当前位置:网站首页>Shell_ 03_ environment variable
Shell_ 03_ environment variable
2022-07-06 16:50:00 【Coke loving w】
Shell_03_ environment variable
environment variable
environment variable : Replace settings or retain data with a set of strings ( Stored in memory )
1) Environment variables are divided into : Global variables 、 local variable
Global and local variables are for parent / Son Shell The difference between :
1) Global variables for all Shell And his son Shell Can be called ;
2) A local variable can only be created by Shell call ;
Variable call form :${ Variable name }
1) Can also pass “$ Variable name ” Form call of
2) If you call the form of the specified value in the array variable :${ Variable name [ Index value ]}
When calling variables , Usable symbols :
| Symbol | explain |
|---|---|
| “ ” ( Double quotes ) | Enable the system to recognize variables Realize escape ( Such as :“/*”) |
| ‘ ’ ( Single quotation marks ) | Make the system unable to recognize variables Can't escape ( Only the contents of single quotation marks will be output as is ) |
| ` ` ( The quotation marks ) | Assign the data obtained after executing the command in the script to the variable Form the enclosed content into a complete expression |
| \ ( The backslash ) | Convert special symbols to general characters Put it in front of a special character to indicate escape |
set command : List the current shell All environment variables in the environment
Command format :set
1) Also list global variables 、 Local variables and user-defined variables ;
2) The order listed is alphabetical ;
Such as : Inquire about set Variables of the command prompt in the file 
| Symbol | meaning |
|---|---|
| \d | Show “ week month Japan ” Information |
| \H | Displays the full host name |
| \h | Display only the name before the first decimal point of the host name |
| \t | Display time 24 Hours “HH:MM:SS” The format of |
| \u | Displays the name of the current user |
| \v | Show BASH Version information |
| \w | Displays the complete current working directory name |
| \W | Only the last directory name of the current working directory is displayed |
| \# | Displays the number of commands executed by the current terminal |
| \$ | Display user identifier |
System variables
Bash Shell At system startup , Special environment variables will be created by default as system variables
1) The name of the system environment variable is all uppercase by default ( Distinguish user variables )
env command (environment): List the current system global variables
Command format :env
Such as : List the current system global variables 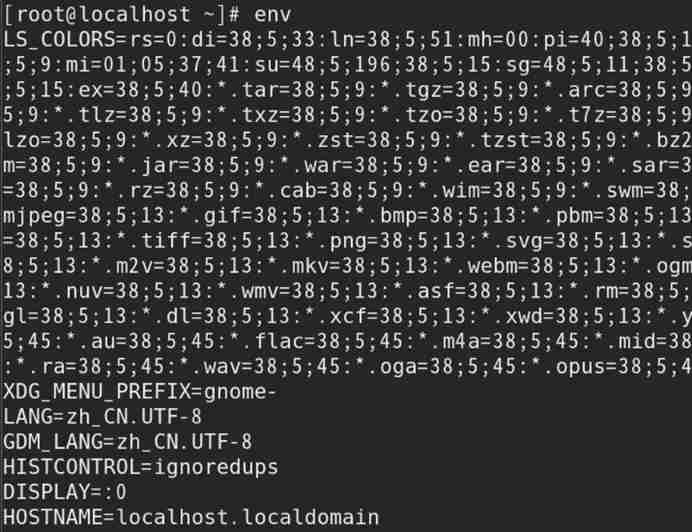
1) And export Command similar , but export Than env More content
