当前位置:网站首页>The difference between GDI and OpenGL
The difference between GDI and OpenGL
2020-11-09 01:10:00 【shzwork】
GDI+ Introduction to :
GDI+ yes Windows XP A subsystem of , It is mainly responsible for the output of relevant information on the display screen and printing device .
It's a group through C++ Class implementation of the application programming interface .
GDI+ To the old Windows In the version GDI optimized , And added a lot of new features . As a graphical device interface GDI+ It enables application developers to output screen and printer information without considering the details of the specific display device , They just call GDI+ Library output class of some methods can complete the graphic operation .
GDI+ How to use :
In the use of GDI+ Of cpp The file contains GdiPlus.h file , And reference the namespace , The code is as follows :
#include <GdiPlus.h>
using namespace Gdiplus;
In project properties , In the linker's input options , Add additional dependencies :gdiplus.lib
GDI+ To initialize :
// GDI+ Resource initialization
ULONG_PTR uToken = 0;
GdiplusStartupInput gdiplusStartupInput;
GdiplusStartup(&uToKen,&gdiplusStartupInput,NULL);
De initialization code :
// The destruction GDI+ resources
GdiplusShutdown(uToken);
GDI+ Color system :
Transparency composition operation :
Transparency is a compositing operation between pixels . Calculation formula :
output color = The foreground *Alpha/255+ Background color *(255-Alpha)/255
such as :ARGB(100,0,0,0)
Background color rgb(255,255,255);
output color (155,155,155);
Bitmap Class construction :
Bitmap(const WCHAR *filename);
// Construct a... From the file name of the image Bitmap object
Bitmap(INT width,INT height,PixelFormat format=PixelFormat32bppARGB);
// By the width of the bitmap , Height , Pixel format to construct an empty Bitmap object , among format The default value of is PixelFormat32bppARGB, representative 32 Bit color information , The color composition is A,R,G,B. There's a lot more in pixel format ,
such as PixelFormat24bppRGB representative 24 Bit color information , The color composition is R,G,B, such as PixelFormat16bppRGB, representative 16 Bit color information , The color composition is R,G,B among R Occupy 5 position ,G Occupy 6 position ,B Occupy 5 position .
Bitmap Common methods of class :
Bitmap* Clone(
[in, ref] const Rect &rect,
[in] PixelFormat format
);
Bitmap* Clone(
[in, ref] const RectF &rect,
[in] PixelFormat format
);
Bitmap* Clone(
[in] REAL x,
[in] REAL y,
[in] REAL width,
[in] REAL height,
[in] PixelFormat format
);
Bitmap* Clone(
[in] INT x,
[in] INT y,
[in] INT width,
[in] INT height,
[in] PixelFormat format
);
The above four methods are Bitmap How to copy , Copy the new bitmap object from the specified area of the source bitmap , And use format Pixel format applied to the new Bitmap In the object .
UINT GetWidth(): Get the width of the bitmap
UINT GetHeight():
GetPixel(INT x,INT y,Color *color);
// Get the color of the specified location
SetPixel(INT x,INT y,const Color &color);
Common brush :
1). SolidBrush: Monochrome brush ;
SolidBrush(const Color &color);
SolidBrush blueBrush(Color(255,0,0,255));
2). HatchBrush: Shadow brush ;
HatchBrush(
[in] HatchStyle hatchStyle,
[in, ref] const Color &foreColor,
[in, ref] const Color &backColor
);
hatchStyle: The type of shadow brush
3). TextureBrush: Texture brush
TextureBrush(
[in] Image *image,
[in] wrapMode wrapMode,
[in, ref] const RectF &dstRect
);
...
4). LinearGradientBrush: Linear gradient brush
LinearGradientBrush(
[in, ref] const PointF &point1,
[in, ref] const PointF &point2,
[in, ref] const Color &color1,
[in, ref] const Color &color2
);
point1: The starting point coordinates of the gradient ;
point2: The coordinates of the end of the gradient ;
color1: The color of the starting point
color2: For the color of the end
Pen Create a brush
Pen(const Color &color,REAL width=1.0f);
// color For the color of the brush ,width For the brush width
Pen(const Brush *brush,REAL width=1.0f);
Graphics Drawing pictures :
DrawImage:
Graphics::DrawImage(Image*,Point*,INT)
Graphics::DrawImage(Image*,INT,INT)
Graphics::DrawImage(Image*,Point&)
..
