当前位置:网站首页>Borg Maze (BFS+最小生成树)(解题报告)
Borg Maze (BFS+最小生成树)(解题报告)
2022-07-06 09:25:00 【是小张张呀 zsy】
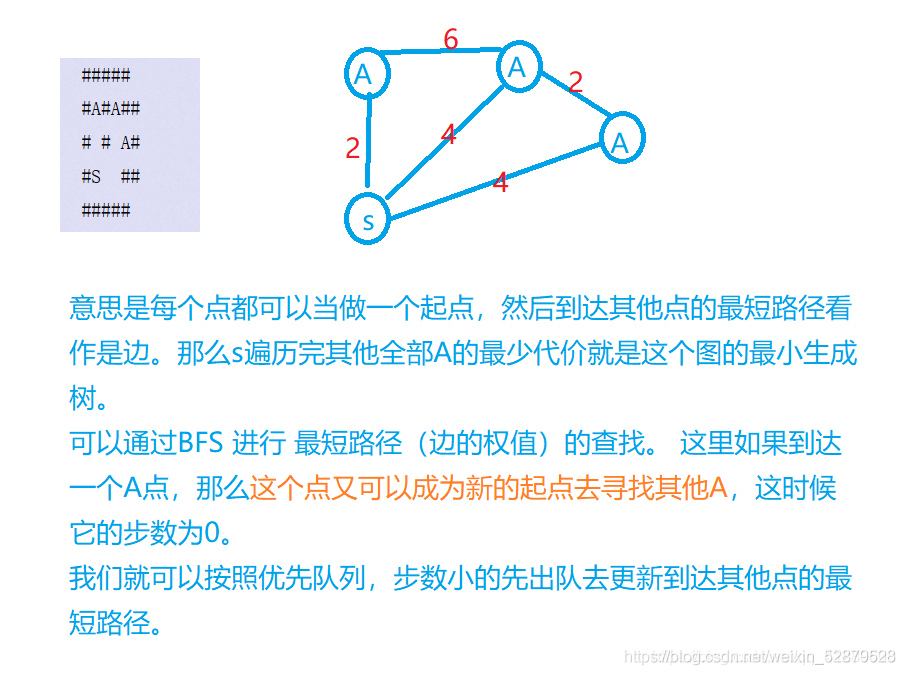
Borg Maze
The Borg is an immensely powerful race of enhanced humanoids from the delta quadrant of the galaxy. The Borg collective is the term used to describe the group consciousness of the Borg civilization. Each Borg individual is linked to the collective by a sophisticated subspace network that insures each member is given constant supervision and guidance.
Your task is to help the Borg (yes, really) by developing a program which helps the Borg to estimate the minimal cost of scanning a maze for the assimilation of aliens hiding in the maze, by moving in north, west, east, and south steps. The tricky thing is that the beginning of the search is conducted by a large group of over 100 individuals. Whenever an alien is assimilated, or at the beginning of the search, the group may split in two or more groups (but their consciousness is still collective.). The cost of searching a maze is definied as the total distance covered by all the groups involved in the search together. That is, if the original group walks five steps, then splits into two groups each walking three steps, the total distance is 11=5+3+3.
Input
On the first line of input there is one integer, N <= 50, giving the number of test cases in the input. Each test case starts with a line containg two integers x, y such that 1 <= x,y <= 50. After this, y lines follow, each which x characters. For each character, a space ‘’ stands for an open space, a hash mark #’’ stands for an obstructing wall, the capital letter A’’ stand for an alien, and the capital letter S’’ stands for the start of the search. The perimeter of the maze is always closed, i.e., there is no way to get out from the coordinate of the ``S’’. At most 100 aliens are present in the maze, and everyone is reachable.
Output
For every test case, output one line containing the minimal cost of a succesful search of the maze leaving no aliens alive.
