当前位置:网站首页>Pointer advanced --- pointer array, array pointer
Pointer advanced --- pointer array, array pointer
2022-07-06 08:20:00 【Pineapple cat Yena】
The pointer , Is the key to learn data structure well . Most students only master the basic concept of pointer , This week , Let's dig deeper knowledge of pointer . To be proficient in industry and to be idle in play , Not lazy , Don't waste , aggressive , Long term vision .
List of articles
Preface
- What is an integer pointer ?
- What is a secondary pointer ?
- What is an array pointer ?
- What is pointer array ?
- How are their usages different ?
In this section, , Let's solve these mysteries .
Tips : The following is the main body of this article , The following cases can be used for reference
1. The basic concept of pointer
The pointer is a Variable , What is stored is the... Of the indicated variable Address , Can also pass through Pointer dereference To find the corresponding address Content
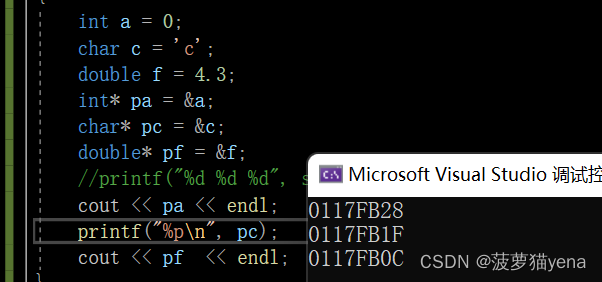
The pointer stores Address , The memory occupied by the address is 4 Bytes (x64 Environmental Science ) or 8 Bytes (x86 Environmental Science ). The following code ,pa,pc,pf All occupy four bytes .
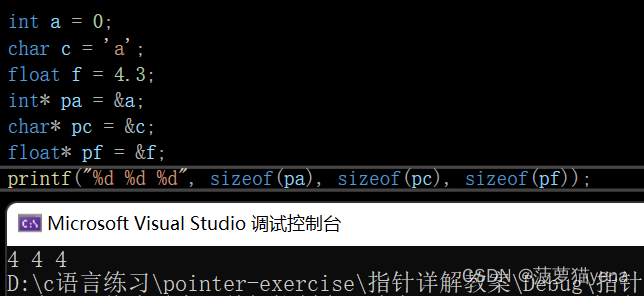
3. Since the size of the pointer is 4/8, So why int *pt,
char* pc And other types of pointers ?int * Is an integer pointer type ,
Indicates that the pointer points to int Data of type , char* Empathy
- Pointer type function 2: Different types of pointers , Add 1, Number of bytes skipped Is different .
int * Type pointer plus one , Skip four bytes ;
char * Type pointer plus one , Skip a byte ;
The same goes for other types , The number of bytes occupied by the data type is the same .
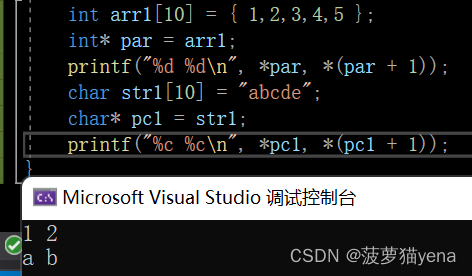
As shown in the figure below ,int * The pointer par+1, Skip four bytes , Point to the second of the array
Elements .char* Pointer to type pc1 Add one , Skip a byte , Pointing to an array
The second element .
2. Character pointer
The character pointer is Pointing character The pointer to . here , We understand through the topic .
- subject 1, For printing results
const char * p = "abcdef";
printf ("%s\n", p);
Let's think about it , What is the result of the above code ?
The result is that abcdef It's printed , Why? ?
here , The pointer p Deposit is The first element of the string is ’a’ The address of , When printing a string , You can start with the first address , meet ’\0’ end , Print string .
because "abcdef" Is a constant string , Add const modification , Prevent warnings .
