当前位置:网站首页>JS --- all basic knowledge of JS (I)
JS --- all basic knowledge of JS (I)
2022-07-06 15:22:00 【Cirrod】
First time to know JavaScirpt
JavaScript Is one of the most popular languages in the world , Is a scripting language that runs on the client side (Script It means script )
Scripting language : No compilation required , During operation, the js Interpreter ( js engine ) Explain and execute line by line
Now it can also be based on Node.js Technology for server-side programming
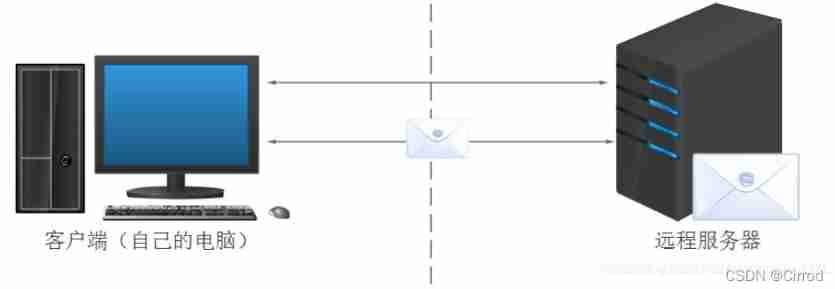
Browser execution JS brief introduction
The browser is divided into two parts : Rendering engine and JS engine
Rendering engine : Used to resolve HTML And CSS, Commonly known as the kernel , such as chrome Browser's blink , The old version of webkit
JS engine : Also known as JS Interpreter . Used to read from the web page JavaScript Code , Run it after processing , such as chrome Browser's V8
The browser itself doesn't execute JS Code , But through the built-in JavaScript engine ( Interpreter ) To execute JS Code .JS When the engine executes the code, it interprets each sentence of source code line by line ( Convert to machine language ), Then it's up to the computer to do , therefore JavaScript Languages are classified as scripting languages , Will explain and execute line by line .
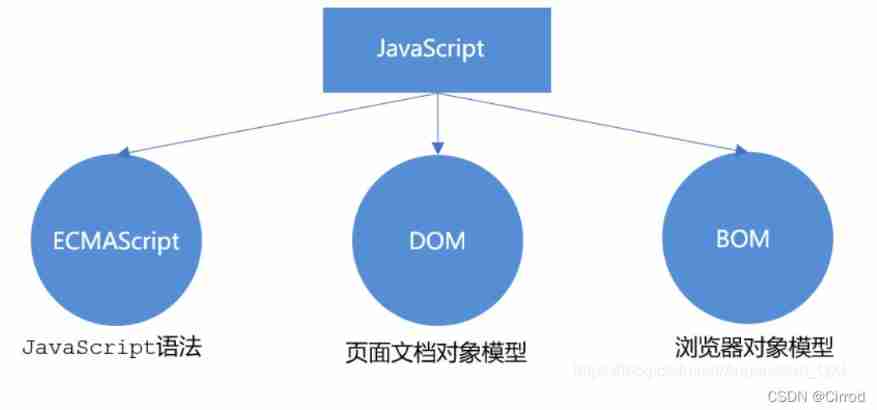
JS The composition of
JavaScript Include ECMAScript、DOM、BOM
ECMAScript
ECMAScript By ECMA The international ( The former European Association of computer manufacturers ) A programming language for standardization , This language is widely used on the world wide web , It is often called JavaScript or JScript, But actually the latter two are ECMAScript Language implementation and extension .
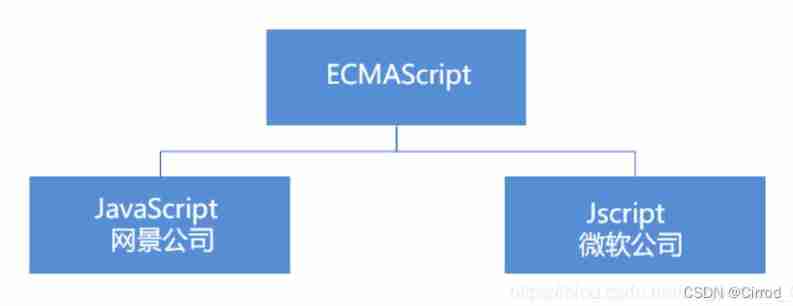
ECMAScript:ECMAScript Specifies the JS Programming syntax and basic core knowledge , It's a set that all browser manufacturers follow JS Grammar industry standard .
DOM Document object model
Document object model (Document Object Model, abbreviation DOM), yes W3C Organization recommended standard programming interface for extensible markup language . adopt DOM The interface provided can operate various elements on the page ( size 、 Location 、 Color, etc. ).
