当前位置:网站首页>6_ Gradient descent method
6_ Gradient descent method
2022-07-27 00:40:00 【Acowardintheworld】
6_ Gradient descent method (Gradient Descent)
Gradient descent method It is an important search strategy in the field of machine learning . In this chapter , We will explain the basic principle of gradient descent method in detail , Step by step to improve the gradient descent algorithm , Let's understand the parameters of gradient descent method , Especially the significance of learning rate .
meanwhile , We will also extend the random gradient descent method and the small batch gradient descent method , Let's have a comprehensive understanding of the gradient descent method family .…
6-1 What is gradient descent method



The derivative represents theta When the unit changes ,J Corresponding changes
Derivative can represent direction , Corresponding J Direction of increase





- Not all functions have unique extreme points ( Multivariate multiple function )



6-3 Gradient descent method in linear regression


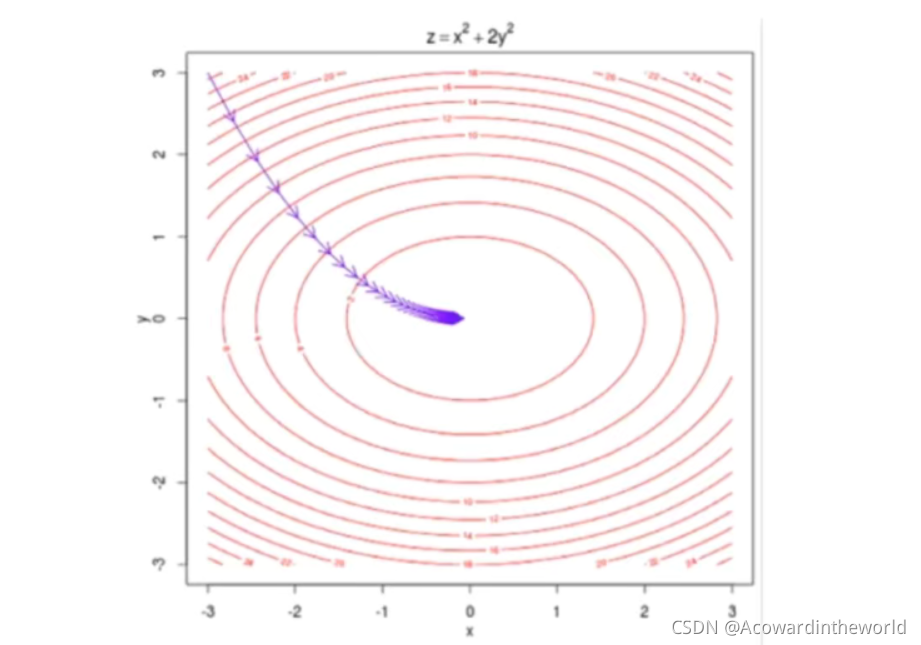

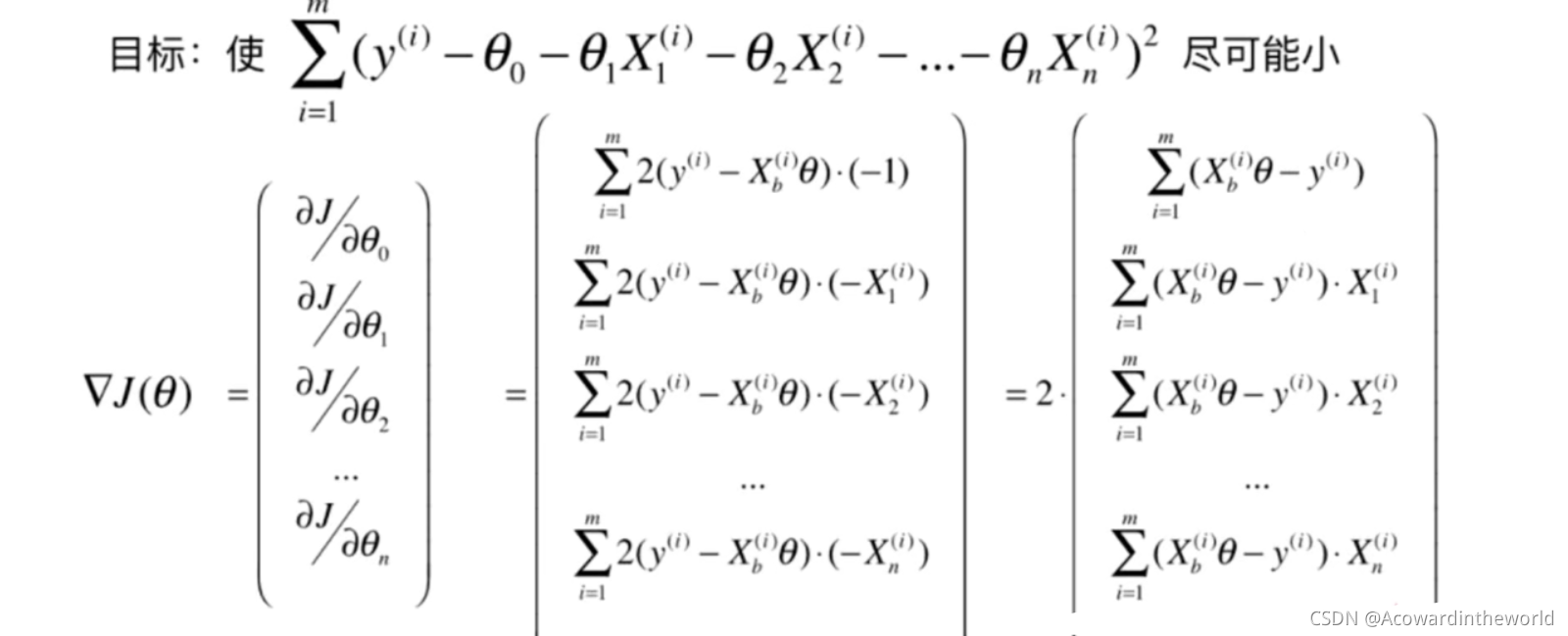
Because the size of the gradient is affected by the number of samples m influence , It's obviously unreasonable , So divide by the number of samples m, So that it is not affected by the number of samples .
6-4 The gradient descent method in linear regression is realized
6-5 Vectorization and data standardization of gradient descent method

