当前位置:网站首页>Li Kou brush question diary /day3/2022.6.25
Li Kou brush question diary /day3/2022.6.25
2022-07-04 18:35:00 【Bobo toilet cleaning spirit】
Novice Village
C Language understanding
Related concepts of linked list
One by one data in logical structure , In actual storage , Did not like The order sheet That's also close to each other . On the contrary , The data is randomly distributed in memory , This storage structure is called The linear table Chained storage
Because of distributed storage , In order to reflect the logical relationship between data elements , Each data element is stored at the same time , It should be equipped with a pointer , Used to point to its immediate successor , That is, each data element points to the next data element ( The last one points to NULL( empty ))
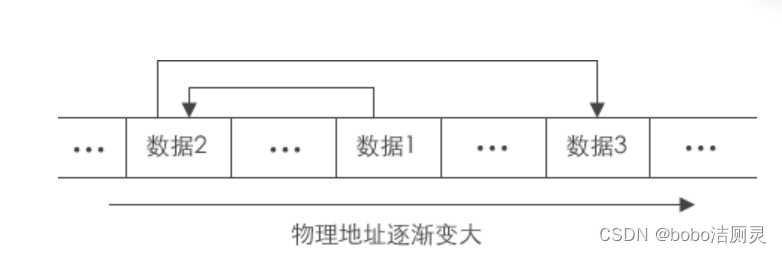
A table generated by the chain storage structure of a linear table , Referred to as “ Linked list ”.
The data element in the linked list consists of two parts , Data fields and pointer fields
The storage structure of each data element is called a node , Nodes are linked to each other through pointer fields , Form a chain
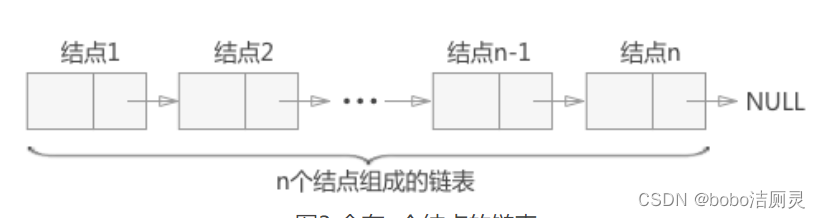
If each node contains only one pointer field , Then this linked list is called linear linked list or single linked list
The realization of linked list
The linked list does not store basic data types , You need to use a struct to implement custom
typedef struct Link{
char elem;// Represents a data field
struct Link * next;// Represents a pointer field , Point to the immediate successor element
}link;understand :
typedef The function is used to establish the alias of a defined data type .
In the form of :typedef There is already a variable name Alias ;
Generally speaking, it is to give another name to the existing data type

The above uses typedef function , take struct Link There is already a variable name and another name is link, The two are equivalent
Here is the second way to write :

The first line of the statement ,Node and struct Node Equivalent ,
In the second line ,struct Node* Is the existing variable name ,LinkList Alias
summary :

