Please state the source of reprint ~, This article was published at luozhiyun The blog of :https://www.luozhiyun.com
This article uses Istio The source code is release 1.5.
This article intends to talk about sidecar, I was just learning Istio There will be some doubts when ,sidecar How to achieve insensible Injection , A lot of learning materials don't talk about this part in detail , Now I'm going to analyze .
Sidecar Introduce
stay Sidecar In the deployment mode, a companion container will be deployed for each application container . about Istio,Sidecar Take over all network traffic in and out of the application container .
Use Sidecar Mode deployment service grid , There is no need to run the agent on the node , But the cluster will run multiple identical Sidecar copy . stay Kubernetes Of Pod in , Run one next to the original application container Sidecar Containers , It can be understood that two containers share storage 、 Network and other resources , In a broad sense, this can be injected into Sidecar Container of Pod It's understood as a mainframe , Two containers share host resources .
Sidecar Injection process
Inject Sidecar It will generate pod When you add two containers :istio-init、istio-proxy.istio-init From the name of this container, you can know that it belongs to k8s Medium Init Containers, It is mainly used to set iptables The rules , Turn in and out of traffic from Sidecar To deal with .istio-proxy Is based on Envoy Implementation of a network proxy container , It's true. Sidecar, Application traffic will be redirected into or out of Sidecar.
We are using Sidecar When injecting automatically, you only need to type the corresponding application deployment's namespace istio-injection=enabled label , Any new... Created in this namespace Pod Will be Istio Inject Sidecar.
After the application is deployed, we can use kubectl describe see pod Inside the container :
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl describe pod details-v1-6c9f8bcbcb-shltm
Name: details-v1-6c9f8bcbcb-shltm
Namespace: default
...
Labels: app=details
pod-template-hash=6c9f8bcbcb
security.istio.io/tlsMode=istio
service.istio.io/canonical-name=details
service.istio.io/canonical-revision=v1
version=v1
Annotations: sidecar.istio.io/status:
{"version":"3bc68d1f27d8b6b9bf1cb3e9904f5d5f8c2ecab1c93d933fbb3d0db76fae2633","initContainers":["istio-init"],"containers":["istio-proxy"]...
Status: Running
IP: 172.20.0.14
IPs:
IP: 172.20.0.14
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/details-v1-6c9f8bcbcb
Init Containers:
istio-init:
Container ID: docker://6d14ccc83bd119236bf8fda13f6799609c87891be9b2c5af7cbf7d8c913ce17e
Image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.5.10
Image ID: docker-pullable://istio/proxyv2@sha256:abbe8ad6d50474814f1aa9316dafc2401fbba89175638446f01afc36b5a37919
...
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
...
Containers:
details:
Container ID: docker://ed216429216ea1b8a1ba20960590edb7322557467c38cceff3c3e847bcff0a14
Image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-details-v1:1.15.1
Image ID: docker-pullable://istio/examples-bookinfo-details-v1@sha256:344b1c18703ab1e51aa6d698f459c95ea734f8317d779189f4638de7a00e61ae
...
istio-proxy:
Container ID: docker://a3862cc8f53198c8f86a911089e73e00f4cc4aa02eea05aaeb0bd267a8e98482
Image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.5.10
Image ID: docker-pullable://istio/proxyv2@sha256:abbe8ad6d50474814f1aa9316dafc2401fbba89175638446f01afc36b5a37919
...
Ready: True
details-v1-6c9f8bcbcb-shltm This app is one we created in the last article details service , There are istio-init、istio-proxy、details These three container.
Sidecar Principle of injection
Sidecar Injection is mainly based on k8s Access controller for Admission Controller To achieve .
The access controller will intercept Kubernetes API Server Requests received , Interception occurs after authentication and authentication , Before objects are persisted . There are two types of Admission webhook:Validating and Mutating.Validating Type of Webhook You can decide whether to reject the request according to the custom admission policy ;Mutating Type of Webhook Requests can be edited according to custom configuration .
We can take a look at the configuration details :
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfiguration istio-sidecar-injector -o yaml
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
annotations:
...
creationTimestamp: "2020-10-18T08:22:01Z"
generation: 2
labels:
app: sidecar-injector
operator.istio.io/component: Pilot
operator.istio.io/managed: Reconcile
operator.istio.io/version: 1.5.10
release: istio
...
webhooks:
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
clientConfig:
caBundle: ...
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Exact
name: sidecar-injector.istio.io
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
istio-injection: enabled
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
...
Here's one namespaceSelector,match The label of is istio-injection: enabled The namespace of , Request rules rules yes CREATE, Means to match all pod Create request for . When apiserver When you receive a request that meets the rules ,apiserver Will give Webhook The service sends a request for admission audit , In the above configuration webhook The designated one is called istiod Of service.