BOM Browser object model
BOM (Browser Object Model, abbreviation BOM) The browser object model , It provides content independent 、 Object structure that can interact with browser windows . adopt BOM You can operate the browser window , Like pop-up boxes 、 Control browser jump 、 Get resolution etc .
1、JS First experience
1.1、 Inline JS
<input type="button" value=" Let me try " onclink="alert('Hello World')" />Single or small JS The code is written in HTML In the event attribute of the tag ( With on The properties of the beginning ), Such as : onclink
Pay attention to the use of single and double quotation marks : stay HTML We recommend using double quotation marks ,JS We recommend using single quotation marks
Poor readability , stay HTML Incorporate JS A lot of code , It's not convenient to read
Use in special cases
1.2、 embedded JS
<script>
alert('Hello World!');
</script>You can do more than one line JS The code writes <script> In the label
Embedded JS It's a common way of learning
1.3、 external JS
<script src="my.js"></script>Good for HTML Page code is structured , Put alone JS The code is independent of HTML Off the page , It's beautiful , It's convenient
Quote external JS Of documents script No code can be written in the middle of the tag
Suitable for JS In the case of large amount of code
2、JS Basic grammar
2.1、 notes
2.1.1、 Single-line comments
// Single-line comments Shortcut key ctrl + /
2.1.2、 Multiline comment
/*
Multiline comment
*/Shortcut key shift + alt + a
vscode Modify shortcut keys in :vscode Preferences button Keyboard shortcuts Find the original shortcut key Change to a new shortcut key Carriage return confirmation
2.2、 I / O statement
| Method | explain | ascription |
| alert(msg); | A warning box pops up in the browser | browser |
| console.log(msg); | Browser console printouts | browser |
| prompt(info); | Browse and see the pop-up input box , User can input | browser |
alert() Mainly used to display messages to users
console.log() Used to show programmers their own runtime messages
2.3、 Variable
Variables are containers for storing data , We get data by variable name , Even the data can be modified
The essence : A variable is a piece of space that a program requests in memory to hold data
2.3.1、 Variable initialization
var It's a JS keyword , Used to declare variables (variable The meaning of a variable is ). After using this keyword to declare variables , The computer automatically allocates memory for variables .
age Is the programmer defined variable name , We need to access the space allocated in memory by variable name
// Declare the variable and assign it to 18
var age = 18;// When multiple variables are declared at the same time , Just write one var, Multiple variable names are separated by commas .
var age = 18, address =' Huoying Village ',salary = 15000;2.3.2、 Declare variable special case
| situation | explain | result |
| var age; console.log(age); | Only declare , No assignment | undefined |
| console.log(age) | Do not declare No assignment Use it directly | Report errors |
| age = 10;console.log(age); | Do not declare Assign only | 10 |
2.3.3、 Variable naming conventions
By letter (A-Z,a-z), Numbers (0-9), Underline (_), Dollar symbol ($) form , Such as :usrAge,num01,__name
Case sensitive . var app; and var App; It's two variables
Cannot start with a number .
It can't be a keyword , Reserved words . for example :var,for,while
Follow the hump nomenclature . Initial lowercase , The first letter of the following words needs to be capitalized .myFirstName
Recommended translation website : youdao ICIBA
2.4、 data type
JavaScript ** It's a weak type or dynamic language .** This means that you don't have to declare the type of the variable in advance , While the program is running , The type will be automatically determined .
var age = 10; // This is a number type
var areYouOk = ' bring '; // This is a string When the code is running , The data type of a variable is defined by JS engine according to = The data type of the variable value on the right is used to judge Of , After running , Variables determine the data type .
JavaScript Have dynamic types , It also means that the same variable can be used as a different type
var x = 6; //x Is the number
var x = "Bill"; //x For the string JS Divide data types into two categories :
Basic data type (Number,String,Boolean,Undefined,Null)
Complex data type (Object)
2.4.1、 Basic data type
| Simple data type | explain | The default value is |
| Number | Digital , Contains integer and floating point values , Such as 21,0.21 | 0 |
| Boolean | Boolean type , Such as true,false , Equivalent to 1 and 0 | false |
| Undefined | var a; Variable declared a But there's no assignment , here a=undefined | undefined( Undefined ) |
| string | String type , Such as “ Zhang San ” | “” |
| Null | var a = null; Variable declared a Null value | null |
2.4.2、 Digital Number
JavaScript Numeric types can be used to hold integer values , You can also save decimals ( Floating point numbers ).
var age = 12; // Integers
var Age = 21.3747; // decimal 2.4.2、 Digital base system
The most common system is binary 、 octal 、 Decimal system 、 Hexadecimal .