common Bash Shell The environment variables are as follows :
| Variable name | explain |
|---|---|
| * | All command line arguments ( Single valued form ) |
| @ | All command line arguments ( Multivalued form ) |
| # | Number of command line arguments |
| ? | The last exit status code of the foreground process |
| - | The current command line option tag |
| $ | At present Shell The process of PID |
| ! | Of the recently executed background process PID |
| 0 | The command name used in the command line |
| _ | Shell The absolute pathname of |
| BASH | call Shell The absolute path of |
| BASHOPTS | Allow colon separated list form Shell Options |
| BASHPID | At present Bash Shell The process of ID |
| BASH_ALIASED | Array of currently used aliases |
| BASH_ARGC | The number of parameters in the subfunction |
| BASH_ARGV | Specify an array of command line parameters |
| BASH_CMDS | An array of internal hash tables of the command |
| BASH_COMMAND | The name of the command currently being executed |
| BASH_ENV | Shell Before the script runs , File executed by default |
| BASH_LINENO | Shell An array of line numbers for each command in the script |
| BASH_REMATCH | An array of text elements that match the specified regular expression |
| BASH_SOURCE | Shell Array of source file names where functions are declared in |
| BASH_SUBSHELL | At present Shell Generated sub Shell number |
| BASH_VERSINFO | At present Shell An array of major version numbers and minor version numbers of |
| BASH_VERSION | At present Shell Version number of |
| COLUMNS | At present Shell The width of the terminal |
| COMP_CWORD | Current cursor position |
| COMP_KEY | Key to call the completion function |
| COMP_LINE | The current command line |
| COMP_POINT | The index of the current cursor position relative to the starting position of the current command |
| COMP_TYPE | Complete the integer value corresponding to the intensity |
| COMP_WORDBREAKS | When completing words , Characters used as word separators |
| COMP_WORDS | An array of all words on the current command line |
| COMPREPLY | from Shell An array of possible completion codes generated by the function |
| COPROC | For anonymous Ctrip I/O Array of file descriptors |
| DIRSTACK | An array of the current contents of the directory stack |
| ENV | Shell With POSIX When the mode is called , File executed by default |
| EUID | The current user's valid UID |
| FCEDIT | fc The default editor used by the command |
| FIGNORE | Colon separated list of suffixes , Ignored in completion |
| FUNCNAME | Currently executed Shell The name of the function |
| FUNCNEST | The highest level of nested functions |
| GLOBIGNORE | File names in the colon delimited list of patterns are ignored when expanded |