Graphics Draw text :
Graphics::DrawString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,RectF&,StringFormat*,Brush*)
Graphics::DrawString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,PointF&,Brush*)
Graphics::DrawString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,PointF&,StringFormat*,Brush*)
Draw text sample code :
{Gdiplus::Font myFont(L"Arial",10);SolidBrush brushA(Color(255,0,0,255));graphics.DrawString(L" Sample text ",-1,&myFont,PointF(200,575),&brushA);
}
The following is the string drawing code with text output format :
{Gdiplus::Font myFont(L"Arial",16);RectF layout(0,0,500.0f,200.0f);// Set alignment ( align horizontal center )StringFormat format;format.SetAlignment(StringAlignmentCenter);SolidBrush brushB(Color(255,0,0,255));graphics.DrawString(L" Sample text ",-1,&myFont,layout,&format,&brushB);}
MeasureString Measuring strings :
Graphics::MeasureString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,RectF&,RectF*)
Graphics::MeasureString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,PointF&,StringFormat*,RectF*)
Graphics::MeasureString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,RectF&,StringFormat*,RectF*,INT*,INT*)
Status MeasureString(
[in] const WCHAR *string,
[in] INT length,
[in] const Font *font,
[in, ref] const RectF &layoutRect,
[in] const StringFormat *stringFormat,
[out] RectF *boundingBox,
[out] INT *codepointsFitted,
[out] INT *linesFilled
) const;
Graphics::MeasureString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,SizeF&,StringFormat*,SizeF*,INT*,INT*)
Status MeasureString(
[in] const WCHAR *string,
[in] INT length,
[in] const Font *font,
[in, ref] const SizeF &layoutRectSize,
[in] const StringFormat *stringFormat,
[out] SizeF *size,
[out] INT *codepointsFitted,
[out] INT *linesFilled
) const;
Graphics::MeasureString(WCHAR*,INT,Font*,PointF&,RectF*)
among
string For the string to be measured
length: The length of the string to measure ,-1 Indicates that the test is to NULL At the end of the string character string
Font: The font used for string output
layoutRect: Text output , Specified rectangular area
layoutRectSize: Text output , Specified dimensions
boundingBox For the measurement result , When all text is contained , The required rectangular area .
size: Measurement results , Represents the size required to hold all text .
codepointsFitted: Measurement results , Represents the number of characters that can be contained in a specified area
linesFilled: Measurement results , Indicates that in a specified area , The number of lines of characters it can hold
origin: Text output starting point
SetTrimming: String ending
SetTrimming(StringTrimming trimming);
StringTrimming enumeration :
None
Character
Word
EllipsisCharacter
EllipsisWord
EllipsisPath
Graphics Draw a straight line :
Graphics::DrawLine(Pen*,Point&,Point&)
Graphics::DrawLine(Pen*,PointF&,PointF&)
Graphics::DrawLine(Pen*,REAL,REAL,REAL,REAL)
Graphics::DrawLine(Pen*,INT,INT,INT,INT)
Graphics::DrawLines(Pen*,Point*,INT)
Graphics::DrawLines(Pen*,PointF*,INT)
Graphics Draw a rectangle ;
DrawRectangle()
Graphics Draw the circle :
Graphics Draw the pie :
DrawPie()
Graphics Filled rectangle :
FillRectangle()
FillPie()
GDI Device description table of DC And GDI+ Of Graphics The role and difference of :
1).DC( Device description table ), yes Windows A data structure used , It is used to store the property information about the ability of the device and how to redraw some items on the device . First you have to get a DC The handle of , How to draw graphics , Pass the handle as an argument to GDI Plot function . Of course, it can also be passed to get or set DC Functions about attributes .
2). utilize GDI+ function , You don't have to use a handle or DC, You can simply create a graphic object (Graphics), Call its method again , Such as myGraphicsObject.DrawLine(parameters).Graphics The object is GDI+ At the heart of , just as DC yes GDI At the core of . They play the same role in different environments , It plays a similar role . The difference : The former uses a handle based programming approach , The latter uses an object-oriented programming approach .
The difference in the use of drawing objects :
GDI: All drawing objects related to the drawing must be selected into the specified device description table ( Use SelectObject function ), To be designated DC Used by the .
GDI+: Before drawing , Pass the drawing object as a parameter to Graphics Call the method of graphic object .
