当前位置:网站首页>MySQL constraints
MySQL constraints
2022-07-03 13:15:00 【Levi Bebe】
1.MySQL constraint
Concept :
Constrained English :constraint
Constraints are actually constraints on the data in the table
effect :
The purpose of adding constraints in the table design is to ensure the records in the table Integrity and effectiveness , For example, the value of some columns in the user table cannot be empty , Some column values cannot be repeated .
classification :
- Primary key constraint (primary key)
- Self increasing constraint (auto_increment)
- Non empty constraint (not null)
- Uniqueness constraint (unique)
- Default constraint (default)
- Zero fill constraint (zerofill)
- Foreign key constraints (foreign key)
1.1 Primary key constraint
Concept :
- MySQL The primary key constraint is what one or more columns do , Its value uniquely identifies each row in the table , Convenient in RDBMS Find a line as soon as possible .
- A primary key constraint is equivalent to a unique constraint + A combination of nonnull constraints , Primary key constraint columns are not allowed to be duplicate , Null values are not allowed .
- Only one primary key is allowed per table
- Keywords are :primary key
Add single column primary key :
CREATE TABLE bianbian.emp1(
eid int PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20),
deptId INT,
salary DOUBLE
);


CREATE TABLE bianbian.emp2(
eid INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
deptId INT,
salary DOUBLE,
CONSTRAINT pk1 PRIMARY KEY(eid) --CONSTRAINT pk1 It can be omitted
);
-- The function of primary key
-- Primary key constraint , The primary key column is not empty and duplicate
INSERT into emp2(eid,name,deptId,salary) VALUES(1001,' Zhang San ',10,5000);
-- Repeat validation
INSERT into emp2(eid,name,deptId,salary) VALUES(1001,' Li Si ',10,6000);
-- Can't be empty
INSERT into emp2(eid,name,deptId,salary) VALUES(NULL,' Li Si ',10,6000);
Combined the primary key :
The so-called federated primary key , The primary key is composed of multiple fields in a table .
Be careful :
1. When the primary key is composed of multiple fields , You cannot declare a primary key constraint directly after a field name
2. A table can only have one primary key , A federated primary key is also a primary key 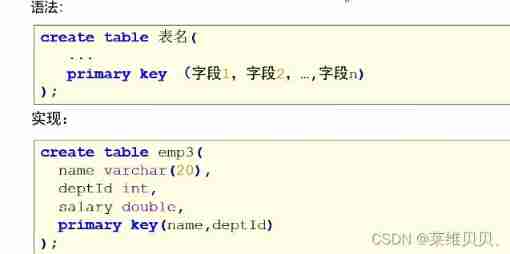
Code :
CREATE TABLE bianbian.emp3(
name VARCHAR(20),
deptId INT,
salary DOUBLE,
PRIMARY KEY(name,deptId)
);
Running results :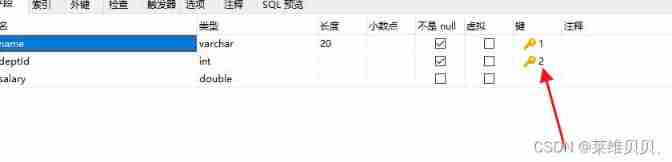
The primary key function :
-- The marked column of the union primary key cannot be duplicate or empty
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(' Zhang San ',10,5000);
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(' Zhang San ',20,5000);
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(' Wang Wu ',20,5000);
-- name and deptId It is the same as the original content , Will report a mistake
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(' Zhang San ',20,5000);
-- An error is also reported if it is empty
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(NULL,20,5000);
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES(' Extrajudicial ',5000);
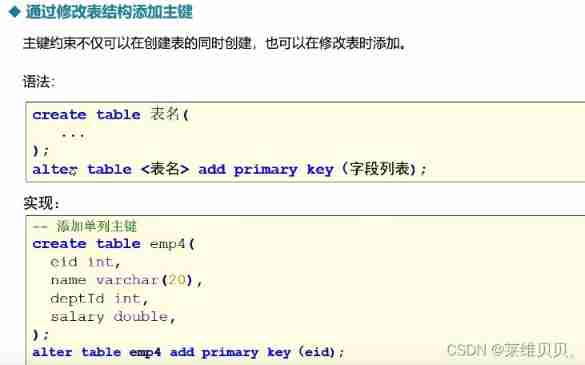
Code :
CREATE TABLE bianbian.emp4(
eid INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
deptId INT,
salary DOUBLE
);
ALTER TABLE emp4 ADD PRIMARY key(eid);
Delete primary key :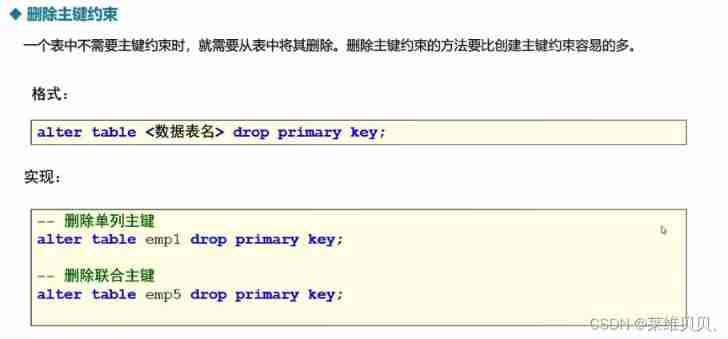
-- There is no single primary key or joint primary key
ALTER table emp4 DROP PRIMARY KEY
1.2 Self growth constraints