| GROUPS | An array of groups to which the current user belongs |
| histchars | Control the characters of history expansion |
| HISTCMD | The number of the current command in history |
| HISTCONTROL | Control which commands remain in the history list |
| HISTFILE | preservation Shell The file name of the history list ( The default is ~/.bash_history) |
| HISTFILESIZE | The maximum number of lines saved in the history file |
| HISTIGNORE | Commands in the colon delimited pattern list are not saved in history |
| HISTSIZE | The maximum number of commands that can be recorded |
| HISTIMEFORMAT | The format string that determines the timestamp of the history file entry |
| HOSTFILE | Shell When completing the hostname , Read file name |
| HOSTNAME | Host name |
| HOSTTYPE | function Shell Terminal |
| IGNOREEOF | Shell On exit , Must receive continuous EOF The number of characters The default value is 1 |
| INPUTRC | readline initialization |
| LANG | Shell The language family of |
| LC_ALL | Shell Overall language environment ( Cover LANG) |
| LC_COLLATE | When sorting string values , The language family used |
| LC_CTYPE | When the file name extension matches the pattern , The language family used |
| LC_MESSAGES | Parsing prefix $ Double quoted string , The language family used |
| LC_NUMERIC | When formatting numbers , The language family used |
| LINENO | Shell The line number of the currently executing code in the script |
| LINES | Defines the number of rows visible on the terminal |
| MACHTYPE | “CPU- company - System ” Format definition system type |
| MAILCHECK | Shell Check the cycle of new messages ( The default is 60s) |
| OLDPWD | Shell Previous working directory |
| OSTYPE | function Shell Operating system of |
| PIPESTATUS | An array of foreground process exit status codes |
| POSIXLY_CORRECT | Bash Whether or not to POSIX mode |
| PPID | Bash Shell Parent process PID |
| PROMPT_COMMAND | Commands executed before the command line main prompt |
| PS1 | The string of the main prompt |
| PS2 | String of secondary prompt |
| PS3 | select Command prompt |
| PWD | working directory |
| RANDOM | return 0~32767 The random number |
| READLINE_LINE | preservation readline Contents of the line buffer |
| READLINE_POINT | At present readline The insertion point position of the row buffer |
| REPLY | read The default variable for the command |
| SECONDS | Shell Elapsed time ( second ) |
| SHELL | Shell The absolute path of |
| SHELLOPTS | Together with Bash Shell A list of options ( Colon separated ) |
| SHLVL | At present Shell Hierarchy |
| TIMEFORMAT | Shell Display the format of the time value |
| TMOUT | select and read Command without input , Waiting time |