GDI+ New features :
Gradient brushes :
Cardinal spline functions
Persistent path objects
Morphing and matrix objects
Scalable area (Regions)
Alpha blend
Multiple image formats support (BMP,JPEG,PNG,GIF,TIFF)
GDI And GDI+ Mixed programming
GDI+ stay GDI The device environment of DC Drawing graphics on :
Graphics gs(hDC)
GDI+ Will put the current hDC As the default target canvas , Then call Graphics Any function in will be drawn to hDC On , Of course, the completion of each function call is not immediately reflected in hDC in , Only when Graphics When a class is destructed , Will copy all the drawing contents to hDC in .
GDI stay GDI+ Drawing on the surface :
hDC=Graphic.GetHDC()
---------------------
This paper mainly solves two problems :
1、OpenGL What the hell is it ?
2、 How to create a using OpenGL The window of ?
1、OpenGL What the hell is it ?
The author is also a beginner C++ The programmer , Determined to learn OpenGL And then I went straight to Google OpenGL Its official website ( Of course, this is to cross the Great Wall ), Think about the next API Just go ahead . However, I slipped a lot on the official website , Leng is not found a download API The place of , On the other hand, it has been on the official websites of various graphic card manufacturers , gray .
After looking for a lot of information on the Internet , Finally I understand a little , This is also a very important point , Namely :OpenGL Not one API(API You should understand this , Anyone who does programming knows . what ? You said you're not programming ? Look at this article , Don't go out and turn right .) library , It's a set of norms , This set of specifications is made by Khronos Group For maintenance. .( Don't ask me. Khronos Group What the hell is it , For writers who can only write introductory text , This is also the first time to see .)
This set of specifications defines a set of functions , What parameters are passed in by this set of functions , What's coming out of it . Because it's just such a set of norms , So as long as it's up to standard , Anyone can implement functions in different ways . This means that you can't find it on the official website API The reason for the library , Usually these API It is implemented by the video card manufacturer . By the way , If installed VS,VS It comes with OpenGL The library of ( At least the author's VS2013 Are there in ).
State machine
OpenGL It's a big state machine in itself : There are many variables that can be set so that we can control their operation .OpenGL The state of is often referred to as context (context). We are operating OpenGL The time is to change the context of its operation by changing its state , such OpenGL We can get the results we want .
2、 How to create a using OpenGL The window of ?
2.1 The tools needed
GLFW library +VS2013+GLAD Source code
What are these things for .
GLFW Is an open source cross platform window Library , It encapsulates the process of creating windows related to the operating system , Let's create a window by calling a small number of functions .( Mom doesn't have to worry anymore that I won't create windows )
VS2013, forehead , Put together a word , You'll see
GLAD Source code is used to encapsulate calls OpenGL Of a function in a library , Let's call OpenGL Function time only needs to use the familiar function call way , There is no need to create a function pointer , Then load dll Function address in , Then call . It's a little abstract , Take an example . Originally, our code would look like this :
-
typedef void (*GL_GENBUFFERS)(GLsizei, GLuint*); -
GL_GENBUFFERS glGenBuffers = (GL_GENBUFFERS)wglGetProcAddress("glGenBuffers"); -
glGenBuffers(1, &buffer); // This is where the function is called , It's just getting the function address
With GLAD After the source , That's all we need to do :
glGenBuffers(1,&buffer); // The operation of getting function address is omitted
2.2 The environment creates :
First step : download GLFW
The official website address is :http://www.glfw.org/download.html( You need to climb over the wall to access )
Select download source file ,
Picture resources come from the Internet
The package name is glfw-3.2.1.zip
Or you can also go to my Baidu network disk to download , link :https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ceyucgFRYImnjmG-LmkuwA password :9smq
The second step : download CMake, compile glfw Source code
GLFW The source code needs to pass CMake Compiled , So we're going to download a CMake To use . don 't worry ,CMake It's very convenient to use .