// 1. Octal number sequence range :0~7
var num1 = 07; // Corresponding to the decimal 7
var Num2 = 019; // Corresponding to the decimal 19
var num3 = 08; // Corresponding to the decimal 8// 2. Range of hexadecimal number sequence :0~9 as well as A~F
var num = 0xA;stay JS Add... Before the octal 0, Hexadecimal is preceded by 0x
① Digital range
JS The maximum value of the median value :Number.MAX_VALUE
JS The minimum value of the median value :Number.MIN_VALUE
consol.log(Number.MAX_VALUE);
consol.log(Number.MIN_VALUE);② Three special values of numeric type
alert(Infinity); //Infinity( infinity )
alert(-Infinity); //-Infinity( An infinitesimal )
alert(NaN); //NaN - Not a Number , Represents any non numeric value Infinity , For infinity , Greater than any number
-Infinity , For infinitesimal , Less than any number
Nan ,Not a Number, Represents a non numerical value
③isNaN
This method is used to judge non numeric , And return a value , If it is a number, it returns false, If it's not a number, it returns true

var userAge = 21;
var isOk = isNan(userAge);
console.log(isNum); //false,21 It's not a non number
var userName = "andy";
console.log(isNan(userName)); //true,"andy" It's a non number 2.4.3、 String type String
String type can be any text in quotation marks , Its grammar is “ Double quotes ” and " Single quotation marks ’’
var strMsg = " I love tian 'anmen square in Beijing ~"; // Use double quotation marks to represent strings
var strMsg = ' I love Beijing '; // Use single quotation marks to represent strings because HTML The attributes in the tag use double quotation marks ,JS Here we recommend using single quotation marks .
① String quotes nested
JS It can be used Single quotes nested double quotes , Or use Double quotes nested single quotes ( Double outside and single inside , Single outside and double inside )
var strMsg =' I am a " Grosvenor LTD handsome "' // It can be used ' ' contain " "
var strMsg2 =" I am a ' Grosvenor LTD handsome '" // It can be used " " contain ''② String escape character
similar HTML The special characters in it , There are also special characters in strings , We call it the escape character .
All the escape characters are \ At the beginning , The common escape characters and their descriptions are as follows :
| Escape character | interpretative statement |
| \n | A newline ,n yes newline |
| \ \ | Slash \ |
| \ ’ | ’ Single quotation marks |
| \ ‘’ | ‘’ Double quotes |
| \ t | tab Indent |
| \ b | Space ,b yes blank It means |
③ String length
A string is made up of several characters , The number of these characters is the length of the string . Through strings length Property to get the length of the entire string .
// Through strings length Property to get the length of the entire string
var strMsg = " I'm rich and handsome !";
alert(strMsg.length); // Show 6④ String splicing
You can use... Between multiple strings + Splicing , The splicing method is character string + Any kind of = The new string after splicing
Any type added to the string will be converted into a string before splicing , And then splice it into a new string
Be careful : character string + Any kind of = The new string after splicing
//1 String addition
alert('hello' + ' ' + 'World'); //hello World//2 Numeric strings are added
alert('100' + '100'); //100100//3 Numeric strings + The number
alert('12'+12); //1212//4 The number + The number
alert(12+12); //24+ To sum up the pithy formula : Add the values , The characters are connected
var age = 18;
console.log(' I this year '+age+' year ');
console.log(' I this year '+age+' year '); // Lead and add , Finally, it is also the above form ⑤ String concatenation strengthens
console.log('Pink teacher ' + 18); // As long as there are characters, they will be connected
var age = 18;
// console.log('Pink teacher age Year old '); // That's not good , Will be output "Pink teacher age Year old "
console.log('Pink teacher ' + age); // Pink teacher 18
console.log('Pink teacher ' + age + ' Years old! '); // Pink teacher 18 Years old! We often splice strings and variables , Because variables can easily modify the values inside
Variables cannot be quoted , Because quoted variables become strings
If you have string concatenation on both sides of the variable , formula ==“ Lead and add ”, Cut out the numbers == Variable write and middle
2.4.4、 Boolean type Boolean
The boolean type has two values :true and false , among true Said really ( Yes ), and false Said the false ( wrong ).
When Boolean and number are added , true The value of is 1 ,false The value of is 0.
var flag = true;
console.log(flag + 1); // 2 true When adding, when 1 Look at ,flase When 0 Look at 2.4.5、undefined Undefined
A variable that is not assigned after declaration has a default value undefined ( If you join or add , Pay attention to the results )
// If a variable declaration is not assigned , Namely undefined Data type not defined
var str;
console.log(str); //undefined
var variable = undefined;
console.log(variable + 'Pink'); //variablePink
console.log(variable + 18); //NaN1.undefined and character string Add up , Concatenate strings
2.undefined and Add the numbers , The end result is NaN
2.4.6、 Null value null
A declaration variable is given to null value , The value stored in it is empty
var space = null;
console.log(space + 'pink'); //nullpink
console.llog(space + 1); // 12.4.7、typeof
typeof Can be used to get the data type of the test variable
var num = 18;
console.log(typeof num) // result numberDifferent types of return values
| type | example | result |
| string | typeof “ The small white ” | “string” |
| number | typeof 18 | “number” |
| boolean | typeof true | “boolean” |
| undefined | typeof undefined | “undefined” |
| null | typeof null | “object” |
2.4.8、 Literal
Literal is a representation of a fixed value in the source code , Generally speaking , This is how literal quantities express this value .