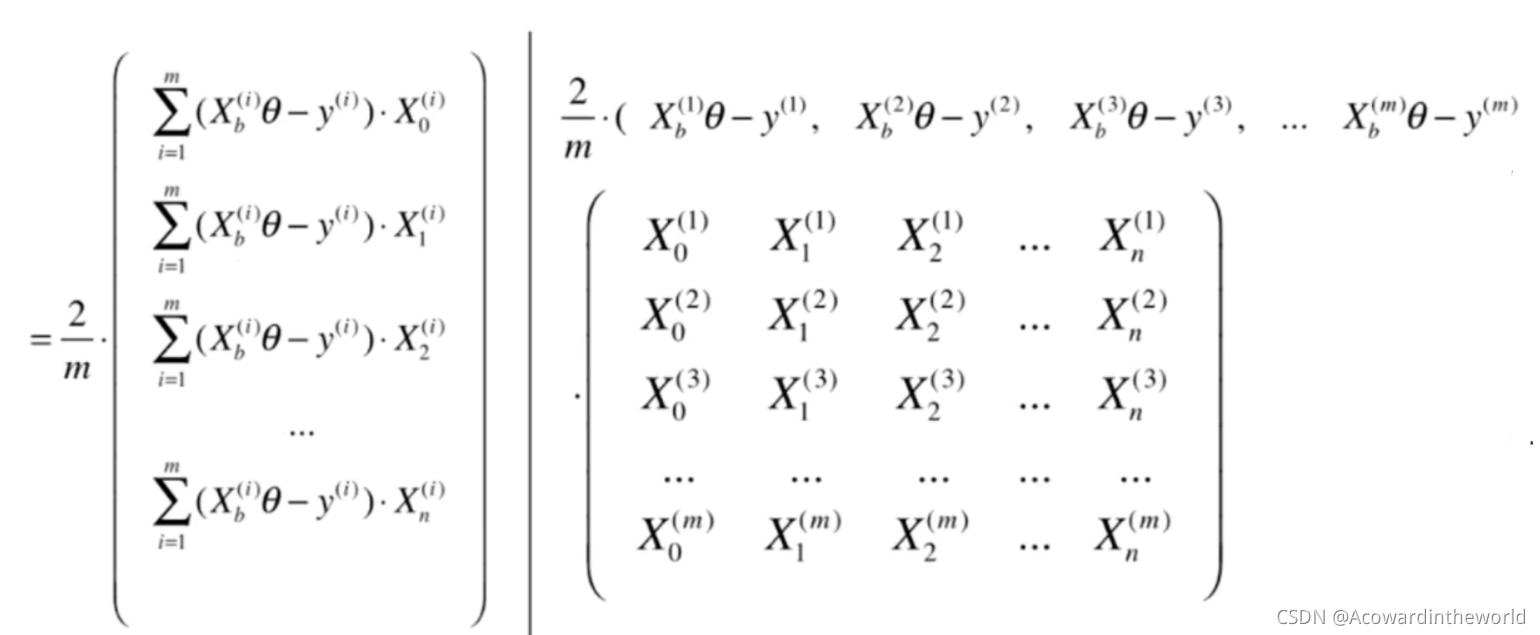


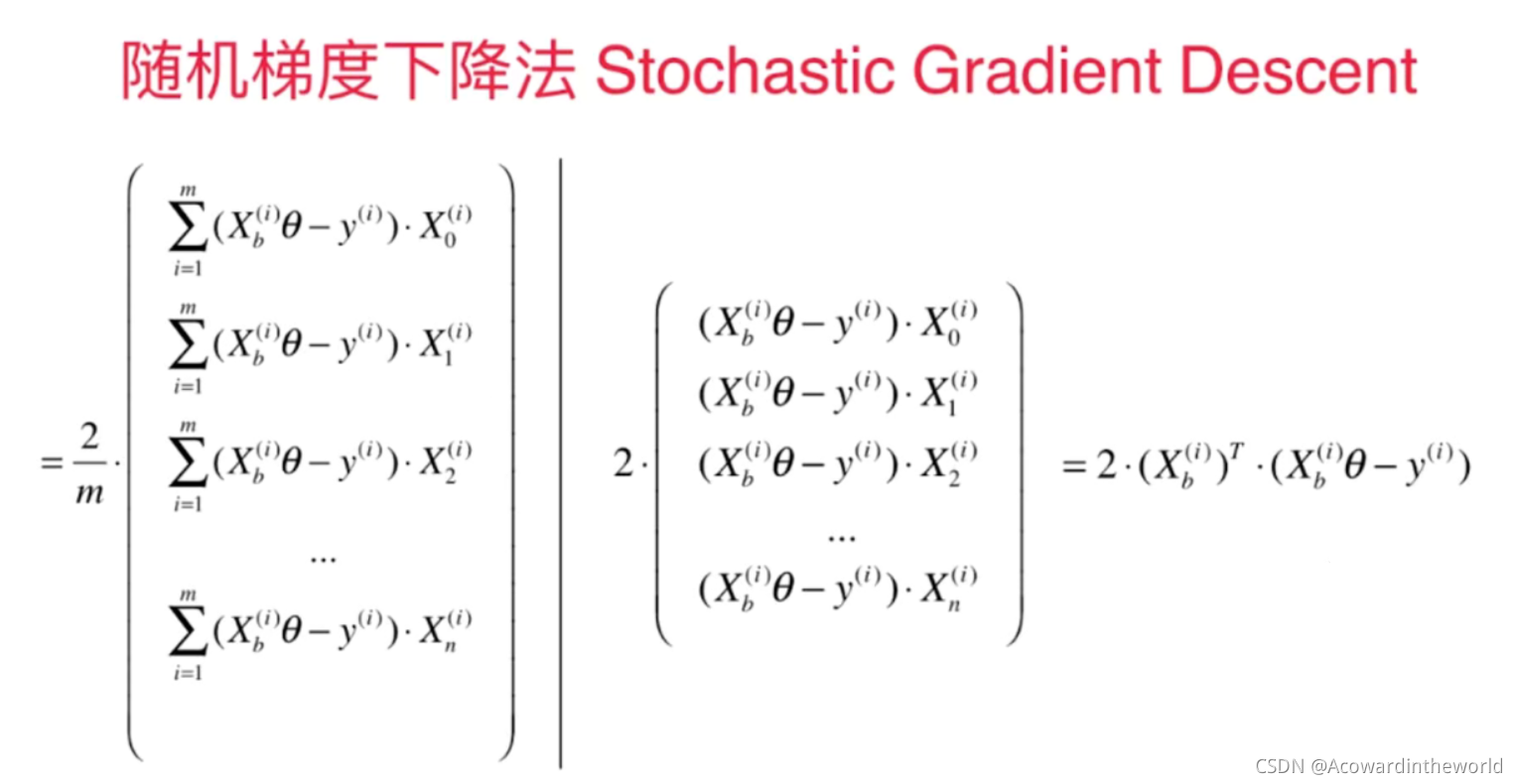
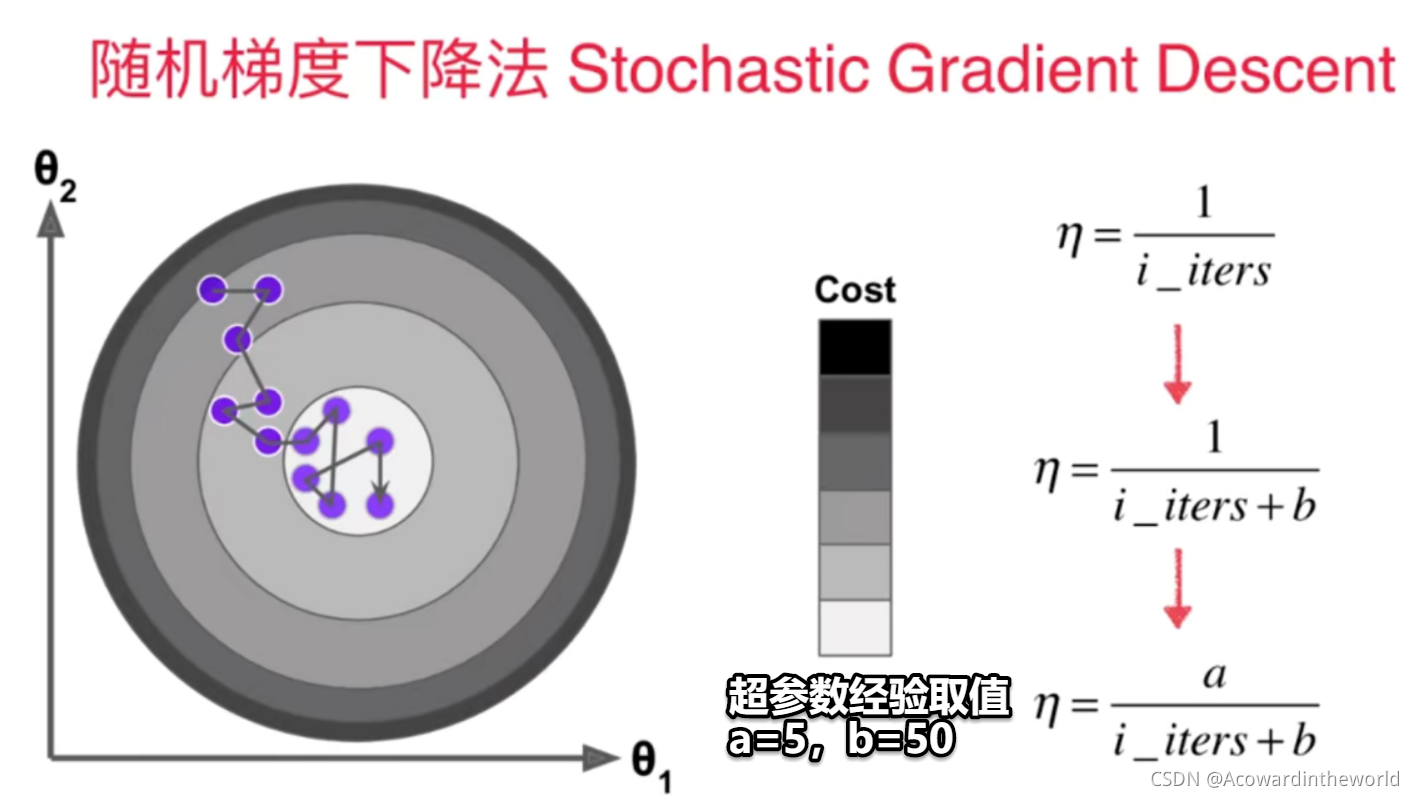
6-6 Random gradient descent method

- The idea of simulated annealing algorithm : Simulated annealing phenomena in nature , It makes use of the similarity between the annealing process of solid matter in physics and general optimization problems .
Start from a certain initial temperature , With the continuous decline of temperature , Combined with the characteristics of probabilistic jump, the global optimal solution is found randomly in the solution space
6-8 How to determine the accuracy of gradient calculation ? Debug gradient descent method