2. subject 2. For printing results
const char* p1 = "abcdef";
const char* p2 = "abcdef";
char arr1[] = "abcdef";
char arr2[] = "abcdef";
if (p1 == p2)
printf("p1==p2\n");
else
printf("p1!=p2\n");
if (arr1 == arr2)
printf("arr1 == arr2\n");
else
printf("arr1 != arr2\n");
give the result as follows , Did you do it right ?
p1==p2
arr1 != arr2
Why? ?
because ,"abcdef" Is a constant string , Put it in the read-only area , Save only one copy . When p2 Also when pointing to a string , The program will not redefine a string ,p1 And p2 Pointing to The same area , therefore p1 == p2.
because arr1 And arr2 It is two independent spaces , although Same content , But the starting and ending addresses are different , So the two arrays are not equal .
3. Pointer array
Pointer array , It's essentially a Array , Every element of an array is Pointer types . The following code
int arr1[] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[] = {
2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[] = {
3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[3] = {
arr1, arr2, arr3 };
int * parr[3] ,parr Is an array , The array type is int * [3],
Open up three spaces , Every element is an integer pointer . Replace
First element address , Save it in the pointer array .
I want to print out the elements with this pointer array , What to do ?
We know , The array name is the first element address , Then the first address of each element has , It's not difficult to print it out .
In the pointer array parr in ,parr[1] That is to say a Array name ,
Namely arr1 The first address of the array , therefore arr1[i] It can be used
*(arr1+i) Express , It can also be used. *(parr[0]+i) Express ,
Empathy ,arr2[3] It can be used *(parr[1]+i) Express , The specific code is as follows
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(parr[i] + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
4. The meaning of array names
In general , The array name represents the address of the first element , But there are two special cases .
- sizeof,sizeof( Array name ) Represents the memory size of the entire array .
int arr[10] = {0};
printf("%d", sizeof(a));
// The answer is 40, ten int Type element ,10*4=40
- & Array name , It takes out the address of the entire array
int arr[7] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int *p = &a+1;
printf("%d", *(p-1));
What is the output result of the above code ?
The answer is 7, Why? ?
&a+1, intend Skip the entire array ,p It's an array The back position 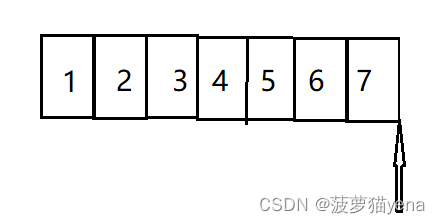
The output is *(p-1), namely p Move an integer byte forward , Yes 7, Dereference pointer , Output 7.
5. Array pointer
Array pointer , It's essentially a pointer , Point to an array .
int arr[10] = { 0 };
int (*p2)[10] = &arr;
p2 Is a pointer , Point to int【10】 An array of types .
6. Array pointer application
Array pointers are mainly used for Two dimensional array . because The first element of a two-dimensional array is the element of the first row , It's a one-dimensional array , therefore , Reception time , When using the pointer , Array pointer is required to receive .
The following code , Pass the two-dimensional array to the function with the array name, that is, the first address , Because of two dimensions
The first address of the array is the first line element , It's a one-dimensional array , therefore , Required number
Group pointer receive .p It's an array pointer , The element type pointed to is int [5], One
A one-dimensional array with five elements .
p Save the address in the first line ,(p+i) That is the first. i+1 The address of the line ,
*(p+i) That is the first. i+1 The address of the element at the beginning of the line ,*(p+i)+j yes
a[i][j] The address of ,*(*(p+0)+j ) Namely a[i][j] The elements of .
