time , Energy and resources , Otherwise, for those who lack experience in database and system management , Realization and MySQL Of ( Master-slave ) Copying may not be easy .
边栏推荐
- TCP shakes hands three times and waves four times. Do you really understand?
- 创客思维在高等教育中的启迪作用
- Lambdaquerywrapper usage
- TCP三次握手,四次挥手,你真的了解吗?
- Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
- From repvgg to mobileone, including mobileone code
- [public class preview]: basis and practice of video quality evaluation
- Redis 排查大 key 的3种方法,优化必备
- 刘锦程荣获2022年度中国电商行业创新人物奖
- QT—绘制其他问题
猜你喜欢
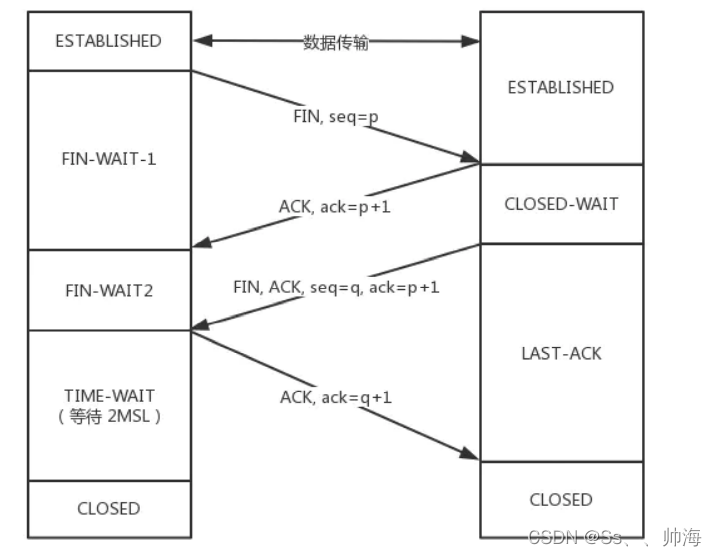
TCP shakes hands three times and waves four times. Do you really understand?
CloudCompare&Open3D DBSCAN聚类(非插件式)
应用实践 | 蜀海供应链基于 Apache Doris 的数据中台建设
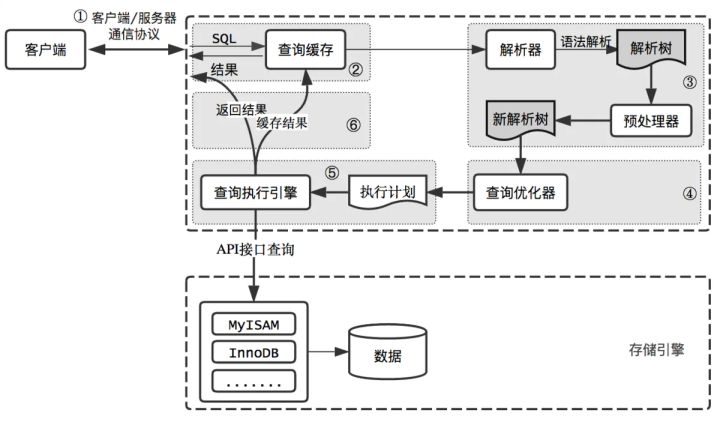
How is the entered query SQL statement executed?

改善机器视觉系统的方法
![[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox](/img/ef/65379499df205c068ee9bc9df797ac.png)
[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox

解析steam教育中蕴含的众创空间

【C語言】符號的深度理解
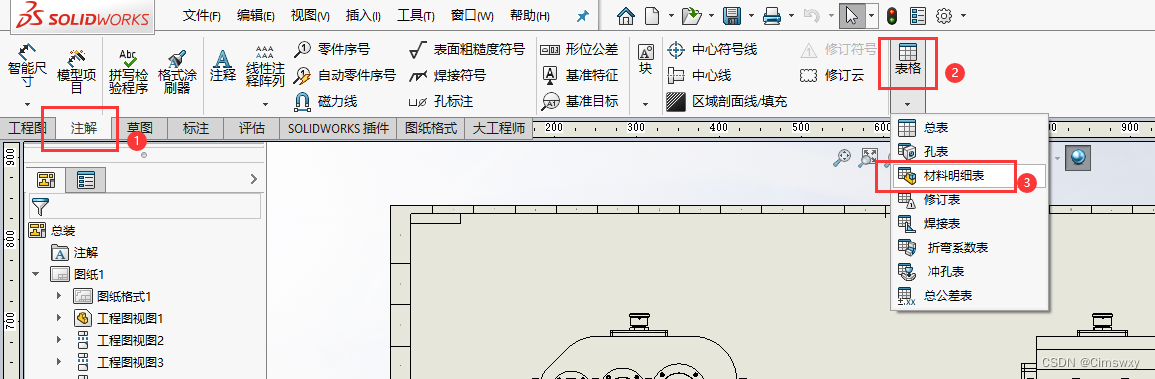
SolidWorks工程图添加材料明细表的操作
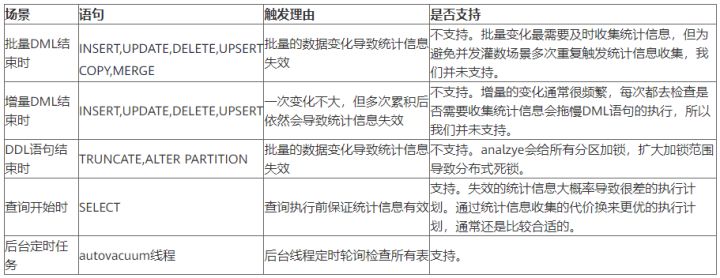
一文掌握数仓中auto analyze的使用
随机推荐
MP3是如何诞生的?
File read write
How is the entered query SQL statement executed?
Word文档中标题前面的黑点如何去掉
Redis03 - network configuration and heartbeat mechanism of redis
MP3是如何诞生的?
Golang面试整理 三 简历如何书写
New intersectionobserver usage notes
[public class preview]: basis and practice of video quality evaluation
MongoDB聚合操作总结
Super detailed tutorial, an introduction to istio Architecture Principle and practical application
Redis 排查大 key 的3种方法,优化必备
El tree combined with El table, tree adding and modifying operations
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
Le module minidom écrit et analyse XML
Maya lamp modeling
旋变串判断
Golang interview finishing three resumes how to write
LambdaQueryWrapper用法
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]