当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #801 (Div. 2)A~C
Codeforces Round #801 (Div. 2)A~C
2022-07-06 09:28:00 【你好_Ä】
Codeforces Round #801 (Div. 2)A~C
Problem - A - Codeforces
Michael and Joe are playing a game. The game is played on a grid with n rows and m columns, filled with distinct integers. We denote the square on the i-th (1≤i≤n) row and j-th (1≤j≤m) column by (i,j) and the number there by aij.
Michael starts by saying two numbers h (1≤h≤n) and w (1≤w≤m). Then Joe picks any h×w subrectangle of the board (without Michael seeing).
Formally, an h×w subrectangle starts at some square (a,b) where 1≤a≤n−h+1 and 1≤b≤m−w+1. It contains all squares (i,j) for a≤i≤a+h−1 and b≤j≤b+w−1.
Finally, Michael has to guess the maximum number in the subrectangle. He wins if he gets it right.
Because Michael doesn’t like big numbers, he wants the area of the chosen subrectangle (that is, h⋅w), to be as small as possible, while still ensuring that he wins, not depending on Joe’s choice. Help Michael out by finding this minimum possible area.
It can be shown that Michael can always choose h,w for which he can ensure that he wins.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤20). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n and m (1≤n,m≤40) — the size of the grid.
Each of the following n lines contains m integers. The j-th integer on the i-th line is aij (−109≤aij≤10 9) — the element in the cell (i,j).
It is guaranteed that all the numbers are distinct (that is, if ai1j1=ai2j2, then i1=i2,j1=j2).
Output
For each test case print a single positive integer — the minimum possible area the subrectangle can have while still ensuring that Michael can guarantee the victory.
Example
input
3
1 1
3
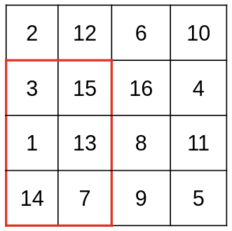
4 4
2 12 6 10
3 15 16 4
1 13 8 11
14 7 9 5
2 3
-7 5 2
0 8 -3
output
1
9
4
问题解析
问题是说,给你一个矩阵,你可以让一个人画一个面积为x(长*高)的子矩阵,然后你猜这个矩阵中的最大的数是多少,问能让你稳赢的子矩阵面积最小是多少。
就是找矩阵中的最大值,然后看这个值的坐标到四个角的矩阵面积,取最大的,这样就能保证子矩阵不管怎么取,都一定能让这个最大值出现在子矩阵里。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
ll mx = -1e10, res = 0;
vector<vector<int>>v(n, vector<int>(m));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
cin >> v[i][j];
if (v[i][j] >= mx)
{
int l_up = (i + 1) * (j + 1);
int r_up = (i + 1) * (m - j);
int l_down = (n - i) * (j + 1);
int r_down = (n - i) * (m - j);
res = max(max(l_up, r_up), max(l_down, r_down));
mx = v[i][j];
}
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - B - Codeforces
Mike and Joe are playing a game with some stones. Specifically, they have n piles of stones of sizes a1,a2,…,an. These piles are arranged in a circle.
The game goes as follows. Players take turns removing some positive number of stones from a pile in clockwise order starting from pile 1. Formally, if a player removed stones from pile i on a turn, the other player removes stones from pile ((imodn)+1) on the next turn.
If a player cannot remove any stones on their turn (because the pile is empty), they lose. Mike goes first.
If Mike and Joe play optimally, who will win?
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤1000). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤50) — the number of piles.
The second line contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤10^ 9) — the size of the piles.
Output
For each test case print the winner of the game, either “Mike” or “Joe” on its own line (without quotes).
Example
input
2
1
37
2
100 100
output
Mike
Joe
问题解析
说有n堆石头,每堆石头有a[i]个石子,一开始mike先从第一堆开始拿,每次可以拿任意数量,下一个人只能去第(i+1)%n堆石头取石子,谁要是先取不到石子,谁就输了。问谁最后能赢。
如果石子是奇数,那么每次只要都拿完,当Joe回到队列开头时就会拿不到石头而输掉,所以n为奇数是mike必赢。
