当前位置:网站首页>C language learning notes
C language learning notes
2022-07-06 16:04:00 【Programming fish 66】
data
Constant
Big classification
- Literal constants : Intuitively written values
constModifier hair constant#defineDefined constant- Enumeration constants
Constant ,const Constant variable
int main()
{
const int num = 1;\\const Indicates the creation of constant attribute variables
num = 8;
return 0;
}
Can't run
int main()
{
const int n = 4;
printf("%d\n", n);
int arr[n] = { 0 };
return 0;
}
int main()
{
const const int n = 4;
printf("%d\n", n);
int arr[n] = { 0 };
return 0;
} It doesn't work , const int n Express n Is a variable with constant properties , Is not a constant .
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 10
int main()
{
int arr[MAX] = { 0 };
return 0;
} This can run , because #define Defines a standard constant
Enumeration constants
enum Sex\\ Enumeration constants
{
MALE,
FEMALE,
SECRET
};// Possible values of enumeration constants , The enumeration constants given in braces cannot be changed , Enumerating variables can be changed
int main()
{
printf("%d",MALE);//0
printf("%d",FEMALE);//1
printf("%d",SECRET);//2
}character string + Escape character + notes
character string
Multiple characters in double quotation marks are strings "hello bit\n"
int main()
{
"abcdef";// character string
"";// An empty string
return 0;
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr1[] = "abc";
//"abc"--'a','b','c','\0' =>'\0' Indicates the end of a string ,'\0' The value of is 0
//char arr2[] = { 'a','b','c' };'c' Should be followed by a 0
char arr2[]={'a','b','c',0};
printf("%s\n", arr1);
printf("%s\n", arr2);
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr1));
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr2));// Print string length ,3
return 0;
}The data stored on the computer is binary , The characters are written with ASCII Code storage .
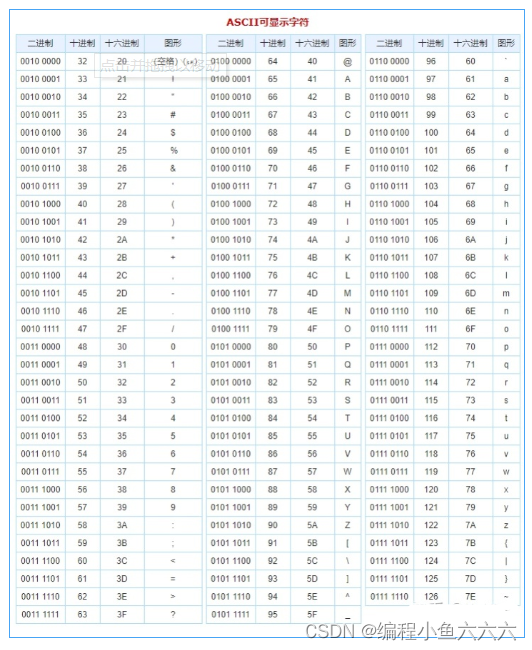
Escape character \
\n Change the original meaning , Make a character no longer the original meaning , Means line break
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("abc\n");
return 0;
}\t It's called horizontal tab , similar Tab key
notes
c Notes /* */ c++ Notes //` Both can be used. Comments are used where the code is difficult to understand
Input and output

Format characters
| Format symbol | effect |
|---|---|
| i, d | Decimal integer |
| x, X | Hexadecimal unsigned integer |
| o | Octal unsigned integer |
| u | An unsigned decimal integer |
| c | Single character |
| s | character string |
| e | Floating point decimal in exponential form |
| f | Decimal form floating point decimal |
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float f=3.1415926;
printf("%2.3f\n",f);
printf("%f\n",f);
return 0;
} among %2.3f2 Representation format ( If it is exceeded, it will be ignored ), 3 It means to reserve the number of decimal places ( rounding )
| Modifier | function |
| m | The output data field is wide , Data length <m, Left padding ; Otherwise, press the actual output |
| .n | For real numbers , Specify the number of digits after the decimal point ( rounding ) |
| The string , Specify the actual output bits | |
| - | The output data is left aligned in the field ( Default right alignment ) |
| + | Specifies that a positive sign is displayed before the positive number of signed numbers (+) |
| 0 | When the output value is specified, the empty position not used on the left side will be filled in automatically 0 |
| # | Show leading before octal and hexadecimal numbers 0,0x |
| l | stay d, o, x, u front , Specify the output precision as long type |
| l | stay e, f, g front , Specify the output precision as double type |
Character input function
putchar()
scanf() If you need a prompt statement , Write a separate line printf, Can not be written in scanf in
Garbage left by input function
That is, enter an integer value and then press enter to enter another character , It will turn carriage return into input . The methods of clearing are
1. use getchar() eat
1. %[ Space ]c or %*cString input function
- gets(s)
- scanf() Spaces will be used as the end flag of string input ( When dealing with continuous character input, you can deal with spaces )
String output function
puts
It will wrap itself
Operator
Arithmetic operator
Add reduce ride except (/) Remainder (%) The remainder cannot be given to floating-point numbers .
