当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 17 process memory
Chapter 17 process memory
2022-07-04 14:22:00 【yaoxin521123】
List of articles
Chapter 17 Process memory
Introduce
Processes use many different resources to achieve their goals . This includes some or all CPU cycle 、 Memory 、 External storage 、 Network bandwidth, etc . This article is about memory usage . say concretely , It handles the memory allocated for data storage , for example :
- Public and private variables
When assigning values to them for the first time , They are allocated memory space . In the case of local arrays , The combination of local variable name plus all subscript values refers to a single variable value .
Except for variables that contain extremely long strings , Variables will take up with $STORAGE Related space . Variables containing extremely long strings are stored in different ways , And it doesn't take up $STORAGE In the space .
- Object instances
Whenever you instantiate an object , Will allocate space to save the current content of the object and the object it refers to . This space is returned when the last object reference is deleted .
- Local
I/Obuffer
Will be associated with the device that the process is using I/O Buffers are stored in the process space .
Manage process space
The process starts with the initial memory pool for the above entities . When applications create them , They consume memory in the pool ; When the application deletes them , Their memory will be returned to the pool . for example , When a routine starts executing , Always create local variables that consume some memory ; When the routine returns and these variables are out of range , The memory used by these variables will be returned and reused .
When an application needs memory , And the process is not large enough in its memory pool ( continuity ) Available memory area to meet the demand , The process will request additional memory blocks from the underlying operating system to be added to its pool . later , If the memory block is completely unused , It will return to the operating system . Because the order of allocating memory for entities and the order of deleting these entities from memory are not necessarily mirror images of each other , So as the execution goes on , Memory will become fragmented to some extent . This will affect the memory allocation and release of the above operating system .
$ZSTORAGE
Processes can use up to 2TB Memory . To help manage memory usage , It provides a way for administrators or applications to set small memory consumption limits . This value is stored in the system variable of each process $ZSTORAGE in , therefore $ZSTORAGE Always include the maximum allowable size of process memory ( With KB In units of ).
$ZSTORAGE The value of 1KB Specify... For units . The minimum allowable value is 256, namely 256KB. The process can be $ZSTORAGE The maximum value set is 2TB (2^31 * 1KB) Memory . Trying to set a value less than the minimum value or greater than the maximum value will default to the minimum value or the maximum value, respectively .
Maximum memory per process
This value is set through the management portal . To access relevant pages , Please select system management > To configure > The system configuration > Memory and startup . On the page that appears , Set up Maximum Per-Process Memory (KB) The value in .
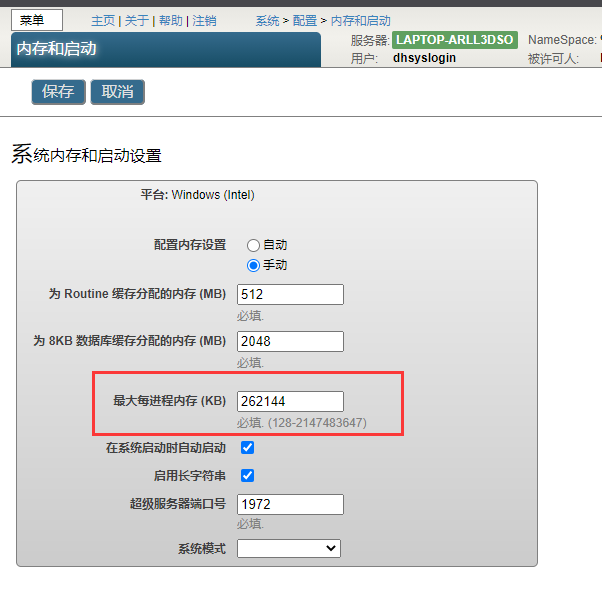
In profile (iris.cpf) in , This parameter is called bbsiz. This value is when the process starts $ZSTORAGE The initial value of the .
Be careful : You can also go through ObjectScript JOB Set the memory limit of the process when the command starts the process .
$STORAGE
System variables $STORAGE Indicates the amount of storage available for processes that are still running . It is in bytes . When the memory request of the process is greater than $STORAGE When the value in or the request to allocate memory from the operating system fails , It will generate <STORE> error .
error
When the memory request of the process is satisfied, it will lead to $STORAGE The value of becomes negative , Or when the request of the operating system to allocate memory fails , It will generate <STORE> error . About handling $STORAGE Become negative <STORE> error , A process can be considered to be in one of two modes : Normal mode and low memory mode .
- Normal mode
When the process is in normal mode and requests memory , Otherwise, it will lead to $STORAGE When it becomes negative , The process throws <STORE> Error and enter low memory mode .
- Low memory mode
In low memory mode , The allowed operation will $STORAGE Push to negative , In order to provide some extra memory for the application to handle errors and clean up . When a process in low memory mode releases memory ,$STORAGE The value of rises to at least 256KB( or $ZSTORAGE Of 25%, If it is lower ), The process will return to normal mode . In low memory mode ,$STORAGE The lower limit of is about -1MB. Otherwise, it will lead to $STORAGE Any operation below this limit will result in <STORE> error . The value of the lower limit is determined by $STORAGE Value definition , subtract 1MB.