Number literal quantity :8,9,10
Literal of a string :‘ Big front end ’,‘ Back end ’
Boolean literal :true、false
Determine the data type through the color of the console
| black | character string |
| Blue | The number |
| gray | undefined and null |
2.5、 Data type conversion
Use forms 、prompt The obtained data is of string type by default , At this point, we can't simply add , You need to convert the data type of the variable . Generally speaking , Is to convert a variable of one data type into another data type .
We usually achieve 3 The transformation of three ways :
Convert to string type
Convert to digital
Convert to Boolean
① Convert to string
| The way | explain | Case study |
| toString() | Convert to string | var num = 1; alert(num.toString()); |
| String() Coercive transformation | Convert to string | var num = 1; alert(String(num)); |
| The plus sign stitches strings | And the result of string stitching is string | var num =1; alert(num+“ I'm a string ”); |
//1. Convert numeric type to string type toString() Variable .toString()
var num = 10;
var str = num.toString();
console.log(str);//2. Coercive transformation
console.log(String(num));toString() and String() It's not the same way
Three ways of conversion , We prefer to use the third plus sign to splice string conversion , This method is also called hermit transformation
② Convert to digital
| The way | explain | Case study |
| parselnt(string) function | take string Type to integer numeric type | parselnt(‘78’) |
| parseFloat(string) function | take string Type to floating-point numeric type | parseFloat(‘78.21’) |
| Number() Cast function | take string Type to numeric | Number(‘12’) |
| js Implicit conversion (- * /) | Implicit conversion to numerical type by arithmetic operation | ‘12’-0 |
// 1.parseInt()
var age =prompt(' Please enter your age ');
consolo.log(parseInt(age)); // Digital 18
consolo.log(parseInt('3.14')); //3 integer
consolo.log(parseInt('3.94')); //3, Will not round off
consolo.log(parseInt('120px')); //120, It's going to take out units // 2.parseFloat()
console.log(parseFloat('3.14')); //3.14
consolo.log(parseFloat('120px')); //120, It's going to take out units // 3. utilize Number( Variable )
var str ='123';
console.log(Number(str));
console.log(Number('12'));// 4. Using arithmetic operations - * / Implicit conversion
console.log('12'-0); // 12
console.log('123' - '120'); //3
console.log('123' * 1); // 1231. Be careful parseInt and parseFloat , These two are the key points
2. Implicit conversion is when we do arithmetic operations ,JS Automatically converted the data type
③ Convert to Boolean
| Method | explain | Case study |
| Boolean() function | Convert other types to Booleans | Boolean(‘true’); |
Representational space , Negative values are converted to false, Such as ’ ’ , 0, NaN , null , undefined
The rest of the values will be converted to true
console.log(Boolean('')); //false
console.log(Boolean(0)); //false
console.log(Boolean(NaN)); //false
console.log(Boolean(null)); //false
console.log(Boolean(undefined)); //false
console.log(Boolean(' The small white ')); //true
console.log(Boolean(12)); //true2.6、 Operator
Operator (operator) Also known as the operator , Is used to implement assignment 、 Symbols that compare and perform functions such as arithmetic operations
JavaScript The operators commonly used in are :
Arithmetic operator
Increment and decrement operators
Comparison operator
Logical operators
Assignment operator
2.6.1、 Arithmetic operator
Concept : Symbols used in arithmetic operations , Used to perform arithmetic operations on two variables or values .
| Operator | describe | example |
| + | Add | 10 + 20 =30 |
| - | reduce | 10 - 20 =-10 |
| * | ride | 10 * 20 =200 |
| / | except | 10 / 20 =0.5 |
| % | Take the remainder ( modulus ) | Returns the remainder of the departure 9 % 2 =1 |
2.6.2、 The precision of floating point numbers
The highest precision of a floating-point value is 17 Decimal place , But the accuracy of arithmetic is far less than that of integer
var result = 0.1 +0.2; // It didn't turn out to be 0.3,0.30000000000000004
console.log(0.07 * 100); // It didn't turn out to be 7, It is 7.000000000000001So don't directly judge whether two floating-point numbers are equal
2.6.3、 Increment and decrement operators
Increasing (++)
Decline (- -)
When you put it in front of a variable , We call it prepositional increment ( Decline ) Operator
When you put it after a variable , We call it post increment ( Decline ) Operator
Be careful : Increment and decrement operators must be used with variables .
