当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces round 797 (Div. 3) no f
Codeforces round 797 (Div. 3) no f
2022-07-06 16:14:00 【Hello_ Ä】
Codeforces Round #797 (Div. 3) nothing F
This fight is too shit , During the day G It's very simple to make up for it , but f Still no clue, woo woo
Problem - A - Codeforces
Given the integer n — the number of available blocks. You must use all blocks to build a pedestal.
The pedestal consists of 3 platforms for 2-nd, 1-st and 3-rd places respectively. The platform for the 1-st place must be strictly higher than for the 2-nd place, and the platform for the 2-nd place must be strictly higher than for the 3-rd place. Also, the height of each platform must be greater than zero (that is, each platform must contain at least one block).
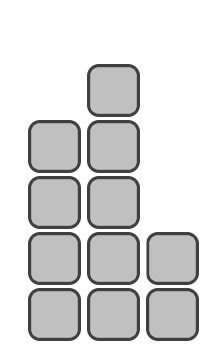
Example pedestal of n=11 blocks: second place height equals 4 blocks, first place height equals 5 blocks, third place height equals 2 blocks.
Among all possible pedestals of n blocks, deduce one such that the platform height for the 1-st place minimum as possible. If there are several of them, output any of them.
Input
The first line of input data contains an integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Each test case contains a single integer n (6≤n≤105) — the total number of blocks for the pedestal. All n blocks must be used.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n values over all test cases does not exceed 106.
Output
For each test case, output 3 numbers h2,h1,h3 — the platform heights for 2-nd, 1-st and 3-rd places on a pedestal consisting of n blocks (h1+h2+h3=n, 0<h3<h2<h1).
Among all possible pedestals, output the one for which the value of h1 minimal. If there are several of them, output any of them.
Example
input
6
11
6
10
100000
7
8
output
4 5 2
2 3 1
4 5 1
33334 33335 33331
2 4 1
3 4 1
Problem analysis
Sign in problem , It means to tell you n Square block , Use this n Three blocks build three pillars , The height of the middle column should be strictly greater than that of the left , The height of the left column should be strictly greater than that of the right , Let you write a method to make the middle column as low as possible .
First look at n Can you be 3 to be divisible by , If possible , The answer is :n/3,n/3+1,n/3-1.
If it can't be 3 to be divisible by , Just look at the parity of the remainder :
If it's odd , The answer can be :n/3+ remainder /2,n/3+ remainder /2+2,n/3-1.
If it's even , The answer can be :n/3+ remainder /2,n/3+ remainder /2+1,n/3-1.
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 1e3 + 50;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
string s;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int ans = n / 3;
if (n % 3 == 0)
{
cout << ans << " " << ans + 1 << " " << ans - 1 << endl;
}
else
{
int res = n % 3;
if (res % 2 == 0)
cout << ans + res / 2 << " " << ans + 1 + res / 2 << " " << ans - 1 << endl;
else
cout << ans + res / 2 << " " << ans + 2 + res / 2 << " " << ans - 1 << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Problem - B - Codeforces
Kristina has two arrays a and b, each containing n non-negative integers. She can perform the following operation on array a any number of times:
apply a decrement to each non-zero element of the array, that is, replace the value of each element ai such that ai>0 with the value ai−1 (1≤i≤n). If ai was 0, its value does not change.
Determine whether Kristina can get an array b from an array a in some number of operations (probably zero). In other words, can she make ai=bi after some number of operations for each 1≤i≤n?
For example, let n=4, a=[3,5,4,1] and b=[1,3,2,0]. In this case, she can apply the operation twice:
after the first application of the operation she gets a=[2,4,3,0];
after the second use of the operation she gets a=[1,3,2,0].
Thus, in two operations, she can get an array b from an array a.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer t (1≤t≤104) —the number of test cases in the test.
The descriptions of the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤5⋅104).
The second line of each test case contains exactly n non-negative integers a1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤109).