Relational operator
>``>=``<=``<
==``!=
Logical operators
!Take the opposite : 1 change 0,0 change 1||or
An operator
For binary bits (0/1)
Bit operations can be performed with any data type
| Operator | Functional specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| ~ | Bit logic inverse | Convert to binary , then 0 1 swap |
| & | Bit logic and | |
| | | Bit logic or | |
| ^ | Bit logic or | Difference is true , Same as false |
| >> | Shift right | |
| << | Shift left | Multiply by two |
Special operators
Assignment operator
Conditional operator ?
The comma operator
z=(x+=5,y=x+0.2)
z The value of is determined by the last expression
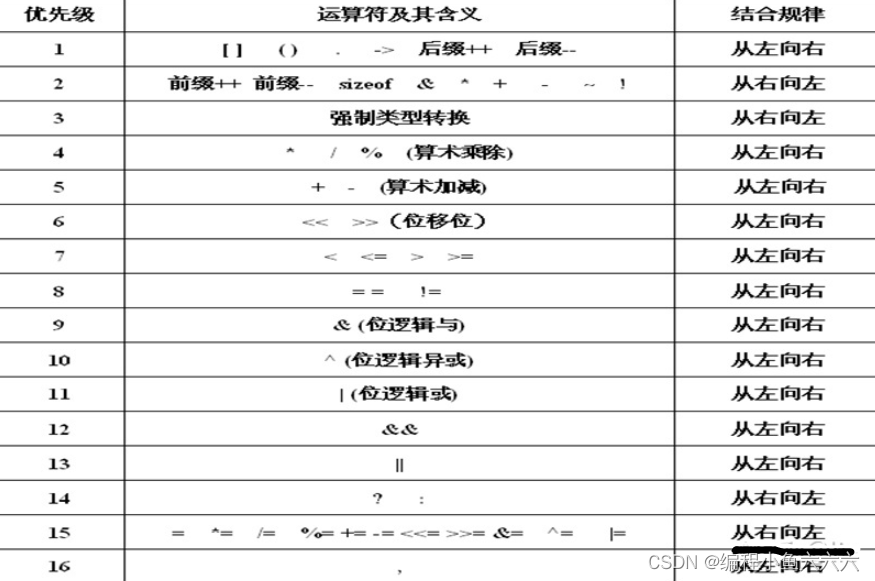
Operator precedence
It is suggested to add more brackets to solve the priority problem
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 1, y = 0, z = 0;
x += y == z,y = x + 2, z = x + y + x > 0;
printf("%d,%d,%d\n", x, y, z);
return 0;
}Add
Dereference operator * The priority of is less than the subscript operator [], Therefore, the array pointer needs to be bracketed, such as int (*p)[10]
Array
One dimensional array
C The language will not judge the array beyond the bounds , You need to limit yourself
- If the array is not initialized , Values are random .