Code :
-- Self growth constraints
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user1(
id int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO t_user1 VALUES(NULL,' Zhang San ');
INSERT INTO t_user1(name) VALUES(' Li Si ');
 Code :
Code :
-- Self growth constraints
-- Mode one : Specify... When creating a table
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user2(
id int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20)
)auto_increment = 100; -- id from 100 Start
-- Mode two : After creating the table, specify
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user3(
id int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
ALTER TABLE t_user3 auto_increment = 200 -- id from 200 Start

DELETE FROM t_user1; -- DELETE After deleting data , Self growth is still the last value plus 1
TRUNCATE t_user1; -- TRUNCATE After deleting data , Start with the default assignment
1.3 Non empty constraint
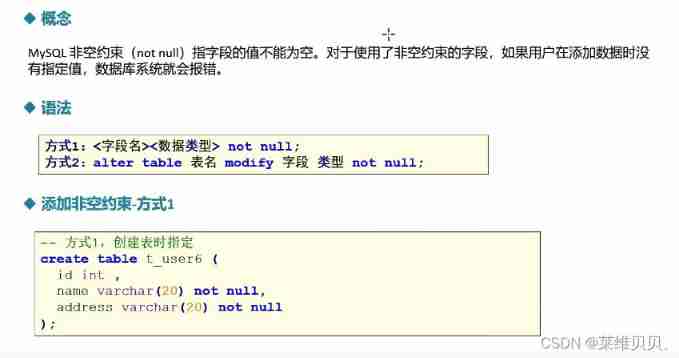
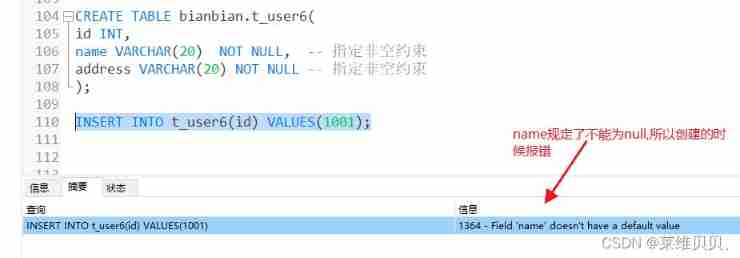
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user7(
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20) ,
address VARCHAR(20)
);
ALTER TABLE t_user7 MODIFY name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL; -- Specify a non NULL constraint
ALTER TABLE t_user7 MODIFY address VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL;-- Specify a non NULL constraint
INSERT INTO t_user7(id) VALUES(1001); -- Report errors
ALTER TABLE t_user7 MODIFY address VARCHAR(20);-- Delete non empty constraints
1.4 Unique constraint