The third line of each test case contains exactly n non-negative integers b1,b2,…,bn (0≤bi≤109).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n values over all test cases in the test does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output on a separate line:
YES, if by doing some number of operations it is possible to get an array b from an array a;
NO otherwise.
You can output YES and NO in any case (for example, strings yEs, yes, Yes and YES will be recognized as a positive response).
Example
input
6
4
3 5 4 1
1 3 2 0
3
1 2 1
0 1 0
4
5 3 7 2
1 1 1 1
5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 6
1
8
0
1
4
6
output
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
Problem analysis
This problem is to give you two arrays a and b, One operation at a time , hold a All non 0 Integers -1, ask a Can the array finally become b Array .
You can use an array first c hold a[i] and b[i] The difference between the c[i] recorded , Record with an array b[i] Is it 0( I used it here pair, Combine the two arrays into one ), Take another one b[i] Not for 0 The difference is the standard . Be careful , If there is a a[i] Greater than b[i], That's it NO.
And then go through it c Array , If the current element is equal to the standard we recorded before, we will find the next element , If not, it depends on this position b[i] Is it 0, If c[i] Less than
standard , And b[i] be equal to 0, Then this is also reasonable , On the contrary, if b[i] Not for 0, perhaps c[i] Greater than standard , All are NO.
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 1e3 + 50;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
string s;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n), b(n);
vector<PII>ans(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cin >> a[i];
bool flag = true;
int res = 1e9;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> b[i];
if (b[i] > a[i])flag = false;
ans[i].first = a[i] - b[i];
ans[i].second = 0;
if (b[i] == 0)ans[i].second = -1;
else res = ans[i].first;
}
if (!flag)
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
continue;
}
if (n == 1)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (ans[i].first != res)
{
if (ans[i].first < res && ans[i].second == -1)continue;
else flag = false;
}
}
if (flag)cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - C - Codeforces
Recently, Polycarp completed n successive tasks.
For each completed task, the time si is known when it was given, no two tasks were given at the same time. Also given is the time fi when the task was completed. For each task, there is an unknown value di (di>0) — duration of task execution.
It is known that the tasks were completed in the order in which they came. Polycarp performed the tasks as follows:
As soon as the very first task came, Polycarp immediately began to carry it out.
If a new task arrived before Polycarp finished the previous one, he put the new task at the end of the queue.
When Polycarp finished executing the next task and the queue was not empty, he immediately took a new task from the head of the queue (if the queue is empty — he just waited for the next task).
Find di (duration) of each task.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The descriptions of the input data sets follow.
The first line of each test case contains one integer n (1≤n≤2⋅105).
The second line of each test case contains exactly n integers s1<s2<⋯<sn (0≤si≤109).
The third line of each test case contains exactly n integers f1<f2<⋯<fn (si<fi≤109).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each of t test cases print n positive integers d1,d2,…,dn — the duration of each task.
Example
input
4
3
0 3 7
2 10 11
2
10 15
11 16
9
12 16 90 195 1456 1569 3001 5237 19275
13 199 200 260 9100 10000 10914 91066 5735533
1
0
1000000000
output
2 7 1
1 1
1 183 1 60 7644 900 914 80152 5644467
1000000000
Problem analysis
This question means that you have n There are tasks to complete , Here are two arrays a and b, These tasks will be in a[i] Sent to you when , Will you be in b[i] When you finish , How long did it take you to complete this task . If you have a task in progress while you are doing it , Then this task will wait , You won't start this task until you finish it .
O(n) The simulation , Record the current time with a variable res, If the distribution time of the current task a[i] Greater than your current time , Then it means we have nothing right now , As soon as the time comes, you can receive the task and b[i] Finish it , Then the time taken is b[i]-a[i], And update the time to the moment when the task is completed . If the current task distribution time is greater than your current time , Explain that you are completing other tasks when this task is distributed , You receive this task immediately after finishing the last task , And it's still b[i] I finished it , So the time you take to complete this task is b[i]-res, And update the time to the moment when the task is completed .