- static Array elements are not assigned , The default is 0
- Assign only partial values , Default after 0
- If there is too much initialization, an error will be reported directly
Example : Bubble sort
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int a[7]={49,38,97,76,13,27,30};
int i = 0,j=6,temp;
for (;j>=0;j--)
{
for(i=0;i<=j;i++)
{
if(a[i]>a[i+1])
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = temp;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<=6;i++)
{
printf("%d\n",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}Two dimensional array
P[ That's ok ][ Column ]
Define the way : The number of rows can be omitted , The number of columns cannot
Two dimensional array storage
Verification of two-dimensional array storage
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int a[4][5]={
{1,2,3,4,5},{6,7,8,9,10},{11,12,13,14,15},{16,17,18,19,20}};
for(int x = 0; x < 4; x++)
{
for(int y = 0; y < 5; y++)
{
printf("The id of a[%d][%d] is %p\n",x,y,&a[x][y] );
}
}
return 0;
}Multidimensional arrays
Example : Print the first ten lines of Yang Hui triangle
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int a[10][10];
for(int x = 0; x < 10; x++)
{
for(int y = 0; y < 10; y++)
{
if(y == 0 ||x == y)
a[x][y]=1;
}
}
for(int x = 2; x < 10; x++)
{
for(int y = 1; y < x; y++)
{
a[x][y]=a[x-1][y-1]+a[x-1][y];
}
}
for(int x = 0; x < 10; x++)
{
for(int y = 0; y <= x; y++)
{
printf("%d ",a[x][y]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Character arrays and strings
C In language , The string is attached to the character array
initialization
- Assign values one by one
- String assignment
"abc" ->a, b, c, \0
0 \0 NULL It's the same thing , ASCII The code value is 0
, '0' It's another thing , ASCII The code value is 48
String array under two-dimensional array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char fruit[][20] = { "bannana","apple","strawmerry","watermelen" };
int i, j, n, m;
n = sizeof(fruit) / sizeof(fruit[0]);
m = sizeof(fruit[0]) / sizeof(fruit[0][0]);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
putchar(fruit[i][j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
sizeof()What you get is total space , Include unassigned parts ,strlenWhat you get is the actual string length ( needstring.h>)
String function
Common string functions <string.h>
strlen Find the length
Calculate the actual length of a string ( It doesn't contain \0), The number of bytes returned , Often a char It's just a byte , Therefore, it can be regarded as length
char s[10] = { 'A', 0, 'b', '\0', '0' };
printf("%zd", strlen(s));// This returns 1, Because I met 0, It's the end of the string
printf("%d", sizeof(s)/sizeof(char));// This returns 10, Represents the entire array When special characters are encountered :
char s[20] = "\t\t\nasdczx0\0qwe";
printf("%zd\n", strlen(s));// return 10 \t,\n Each is treated as a character
printf("%d", sizeof(s)/sizeof(char));// return 20
char s[20] = "\x69\141\n"; // \xhh Represents the symbol represented by hexadecimal numbers , \ddd Represents the symbol represented by octal numbers It is generally not recommended to write
printf("%zd\n", strlen(s));strcpy String copy
strcpy( A character array 1, A character array 2)- The string 2 Copy to string 1 In the middle , Returns an array of characters 1 The first address .( Must be a string )
- A character array 1 It has to be big enough
strcat String concatenation function
strcpy( A character array 1, A character array 2)- The string 2 Connect to string 1 Back , Returns an array of characters 1 The first address .( Must be a string )
- A character array 1 It has to be big enough
- Before connection , Both are based on
'\0'The end of the , After connection strand 1 Of'\0Cancel , Add... At the end of the new string'\0'
strcmp String comparison function
strcmp( character string 1, character string 2)
- Compare the rules : The two strings are compared from left to right ASCII Code value , if
1<2Returns a negative integer , if1==2return 0, if1>2Returns a positive integer . - If the lengths are not equal , Empty positions are equivalent to and
\0Than ,
Be careful : The premise of using string function must be string or with '\0' Array of characters , Otherwise, unpredictable problems will occur .
Extended usage of string functions
strncpy(p,p1,n) Copy a string of specified length
strncat(p,p1,n) Connect a string of specified length
strcasecmp Ignore case comparison strings
strncmp(p, p1, n) Compare a specified length string
strchr(p, c) Find the specified character in a string
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc, char const* argv[])
{
char s1[]="123aeqw$asdsa";
int ch;
ch='$';
printf("%p,%p,\n\n",s1,strchr(s1,ch));
return 0;
}strstr(p, p1) Find string
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc, char const* argv[])
{
char s1[]="how are you";
char s2[]="are";
printf("%ld\n",strstr(s1,s2)-s1);
return 0;
} Functions about characters , need #include<ctype.h>
isalpha() Check for alphabetic characters
isupper() Check whether it is an uppercase character
islower() Check for lowercase characters
isdigit() Check if it's a number
The pointer
stay C In language , The address of a memory unit is called a pointer . Without affecting understanding , Address , The pointer , Pointer variables are not distinguished .