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get svc --namespace=istio-system | grep istiod
istiod ClusterIP 10.68.222.38 <none> 15012/TCP,443/TCP
32h
Usually Sidecar Injection is accomplished by the following steps :
- analysis Webhook REST request , take AdmissionReview Raw data deserialization ;
- analysis pod, take AdmissionReview Medium AdmissionRequest Deserialization ;
- utilize Pod And grid configuration rendering Sidecar The configuration template ;
- utilize Pod And create the template after rendering Json Patch;
- structure AdmissionResponse;
- structure AdmissionReview, Send it to apiserver;
The source code flow is almost like this :
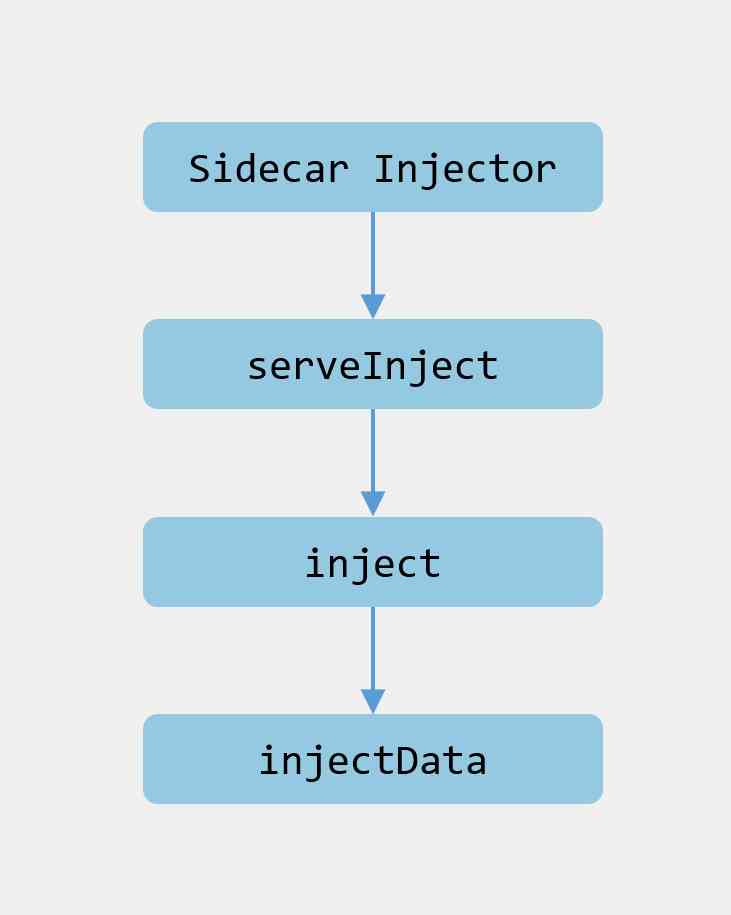
Let's look at the source code .
Source location :pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go
func NewWebhook(p WebhookParameters) (*Webhook, error) {
wh := &Webhook{
...
}
...
if p.Mux != nil {
p.Mux.HandleFunc("/inject", wh.serveInject)
mux = p.Mux
} else {
wh.server = &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%v", p.Port),
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{GetCertificate: wh.getCert},
}
mux = http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/inject", wh.serveInject)
wh.server.Handler = mux
}
...
}
Initializing Webhook The instance will be registered /inject The corresponding processor , That is to say apiserver Callback /inject When requested, it will call serveInject In the method .
And then we went into serveInject In the method :
file location :pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go
func (wh *Webhook) serveInject(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
totalInjections.Increment()
var body []byte
if r.Body != nil {
// Read request body
if data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body); err == nil {
body = data
}
}
...
var reviewResponse *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse
ar := v1beta1.AdmissionReview{}
// Decode request body
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, &ar); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not decode body: %v", err))
reviewResponse = toAdmissionResponse(err)
} else {
// Decode successful call inject Method , And pass in AdmissionReview
reviewResponse = wh.inject(&ar)
}
// structure AdmissionReview Returned to the caller as an argument
response := v1beta1.AdmissionReview{}
if reviewResponse != nil {
response.Response = reviewResponse
if ar.Request != nil {
response.Response.UID = ar.Request.UID
}
}
resp, err := json.Marshal(response)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not encode response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not encode response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
if _, err := w.Write(resp); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not write response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not write response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}
This method is very simple , The main thing is to read the request body and decode it , And then call inject Method , structure AdmissionReview Returned to the caller as an argument .
The main logic can be seen from here inject Method inside , Let's take a look at this method :
func (wh *Webhook) inject(ar *v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse {
req := ar.Request
var pod corev1.Pod
//json Deserialize request data
if err := json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &pod); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not unmarshal raw object: %v %s", err,
string(req.Object.Raw)))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
...
// Encapsulate template data
spec, iStatus, err := InjectionData(wh.Config.Template, wh.valuesConfig, wh.sidecarTemplateVersion, typeMetadata, deployMeta, &pod.Spec, &pod.ObjectMeta, wh.meshConfig.DefaultConfig, wh.meshConfig) // nolint: lll
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Injection data: err=%v spec=%v\n", err, iStatus))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
...
// What will need to be injected is istio-init/istio-proxy container Encapsulated into patch operation
// You can see it here :https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/extensible-admission-controllers/#response
patchBytes, err := createPatch(&pod, injectionStatus(&pod), annotations, spec, deployMeta.Name)
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("AdmissionResponse: err=%v spec=%v\n", err, spec))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
log.Debugf("AdmissionResponse: patch=%v\n", string(patchBytes))
// Will need patch The configuration of is packaged as AdmissionResponse return
reviewResponse := v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
Patch: patchBytes,
PatchType: func() *v1beta1.PatchType {
pt := v1beta1.PatchTypeJSONPatch
return &pt
}(),
}
totalSuccessfulInjections.Increment()
return &reviewResponse
}
inject Method logic is divided into the following steps :
- json Deserialize request data to pod in ;
- call InjectionData Encapsulate the data according to the template , It's mainly the structure istio-init、istio-proxy Wait for container configuration ;
- call createPatch Method to convert template data into json form , When the container is created, it will patch To create the container configuration , You can see it here :https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/extensible-admission-controllers/#response
- Finally, encapsulate the data into AdmissionResponse return ;
summary
This article focuses on Sidecar Container injection implementation principle , By using k8s Access controller to do in each new pod There's no perceptual creation in it sidecar Do traffic hosting .
Reference
https://github.com/istio/istio.io/blob/release-1.1/content/blog/2019/data-plane-setup/index.md
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/extensible-admission-controllers/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/
https://jimmysong.io/blog/envoy-sidecar-injection-in-istio-service-mesh-deep-dive/