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 1e3 + 50;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
string s;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n), b(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cin >> b[i];
int res = a[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (res <= a[i])
{
cout << b[i] - a[i] << " ";
res = b[i];
}
else
{
cout << b[i] - res << " ";
res = b[i];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - D - Codeforces
You have a stripe of checkered paper of length n. Each cell is either white or black.
What is the minimum number of cells that must be recolored from white to black in order to have a segment of k consecutive black cells on the stripe?
If the input data is such that a segment of k consecutive black cells already exists, then print 0.
Input
The first line contains an integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Next, descriptions of t test cases follow.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and k (1≤k≤n≤2⋅10^5). The second line consists of the letters ‘W’ (white) and ‘B’ (black). The line length is n.
It is guaranteed that the sum of values n does not exceed 2⋅10^5.
Output
For each of t test cases print an integer — the minimum number of cells that need to be repainted from white to black in order to have a segment of k consecutive black cells.
Example
input
4
5 3
BBWBW
5 5
BBWBW
5 1
BBWBW
1 1
W
output
1
2
0
1
Problem analysis
The title is to give you one that is only made up of ‘B’ and ‘W’ Composed string , You can choose one at a time ’W’ become ‘B’, Ask you to make this string have a length of k The substring of all consists of ’B’ form , How many operations should be carried out at least .
Here I use prefix and ( You can also use a sliding window ), First preprocess prefixes and arrays ,‘W’ As 0,‘B’ As 1 To calculate the prefix and , Then calculate the length as k The range of , The number of intervals and indicates how many operations we need to perform , Maintain the minimum value .
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
int n, m;
string s;
int sum[N];
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + (s[i - 1] == 'W' ? 1 : 0);
}
int res=1e9;
for (int i = m; i <= n; i++)
{
res=min(res,sum[i]-sum[i-m]);
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - E - Codeforces
A batch of n goods (n — an even number) is brought to the store, i-th of which has weight ai. Before selling the goods, they must be packed into packages. After packing, the following will be done:
There will be n/2 packages, each package contains exactly two goods;
The weight of the package that contains goods with indices i and j (1≤i,j≤n) is ai+aj.
With this, the cost of a package of weight x is always ⌊x/k⌋ burles (rounded down), where k — a fixed and given value.
Pack the goods to the packages so that the revenue from their sale is maximized. In other words, make such n2 pairs of given goods that the sum of the values ⌊xik⌋, where xi is the weight of the package number i (1≤i≤n2), is maximal.
For example, let n=6,k=3, weights of goods a=[3,2,7,1,4,8]. Let’s pack them into the following packages.
In the first package we will put the third and sixth goods. Its weight will be a3+a6=7+8=15. The cost of the package will be ⌊153⌋=5 burles.
In the second package put the first and fifth goods, the weight is a1+a5=3+4=7. The cost of the package is ⌊7/3⌋=2 burles.
In the third package put the second and fourth goods, the weight is a2+a4=2+1=3. The cost of the package is ⌊3/3⌋=1 burle.
With this packing, the total cost of all packs would be 5+2+1=8 burles.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer t (1≤t≤104) —the number of test cases in the test.
The descriptions of the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n (2≤n≤2⋅10^5) and k (1≤k≤1000). The number n — is even.
The second line of each test case contains exactly n integers a1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤10^9).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all the test cases does not exceed 2⋅10^5.
Output
For each test case, print on a separate line a single number — the maximum possible total cost of all the packages.
Example
input
6
6 3
3 2 7 1 4 8
4 3
2 1 5 6
4 12
0 0 0 0
2 1
1 1
6 10
2 0 0 5 9 4
6 5
5 3 8 6 3 2
output
8
4
0
2
1
5
Problem analysis
The title is that there are n Goods , Weight of each cargo ki, Give me another number k, You have to pack them in pairs , The benefit of packing is the sum of the weight of the two goods divided by k, What is the best interest .