Pointer arithmetic
- Only pointer to the same type
- The number of separated data is obtained by subtracting the pointer , Not the address difference .
assignment
You can assign an address to a pointer .
Quoting
* Operator gives a pointer to the stored value on the address
address-of
Like all variables , Pointer variables also have their own addresses and values . & Operator gives the address of the pointer itself .
Add a pointer to an integer
Integers are multiplied by the size of the type pointed to by the pointer , Then add the result to the initial address .
Increment pointer
Incrementing the pointer to an array element moves the pointer to the next element of the array . therefore ptr1 Point to urn[1].
Pointer minus an integer
The pointer must be a minuend . The rest is similar to addition .
Decrement pointer
Similar increment , For arrays
Pointer difference
Pointers and arrays
The array name is a pointer to the first element of the array .
A pointer in a two-dimensional array
int a[3][2]={
{1,6},{9,12},{61,12}};
int *p,i,n;
n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);
p=a;//warningIt's not right to write like this , a And p Types are different , One p Point to four bytes , But one a Point to 8 Bytes , It should be :
p=a[0] in other words If you need to traverse a two-dimensional array with a first-order pointer , need for loop
A two-dimensional array consists of multiple arrays ,
In the above code a Is the a[0] a[1] a[2] Three arrays form .
A dereference of the two-dimensional array name will get a pointer to the number of rows .
Character pointer and string
If you directly point the pointer to the string
char *p="hello world";The pointer stores the starting address of the string constant , Cannot modify with pointer Point to the value of the object . You cannot do this for arrays , This is also the difference between string and character array .
Pointer array
An array of pointer variables with the same storage type .
double *pa[2], a[2][3]* Just one
Pointer arrays can be used for two-dimensional arrays .
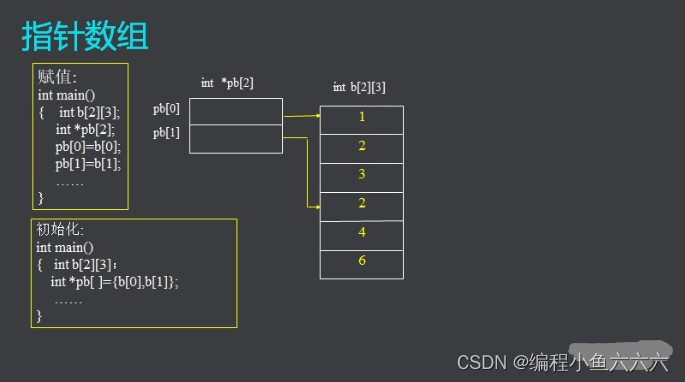
Multi level pointer
void The pointer
void * [ Pointer name ] It can be changed to other types of pointers by forcing type conversion
Display conversion
Implicit conversion
An explicit call refers to calling Implicit calls are compiler background calls
function
Definition and Usage
l A function is a code module that performs a specific function , Its program code is independent , Usually a return value is required , It can also be null . It is called function body in braces
l The general form is as follows :
< data type > < The name of the function >( < Formal parameter description > ) {
Statement sequence ;
return[(< expression >)];
} for example
double p(int x);call
Function name ( The actual parameter )
Arguments are when using functions , The data passed by the calling function to the called function . Exact data is needed
A function call can appear in an expression as an operand , It can also form a single statement . For functions that have no return value , Only one function call statement can be formed .
Parameter passing (C The language does not quote )
Passing array parameters ( The string ) You need to pass the size of the array at the same time .
Copy the delivery method
The value of the argument is assigned to the formal parameter
- The calling function passes the arguments to the called function , The called function will create formal parameters of the same type and initialize with arguments
- Formal parameters are newly developed storage space , therefore , Change the value of formal parameter in function , It doesn't affect the arguments
Pointer function
Usage of pointer function
A pointer function is a function whose return value is a pointer .
The space in the function will be released at the end , This makes the pointer inaccessible , You can apply the variable in the function as static Variable extended probation .