① Pre increment operator
++num num = num + 1
Use the pithy formula : Add it first , Then return the value
var num = 10;
alert (++num + 10); // 21Add it first 10+1=11, return 11, here num=11
② Post increment operator
num ++ num = num +1
Use the pithy formula : Return the original value first , Post autoplus
var num = 10;
alert(10 + num++); // 20③ Summary
Pre increment and post increment operators can simplify the writing of code , Let the value of the variable + 1 Easier to write than before
When used alone , The running results are the same , When used with other code , The execution results will be different
When developing , Most use post increment / reduce , And the code has a single line
2.6.4、 Compare ( Relationship ) Operator
The comparison operator is the operator used when comparing two data , After comparison , Will return a Boolean value (true / false) As a result of the comparison operation .
| Operator name | explain | Case study | result |
| < | Less than no. | 1 < 2 | true |
| > | More than no. | 1 > 2 | false |
| >= | Greater than or equal to ( Greater than or equal to ) | 2 >= 2 | true |
| <= | Less than or equal to sign ( Less than or equal to ) | 3 <= 2 | false |
| == | Equal sign ( It will transform ) | 37 == 37 | true |
| != | Unequal sign | 37 != 37 | false |
| === !== | Congruence The values and data types are required to be the same | 37 === ‘37’ | false |
①===== Summary
| Symbol | effect | usage |
| = | assignment | Give the right to the left |
| == | Judge | Judge whether the values on both sides are equal ( Note that there is a hermit conversion at this time ) |
| === | Congruence | Determine whether the values and data types on both sides are exactly the same |
console.log(18 == '18'); //true
console.log(18 === '18'); //false2.6.5、 Logical operators
Logical operators are operators used for Boolean operations , Its return value is also Boolean
| Logical operators | explain | Case study |
| && | “ Logic and ”, abbreviation " And " and | true && false |
| || | “ Logic or ”, abbreviation " or " or | true || false |
| ! | “ Logic is not ”, abbreviation " Not " not | !true |
Logic and : On both sides true To return to true, Otherwise return to false
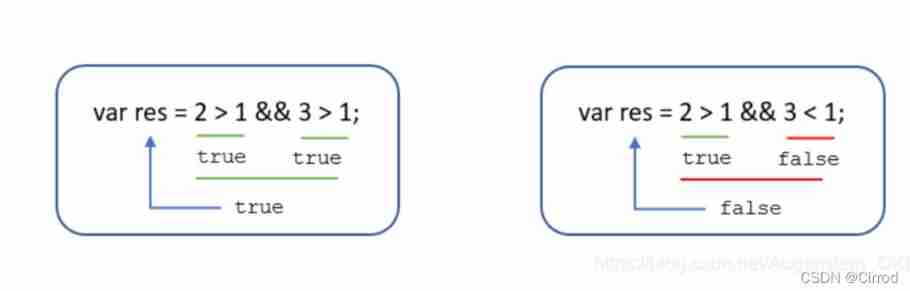
Logic or : On both sides false To return to false, Otherwise, it's all for true
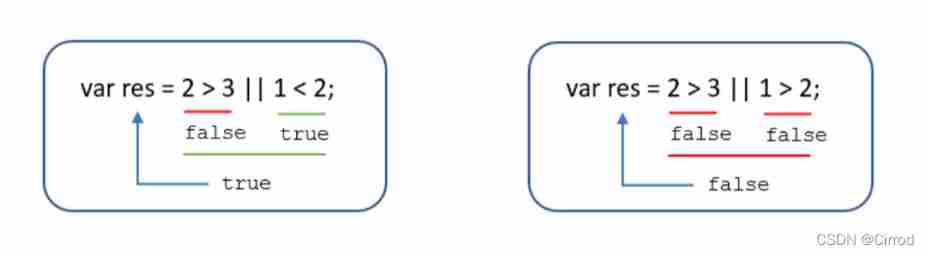
Logic is not : Logic is not (!) It's also called the negation , Used to take a value that is the opposite of a Boolean value , Such as true The opposite of this is false
var isOk = !true;
console.log(isOk); // false
// Logic is not (!) It's also called the negation , Used to take a value that is the opposite of a Boolean value , Such as true The opposite of this is false2.6.5.1、 Short-circuit operation ( Logic break )
The principle of short circuit operation : When there are multiple expressions ( value ) when , When the value of the expression on the left can determine the result , The value of the expression on the right will no longer be evaluated
① Logic and
grammar : expression 1 && expression 2
If the value of the first expression is true , Then return the expression 2
If the value of the first expression is false , Then return the expression 1
console.log(123 && 456); //456
console.log(0 && 456); //0
console.log(123 && 456 && 789); //789② Logic or
grammar : expression 1 || expression 2
If the value of the first expression is true , Then return the expression 1
If the value of the first expression is false , Then return the expression 2
console.log(123 || 456); //123
console.log(0 || 456); //456
console.log(123 || 456 || 789); //123
var num = 0;
console.log(123 || num++);
// Return to plus first , amount to (123 || 0)
console.log(num); // 1232.6.6、 Assignment operator
Concept : Operators used to assign data to variables .