int arr[3][5] = { 1,2,3,4,5,2,3,4,5,6,3,4,5,6,7 };
print2(arr, 3, 5);
void print2(int (*p)[5], int r, int c)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < r; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < c; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j));
//printf("%d ", p[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
7. Array parameters
7.1 Two dimensional array parameters
int a[3][5];
fun11(a);// It is a one-dimensional array address
fun2(a);
void fun1(int a[][5])// The number of columns must be indicated
void fun2(int (*arr)[5])// Array pointer
Receive a two-dimensional array with a pointer ,int a[3][5]
The address of the first element of the array name , The first element of the two-dimensional array is the first line ,
Is the address of a one-dimensional array
void fun(int (*p)[5],int r,int c)
For printing printf("%d"*(*(p+i)+j)));
*(p+i) Equivalent to a row of array names ,p[i]
p, Pointer to array ,int (*)[5],p+1, skip 5 Elements
perhaps void fun(int a[][5],int r,int c)
Be careful , Rows of a two-dimensional array can be omitted , The number of columns cannot be omitted
7.2 One dimensional integer array passes parameters
int a[5]={
0};
fun1(a);
fun2(a);
void fun1(int a[])
{
}
void fun2(int *a)
{
}
7.3 One dimensional pointer array parameter transfer
One dimensional pointer array , Every element is The pointer , Pass the address of the first element of the pointer , use The secondary pointer receive . The secondary pointer , It stores the address of the first level pointer .
int *arr[5]={
0};
fun1(a);
void fun(int *arr[])
{
}
void fun(int **a)// The secondary pointer can store the address of the primary pointer
{
}
int *arr[5]={0};
fun(a);
void fun(int *arr[])
{}
void fun(int **a)// The secondary pointer can store the address of the primary pointer
{}
summary
There are many places where the knowledge points of pointer can be excavated , Need to be understood repeatedly . For a better future , Let's refuel ~
边栏推荐
- Restore backup data on S3 compatible storage with tidb lightning
- Asia Pacific Financial Media | art cube of "designer universe": Guangzhou community designers achieve "great improvement" in urban quality | observation of stable strategy industry fund
- [research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached
- 2022 Inner Mongolia latest water conservancy and hydropower construction safety officer simulation examination questions and answers
- VMware 虚拟化集群
- Artcube information of "designer universe": Guangzhou implements the community designer system to achieve "great improvement" of urban quality | national economic and Information Center
- [research materials] 2021 Research Report on China's smart medical industry - Download attached
- Secure captcha (unsafe verification code) of DVWA range
- It's hard to find a job when the industry is in recession
- Uibehavior, a comprehensive exploration of ugui source code
猜你喜欢
![[cloud native] teach you how to build ferry open source work order system](/img/fb/507f763791235bd00bc8201e5d7741.png)
[cloud native] teach you how to build ferry open source work order system

IoT -- 解读物联网四层架构
ESP series pin description diagram summary

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
Easy to use tcp-udp_ Debug tool download and use

Make learning pointer easier (3)
C语言 - 位段
Leetcode question brushing record | 203_ Remove linked list elements
A Closer Look at How Fine-tuning Changes BERT
Wincc7.5 download and installation tutorial (win10 system)
随机推荐
Restore backup data on S3 compatible storage with br
Remote storage access authorization
Upgrade tidb with tiup
CAD ARX 获取当前的视口设置
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
面向个性化需求的在线云数据库混合调优系统 | SIGMOD 2022入选论文解读
Golang DNS 随便写写
Migrate data from a tidb cluster to another tidb cluster
[Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 010 prefabricated parts
使用 TiUP 升级 TiDB
What is the use of entering the critical point? How to realize STM32 single chip microcomputer?
23. Update data
21. Delete data
让学指针变得更简单(三)
Upgrade tidb operator
使用 Dumpling 备份 TiDB 集群数据到兼容 S3 的存储
Pyqt5 development tips - obtain Manhattan distance between coordinates
2022 Inner Mongolia latest water conservancy and hydropower construction safety officer simulation examination questions and answers
Convolution, pooling, activation function, initialization, normalization, regularization, learning rate - Summary of deep learning foundation
Analysis of pointer and array written test questions