当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of binary search tree
Implementation of binary search tree
2022-07-07 03:56:00 【Wuhu kaichong ~】
Be careful : This article adopts c++, stay vs2022 Bottom debugging
Catalog
Binary search tree node implementation
Property setting of binary search tree
Deletion of binary search tree
Of binary search trees Find function
Middle order traversal of binary search tree
Binary search tree concept
Binary search tree is also called binary sort tree , It could be an empty tree , Or a binary tree with the following properties :
If its left subtree is not empty , Then the values of all nodes on the left subtree are smaller than the values of the root nodes
If its right subtree is not empty , Then the value of all nodes on the right subtree is greater than the value of the root node
Its left and right subtrees are also binary search trees
To put it bluntly , It is a sort tree , Its left sub tree is smaller than it , The right subtree is bigger than it , So it happens to be an ordered sequence after the sequence traversal
Binary search tree node implementation
Here is the node implemented by the template method , Each value of a node is a key value pair
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode {
BSTreeNode(const K& key = K(), const V& value = V())
:_val(key, value)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
{}
BSTreeNode* _left;
BSTreeNode* _right;
pair<K, V> _val;
};Property setting of binary search tree
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
Node* _root = nullptr;Binary search tree insertion
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) {
Node* cur = new Node(key, value);
// Empty tree
if (_root == nullptr) {
_root = cur;
return true;
}
// Non empty
// look for cur Insertion position
Node* prev = cur; // Save it cur Value
cur = _root;
Node* parent = _root;
while (cur) {
if (key > parent->_val.first) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < parent->_val.first) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Found the location of the parent node , Insert
cur = prev;
if (cur->_val.first > parent->_val.first) {
parent->_right = cur;
}
else {
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}Deletion of binary search tree
The deletion of binary search tree can be divided into four cases , The node to be deleted is a leaf node , Only the left child , Only the right child , Both the left and right children have ,
among , If the node to be deleted is a leaf node, it can be merged with only the left child or only the right child , Then there are only three cases ,
Only the left child and only the right child are easy to say , Just pass on its children to their parents , The difficulty is that both left and right children have , Then you can only find a replacement node , This replacement node is usually the largest in its left subtree ( The most right ) Or the smallest node in the right subtree ( Leftmost left ) That node of , Put the value of that node in the node to be deleted , Then delete that node
bool Erase(const K& key) {
if (_root == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// Find node
Node* delnode = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (delnode) {
if (delnode->_val.first == key) {
break;
}
else if (delnode->_val.first > key) {
parent = delnode;
delnode = delnode->_left;
}
else {
parent = delnode;
delnode = delnode->_right;
}
}
// I didn't find it
if (delnode == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// There are only right subtrees or leaf nodes
if (delnode->_left == nullptr) {
if (parent == nullptr) {
_root = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
else {
if (delnode == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
else {
parent->_right = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
}
}
// Only the left sub tree
else if (delnode->_right == nullptr) {
// If delnode yes _root node
if (parent == nullptr) {
_root = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
else {
if (delnode == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
else {
parent->_right = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
}
}
// There are... In both the left and right subtrees
else {
Node* firstinorder = delnode->_right;
parent = delnode;
// It's not easy to delete directly , Find a replacement node
while (firstinorder->_left) {
parent = firstinorder;
firstinorder = firstinorder->_left;
}
// Replace the node val Assign a value to delnode, Then delete the replacement node
delnode->_val = firstinorder->_val;
if (firstinorder == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = firstinorder->_right;
}
else {
parent->_right = firstinorder->_right;
}
delete firstinorder;
return true;
}
}Of binary search trees Find function
Node* Find(const K& key) {
return _Find(_root, key);
}
Node* _Find(const Node* root, const K& key) {
if (key == root->_val.first) {
return root;
}
Node* cur = _Find(root->_left, key);
if (cur) {
return cur;
}
cur = _Find(root->_right, key);
if (cur) {
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}Middle order traversal of binary search tree
void InOrder() {
_InOrder(_root);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
cout << root->_val.first << ":" << root->_val.second << endl;
_InOrder(root->_left);
_InOrder(root->_right);
}The overall code
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode {
BSTreeNode(const K& key = K(), const V& value = V())
:_val(key, value)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
{}
BSTreeNode* _left;
BSTreeNode* _right;
pair<K, V> _val;
};
// Appointment ,value There's not the same
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) {
Node* cur = new Node(key, value);
// Empty tree
if (_root == nullptr) {
_root = cur;
return true;
}
// Non empty
// look for cur Change the insertion position
Node* prev = cur;
cur = _root;
Node* parent = _root;
while (cur) {
if (key > parent->_val.first) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < parent->_val.first) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
cur = prev;
if (cur->_val.first > parent->_val.first) {
parent->_right = cur;
}
else {
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key) {
return _Find(_root, key);
}
bool Erase(const K& key) {
if (_root == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// Find node
Node* delnode = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (delnode) {
if (delnode->_val.first == key) {
break;
}
else if (delnode->_val.first > key) {
parent = delnode;
delnode = delnode->_left;
}
else {
parent = delnode;
delnode = delnode->_right;
}
}
// I didn't find it
if (delnode == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// There are only right subtrees or leaf nodes
if (delnode->_left == nullptr) {
if (parent == nullptr) {
_root = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
else {
if (delnode == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
else {
parent->_right = delnode->_right;
delete delnode;
}
}
}
// Only the left sub tree
else if (delnode->_right == nullptr) {
if (parent == nullptr) {
_root = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
else {
if (delnode == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
else {
parent->_right = delnode->_left;
delete delnode;
}
}
}
// There are... In both the left and right subtrees
else {
Node* firstinorder = delnode->_right;
parent = delnode;
// It's not easy to delete directly , Find a replacement node
while (firstinorder->_left) {
parent = firstinorder;
firstinorder = firstinorder->_left;
}
// Replace the node val Assign a value to delnode, Then delete the replacement node
delnode->_val = firstinorder->_val;
if (firstinorder == parent->_left) {
parent->_left = firstinorder->_right;
}
else {
parent->_right = firstinorder->_right;
}
delete firstinorder;
return true;
}
}
void InOrder() {
_InOrder(_root);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
cout << root->_val.first << ":" << root->_val.second << endl;
_InOrder(root->_left);
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _Find(const Node* root, const K& key) {
if (key == root->_val.first) {
return root;
}
Node* cur = _Find(root->_left, key);
if (cur) {
return cur;
}
cur = _Find(root->_right, key);
if (cur) {
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
边栏推荐
- QT item table new column name setting requirement exercise (find the number and maximum value of the array disappear)
- Top 50 hit industry in the first half of 2022
- MySQL storage engine
- tflite模型转换和量化
- opencv第三方库
- VHDL implementation of arbitrary size matrix addition operation
- Hongmi K40S root gameplay notes
- Depth analysis of compilation constants, classloader classes, and system class loaders
- PHP lightweight Movie Video Search Player source code
- Codeworks 5 questions per day (1700 average) - day 7
猜你喜欢

23. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS ellipse collection (sketchviewmodel)
卡尔曼滤波-1
Optimization cases of complex factor calculation: deep imbalance, buying and selling pressure index, volatility calculation

Leetcode: interview question 17.24 Maximum cumulative sum of submatrix (to be studied)
Docker部署Mysql8的实现步骤
10 ways of interface data security assurance
GPT-3当一作自己研究自己,已投稿,在线蹲一个同行评议
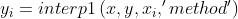
Preprocessing - interpolation
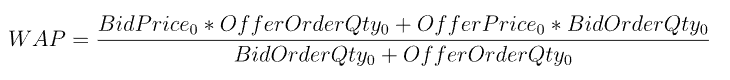
复杂因子计算优化案例:深度不平衡、买卖压力指标、波动率计算

Restcloud ETL Community Edition June featured Q & A
随机推荐
.net中 接口可以有默认实现了
自适应非欧表征广告检索系统AMCAD
Class常量池与运行时常量池
维护万星开源向量数据库是什么体验
Baidu map JS development, open a blank, bmapgl is not defined, err_ FILE_ NOT_ FOUND
1200.Minimum Absolute Difference
QT opens a file and uses QFileDialog to obtain the file name, content, etc
代码质量管理
Ggplot facet detail adjustment summary
OSCP工具之一: dirsearch用法大全
HW-小记(二)
如何自定义Latex停止运行的快捷键
10 ways of interface data security assurance
Restcloud ETL Community Edition June featured Q & A
List interview common questions
codeforces每日5题(均1700)-第七天
CMB's written test - quantitative relationship
About Tolerance Intervals
map和set的实现
20. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS surface collection (sketchviewmodel)