当前位置:网站首页>Basic principles of video compression coding and audio compression coding
Basic principles of video compression coding and audio compression coding
2022-07-06 16:41:00 【Dog egg L】
1. Basic principles of video coding
(1) Redundant information of video signal
To record digital video YUV Take the component format as an example ,YUV Represent brightness and two color difference signals respectively . For example, for existing PAL TV system , Its brightness signal sampling frequency is 13.5MHz; The frequency band of chrominance signal is usually half or less than that of luminance signal , by 6.75MHz or 3.375MHz. With 4:2:2 Sampling frequency of ,Y The signal uses 13.5MHz, Chroma signal U and V use 6.75MHz sampling , Sample the signal to 8bit quantitative , Then the bit rate of digital video can be calculated as :
13.5 * 8 + 6.75 * 8 + 6.75 * 8= 216Mbit / s
If such a large amount of data is directly stored or transmitted, it will encounter great difficulties , Therefore, compression technology must be used to reduce the bit rate . The digital video signal can be compressed mainly according to two basic conditions :
- data redundancy . For example, spatial redundancy 、 Time redundancy 、 Structural redundancy 、 Information entropy redundancy , That is, there is a strong correlation between the pixels of the image . Eliminating these redundancies does not result in loss of information , Lossless compression .
- Visual redundancy . Some characteristics of human eyes, such as brightness discrimination threshold , Visual threshold , Different sensitivity to brightness and chroma , So that an appropriate amount of error is introduced during coding , Will not be detected . The visual characteristics of human eyes can be used , Exchange certain objective distortion for data compression . This compression belongs to lossy compression .
The compression of digital video signal is based on the above two conditions , So that the amount of video data can be greatly compressed , Conducive to transmission and storage . General digital video compression and coding methods are hybrid coding , About to change the code , Motion estimation and motion compensation , And entropy coding to compress the code . Transform coding is usually used to eliminate the intra redundancy of images , Motion estimation and motion compensation are used to remove the inter frame redundancy of the image , Entropy coding is used to further improve the efficiency of compression . The following briefly introduces these three compression coding methods .
(2) Compression coding method
(a) Transcoding
The function of transform coding is to transform the image signal described in spatial domain into frequency domain , Then the transformed coefficients are encoded . Generally speaking , Images have strong spatial correlation , Transformation to frequency domain can realize decorrelation and energy concentration . The commonly used orthogonal transform is discrete Fourier transform , Discrete cosine transform and so on . Discrete cosine transform is widely used in digital video compression .
The discrete cosine transformation is called DCT Transformation . It can be LL The image block is transformed from spatial domain to frequency domain . therefore , Based on DCT In the process of image compression and coding , First, we need to divide the image into non overlapping image blocks . Suppose the size of an image is 1280720, First, it is divided into 16090 A dimension for 88 There are no overlapping image blocks , Then, each image block can be DCT Transformation .
After segmentation , Every 88 The image block of points is sent DCT Encoder , take 88 The image block is transformed from spatial domain to frequency domain . The figure below shows an actual 8*8 Image block example of , The number in the figure represents the brightness value of each pixel . As you can see from the diagram , In this image block, the brightness value of each pixel is relatively uniform , In particular, the brightness value of adjacent pixels does not change much , It shows that the image signal has a strong correlation .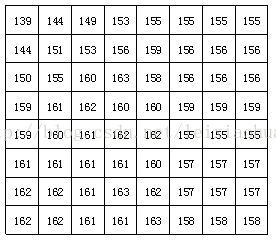
A reality 8 * 8 Image block
The following figure shows how the image block in the above figure passes DCT The result of the transformation . It can be seen from the picture that DCT After transformation , The low-frequency coefficient in the upper left corner concentrates a lot of energy , The energy on the high-frequency coefficient in the lower right corner is very small .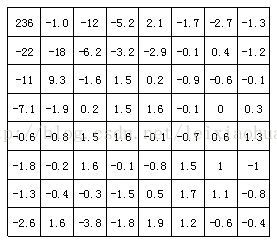
Image block passing DCT Coefficient after transformation
The signal went through DCT Quantization is needed after transformation . Because the human eye is very sensitive to the low-frequency characteristics of the image, such as the overall brightness of the object , It is not sensitive to the high-frequency detail information in the image , Therefore, in the transmission process, less or no high-frequency information can be transmitted , Only transmit the low-frequency part . The quantization process is through the fine quantization of the coefficients in the low-frequency region , The coefficients in the high-frequency region are roughly quantized , It removes the high-frequency information that is not sensitive to human eyes , Thus reducing the amount of information transmission . therefore , Quantization is a lossy compression process , And it is the main cause of quality damage in video compression coding .