Be careful : The process can put $ZSTORAGE Set to any value within its allowable range . If $ZSTORAGE Set to less than the currently used value , be $STORAGE Will have a negative value . If this happens when the process is in normal mode , The next operation to allocate memory will result in the process getting <STORE> Error and enter low memory mode , The lower limit is equal to this value minus 1MB. If this happens when the process is already in low memory mode , Then the lower limit remains unchanged .
For reasons beyond -1MB Low memory mode limit or failure to allocate memory from the operating system <STORE> error , Because there is too little memory available , The behavior of the process is unpredictable . Into the <STORE> error , Or the error handler may not be called and the process may stop .
Error handlers can be resolved in one or more of the following ways <STORE> error :
- Abort the calculation that caused the memory request , It may be possible to release calculations when they occur
<STORE>Any storage space obtained before the error . - Try to generate more available memory by deleting unwanted data .
- Carry out any necessary cleaning work ( For example, close the open file ), And then terminate the program .
- take
$ZSTORAGESet the value of to a larger value , To allow the process to continue and request more memory in the future .
Special notes
platform
Most instances have less allocable space per process than 2TB Running on the system . On such systems , When The process ran out of available system memory ( Actual physical memory plus available swap space ) when , The underlying system may handle this situation in many ways . Some examples are :
- On some platforms , The system will send a signal , guide Process termination .
- On some platforms ( for example Linux and AIX) On , The system uses heuristic algorithms to kill the process it considers the most aggressive . This may be a process , But it may also be another alternative process .
- Some systems generate kernels that crash the underlying operating system “ panic
panic” To handle memory exhaustion . - Some systems can handle memory exhaustion , But recovery may lead to access conflicts in the process .
Good programming practice shows that the process should not rely on the error recovery algorithm used by the underlying platform . contrary , Such processes should provide adequate design 、 Testing and logging , To allow the process to properly estimate and manage its own resource needs .
边栏推荐
- ML:SHAP值的简介、原理、使用方法、经典案例之详细攻略
- C# wpf 实现截屏框实时截屏功能
- R language uses follow up of epidisplay package The plot function visualizes the longitudinal follow-up map of multiple ID (case) monitoring indicators, and uses stress The col parameter specifies the