| TMPDIR | Shell Directory of temporary files |
| UID | function Shell Users of UID |
Such as : Use $? Variables determine the execution of commands 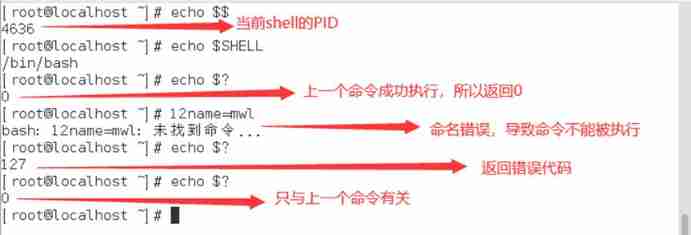
Shell Script default variables : The implementation is similar to Linux Options in built-in commands
The essence : Let the system pass options to commands through variables
Accept variables :
${0} // Order itself
${1} // First option
${2} // The second option
${N} // The first N An option
(1) Also available “$N” The form
1) But when N Greater than 9 when , You have to use “${N}” form
(2) among 3 Special system variables
1)$#: Number of parameters ( There are several options , be equal to N)
2)[email protected]: representative “$1” “$2” “$3” “$N”
3)$*: representative “$1 Separator $2 Separator $3 Separator $N”
Such as :test13.sh The script can accept three external options and output
1) To write test13.sh Script files 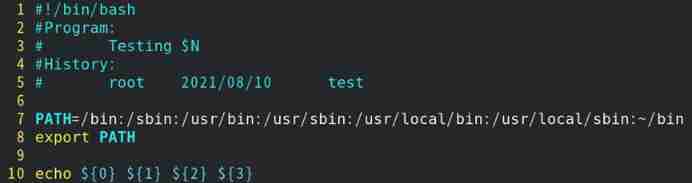
2) call test13.sh Script files 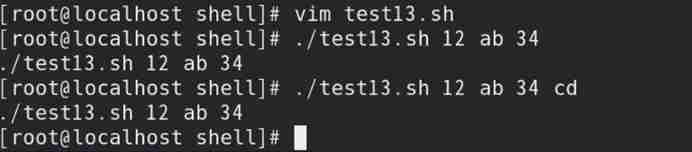
// If the passed in parameter contains spaces , Use double quotation marks
shift command : Parameter variable offset
Command format :shift N
1)N Is the number , Specify the number of offset digits ( If not specified N, The default offset is one digit )
2) The essence :$1 And the movement of subsequent variables ,$0 It's fixed
Such as : Use shift_paras.sh Script file printing 1、2、3、4、5、6
1) To write shift_paras.sh Script files 
2) call shift_paras.sh Script files 
Such as : The implementation script file can accept both options and parameters
1) To write test17.sh Script files 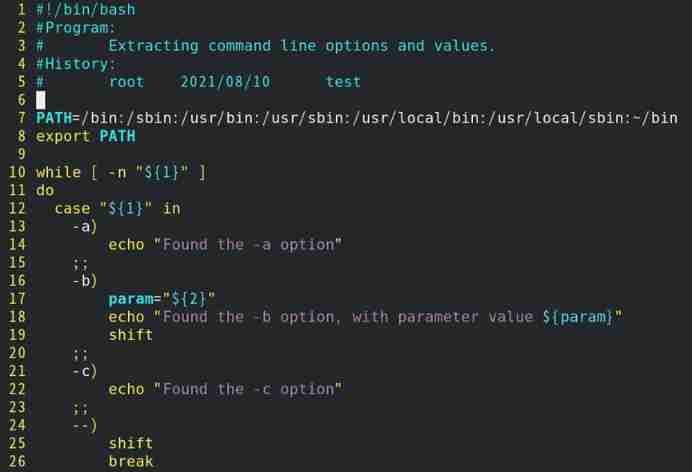
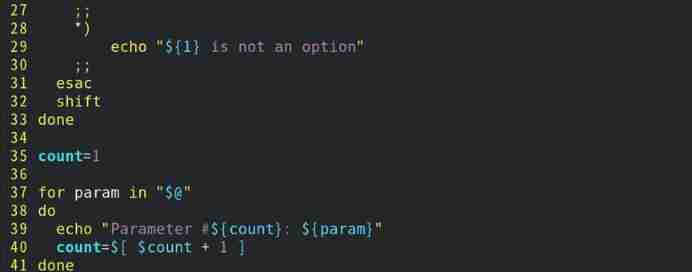
//Linux By default, the double slope polyline is used as the separation of options and parameters
2) call test17.sh Script files 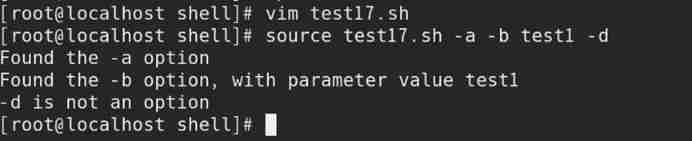
Custom variable
Variable name rules :
1) Only English letters 、 Numbers and underscores ( The first character cannot be a number );
2) Cannot contain spaces and punctuation , Special keywords cannot be used ;
3) Variable names are case sensitive , And the length should not exceed 20 Characters ;
// It is recommended that the custom variable name be lowercase ( Distinguish system environment variables )
The assignment form of variables : Variable name = A variable's value
1) There should be no spaces or other symbols on the left and right sides of the equal sign ;
2) When an undefined variable is called , By default, its content is empty ;
3) If the variable value contains special contents, you can use single / Double quotation marks are reserved or converted ;