Or use String constant :
char *str = "hello" But it can't be modified *str
in general , The return of the pointer function can be :
- The address of the global variable
- static The address of the variable
- The address of the string constant
- Dynamic memory
Recursive functions and function pointers
Recursion is recursion plus regression
Example 1: Find the factorial
#include<stdio.h>
int calcu(int x);
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",calcu(10));
return 0;
}
int calcu(int x)
{
if (x==0)
{
return 1;
}
double factorial = x;
factorial*=calcu(x-1);
return factorial;
}Example 2: Fiboracci series
int main()
{
for(int num = 1; num <= 10; num++)
{
printf("%d\n",fib(num));
}
return 0;
}
int fib(int x)
{
int fibx;
if (x == 1 || x == 2)
{
return 1;
}
fibx = fib(x-1)+fib(x-2);
return fibx;
}A function pointer
The core of a function pointer is a pointer , Store the address of the function
The function address represents the entry address of the function ( Function name )
#include<stdio.h>
int add(int, int);
int main()
{
int m = 10,n = 20;
int (*p)(int ,int );
p=add;
printf("%d\n",p(m,n));
return 0;
}
int add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
} Function pointers should be related to functions , Therefore, the return value type and parameter list should be consistent with the prototype of the function , Note the de quotation here * The priority of the , Need to add ()
Function pointer array
The return type of the function pointer pointing to the function in the array is consistent with the parameter list .
Example : call qsort Sort
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int stol(const void *x, const void *y);
int main()
{
int a[10] = {5.7,3,6,4,2,8,9,1};
qsort(a,sizeof(a)/sizeof(int),sizeof(int),stol);
for(int k = 0; k<= 9; k++)
{
printf("%d\n",a[k] );
}
return 0;
}
int stol(const void *x, const void *y)
{
return *(int *)x - *(int *)y;
}resources & More in-depth readings :
Open the mysterious channel to get information, click the link to join the group chat 【C Language /C++ Programming learning base 】:828339809
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
PySide6 信号、槽
frida hook so层、protobuf 数据解析
Essai de pénétration (1) - - outils nécessaires, navigation
渗透测试 ( 3 ) --- Metasploit Framework ( MSF )
Nodejs+vue online fresh flower shop sales information system express+mysql

Penetration test (1) -- necessary tools, navigation
b站 实时弹幕和历史弹幕 Protobuf 格式解析
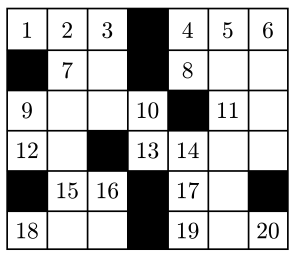
【练习-7】Crossword Answers
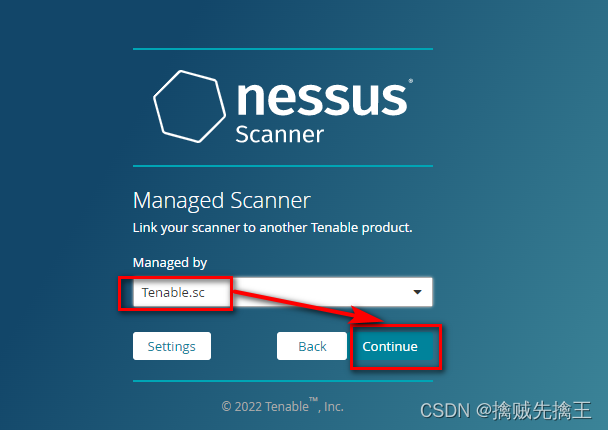
渗透测试 ( 7 ) --- 漏洞扫描工具 Nessus
入门C语言基础问答
随机推荐
Nodejs crawler
程序员的你,有哪些炫技的代码写法?
Borg Maze (BFS+最小生成树)(解题报告)
JS call camera
【练习-10】 Unread Messages(未读消息)
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of geosynthetic clay liner in China
最全编程语言在线 API 文档
B - Code Party (girls' competition)
渗透测试 ( 5 ) --- 扫描之王 nmap、渗透测试工具实战技巧合集
The most complete programming language online API document
F - Birthday Cake(山东省赛)
Shell Scripting
[exercise-1] (UVA 673) parentheses balance/ balanced brackets (stack)
Perform general operations on iptables
Opencv learning log 16 paperclip count
[exercise-7] (UVA 10976) fractions again?! (fraction split)
C语言是低级和高级的分水岭
[exercise-4] (UVA 11988) broken keyboard = = (linked list)
Flink 使用之 CEP
Write web games in C language