First , Since it is the sum of weight divided by k What we get is our interests , Then the weight of a single cargo is divided by k The benefit of is what we have to get , We can calculate the benefits of a single item first . To add new benefits in pairs , Then we should make these two goods right k The sum of the remainder of is greater than or equal to k, In this way, you can get more benefits . Then we can calculate the benefits of individual goods , Turn them into %k. Then arrange the order from small to large , Push the head and tail of the double pointer towards the middle , If the current minimum + The sum of the maximum value cannot be greater than or equal to k, Then find a slightly larger minimum , When the sum of them is greater than or equal to k after , Our head pointer and tail pointer both take a step towards the middle , At the same time, interests ++.
Because the current weight of all goods is k The remainder of , Therefore, the maximum energy that can be obtained by the two goods can only be 1, To reach 2 Of , So this solution can get the greatest benefit .
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
int n, m;
string s;
bool cmp2(PII a, PII b)
{
if (a.first > b.first)return true;
else if (a.first < b.first)return false;
return a.second < b.second;
}
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int res = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<ll>v(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> v[i];
res += v[i] / m;
v[i] %= m;
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (v[l] + v[r] < m)l++;
else
{
res++;
r--;
l++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - G - Codeforces
There are n of independent carriages on the rails. The carriages are numbered from left to right from 1 to n. The carriages are not connected to each other. The carriages move to the left, so that the carriage with number 1 moves ahead of all of them.
The i-th carriage has its own engine, which can accelerate the carriage to ai km/h, but the carriage cannot go faster than the carriage in front of it. See example for explanation.
All carriages start moving to the left at the same time, and they naturally form trains. We will call trains — consecutive moving carriages having the same speed.
For example, we have n=5 carriages and array a=[10,13,5,2,6]. Then the final speeds of the carriages will be [10,10,5,2,2]. Respectively, 3 of the train will be formed.
There are also messages saying that some engine has been corrupted:
message “k d” means that the speed of the k-th carriage has decreased by d (that is, there has been a change in the maximum speed of the carriage ak=ak−d).
Messages arrive sequentially, the processing of the next message takes into account the changes from all previous messages.
After each message determine the number of formed trains.
Input
The first line of input data contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) —the number of input test cases.
This is followed by descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case is empty.
The second line of the test case contains two integers n and m (1≤n,m≤105) —the number of carriages and the number of messages to slow down the carriage, respectively.
The third line contains n integers: a1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤109) — the number ai means that the carriage with number i can reach a speed of ai km/h.
The next m lines contain two integers kj and dj (1≤kj≤n, 0≤dj≤akj) —this is the message that the speed of the carriage with number kj has decreased by dj. In other words, there has been a change in its maximum speed akj=akj−dj. Note that at any time the speed of each carriage is non-negative. In other words, ai≥si, where si —is the sum of such dj that kj=i.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 105. Similarly, it is guaranteed that the sum of m over all test cases does not exceed 105.
Output
Print t lines. On each line print the answer for the corresponding test case.
For each test case print m numbers: the number of trains formed after each message.
Example
input
3
4 2
6 2 3 7
3 2
4 7
5 4
10 13 5 2 6
2 4
5 2
1 5
3 2
13 4
769 514 336 173 181 373 519 338 985 709 729 702 168
12 581
6 222
7 233
5 117
output
3 4
4 4 2 3
5 6 6 5
Problem analysis
This question is about n A carriage , They will start with a[i]km/h Speed left , The one on the right will follow the slow car on the left and form a whole carriage . Then there is k operations , Every time I put the number x Slow down the initial speed of each carriage y, How many carriages will the train form after it starts .
First of all, we can know , The one on the right will follow the slow one in front , For example, the example of :10,13,5,2,6, Will become 10,10,5,2,2, There are three cars in total . After the first operation, the initial speed of the second carriage decreased 4, It becomes :10,9,5,2,6, It will become :10,9,5,2,2. If the speed of the second carriage becomes slower than that of the back , such as :10,4,5,2,6, Then in the end it will be 10,4,4,2,2. That is to say, we need a carriage that can quickly find the corresponding position , And it can merge the data structure of the carriage that is faster than it , So here I'm going to use theta map, With the number of the carriage ( Subscript ) do key, The speed of the carriage val.