Sample Input
2
6 5
#####
#A#A##
# # A#
#S ##
#####
7 7
#####
#AAA###
# A#
# S ###
# #
#AAA###
#####
Sample Output
8
11
有没有大佬们解释一下,为什么这里消除换行用gets(g[0]);而getchar()不行,找bug找了半天,才找到,qaq
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int const INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
char g[100][100];
int n,m,tol,k;
int a[100][100],cost[1100][1100],t[1000][1000];
int mo[][2]={
{
-1,0},{
1,0},{
0,1},{
0,-1}};
bool vis[1100];
int dis[1100];
void bfs(int sx,int sy)
{
queue<pair<int,int> >q;
while(!q.empty())
q.pop(); //清空队列;pop在对列头弹出元素;
memset(t,-1,sizeof(t));//t[][]标记是否走过,以及记录距离;
t[sx][sy]=0;
q.push(make_pair(sx,sy));//push在对尾压入元素
while(!q.empty())
{
pair<int,int> now=q.front();//访问队头元素
q.pop();
if(a[now.first][now.second]!=-1)//遇到A或S字符,更新距离cost;
{
cost[a[sx][sy]][a[now.first][now.second]]=t[now.first][now.second];
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int tx=now.first+mo[i][0];//当前点的上下左右;
int ty=now.second+mo[i][1];
if(g[tx][ty]=='#'||t[tx][ty]!=-1)//t[][]标记是否走过;
continue;
else
{
t[tx][ty]=t[now.first][now.second]+1;//记录距离;
q.push(make_pair(tx,ty));
}
}
}
}
int Prim(int tol)//又是熟悉的prim算法;
{
int ans=0,p;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<tol;i++)
dis[i]=cost[0][i];
for(int i=1;i<tol;i++)
{
int minn=INF;
p=-1;
for(int j=0;j<tol;j++)
{
if(vis[j]==0&&minn>dis[j])
{
p=j;
minn=dis[j];
}
}
if(minn==INF)
return -1;
vis[p]=1;
ans+=minn;
for(int j=0;j<tol;j++)
{
if(vis[j]==0&&dis[j]>cost[p][j])
dis[j]=cost[p][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int k;
scanf("%d",&k);
while(k--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
gets(g[0]);
tol=0;
memset(a,-1,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
gets(g[i]);//输入字符,gets必须有清除空格;
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(g[i][j]=='A'||g[i][j]=='S')
a[i][j]=tol++;//用a数组标记A和S,(从第几个A/S到第几个A/S);
//总计有tol个A和S,注意tol从0开始;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=-1)//让每个点都做一边起点;
bfs(i,j);
}
}
printf("%d\n",Prim(tol));
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- China's earthwork tire market trend report, technical dynamic innovation and market forecast
- C4D quick start tutorial - Introduction to software interface
- ucorelab3
- Brief introduction to libevent
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of Chinese hospital cleaning chemicals industry
- Optimization method of path problem before dynamic planning
- 基于485总线的评分系统
- STM32學習記錄:輸入捕獲應用
- Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of lip care products in China and Indonesia
- 学习记录:TIM—电容按键检测
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
力扣刷题记录--完全背包问题(一)
51 lines of code, self-made TX to MySQL software!
Cost accounting [17]
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of Chinese hospital respiratory humidification equipment
0-1 knapsack problem (I)
UCORE lab5 user process management experiment report
C语言数组的概念
差分(一维,二维,三维) 蓝桥杯三体攻击
Es6---es6 content details
Learning record: use stm32f1 watchdog
12306: mom, don't worry about me getting the ticket any more (1)
Medical colposcope Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
China's PCB connector market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast
How to build a nail robot that can automatically reply
Intensive learning notes: Sutton book Chapter III exercise explanation (ex17~ex29)
JS --- all basic knowledge of JS (I)
Cost accounting [22]
Cost accounting [20]
Want to change jobs? Do you know the seven skills you need to master in the interview software test
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of geosynthetics industry in China