# ipynb The code on , No, print()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(666)
X = np.random.random(size = (1000,10))
true_theta = np.arange(1,12,dtype = float)
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X),1)),X] )
y = X_b.dot(true_theta) + np.random.normal(size = 1000)
print(X.shape)
print(y.shape)
print(true_theta)
def J(theta,X_b,y): # Define the loss function
try:
return np.sum((y-X_b.dot(theta))**2 ) / len(X_b)
except:
return float("inf")
def dJ_math(theta,X_b,y): # Define the gradient Mathematical formula calculation
return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y)*2. / len(y)
def dJ_debug(theta,X_b,y,epsilon=.01): # Define the gradient debug Calculation
res = np.empty(len(theta))
for i in range(len(theta)):
theta_1 = theta.copy()
theta_1[i] += epsilon
theta_2 = theta.copy()
theta_2[i] -= epsilon
res[i] = (J(theta_1,X_b,y) - J(theta_2,X_b,y))/(2*epsilon)
return res
def gradient_descent(dJ,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta=1e-2,epsilon=1e-8,n_iters=1e4):
theta = initial_theta
i_iters = 0
while i_iters < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta,X_b,y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta,X_b,y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y)))< epsilon:
break
i_iters += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack( ( np.ones((len(X),1)),X) )
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
eta = 0.01
%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_debug,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta)
theta
%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_math,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta)
theta
tip
dJ_debug Used to verify the debug gradient , Slower , A small number of samples can be taken dJ_debug Get the right results , Then use the formula to deduce the mathematical solution , Comparing the results .
dJ_debug Not affected by the current loss function J Influence , Finding the gradient is universal .
6-9 More in-depth discussion on gradient descent method

BGD: You need to traverse the entire sample every time , The direction of the fastest descent of each gradient must be , Stable but slow .
SGD: Only one sample at a time , The direction of gradient descent is uncertain , It may even move in the opposite direction , Fast but unstable .
MBGD: Compromise between two extreme methods , But every time k Samples ,k It also becomes a super parameter .



summary : Some related code can only be used in VSC function ,Jupyter Can't run , especially hstack() function .
边栏推荐
- MySQL common functions (summary)
- Drawing warehouse-2 (function image)
- Friend friend function and singleton mode
- Linux系统中安装Redis-7.0.4
- "Could not load host key" error when xshell connects to the server
- Web middleware log analysis script 2.0 (shell script)
- [acwing game 61]
- Fourier analysis (basic introduction)
- postman的使用
- In JS, the common writing methods and calling methods of functions - conventional writing, anonymous function writing, taking the method as an object, and adding methods to the object in the construct
猜你喜欢

继承,继承,继承

10_ Evaluate classification

Configure deeplobcut2 with your head covered

【 Educational Codeforces Round 132 (Rated for Div. 2) A·B·C】

c语言 static运用,灵活改变生命周期,让你写代码如鱼得水

CDs simulation of minimum dominating set based on MATLAB
![[3. Basic search and first knowledge of graph theory]](/img/a2/dced231f746cc049d310e364a81856.png)
[3. Basic search and first knowledge of graph theory]

Shufflenet series (2): explanation of shufflenet V2 theory

Knowledge distillation -- pytorch implementation

9_逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
随机推荐
Huffman encoding and decoding
放图仓库-3(功能图像)
[qt] attribute
Resolve Microsoft 365 and Visio conflicts
【4.7 高斯消元详解】
Crop TIF image
[2. TMUX operation]
并行MPI程序传递发送消息
torch.相关函数
12_ Decision tree
Matlab simulation of image reconstruction using filtered back projection method
2022-07-17:1, 2, 3... N-1, N, n+1, n+2... In this sequence, only one number has repetition (n). This sequence is unordered. Find the repeated number n. This sequence is ordered. Find the repeated numb
[4.10 detailed explanation of game theory]
【4.1 质数及线性筛】
Based on the theoretical principle and simulation results of MATLAB spherical decoding, compare 2norm spherical decoding, infinite norm spherical decoding, ML detection
V-viewer use
八皇后 N皇后
Uni app learning (II)
Dynamic binding, static binding, and polymorphism
Deployment of yolov5 on Jetson nano deepstream