Initially, you can use a large variable as the standard , When the inserted element is larger than this standard , We won't insert map in ( As this carriage merges with the carriage in front ), If the speed of a car is less than the standard , Let's insert this carriage map in , And turn the standard into the speed of the current carriage , such map Of size It's the number of carriages after starting .
As for the operation of reducing the speed of the carriage , You can insert the reduced element according to the subscript map in , According to find Function to find the iterator at this location , According to prev Function to get the iterator in front of this iterator ( Like a linked list ), To see if the speed of the car in front is less than that of the car we inserted , If it is less than , It means that even if the car slows down, it will be connected to the car in front , Then this deceleration actually makes no sense , Because you want to slow down and change the number of cars , Then its speed should be less than that of the car in front . Then we can delete the newly inserted carriage directly , Then record the current map Of size, It's the trunk count .
If the speed of this car is lower than that of the car in front after deceleration , Then we will continue to assimilate the cars behind , We can use next Function to get the next iterator of the current iterator , Then we will see whether the speed of the car behind us is lower than that of the newly inserted car , If it is less than, delete the back carriage ( Assimilated to the back of our carriage ), Until there is no car behind or there is a slower car behind . after map Of size It's the number of cars .
AC Code
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
int n, m;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, m, x, y, index = 1e10;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int>v(n + 1);
map<int, int>mymap;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> v[i];
if (v[i] < index)mymap[i] = v[i],index=v[i];
}
vector<int>cnt;
while (m--)
{
cin >> x >> y;
v[x] -= y;
mymap[x] = v[x];
auto ans = mymap.find(x);
if (ans != mymap.begin() && (*ans).second >= (*prev(ans)).second)
{
mymap.erase(ans);
cnt.push_back(mymap.size());
continue;
}
while(next(ans)!=mymap.end()&&(*ans).second<=(*next(ans)).second)mymap.erase(next(ans));
cnt.push_back(mymap.size());
}
for (auto i : cnt)cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- What is the difficulty of programming?
- C language learning notes
- (POJ - 3258) River hopper (two points)
- Penetration test (3) -- Metasploit framework (MSF)
- Effet d'utilisation, déclenché lorsque les composants de la fonction sont montés et déchargés
- antd upload beforeUpload中禁止触发onchange
- Codeforces Round #801 (Div. 2)A~C
- 读取和保存zarr文件
- Maximum product (greedy)
- Programmers, what are your skills in code writing?
猜你喜欢
QT有关QCobobox控件的样式设置(圆角、下拉框,向上展开、可编辑、内部布局等)
Essai de pénétration (1) - - outils nécessaires, navigation
Penetration test (4) -- detailed explanation of meterpreter command

605. Planting flowers

Information security - threat detection engine - common rule engine base performance comparison
快速转 TypeScript 指南

2078. Two houses with different colors and the farthest distance

Openwrt source code generation image

The concept of C language array

Pytorch extract skeleton (differentiable)
随机推荐
Gartner: five suggestions on best practices for zero trust network access
[teacher Gao UML software modeling foundation] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class
QT实现窗口置顶、置顶状态切换、多窗口置顶优先关系
409. Longest palindrome
Generate random password / verification code
Find 3-friendly Integers
[exercise -11] 4 values why sum is 0 (and 4 values of 0)
(POJ - 3579) median (two points)
Opencv learning log 27 -- chip positioning
Penetration test (2) -- penetration test system, target, GoogleHacking, Kali tool
1903. Maximum odd number in string
渗透测试 ( 4 ) --- Meterpreter 命令详解
QT模拟鼠标事件,实现点击双击移动拖拽等
Analysis of protobuf format of real-time barrage and historical barrage at station B
PySide6 信号、槽
Classic application of stack -- bracket matching problem
Understand what is a programming language in a popular way
Luogu P1102 A-B number pair (dichotomy, map, double pointer)
TCP's three handshakes and four waves
Interval sum ----- discretization