如果是偶数,那么mike每次都拿的是奇数位的石头,joe拿的是偶数位的石头。也就是谁先取完自己队列的任意一个石堆,他就输了,所以我们对比两边数量最少的石堆有多少石子就行,最少的那个就输了,如果一样,就看那堆在前面,在前面的输。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>v(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cin >> v[i];
if (n % 2 == 1)
{
cout << "Mike" << endl;
continue;
}
int mn_j = 1e18, mn_o = 1e18, pos_j = -1, pos_o = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2)
{
if (mn_j > v[i])
{
mn_j = v[i];
pos_j = i;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i += 2)
{
if (mn_o > v[i])
{
mn_o = v[i];
pos_o = i;
}
}
if (mn_j<mn_o||(mn_j==mn_o&&pos_j<pos_o))cout << "Joe" << endl;
else cout << "Mike" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem - C - Codeforces
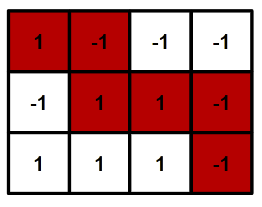
You are given a grid with n rows and m columns. We denote the square on the i-th (1≤i≤n) row and j-th (1≤j≤m) column by (i,j) and the number there by aij. All numbers are equal to 1 or to −1.
You start from the square (1,1) and can move one square down or one square to the right at a time. In the end, you want to end up at the square (n,m).
Is it possible to move in such a way so that the sum of the values written in all the visited cells (including a11 and anm) is 0?
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤104). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n and m (1≤n,m≤1000) — the size of the grid.
Each of the following n lines contains m integers. The j-th integer on the i-th line is aij (aij=1 or −1) — the element in the cell (i,j).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n⋅m over all test cases does not exceed 106.
Output
For each test case, print “YES” if there exists a path from the top left to the bottom right that adds up to 0, and “NO” otherwise. You can output each letter in any case.
Example
input
5
1 1
1
1 2
1 -1
1 4
1 -1 1 -1
3 4
1 -1 -1 -1
-1 1 1 -1
1 1 1 -1
3 4
1 -1 1 1
-1 1 -1 1
1 -1 1 1
output
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
问题解析
题目是说给你一个矩阵,只由1和-1组成,一开始从左上角出发,只能走右和下,问你能不能找出一条路使得这条路上的和为0.
首先,矩阵的长n和宽m相加必须为奇数,如果是偶数,那么路径上就会有奇数个数,是不可能为0的。
然后我们可以直接求一下从左上走到坐下的最大值和最小值分别为多少,只要这个最大值和最小值形成的范围能包含0,那就能找一条路出来,反之不行。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<numeric>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iterator>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#define endl '\n'
#define int ll
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<ll, ll>PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 50;
int n, m;
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>>v(n, vector<int>(m)), f(n, vector<int>(m));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> v[i][j];
}
if ((n+m)%2==0)
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
continue;
}
int mn = v[0][0], mx = v[0][0];
f[0][0] = v[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
f[i][0] = f[i - 1][0] + v[i][0];
}
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
{
f[0][j] = f[0][j - 1] + v[0][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
{
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]) + v[i][j];
}
}
mx = f[n - 1][m - 1];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++)
{
f[i][j] = min(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]) + v[i][j];
}
}
mn = f[n - 1][m - 1];
if (mx >= 0 && mn <= 0)cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- QT按钮点击切换QLineEdit焦点(含代码)
- [exercise-1] (UVA 673) parentheses balance/ balanced brackets (stack)
- Openwrt source code generation image
- [teacher Gao UML software modeling foundation] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class
- socket通讯
- 最全编程语言在线 API 文档
- Vs2019 initial use
- (POJ - 3685) matrix (two sets and two parts)
- 树莓派4B安装opencv3.4.0
- Opencv learning log 30 -- histogram equalization
猜你喜欢