The process of quantification can be expressed by the following formula :
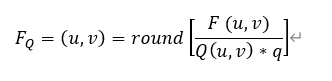 among FQ(u,v) It means after quantification DCT coefficient ;F(u,v) It means before quantification DCT coefficient ;Q(u,v) Represents the quantization weighting matrix ;q Represents the quantization step size ;round It means rounding , Take the output value as the nearest integer value .
among FQ(u,v) It means after quantification DCT coefficient ;F(u,v) It means before quantification DCT coefficient ;Q(u,v) Represents the quantization weighting matrix ;q Represents the quantization step size ;round It means rounding , Take the output value as the nearest integer value .
Choose the quantification coefficient reasonably , The result of quantizing the transformed image block is shown in the figure .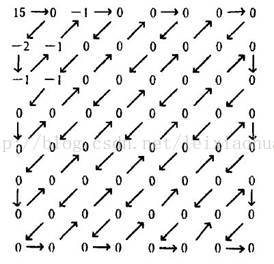
After quantification DCT coefficient
DCT After quantification, most of the coefficients become 0, Only a few coefficients are non-zero , At this time, you only need to put these non 0 Value can be compressed and encoded .
(b) Entropy coding
Entropy coding is named because the average code length after coding is close to the source entropy . Entropy coding uses variable word length coding (VLC,Variable Length Coding) Realization . Its basic principle is to assign short codes to symbols with high probability in the source , For symbols with low probability of occurrence, long codes are assigned , Thus, a shorter average code length is obtained statistically . Variable word length coding usually has Huffman coding 、 Arithmetic coding 、 Run length coding, etc . Run length coding is a very simple compression method , Its compression efficiency is not high , But coding 、 Fast decoding speed , It is still widely used , In particular, run length coding is used after transform coding , Good results .
First of all, the AC coefficient immediately following the output DC coefficient of the quantizer should be Z Type scan ( As shown by the arrow line in the figure ).Z Type scan converts two-dimensional quantization coefficients into one-dimensional sequences , And on this basis, run length coding . Finally, another variable length coding is performed on the run length encoded data , For example, Hoffman code . Through this variable length coding , Further improve the efficiency of coding .
(c) Motion estimation and motion compensation
motion estimation (Motion Estimation) Motion compensation (Motion Compensation) It is an effective means to eliminate the temporal correlation of image sequences . As described above DCT Transformation 、 quantitative 、 The entropy coding method is based on one frame of image , Through these methods, the spatial correlation between pixels in the image can be eliminated . In fact, in addition to the spatial correlation of image signals , And time correlation . For example, for the background like news broadcast , Digital video in which the motion of the main body of the picture is small , The difference between each picture is very small , There is a great correlation between pictures . In this case, it is not necessary to encode each frame of image separately , Instead, only the changed parts in adjacent video frames can be encoded , So as to further reduce the amount of data , This work is realized by motion estimation and motion compensation .
Motion estimation technology generally divides the current input image into several small image sub blocks that do not overlap each other , For example, the size of an image is 1280720, First, it is divided into 4045 A dimension for 16*16 There are no overlapping image blocks , Then search for the most similar image block for each image block within a search window of the previous image or the next image . This search process is called motion estimation . By calculating the position information between the most similar image block and the image block , You can get a motion vector . In this way, the block in the current image can be subtracted from the most similar image block pointed to by the motion vector of the reference image , Get a residual image block , Because the value of each pixel in the residual image block is very small , Therefore, higher compression ratio can be obtained in compression coding . This subtraction process is called motion compensation .
