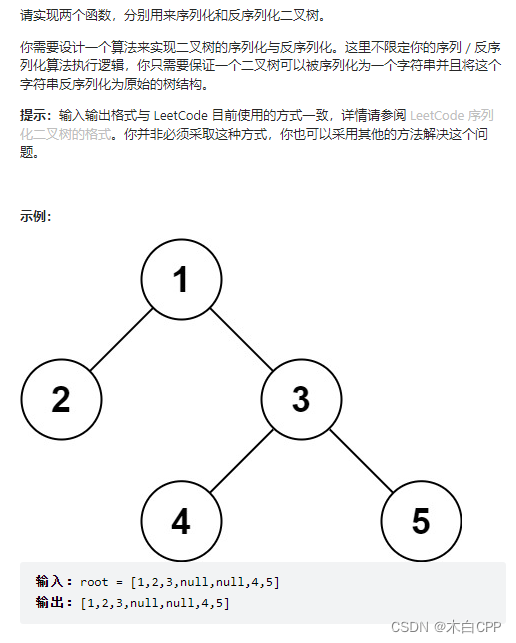
当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode力扣(剑指offer 36-39)36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表37. 序列化二叉树38. 字符串的排列39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
LeetCode力扣(剑指offer 36-39)36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表37. 序列化二叉树38. 字符串的排列39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
2022-07-07 17:44:00 【木白CPP】
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
题解:
思路很简单,就是一个中序遍历,一边遍历一边把节点连接起来。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
Node *pre,*head;
void dfs(Node* root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left);
if(pre==nullptr) head=root;//这是个头节点
else
pre->right=root;
root->left=pre;
pre=root;
dfs(root->right);
}
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return root;
dfs(root);
head->left=pre;
pre->right=head;
return head;
}
};结果:
剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
题解:
序列化一般采用前序,中序,后序,这里采用前序。
序列化,用前序遍历将二叉树的节点保存到一个字符串中,每个节点之间用’,‘隔开。值得注意的是,在遍历的过程中需要将二叉树看成一颗满二叉树,空节点用’null‘表示。
反序列化,将字符串放在队列que中,用’,‘判断并推入到队列中。通过前序遍历,一边前序遍历一边建立二叉树节点。
代码:
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return "null,";
string str=to_string(root->val)+',' ;
str+=serialize(root->left);
str+=serialize(root->right);
return str;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
queue<string> que;
string str;
for(auto i:data){
if(i==','){
que.push(str);
str.clear();
}
else
str.push_back(i);
}
return rdeserialize(que);
}
TreeNode* rdeserialize(queue<string> &que){
if (que.front() == "null") {
que.pop();
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(que.front()));
que.pop();
root->left = rdeserialize(que);
root->right = rdeserialize(que);
return root;
}
};结果:
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
题解:
最关键是去重复,因为有重复的字符。可以用一个标志位,判断当前的字符是否出现在前面的字符串中。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
void dfs(string &s,int sz,int pos){
if(pos==sz) res.push_back(s);
for(int i=pos;i<sz;++i){
bool flag=true;
for(int j=pos;j<i;++j){
if(s[j]==s[i]) flag=false;
}
if(flag){
swap(s[i],s[pos]);
dfs(s,sz,pos+1);
swap(s[i],s[pos]);
}
}
}
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
dfs(s,s.size(),0);
return res;
}
};结果:
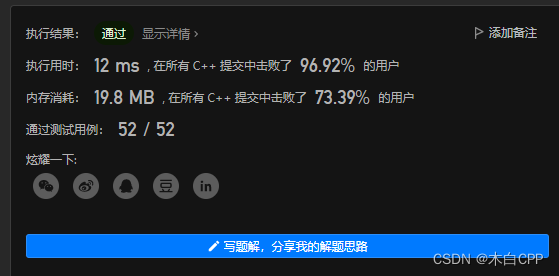
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
题解:
方法一:排序
如果重复字符有超过一半的,排序后必然会在数组中间位置。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
return nums[nums.size()/2];
}
};结果:
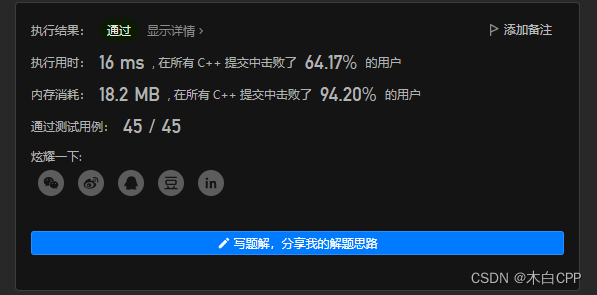
方法二:哈希
用哈希存储,一旦这个值大于数组长度的一半就返回该值。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int,int>map;
for(auto i:nums){
++map[i];
if(map[i]>nums.size()/2) return i;
}
return -1;
}
};结果:
边栏推荐
- 华南X99平台打鸡血教程
- el-upload上传组件的动态添加;el-upload动态上传文件;el-upload区分文件是哪个组件上传的。
- How to share the same storage among multiple kubernetes clusters
- 浏览积分设置的目的
- 杰理之相同声道的耳机不允许配对【篇】
- Jerry's headphones with the same channel are not allowed to pair [article]
- Kunpeng developer summit 2022 | Kirin Xin'an and Kunpeng jointly build a new ecosystem of computing industry
- 炒股如何开户?请问一下手机开户股票开户安全吗?
- LeetCode 535(C#)
- 凌云出海记 | 赛盒&华为云:共助跨境电商行业可持续发展
猜你喜欢
PMP對工作有益嗎?怎麼選擇靠譜平臺讓備考更省心省力!!!
让这个 CRMEB 单商户微信商城系统火起来,太好用了!
![[RT thread env tool installation]](/img/bc/9b39651d40a240f0893200793f67e9.png)
[RT thread env tool installation]

2022.07.02
RESTAPI 版本控制策略【eolink 翻译】
648. 单词替换
一张图深入的理解FP/FN/Precision/Recall

Kirin Xin'an won the bid for the new generation dispatching project of State Grid!

Kirin Xin'an cloud platform is newly upgraded!
Empowering smart power construction | Kirin Xin'an high availability cluster management system to ensure the continuity of users' key businesses
随机推荐
AI writes a poem
ASP.NET幼儿园连锁管理系统源码
what‘s the meaning of inference
华南X99平台打鸡血教程
UCloud是基础云计算服务提供商
杰理之关于 TWS 声道配置【篇】
最多可以参加的会议数目[贪心 + 优先队列]
时间工具类
Longest common prefix (leetcode question 14)
ant desgin 多选
现在股票开户可以直接在网上开吗?安全吗。
el-upload上传组件的动态添加;el-upload动态上传文件;el-upload区分文件是哪个组件上传的。
2022年投资哪个理财产品收益高?
How to buy stocks on your mobile phone and open an account? Is it safe to open an account
我的创作纪念日
Chief technology officer of Pasqual: analog quantum computing takes the lead in bringing quantum advantages to industry
IP 工具类
R language uses ggplot2 function to visualize the histogram distribution of counting target variables that need to build Poisson regression model, and analyzes the feasibility of building Poisson regr
Introduction to bit operation
Make this crmeb single merchant wechat mall system popular, so easy to use!