1. Classical code
1.1 Substitution method
Single label replacement : Plaintext 、 Ciphertext uses the same table
Multiple table replacement :
1.2 Shift method
Move the letters according to their position in the alphabet
Caesar code
Code implementation : link
1.3 Decrypt
Frequency analysis
Guess without knowing the secret key , for example :E Highest probability of occurrence
2. Modern cryptography
Enigma Cipher machine : Machine level “ displacement ”、“ Replace ”
3. Modern cryptography
3.1 Hash function
Hash function 、 Digital summary 、 A summary of the news
Is the only value corresponding to the fixed length of a message or text , By one way Hash Encryption functions act on messages to produce
The values generated using a digital digest are not tamperable , Keep the original documents safe
Common algorithms :
MD5: Generate any length text into a 128 Bit hash value
SHA-1: Generate any length text into a 160 Bit hash value
SHA-256
SHA-512
3.2 Symmetric encryption
Stream encryption ( Sequence code )
Block encryption ( Group password ):
DES and AES
3.3 Asymmetric encryption
Common algorithms :
RSA
ECC
4. Base64
Reference resources : link
One Chinese corresponds to three bytes , But the encoding format is different , The corresponding bytes are not the same (UTF-8:3 Bytes 、GBK: Two bytes )
base64: Objective to enhance readability
from 64 Characters make up : Capital A - Z, Lowercase letters :a - z, Numbers :0 - 9, Two symbols :+ and /
Base58: For bitcoin , It's a way of encoding bitcoin
There are no numbers 0, There are no lower case letters o and i, No capital letters I, There are no two symbols
4.1 principle
Three bytes in a group , A byte 8 position , If at output , Not enough 3 Bytes , Then use = A filling
base64 Convert three bytes to 4 Group , Each group 6 position
A byte 8 position , The lack of 2 position , Make up at the highest position ( repair 0)
base64 After taking 6 position , front 2 Let go of your position , You can put base64 Control in 0~63 Between
4.2 give an example
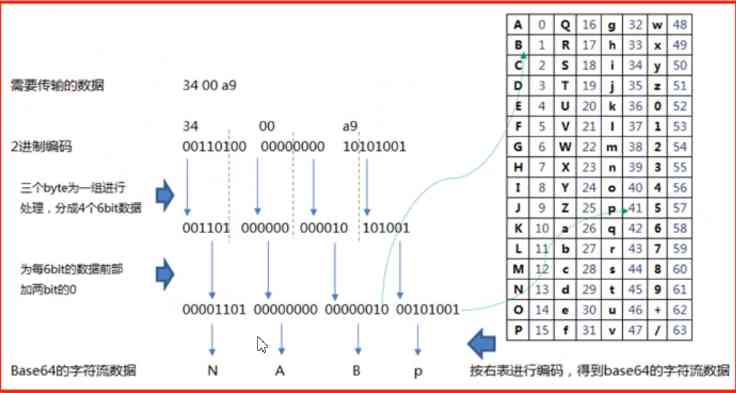
5. Encryption mode
5.1 ECB
Electronic codebook , The message to be encrypted is divided into several blocks according to the block size of block cipher , Each block is encrypted independently
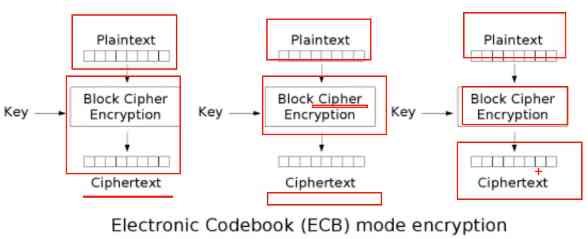
advantage : It can be processed in parallel
shortcoming : The same plaintext generates the same ciphertext , Weak confidentiality
5.2 CBC
Cipher block link , Each plaintext block is XOR with the previous ciphertext block first and then , Then encrypt , Each ciphertext block depends on all previous plaintext blocks
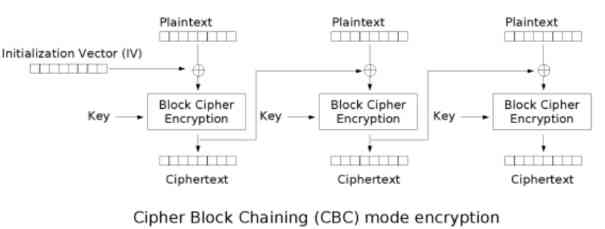
shortcoming : Encryption speed is slow , Depending on the previous plaintext , There is an error transmission