Because the reference image needs to be used for motion estimation and motion compensation in the coding process , Therefore, the selection of reference image is very important . Generally, the encoder divides each input frame image into different reference images 3 Different types :I(Intra) frame 、B(Bidirection prediction) frame 、P(Prediction) frame . As shown in the figure .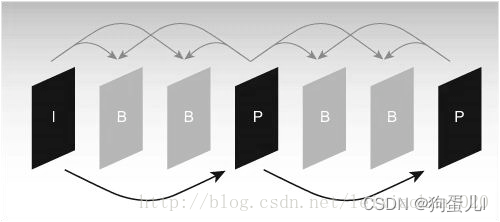
Typical I,B,P Frame structure order
As shown in the figure ,I Frames are encoded using only the data within the frame , In the process of coding, it does not need motion estimation and motion compensation . obviously , because I Frames don't eliminate temporal correlation , So the compression ratio is relatively low .P Frames are encoded using a previous I The frame or P The frame is used as the reference image for motion compensation , In fact, it encodes the difference between the current image and the reference image .B Frame encoding and decoding P Frame similarity , The only difference is that it uses a previous one in the encoding process I The frame or P Frame and one after it I The frame or P Frame prediction . thus it can be seen , every last P Frame coding needs to use an image as a reference image , and B Frames need two images as references . by comparison ,B Frame ratio P Frames have a higher compression ratio .
(d) Mixed encoding
The above introduces several important methods in the process of video compression and coding . In practical application, these methods are not separated , They are usually used together to achieve the best compression effect . The following figure shows hybrid coding ( That is, transform coding + Motion estimation and motion compensation + Entropy coding ) Model of . This model is widely used in MPEG1,MPEG2,H.264 Etc .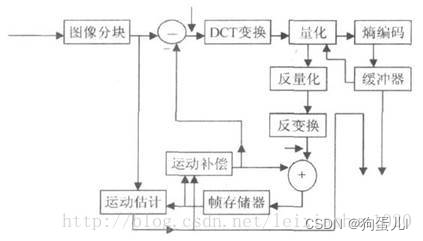
We can see from the picture , The currently input image must be partitioned first , The image block obtained by blocking should be subtracted from the predicted image after motion compensation to obtain the difference image X, Then, the difference image block is DCT Transform and quantify , There are two different places for quantized output data : One is to send it to entropy encoder for coding , The encoded code stream is output to a buffer for storage , Waiting for transmission . Another application is the received signal after inverse quantization and inverse change X’, This signal will be added to the image block output by motion compensation to obtain a new predicted image signal , And send the new predicted image block to the frame memory .
2. Basic principle of audio coding
(1) Redundant information of audio signal
If the digital audio signal is transmitted directly without compression , It will take up a lot of bandwidth . for example , A set of dual channel digital audio if the sampling frequency is 44.1KHz, For each value, press 16bit quantitative , Then the bit rate is :
2 * 44.1kHz * 16bit=1.411Mbit / s
Such a large bandwidth will bring many difficulties to signal transmission and processing , Therefore, we must adopt audio compression technology to process audio data , In order to effectively transmit audio data .
Digital audio compression coding ensures that the signal does not produce distortion in terms of hearing , Compress the audio data signal as much as possible . Digital audio compression coding is realized by removing redundant components in sound signal . The so-called redundant component refers to the signal in the audio that cannot be perceived by the human ear , They are important for determining the timbre of sound , Tone and other information don't help .
Redundant signals include audio signals beyond the range of human hearing and audio signals masked . for example , The frequency range of the sound signal that the human ear can detect is 20Hz~20KHz, Other frequencies are imperceptible to the human ear , All can be regarded as redundant signals . Besides , According to the physiological and psychoacoustic phenomena of human hearing , When a strong tone signal and a weak tone signal exist at the same time , The weak signal will be masked by the strong signal , In this way, the weak tone signal can be regarded as redundant signal instead of transmission . This is the masking effect of human hearing , It is mainly manifested in spectrum masking effect and time domain masking effect , Now we will introduce them as follows :
(a) Spectrum masking effect
After the sound energy of a frequency is less than a certain threshold , The human ear will not hear , This threshold is called the minimum audible threshold . When there's another sound with more energy , The threshold near the sound frequency will increase a lot , The so-called masking effect . As shown in the figure :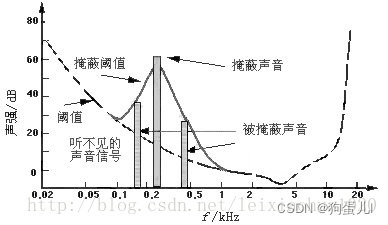
From the picture we can see that the human ear is right 2KHz~5KHz Your voice is the most sensitive , And it is very slow to sound signals with too low or too high frequency , When there is a frequency of 0.2KHz、 The intensity is 60dB When the sound of , The threshold near it has increased a lot . We can see from the picture that 0.1KHz following 、1KHz The above part , Because of leaving 0.2KHz The strong signal is far away , Not subject to 0.2KHz Strong signals affect , The threshold is not affected ; And in the 0.1KHz~1KHz Range , because 0.2KHz The emergence of a tonic , The threshold has been greatly improved , The minimum sound intensity that the human ear can feel in this range is greatly increased . If 0.1KHz~1KHz The intensity of the sound signal in the range is below the raised threshold curve , Because it was 0.2KHz It's masked by a strong signal , At this time, our ears can only hear 0.2KHz I can't hear any other weak signal at all , These and 0.2KHz If the strong tone signal exists at the same time, the weak tone signal can be regarded as redundant signal without transmission .