struct Node Equivalent to Node
struct Node* Equivalent to LinkList
Node The object of is structure
LinkList The object of is pointer field
LinkList L // Define a pointer variable to the structure L
Node *P Equivalent to LinkList L //Node* Can replace LinkList
**P Pointer value operation
summary 2:
Suppose we define a pointer p.
Then three symbols are often used :
1,p;
2,*p;
3,&p;
Beginners often feel confused , What do these three symbols mean ?
p Is the name of a pointer variable , Indicates the memory address pointed to by this pointer variable , If you use %p To output , It will be a 16 Hexadecimal number .
*p Indicates the contents stored in the memory address pointed to by this pointer , Generally, it is a variable or constant consistent with the pointer type . And we know that ,& Is the address operator ,&p It's just a pointer p The address of .
p The content in the address pointed to is used *p Express .
*p and **p The difference between
int *p : First level pointer , Express p The address pointed to is a int Type value
int **p : The secondary pointer , Express p What is stored in the address pointed to is a point to int Pointer to type ( namely p In the address pointed to, there is a point to int The first level pointer of )
for example :
int i=10; // An integer variable is defined
int *p=&i; // Defines a pointer to this variable
int **p1=&p; // Defines a secondary pointer to p The pointer
Then take out 10 The value method of is :
printf(“i=[%d]\n”,*p);
printf(“i=[%d]\n”,**p1);
Three knowledge points
Head node , The head pointer , Primary node
Head node : Sometimes , An additional node will be added before the first node of the list , The data field of a node generally does not store data ( In some cases, you can also store the length of the linked list and other information ), This node is called the head node .
If the pointer field of the header node is empty (NULL), Indicates that the list is empty . The head node is for the list , It's not necessary , When dealing with certain problems , Adding a head node to a linked list makes the problem simple .
First element node : The node of the first element in the list , It is the first node behind the head node .
The head pointer : Always point to the location of the first node in the list ( If the list has head nodes , The head pointer points to the head node ; otherwise , The head pointer points to the head node ).
The difference between head node and head pointer : The head pointer is a pointer , The head pointer points to the head node or the first element node of the linked list ; The head node is an actual node , It contains data fields and pointer fields . The direct embodiment of the two in the procedure is : The header pointer only declares and does not allocate storage space , The header node declares and allocates the actual physical memory of a node .
There can be no head nodes in a single chain table , But not without a head pointer !
Creation of linked list , lookup , add to , Delete (C Language )
Everything is difficult at the beginning , The first thing to do to initialize the linked list is Create the head node or first element node of the linked list . While creating , Make sure that a pointer always points to the header of the linked list , In this way, the linked list will not be lost .
// Creation of linked list
link * initLink(){
link * p=(link*)malloc(sizeof(link));// Create a header node
link * temp=p;// Declare a pointer to the head node , Used to traverse a linked list
// Generate linked list
for (int i=1; i<5; i++) {
link *a=(link*)malloc(sizeof(link));
a->elem=i;
a->next=NULL;
temp->next=a;
temp=temp->next;
}
return p;
}
// Query of nodes
int selectElem(link * p,int elem){
link * t=p;
int i=1;
while (t->next) {
t=t->next;
if (t->elem==elem) {
return i;
}
i++;
}
return -1;
}
// Change the value of a node , Update function , among ,add Indicates to change the position of the node in the linked list ,newElem For the value of the new data field
link *amendElem(link * p,int add,int newElem){
link * temp=p;
temp=temp->next;// Before traversing ,temp Point to the initial node
// Traverse to the deleted node
for (int i=1; i<add; i++) {
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->elem=newElem;
return p;
}
// Insertion of linked list , Realize the idea
// Will the new node of next The pointer points to the node after the insertion position ; The node before the insertion position next The pointer points to the insertion node ;
link * insertElem(link * p,int elem,int add){
link * temp=p;// Create a temporary node temp
// First find the previous node where you want to insert
for (int i=1; i<add; i++) {
if (temp==NULL) {
printf(" Invalid insertion position \n");
return p;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
// Create insert node c
link * c=(link*)malloc(sizeof(link));
c->elem=elem;
// Insert nodes into the linked list
c->next=temp->next;
temp->next=c;
return p;
}
// Delete node , Realize the idea
// Remove the node from the linked list ; Release node manually , Reclaim the memory space occupied by the node ;
link * delElem(link * p,int add){
link * temp=p;
//temp Point to the previous node of the deleted node
for (int i=1; i<add; i++) {
temp=temp->next;
}
link * del=temp->next;// Set a pointer to the deleted node separately , In case of loss
temp->next=temp->next->next;// The way to delete a node is to change the pointer field of the previous node
free(del);// Release the node manually , Prevent memory leaks
return p;
}
Use malloc Function application space , Be sure to pay attention to manual free fall . Otherwise, in the whole process of running the program , The requested memory space will not be released by itself ( Only when the whole program is finished , This memory will be recycled ), Memory leak , Don't think of it as a small problem
understand
java in LinkedList Corresponding linked list
Example

Their thinking :
With two Pointers , Traversing a single linked list , The fast pointer traverses two nodes at a time , The slow pointer traverses one node at a time , When the fast pointer traverses the linked list , The slow pointer just traverses to the middle
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head,slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
边栏推荐
- 力扣刷题日记/day1/2022.6.23
- 输入的查询SQL语句,是如何执行的?
- 【Hot100】32. Longest valid bracket
- [HCIA continuous update] WAN technology
- ISO27001 certification process and 2022 subsidy policy summary
- Li Kou brush question diary /day7/6.30
- 【210】PHP 定界符的用法
- 12 - explore the underlying principles of IOS | runtime [isa details, class structure, method cache | t]
- 中国农科院基因组所汪鸿儒课题组诚邀加入
- Face_ Attendance statistics of recognition face recognition
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
What types of Thawte wildcard SSL certificates provide
删除二叉搜索树中的节点附图详解
The money circle boss, who is richer than Li Ka Shing, has just bought a building in Saudi Arabia
力扣刷題日記/day6/6.28
Five thousand words to clarify team self-organization construction | Liga wonderful talk
为啥有些线上演唱会总是怪怪的?
力扣刷题日记/day2/2022.6.24
Is it science or metaphysics to rename a listed company?
【每日一题】556. 下一个更大元素 III
Li Kou brush question diary /day5/2022.6.27
LD_LIBRARY_PATH 环境变量设置
Neglected problem: test environment configuration management
Halcon模板匹配
[daily question] 871 Minimum refueling times
Imitation of numpy 2
mysql5.7安装教程图文详解
ISO27001认证办理流程及2022年补贴政策汇总
基于NCF的多模块协同实例
力扣刷题日记/day7/2022.6.29
File processing examples of fopen, FREAD, fwrite, fseek