4) If you define an array variable , You can enclose the array values in parentheses , And use spaces to separate
Assign the command to the variable form : Variable name =` command `
1) Also available “ Variable name =$( command )” form ;
Variable value append form : Variable name =${${ Variable name } The new content }
1) Two variable names can also be different , You can assign a value to a specified variable after adding content to it ;
Such as : Set up test2.sh The script can print the current time 
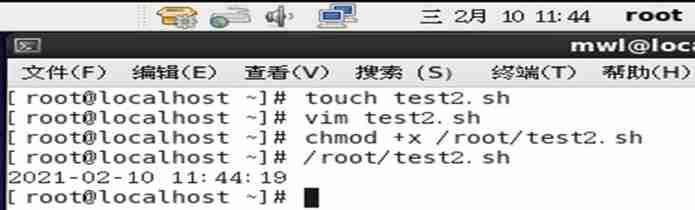
1) Father Shell The custom variable of cannot be in sub Shell Used internally
// Father Shell The global variable of is a child Shell serviceable
2) Son Shell after , Son Shell All variables of will be unregistered ( Will not be passed back to the father Shell)
export command : Make a local variable a global variable
Command format :export Variable name
1) If there is no variable name , All environment variables are displayed by default
2) Custom variables are local variables by default
Such as : Set up name Variables and assign values in subroutine calls 
Special custom variables
read command : Define input variables
Command format :read Options Variable name
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -p | Set input prompt Before entering variables , Display prompt message |
| -t | Set the waiting time If the time ends , End input directly |
| -n | Set the number of characters accepted If the number of accepted characters reaches the specified value , The default is to start execution |
| -s | Hide input |
1) If there is a space in the prompt message , It needs to be enclosed in single quotes ;
2) The input variable : Wait for user input , Continue with the script ;
3) if read The command does not specify variables , By default, the input data is stored in REPLY variable ;
Such as :test4.sh The script can be based on the path entered by the user , Create a file under this path ( And list )

readonly command : Define read-only variables or functions
Command format :readonly Options Variable name
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -f | Define read-only functions |
| -a | Define system array variables |
| -p | Display all read-only variables in the system |
1) Don't follow the options , Read only variables are defined by default
2) A read-only variable (readonly): Variables can only be read , Can't assign a value
Such as :test3.sh In the script a The variable is assigned to 1, Set as a read-only variable and assign a value of 2

unset command : Delete the specified variable
Command format :unset Variable name
1) When deleting a value in an array variable , The index bit of this value in the array will be set to null ( Still occupied );