The official website address is :https://cmake.org/download/( You also need to climb over the wall to access ), Download the latest version 3.9.3,windows 32 Bit version ,
Picture resources come from the Internet
Or you can also go to my Baidu network disk to download , link :http://pan.baidu.com/s/1clPRIm password :ct24
After installation , open CMake, Set it as follows
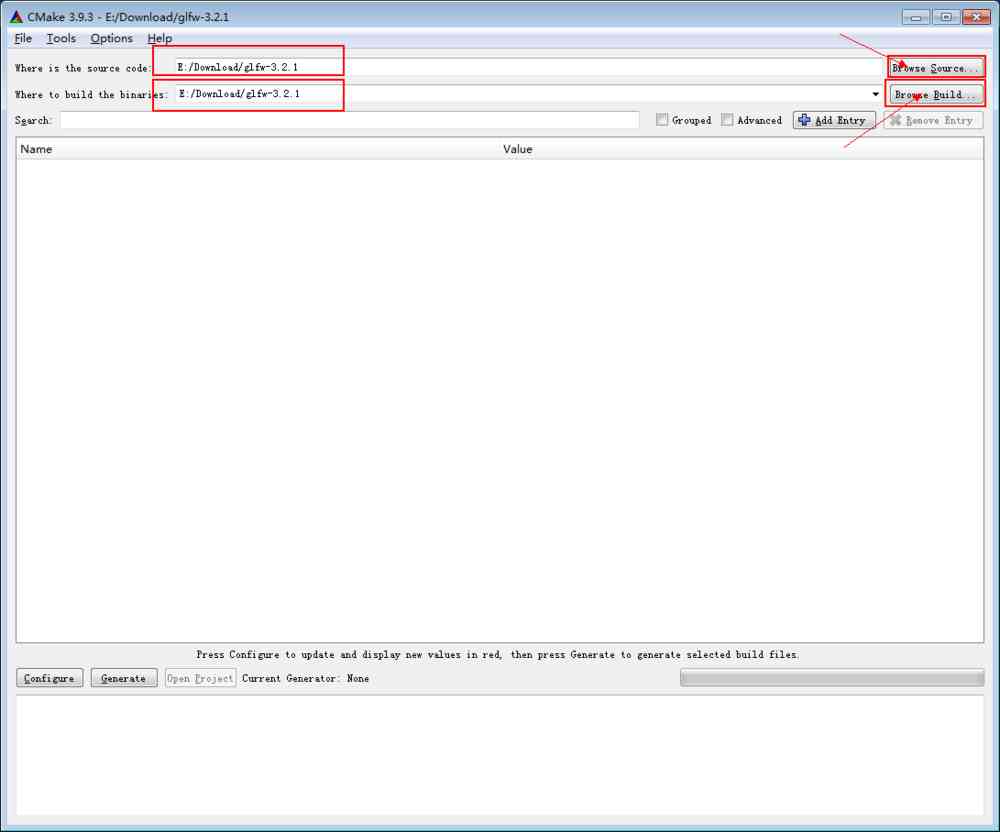
CMake Compile settings for
Set the directory of the source file and the compiled project file to be generated , Set it to the same directory . We set it to the root directory after decompression .
Click on the bottom left corner Configure Button , In the pop-up window, select compiler “Visual Studio 12 2013”, Here's the picture

Compiler settings
Click on “Finish”, After waiting for a while , The following interface appears

After setting up the compiler
Don't worry about anything , Click directly on the bottom left corner of Generate Button , After the very fast progress bar , Open and unzip GLFW The catalog of , You can see VS2013 Version of GLFW Engineering.

Generate the state of a good project
Some readers may have problems compiling , I don't know why , Here you can directly provide compiled library For your use .