| Assignment operator | explain | Case study |
| = | Direct assignment | var usrName = ‘ I'm worth it ’ |
| += ,-= | Add , Subtract a number and assign a value | var age = 10; age+=5;//15 |
| *=,/=,%= | become , except , Take the module and then assign the value | var age = 2; age*=5; //10 |
var age = 10;
age += 5; // amount to age = age + 5;
age -= 5; // amount to age = age - 5;
age *= 10; // amount to age = age * 10;2.6.7、 Operator priority
| priority | Operator | The order |
| 1 | parentheses | () |
| 2 | Unary operator | ++ – ! |
| 3 | Arithmetic operator | First * / after + - |
| 4 | Relational operator | >, >= , < , <=, |
| 5 | Equality operator | ,!=,=,!== |
| 6 | Logical operators | First && after ||( First and then or ) |
| 7 | Assignment operator | = |
| 8 | The comma operator | , |
1. The logical non priority in unary operators is very high
2. Logic and Than Logic or High priority
3. Exercises
console.log( 4 >= 6 || ' people ' != ' "Avatar" ' && !(12 * 2 == 144) && true) // true
var a = 3 > 5 && 2 < 7 && 3 == 4;
console.log(a); //false
var b = 3 <= 4 || 3 > 1 || 3 != 2;
console.log(b); //true
var c = 2 === "2";
console.log(c); //false
var d = !c || b && a ;
console.log(d); //true
2.7、 Process control
There are three main structures of process control , They are sequence structure 、 Branch and loop structures , These three structures represent the order in which the three codes are executed
2.7.1、 Branching structure
JS Language provides two branch structure statements :if sentence switch sentence
①if sentence
// If the condition holds, execute the code , Otherwise, do nothing
if ( Conditional expression ) {
// The code statement executed when the condition is true
}Case study : Enter the Internet bar
Pop up an input box , Ask the user to enter age , If age is greater than or equal to 18 year , Allow access to Internet cafes
var usrAge = prompt(' Please enter your age :');
if(usrAge >= 18)
{
alert(' Your age is legal , Welcome to Laozi Internet cafe to enjoy learning !');
}②if else sentence
// Conditions established , perform if Code inside , Otherwise execution else Code inside
if( Conditional expression )
{
//[ If ] Conditional execution code
}
else
{
//[ otherwise ] Executed code
}Case study : Judgement of leap year
Receive the year entered by the user , If it's a leap year, it pops up a leap year , Otherwise, it's a normal year
Algorithm : Can be 4 Divisible and not divisible 100 Leap year ( Such as 2004 Year is leap year ,1901 Year is not a leap year ) Or can be 400 Divisible is leap year
var year = prompt(' Please enter the year ');
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 || year % 400 ==0)
{
alert(' This year is a leap year ');
}
else
{
alert(' This year is a normal year ');
}③if else if sentence
if( Conditional expression 1)
{
sentence 1;
}
else if( Conditional expression 2)
{
sentence 2;
}
else if( Conditional expression 3)
{
sentence 3;
}
else
{
// None of the above conditions holds. Execute the code here
}Case study : Receive user entered scores , Output the corresponding grade letter according to the score A、B、C、D、E
among :
90 branch ( contain ) above , Output :A
80 branch ( contain )~ 90 branch ( Not included ), Output :B
70 branch ( contain )~ 80 branch ( Not included ), Output :C
60 branch ( contain )~ 70 branch ( Not included ), Output :D
60 branch ( Not included ) following , Output : E
var score = prompt(' Please enter the score :');
if (score >= 90) {
alert(' baby , You are my pride ');
} else if (score >= 80) {
alert(' baby , You are already excellent ');
} else if (score >= 70) {
alert(' You have to keep refueling ');
} else if (score >= 60) {
alert(' children , You are very dangerous ');
} else {
alert(' Can you work harder , You're great , But not good enough ');
}2.7.2、 Ternary expression
Grammatical structure : expression 1 ? expression 2 : expression 3
Execution ideas
If the expression 1 by true, Then return the expression 2 Value , If the expression 1 by false, Then return the expression 3 Value
Case study : Number complement 0
The user enters numbers , If the number is less than 10, Then fill in the front 0, such as 01,09,
If the number is greater than 10, There is no need to make up , such as 20
var figuer = prompt(' Please enter 0~59 A number between ');
var result = figuer < 10 ? '0' + figuer : figue
alert(result);2.7.3、switch
switch( expression ){
case value1:
// The expression is equal to value1 Code to execute when