921. Minimum additions to make parentheses valid
b站 实时弹幕和历史弹幕 Protobuf 格式解析

2027. Minimum number of operations to convert strings
Candy delivery (Mathematics)

969. Pancake sorting

读取和保存zarr文件
![MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’](/img/e6/f4a696179282fe1f4193410c5a493a.png)
MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’

(POJ - 3579) median (two points)
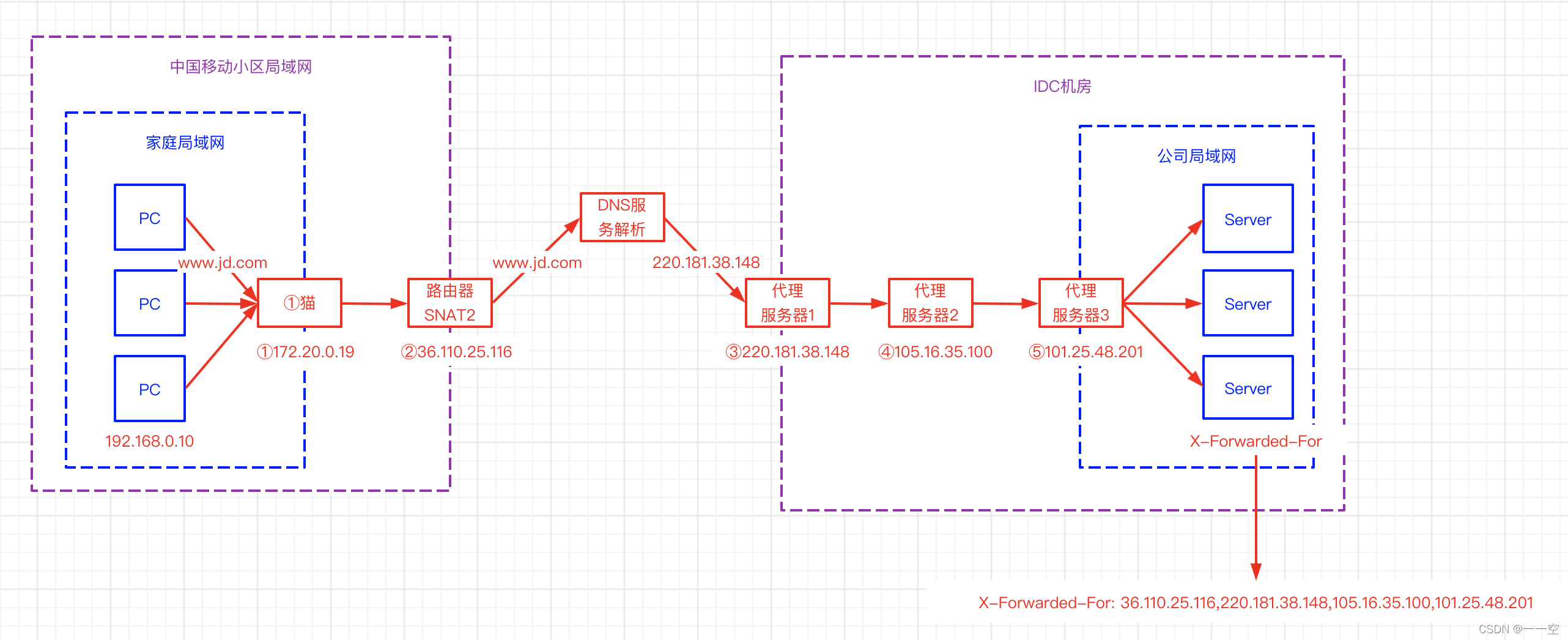
X-Forwarded-For详解、如何获取到客户端IP
Web based photo digital printing website
随机推荐
【练习-7】(Uva 10976)Fractions Again?!(分数拆分)
b站 实时弹幕和历史弹幕 Protobuf 格式解析
Programmers, what are your skills in code writing?
【高老师UML软件建模基础】20级云班课习题答案合集
Sword finger offer II 019 Delete at most one character to get a palindrome
Essai de pénétration (1) - - outils nécessaires, navigation
Opencv learning log 26 -- detect circular holes and mark them
【练习-2】(Uva 712) S-Trees (S树)
Socket communication
【练习-6】(PTA)分而治之
1529. Minimum number of suffix flips
QNetworkAccessManager实现ftp功能总结
Understand what is a programming language in a popular way
D - function (HDU - 6546) girls' competition
[exercise 4-1] cake distribution
【练习-7】Crossword Answers
Is the sanic asynchronous framework really so strong? Find truth in practice
信息安全-史诗级漏洞Log4j的漏洞机理和防范措施
Penetration test (4) -- detailed explanation of meterpreter command
Data storage in memory & loading into memory to make the program run