The third step : download GLAD
Official website address :http://glad.dav1d.de/( Continue to turn ), Choose the version and mode you want
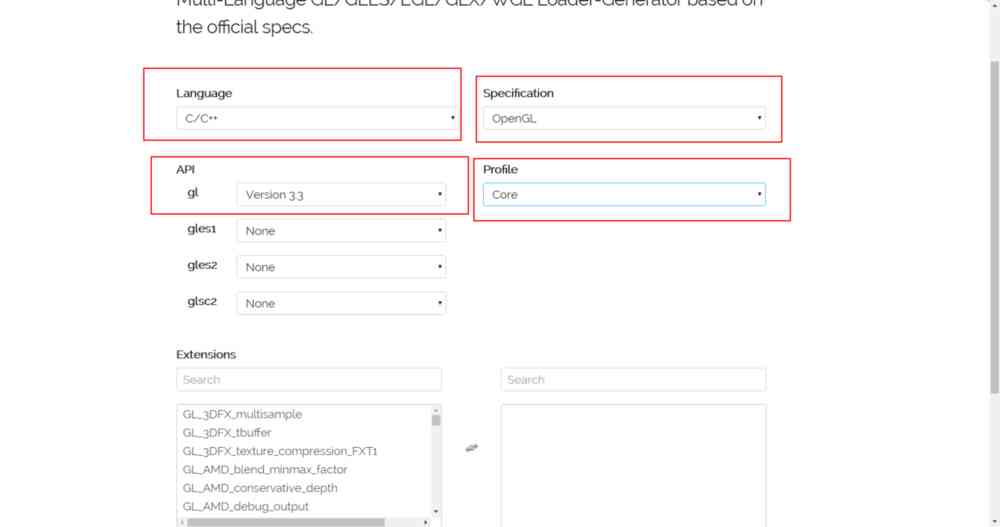
Choose the version to download
Click at the bottom right corner of the page GENERATE Button , In the page that pops up later , Click on glad.zip Download
download zip
Step four : Assembly Development Library Directory
Create a new folder , named OpenGL, take GLFW In the directory include Copy directory to OpenGL Go to the catalogue
stay OpenGL Create a new folder under the folder , named lib, Will be compiled GLFW Copy the library to lib Under the folder ,GLFW The location of the library is :glfw-3.2.1\src, The inside Debug and Release Two directories copy , copy to lib Under the folder .
Copy glad Unzip the folder ,include Two folders under the directory glad and KHR Copy , copy to OpenGL Under the table of contents ,include In the folder
When it's done , our OpenGL It's like this under the folder
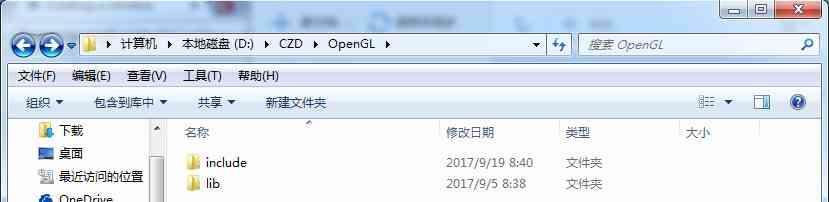
OpenGL Catalog
include It's like this under the folder
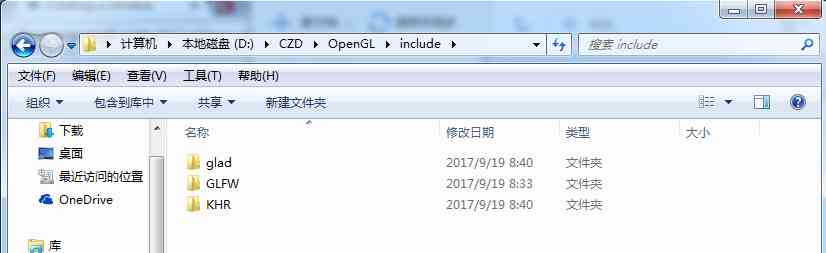
include Catalog
lib It's like this under the folder

lib Catalog
Step five : Create project , Set the path
use VS2013 Create a HelloWindow Empty project engineering , take glad Under folder glad.c Copy the file to the project , And will glad.c Files added to the project
Open project properties , choice VC++ Catalog tags , Set the include directory and Library Directory to the path we set before , Pictured