- Ml: introduction, principle, use method and detailed introduction of classic cases of snap value
- 【MySQL从入门到精通】【高级篇】(五)MySQL的SQL语句执行流程
- R语言使用epiDisplay包的dotplot函数通过点图的形式可视化不同区间数据点的频率、使用by参数指定分组参数可视化不同分组的点图分布
- Whether the loyalty agreement has legal effect
- Assertion of unittest framework
- 2022 practice questions and mock exams for the main principals of hazardous chemical business units
- Test process arrangement (2)
猜你喜欢
Innovation and development of independent industrial software
Excel quickly merges multiple rows of data
![Supprimer les lettres dupliquées [avidité + pile monotone (maintenir la séquence monotone avec un tableau + Len)]](/img/af/a1dcba6f45eb4ccc668cd04a662e9c.png)
Supprimer les lettres dupliquées [avidité + pile monotone (maintenir la séquence monotone avec un tableau + Len)]
Huahao Zhongtian rushes to the scientific and Technological Innovation Board: the annual loss is 280million, and it is proposed to raise 1.5 billion. Beida pharmaceutical is a shareholder
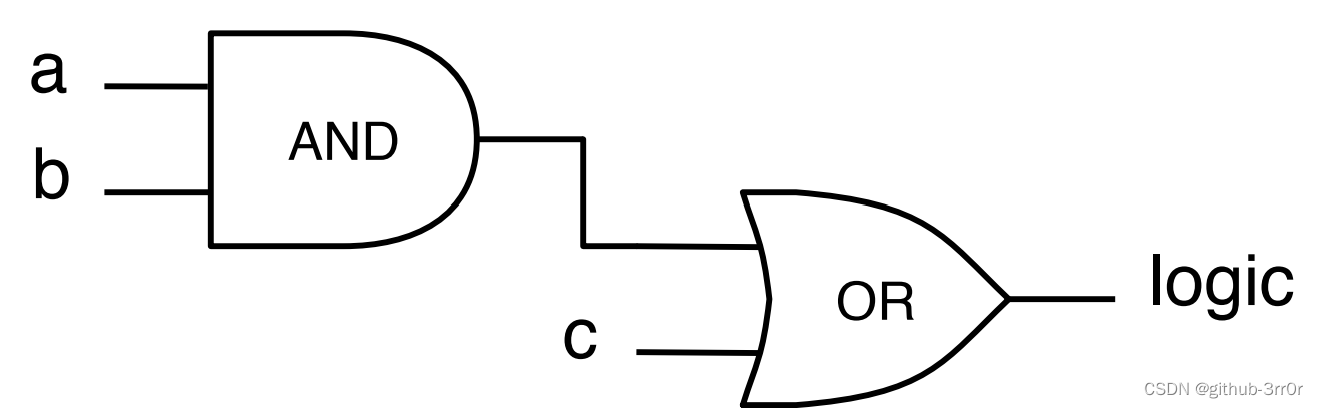
Understand chisel language thoroughly 05. Chisel Foundation (II) -- combinational circuits and operators
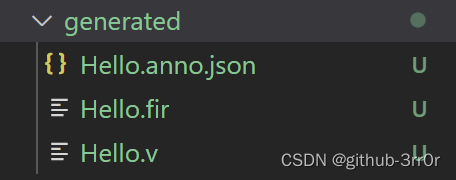
Understand chisel language thoroughly 10. Chisel project construction, operation and testing (II) -- Verilog code generation in chisel & chisel development process
![递增的三元子序列[贪心训练]](/img/92/7efd1883c21c0e804ffccfb2231602.png)
递增的三元子序列[贪心训练]

C# wpf 实现截屏框实时截屏功能
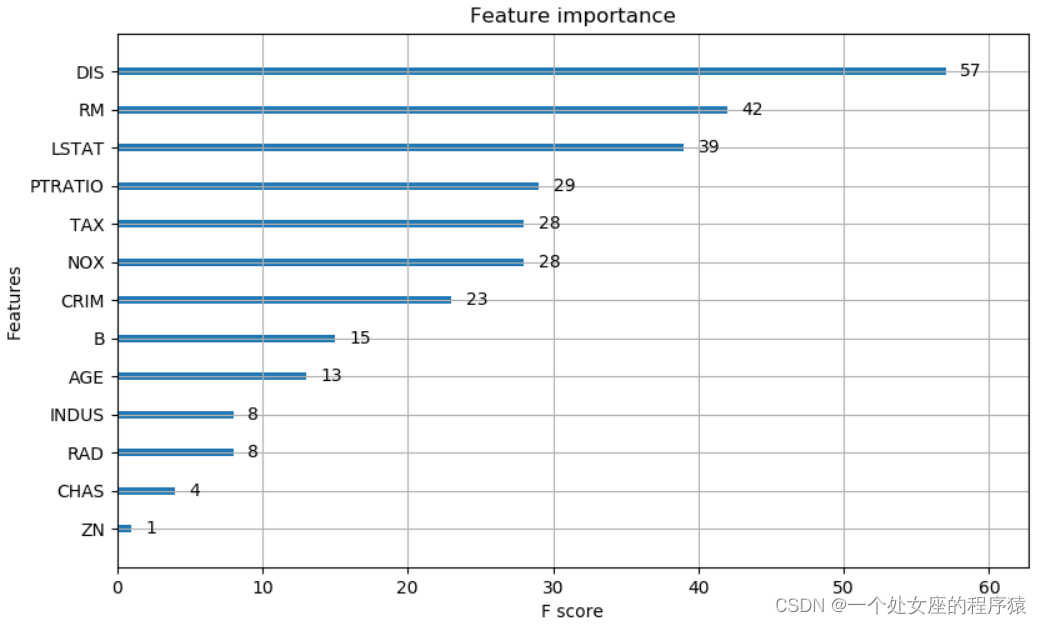
ML之shap:基于boston波士顿房价回归预测数据集利用shap值对XGBoost模型实现可解释性案例

China Post technology rushes to the scientific innovation board: the annual revenue is 2.058 billion, and the postal group is the major shareholder
随机推荐
ARouter的使用
Leetcode 61: 旋转链表
流行框架:Glide的使用
AI and Life Sciences
R language uses the mutation function of dplyr package to standardize the specified data column (using mean function and SD function), and calculates the grouping mean of the standardized target varia
China Post technology rushes to the scientific innovation board: the annual revenue is 2.058 billion, and the postal group is the major shareholder
【MySQL从入门到精通】【高级篇】(五)MySQL的SQL语句执行流程
Can mortgage with housing exclude compulsory execution
Test process arrangement (3)
使用CLion编译OGLPG-9th-Edition源码
为什么图片传输要使用base64编码
Haobo medical sprint technology innovation board: annual revenue of 260million Yonggang and Shen Zhiqun are the actual controllers
【FAQ】華為帳號服務報錯 907135701的常見原因總結和解决方法
去除重复字母[贪心+单调栈(用数组+len来维持单调序列)]
Common content type correspondence table
R language dplyr package summary_ If function calculates the mean and median of all numerical data columns in dataframe data, and summarizes all numerical variables based on conditions
Leetcode T49: 字母异位词分组
ML之shap:基于boston波士顿房价回归预测数据集利用Shap值对LiR线性回归模型实现可解释性案例
Error in find command: paths must precede expression (turn)
gin集成支付宝支付