break;
case value2:
// The expression is equal to value2 Code to execute when
break;
default:
// The expression is not equal to any one value Code to execute when
}switch : switch transformation , case : Small example Options
keyword switch The following parentheses can be expressions or values , It's usually a variable
keyword case , An expression or value followed by an option , Followed by a colon
switch The value of the expression will be the same as case Compare the values of
If there is matching congruence (===) , Then it is related to the case The associated block of code is executed , And meet break Stop when , Whole switch End of statement code execution
If all case Does not match the value of the expression , execute default Code in
perform case The sentence inside is , without break, Then proceed to the next case The words in it
// The user enters a fruit in the pop-up box , If so, the price of the fruit will pop up , If you don't have the fruit, pop it up “ Without this fruit ”
var fruit = prompt(' Please enter the apple you want to query ');
switch (fruit) {
case ' Apple ':
alert(' The price of apple is 3.5 element / kg ');
break;
case ' Banana ':
alert(' The price of bananas is 3 element / kg ');
break;
default:
alert(' There is no such fruit ');
}3、 Breakpoint debugging
Press in browser F12–> sources --> Find the file you need to debug –> Set breakpoints on one line of the program ( I'm good at counting )
Refresh the browser
Watch: monitor , adopt watch You can monitor the value of variables , Very often
F11: Step by step , Let the program execute line by line , This is the time , Observe watch The change in the value of a variable in
4、 loop
4.1、for loop
In the program , A set of statements that are repeatedly executed is called a loop body , Can you continue to repeat , Depending on the termination condition of the loop . A statement consisting of the body of a loop and its termination conditions , It's called a loop statement
for( Initialize variable ; Conditional expression ; Operation expression )
{
// The loop body
}1. Input 10 sentence " Good night, madam !"
// The basic way of writing
for(var i = 1; i<=10; i++ )
{
console.log(' Good night, madam ');
}// Number of user inputs
var num = prompt(' Please enter the number of times :');
for(var i = 1; i<= num ;i++)
{
console.log(' Good night, madam ');
}2. seek 1-100 The cumulative sum of all integers between
// seek 1-100 So the sum of integers
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
var sum = sum + i;
}
console.log(sum);3. seek 1-100 The average of all numbers between
// 3. seek 1-100 The average of all numbers between
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
var sum = sum + i;
}
console.log(sum / 100);4. seek 1-100 The sum of all even and odd numbers
// 4. seek 1-100 The sum of all even and odd numbers
var sum1 = 0;
var sum2 = 0;
for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
sum1 = sum1 + i;
} else {
sum2 = sum2 + i;
}
}
console.log(' Even sum is ' + sum1);
console.log(' Odd sum is ' + sum2);5. seek 1-100 Between all can be 3 The sum of divisible numbers
// 5. seek 1-100 Between all can be 3 The sum of divisible numbers
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
sum += i;
}
}
console.log(sum);6. Ask the user to enter the number of classes , Then enter the grades of each student in turn , Finally, print out the total score and average score of the class .
var num = prompt(' Please enter the total number of people in the class :'); // num The total number of people in the class
var sum = 0; // Total score
var average = 0; // Average score
for (var i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
var score = prompt(' Please enter the first ' + i + ' Results of students ');
// What is received here is str, Must be converted to a numeric value
sum = sum + parseFloat(score);
}
average = sum / num;
alert(' The total grade of the class is :' + sum);
alert(' The total average grade of the class is :' + average);7. One line printing 5 A star
We append strings , This will print to the console
var star = '';
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
star += '*';
}
console.log(star);4.2、 double for loop
Loop nesting refers to defining the syntax structure of a loop statement in a loop statement , For example, in for In loop statement , You can nest another for loop , In this way for Loop statements are called Double for loop .