(b) Time domain masking effect
When a strong signal and a weak signal appear at the same time , There is also a time-domain masking effect . That is, when the occurrence time of the two is very close , There's also a masking effect . The time-domain masking process curve is shown in the figure , Divided into front masking 、 Simultaneous masking and post masking .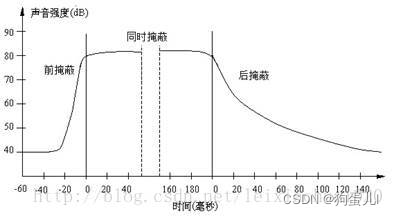
Time domain masking effect
We can see from the picture , There are three kinds of temporal masking effects : Front cover , At the same time masking , Back cover . Front masking refers to the short time before the human ear hears a strong signal , The existing weak signal will be masked and not heard . Simultaneous masking refers to when strong signals and weak signals exist at the same time , Weak signals are masked by strong signals and can't be heard . Post masking refers to when the strong signal disappears , It takes a long time to hear the weak signal again , It's called post masking . These masked weak signals can be regarded as redundant signals .
(2) Compression coding method
At present, there are different coding schemes and implementation methods in the field of digital audio coding , But the basic coding ideas are similar , As shown in the figure .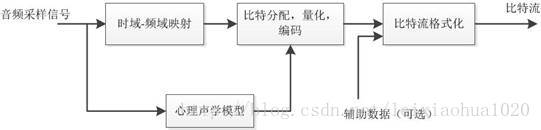
Digital audio coding system model
Sample the audio signal in each audio channel , First, map them to the frequency domain , This mapping from time domain to frequency domain can be realized by subband filter . The audio sampling block in each channel should first calculate the masking threshold according to the psychoacoustic model , Then, the number of bits in different frequency domains allocated to the channel from the common bit pool is determined by the calculated masking threshold , And then the coding and quantization , Finally, the control parameters and auxiliary data are added to the data , Generate the encoded data stream .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Installation and configuration of MariaDB
第5章 消费者组详解
Codeforces Round #802(Div. 2)A~D
Sublime text code formatting operation
![Solve the problem of intel12 generation core CPU [small core full, large core onlookers] (win11)](/img/92/9465a6c9f1ab88c4851a47fabe750c.jpg)
Solve the problem of intel12 generation core CPU [small core full, large core onlookers] (win11)
QT simulates mouse events and realizes clicking, double clicking, moving and dragging
QT realizes window topping, topping state switching, and multi window topping priority relationship
Raspberry pie 4b64 bit system installation miniconda (it took a few days to finally solve it)
第5章 NameNode和SecondaryNameNode

antd upload beforeUpload中禁止触发onchange
随机推荐
顺丰科技智慧物流校园技术挑战赛(无t4)
CMake速成
QT implementation window gradually disappears qpropertyanimation+ progress bar
Bidirectional linked list - all operations
视频压缩编码和音频压缩编码基本原理
Generate random password / verification code
Codeforces Round #797 (Div. 3)无F
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of double-sided foam tape in China
ffmpeg命令行使用
How to insert mathematical formulas in CSDN blog
(lightoj - 1370) Bi shoe and phi shoe (Euler function tabulation)
Chapter 7__ consumer_ offsets topic
Acwing: the 56th weekly match
力扣——第298场周赛
Codeforces Round #802(Div. 2)A~D
Spark独立集群动态上线下线Worker节点
第5章 消费者组详解
Tert butyl hydroquinone (TBHQ) Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
图像处理一百题(1-10)
(lightoj - 1354) IP checking (Analog)