当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode 1636. Sort the array in ascending order by frequency
LeetCode 1636. Sort the array in ascending order by frequency
2022-07-06 16:43:00 【Daylight629】
1636. Sort the array in ascending order by frequency
Give you an array of integers nums , Please arrange the array according to the frequency of each value Ascending Sort . If there are multiple values with the same frequency , Please put them according to the value itself Descending Sort .
Please return the sorted array .
Example 1:
Input :nums = [1,1,2,2,2,3]
Output :[3,1,1,2,2,2]
explain :'3' The frequency is 1,'1' The frequency is 2,'2' The frequency is 3 .
Example 2:
Input :nums = [2,3,1,3,2]
Output :[1,3,3,2,2]
explain :'2' and '3' The frequencies are 2 , So they are sorted in descending order according to the value itself .
Example 3:
Input :nums = [-1,1,-6,4,5,-6,1,4,1]
Output :[5,-1,4,4,-6,-6,1,1,1]
Tips :
1 <= nums.length <= 100-100 <= nums[i] <= 100
Two 、 Method 1
Hash + Priority queue
class Solution {
public int[] frequencySort(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : nums) {
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2)
-> o1[0] == o2[0] ? o2[1] - o1[1] : o1[0] - o2[0]
);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: map.entrySet()) {
queue.add(new int[]{
entry.getValue(), entry.getKey()});
}
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
int idx = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i< pos[0]; i++) {
res[idx++] = pos[1];
}
}
return res;
}
}
Complexity analysis
Time complexity :O(n).
Spatial complexity :O(n).
边栏推荐
- 视频压缩编码和音频压缩编码基本原理
- (lightoj - 1369) answering queries (thinking)
- One hundred questions of image processing (1-10)
- Discussion on QWidget code setting style sheet
- Native JS realizes the functions of all selection and inverse selection -- Feng Hao's blog
- Two weeks' experience of intermediate software designer in the crash soft exam
- 【锟斤拷】的故事:谈谈汉字编码和常用字符集
- Chapter 1 overview of MapReduce
- Problem - 1646C. Factorials and Powers of Two - Codeforces
- js时间函数大全 详细的讲解 -----阿浩博客
猜你喜欢
Chapter 2 shell operation of hfds
Advancedinstaller installation package custom action open file
音视频开发面试题
SF smart logistics Campus Technology Challenge (no T4)
Raspberry pie 4B installation opencv3.4.0
ffmpeg命令行使用
Chapter 5 namenode and secondarynamenode
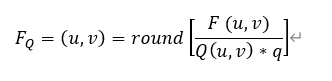
视频压缩编码和音频压缩编码基本原理
![Story of [Kun Jintong]: talk about Chinese character coding and common character sets](/img/d5/9a9e3a0ba57328749d80ec71cb9467.png)
Story of [Kun Jintong]: talk about Chinese character coding and common character sets
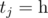
Problem - 922D、Robot Vacuum Cleaner - Codeforces
随机推荐
Cmake Express
第6章 DataNode
Codeforces - 1526C1&&C2 - Potions
提交Spark应用的若干问题记录(sparklauncher with cluster deploy mode)
腾讯面试算法题
One hundred questions of image processing (11-20)
Research Report on hearing health care equipment industry - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
CMake Error: Could not create named generator Visual Studio 16 2019解决方法
Li Kou: the 81st biweekly match
LeetCode 1560. The sector with the most passes on the circular track
业务系统兼容数据库Oracle/PostgreSQL(openGauss)/MySQL的琐事
Summary of game theory
useEffect,函数组件挂载和卸载时触发
<li>圆点样式 list-style-type
Ffmpeg command line use
Advancedinstaller installation package custom action open file
Research Report of desktop clinical chemical analyzer industry - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
Li Kou - 298th weekly match
Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2)
Classic application of stack -- bracket matching problem