Code :
-- 1. Add unique constraints - The way 1- Specify... When creating a table
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user8(
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
phone_number INT UNIQUE -- Specify a unique constraint
);
-- 2. Add unique constraints - The way 2 Specify... When creating a table
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user9(
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
phone_number INT -- Specify a unique constraint
);
ALTER TABLE t_user9 ADD CONSTRAINT phone_unique UNIQUE(phone_number);
-- 3. Delete unique constraint
-- Format : ALTER TABLE Table name DROP INDEX Unique constraint name
ALTER TABLE t_user9 DROP INDEX phone_unique;
1.5 Default constraint
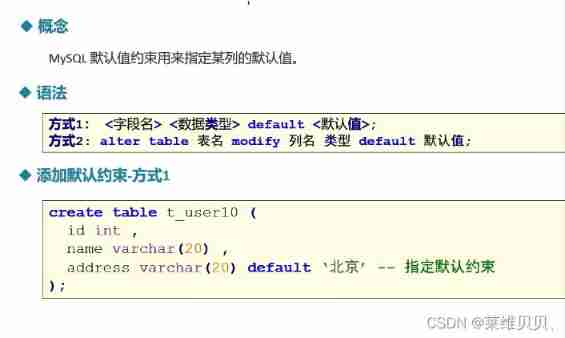
Code :
CREATE TABLE bianbian.t_user11(
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
address VARCHAR(20)
);
ALTER TABLE t_user11 MODIFY address VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT ' Shenzhen '; -- Add default constraint
ALTER TABLE t_user11 MODIFY address VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL; -- Delete default constraint
Reference resources
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iF411z7Pu?p=39
边栏推荐
- Flink SQL knows why (VIII): the wonderful way to parse Flink SQL tumble window
- Seven habits of highly effective people
- Create a dojo progress bar programmatically: Dojo ProgressBar
- 【R】【密度聚类、层次聚类、期望最大化聚类】
- CVPR 2022 图像恢复论文
- php:  The document cannot be displayed in Chinese
- 2022-02-14 analysis of the startup and request processing process of the incluxdb cluster Coordinator
- Quickly learn member inner classes and local inner classes
- C graphical tutorial (Fourth Edition)_ Chapter 13 entrustment: what is entrustment? P238
- 已解决(机器学习中查看数据信息报错)AttributeError: target_names
猜你喜欢
2022-02-14 analysis of the startup and request processing process of the incluxdb cluster Coordinator

【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第六章习题】
![【R】 [density clustering, hierarchical clustering, expectation maximization clustering]](/img/a2/b287a5878761ee22bdbd535cae77eb.png)
【R】 [density clustering, hierarchical clustering, expectation maximization clustering]

Huffman coding experiment report
![[comprehensive question] [Database Principle]](/img/d7/8c51306bb390e0383a017d9097e1e5.png)
[comprehensive question] [Database Principle]
已解决TypeError: Argument ‘parser‘ has incorrect type (expected lxml.etree._BaseParser, got type)

Flink SQL knows why (16): dlink, a powerful tool for developing enterprises with Flink SQL

【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第三章习题】
![[data mining review questions]](/img/96/00f866135e06c4cc0d765c6e499b29.png)
[data mining review questions]

Brief introduction to mvcc
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of multithreading
The 35 required questions in MySQL interview are illustrated, which is too easy to understand
2022-02-11 heap sorting and recursion
Analysis of the influence of voltage loop on PFC system performance
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter III exercises]
[problem exploration and solution of one or more filters or listeners failing to start]
Deeply understand the mvcc mechanism of MySQL
[network counting] Chapter 3 data link layer (2) flow control and reliable transmission, stop waiting protocol, backward n frame protocol (GBN), selective retransmission protocol (SR)
Flink code is written like this. It's strange that the window can be triggered (bad programming habits)
有限状态机FSM
Annotation and reflection
2022-01-27 redis cluster brain crack problem analysis
Logback log framework
道路建设问题
[colab] [7 methods of using external data]
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 7 exercises]
已解决(机器学习中查看数据信息报错)AttributeError: target_names
剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
01 three solutions to knapsack problem (greedy dynamic programming branch gauge)
PostgreSQL installation