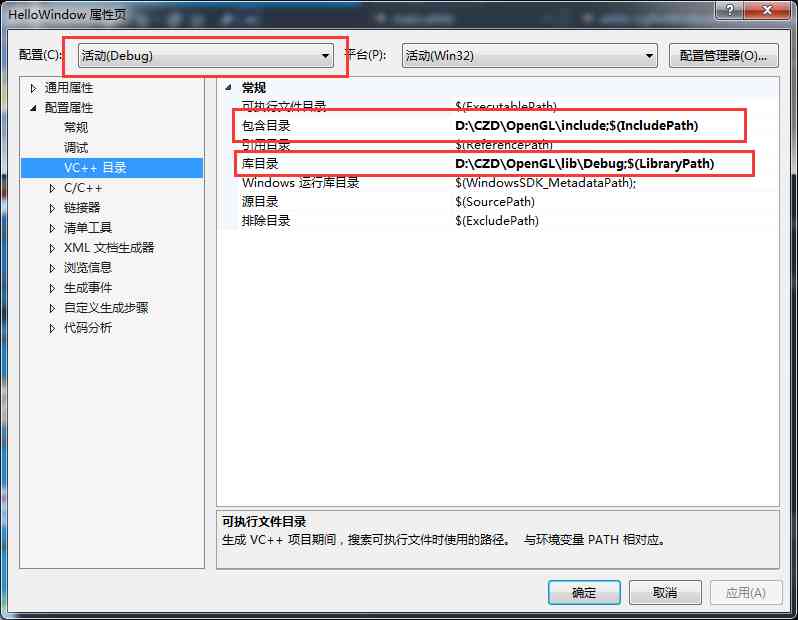
Project directory settings
Be careful debug It's set like this ,Release Specify the library directory to Release The catalogue will do
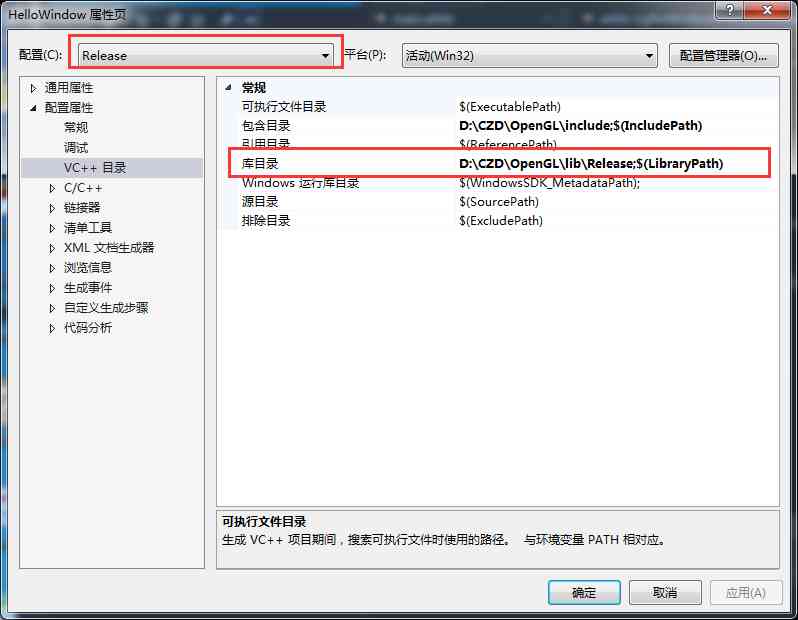
Release Directory settings
Click linker , Select input tag , Add... To additional dependencies opengl32.lib;glfw3.lib; two ,Debug and Release In mode, the name is the same
determine , In this way, our project setup is completed .
Step six : create a window
add to cpp file , named main.cpp, stay main Add the following code to the function
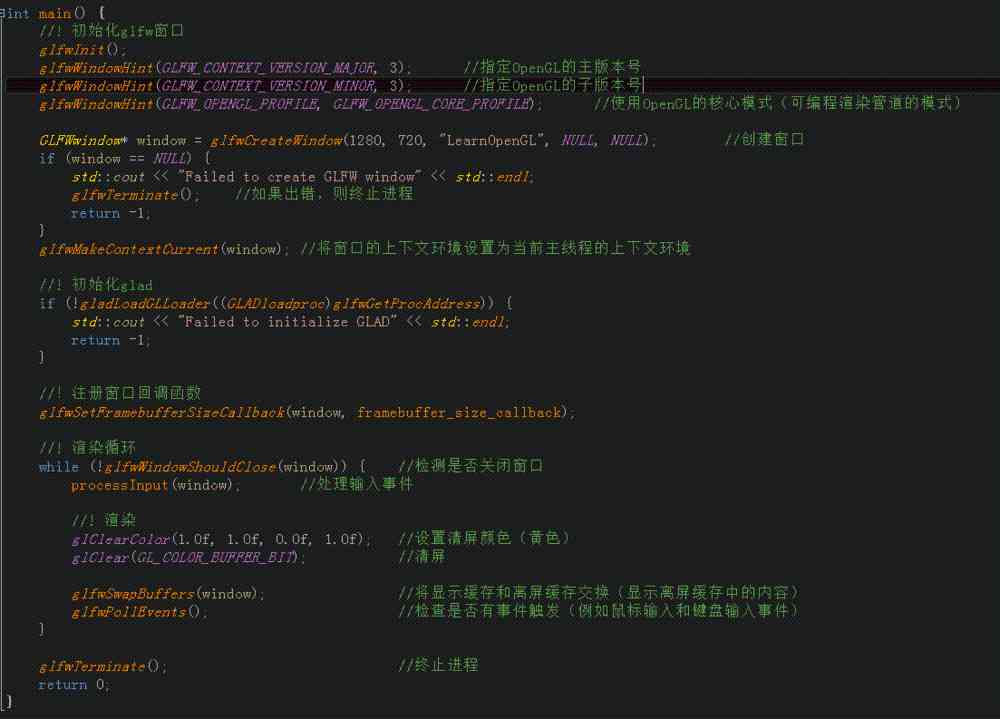
Main function code
among framebuffer_size_callback and processInput Are two functions that handle messages
framebuffer_size_callback Used when the window size changes , change OpenGL The size of the area of the viewport
processInput Function handles input events
The implementation of the two functions is as follows :
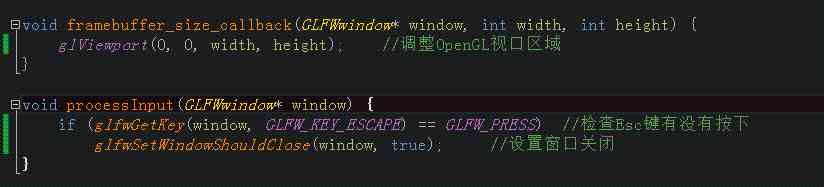
Sub function code
Compile the project , It works

Run the renderings
author : Lightning blue Panda
link :https://www.jianshu.com/p/d83a519ae2d0
source : Simple books
The author owns the copyright of Jianshu , For any reprint, please contact the author for authorization and indicate the source .
版权声明
本文为[shzwork]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- AQS 都看完了,Condition 原理可不能少!
- Travel notes of csp-s 2020