// When indexing variables , The index bit still needs to be calculated
declare command : Declare variable type
Command format :declare Options Variable name
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -a (array) | Defined as an array variable |
| -i (integer) | Defined as an integer variable |
| -x | Defined as an environment variable |
| -r | Defined as readonly type And can't be unset |
| -p | List the types of variables |
1)declare and typeset Is exactly the same use and function ;
2) The variable type defaults to string ;
3)“-” become “+”, Is to cancel the corresponding variable type (-p With the exception of );
4) The variable is set to readonly when , The type of variable can be restored by logging out and then logging in
边栏推荐
- ~73 other text styles
- [unsolved]7-14 calculation diagram
- Cartesian tree (modified)
- Double specific tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
- ByteDance open source Gan model compression framework, saving up to 97.8% of computing power - iccv 2021
- Ffmpeg command line use
- [unsolved] 7-15 shout mountain
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of Chinese table lamp industry
- Audio and video development interview questions
- 7-6 sum of combinatorial numbers
猜你喜欢
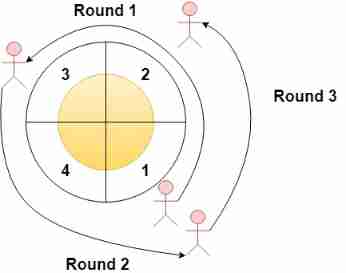
LeetCode 1560. The sector with the most passes on the circular track
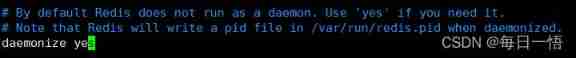
Redis standalone startup

One hundred questions of image processing (11-20)
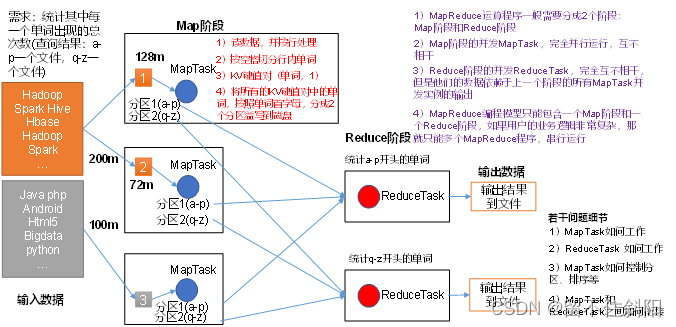
第一章 MapReduce概述

Chapter III principles of MapReduce framework

字节跳动多篇论文入选 CVPR 2021,精选干货都在这里了

ByteDance new programmer's growth secret: those glittering treasures mentors

字节跳动2022校招研发提前批宣讲会,同学们最关心的10个问题
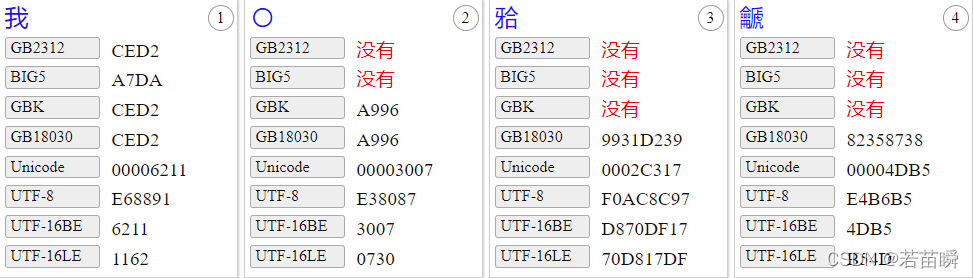
【锟斤拷】的故事:谈谈汉字编码和常用字符集
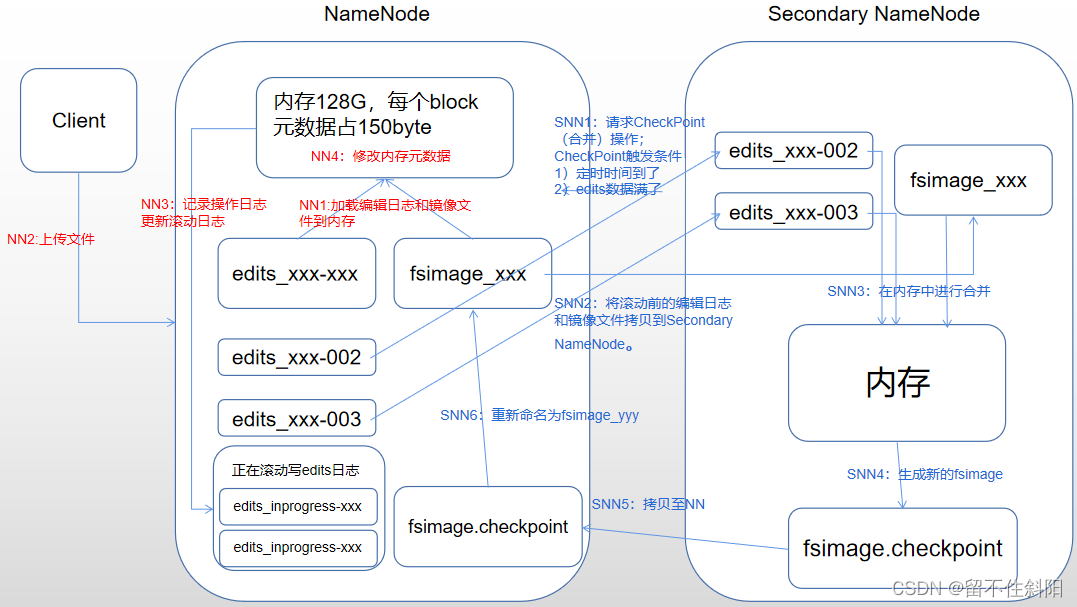
Chapter 5 namenode and secondarynamenode
随机推荐
LeetCode 1545. Find the k-th bit in the nth binary string
LeetCode 1560. The sector with the most passes on the circular track
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of tabletop dishwashers in China
~81 long table
Li Kou leetcode 280 weekly match
~68 Icon Font introduction
Spark的RDD(弹性分布式数据集)返回大结果集
Market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast of desktop electric tools in China
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's tetraacetylethylenediamine (TAED) industry
LeetCode 1562. Find the latest group of size M
这116名学生,用3天时间复刻了字节跳动内部真实技术项目
Introduction to microservices
MP4格式详解
~84 form supplement
~74 JD top navigation bar exercise
Chapter 7__ consumer_ offsets topic
Saw local status change event StatusChangeEvent [timestamp=1644048792587, current=DOWN, previous=UP]
第三章 MapReduce框架原理
谢邀,人在工区,刚交代码,在下字节跳动实习生
第5章 消费者组详解