- Introduction skills of big data software learning
- Linked list
- How does pipedrive support quality publishing with 50 + deployments per day?
- Database design: paradigms and anti paradigms
- Realization of file copy
- 代码保存
- APP 莫名崩溃,开始以为是 Header 中 name 大小写的锅,最后发现原来是容器的错!
- Service grid is still difficult - CNCF
猜你喜欢

14.Kubenetes简介
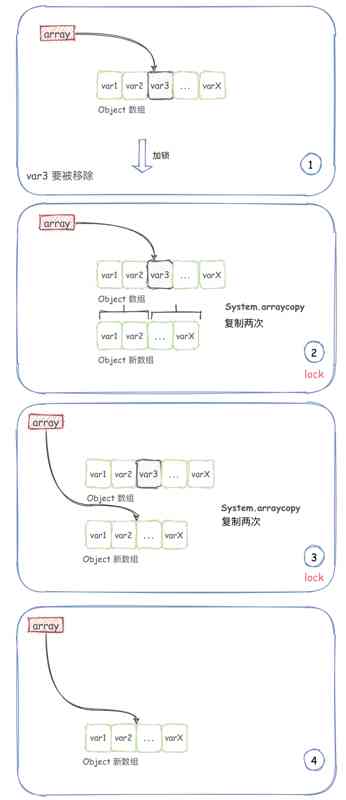
写时复制集合 —— CopyOnWriteArrayList
Installation record of SAP s / 4hana 2020

How to make scripts compatible with both Python 2 and python 3?

SaaS: another manifestation of platform commercialization capability
Programmers should know the URI, a comprehensive understanding of the article
LeetCode-11:盛水最多的容器
A few lines of code can easily transfer traceid across systems, so you don't have to worry about losing the log!

Operation 2020.11.7-8
基于链表的有界阻塞队列 —— LinkedBlockingQueue
随机推荐
为什么我们不使用GraphQL? - Wundergraph
c++11-17 模板核心知识(二)—— 类模板
leetcode之反转字符串中的元音字母
The road of cloud computing - going to sea - small goal: Hello world from. Net 5.0 on AWS
第五章编程
leetcode之反转字符串中的元音字母
How does FC game console work?
简单介绍c#通过代码开启或关闭防火墙示例
API部分的知识点复习
Copy on write collection -- copyonwritearraylist
1.操作系统是干什么的?
数据库设计:范式与反范式
Test comparison of three domestic cloud databases
Save code
服务网格仍然很难 - cncf
How to deploy pytorch lightning model to production
A few lines of code can easily transfer traceid across systems, so you don't have to worry about losing the log!
代码保存
写时复制集合 —— CopyOnWriteArrayList
大数据岗位基础要求有哪些?