for( The beginning of the outer loop ; The condition of the outer loop ; Operation expression of profile loop ){
for( The beginning of the inner loop ; The condition of the inner loop ; The operation expression of inner loop ){
Code to execute ;
}
}The inner loop can be regarded as the statement of the outer loop
The order of inner loop execution should also follow for The execution order of the loop
The outer loop is executed once , The inner loop is executed all the times
① Print five lines and five columns of stars
The core :
The inner loop is responsible for printing five stars on a line
The outer loop is responsible for printing five lines
var star = '';
for(var j = 1;j<=5;j++)
{
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
star += '*'
}
// Every time it's full 5 One star plus one line break
star +='\n'
}
console.log(star);② Print n That's ok n The stars of the column
The user is required to enter the number of rows and columns , Then print out the number of rows and columns entered by the user on the console
var star = '';
var row = prompt(' Please enter the number of lines ');
var col = prompt(' Please enter the number of columns ');
for (var j = 1; j <= col; j++) {
for (var i = 1; i <= row; i++) {
star += '*';
}
star += '\n';
}
console.log(star);③ Print inverted triangle

Altogether 10 That's ok , But the number of stars in each row is different , So you need to use double for loop
The outer for Control the number of lines i , loop 10 You can print 10 That's ok
The inner layer of the for Control the number of stars per row j
The core algorithm : The number of stars in each row : j = i ; j <= 10; j++
After each line is printed , Need to change a new line
var star = '';
var row = prompt(' Please enter the number of lines ');
var col = prompt(' Please enter the number of columns ');
for (var i = 1; i <= row; i++) {
for (var j = i; j <= col; j++) {
star += '*';
}
star += '\n';
}
console.log(star);4.3、while loop
while( Conditional expression ){
// Loop body code
}Execution ideas :
First execute the conditional expression , If the result is true, The loop body code is executed ; If false, Then exit the loop , Execute the following code
Execute the loop body code
After the loop body code is executed , The program will continue to judge the execution condition expression , If the condition is still true, The loop body will continue to execute , Until the cycle condition is false when , The whole cycle will end
Be careful :
Use while Be sure to pay attention to , It has to have exit conditions , Otherwise it will be called an endless cycle
while Circulation and for The difference between loops is while Loops can make more complex conditional judgments , For example, judge the user name and password
① Print one's life
from 1 To the age of 99 year
var age = 0;
while (age <= 100) {
age++;
console.log(' This year you ' + age + ' Year old ');
}② Calculation 1 ~ 100 The sum of all integers between
var figure = 1;
var sum = 0;
while (figure <= 100) {
sum += figure;
figure++;
}
console.log('1-100 The sum of integers is ' + sum);4.4、do while loop
do {
// Loop body code - The conditional expression is true Repeat the loop one code when
}while( Conditional expression );Execution ideas :
First execute the loop body code once
Then execute the expression , If the result is true, Then continue to execute the loop body code , If false, Then exit the loop , Continue with the rest of the code
Execute first and then judge the loop body , therefore dowhile The loop statement executes the loop body code at least once
demand : Pop up a prompt box , Do you love me? ? If I love you , It will prompt the end , otherwise , Keep asking
do {
var love = prompt(' Do you love me? ?');
} while (love != ' I love you! ');
alert(' Login successful ');4.5、continue keyword
continue Keyword is used to jump out of the loop immediately , So let's go to the next loop ( In this cycle continue After that, the code will be executed once less ).
for example , eat 5 A steamed bun , The first 3 There are worms , Just throw away number one 3 individual , Go on eating No 4 First paragraph 5 A steamed bun
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
console.log(' This steamed bun has worms , Throw away ');
continue; // Jump out of this cycle , It's No 3 Secondary cycle
}
console.log(' I'm eating No ' + i + ' How about a steamed bun ');
}4.6、break keyword
break Keyword is used to jump out of the loop immediately
for example , eat 5 A steamed bun , Eat to the end 3 I found half a bug in it , Don't eat the rest
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
break; // Exit the whole for loop , Jump to the whole thing for The following statement
}
console.log(' I'm eating No ' + i + ' How about a steamed bun ');
}5、 Array
Array (Array) A collection of data , Each of these data is called an element , Any type of element can be stored in the array . Arrays are an elegant way to store a set of data under a single variable name .
// Ordinary variables can only store one value at a time
var num = 10;
// Arrays can store multiple values at a time
var arr =[1,2,3,4,5];5.1、 Create array
JavaScript There are two ways to create arrays in :
utilize new Create array
Create an array using array literals
① utilize new Create array
var Array name = new Array();
var arr = new Array(); // Create a new empty array In this way, let's understand , Wait until you finish learning
Be careful Array(),A Use capital letters
② Create an array using array literals
// 1. Create an empty array using array literal
var Array name =[];
// 2. Create an array with an initial value using array literal
var Array name =[' The small white ',' Little black ',' Xiao Huang ',' Ricky '];
// 3. Array can store any type of data , Like strings , Numbers , Boolean value, etc
var arrStus =[' The small white ',12,true,28.9];The literal of the array is square brackets []
Declaring an array and assigning values is called array initialization
This literal way is also the way we use most in the future
5.2、 Index of array ( Subscript )
Indexes ( Subscript ) : The ordinal number used to access an array element ( Array index from 0 Start )
// Define an array
var arrStus = [1,2,3];
// Gets the number... In the array 2 Elements
alert(arrStus[1]);5.3 Traversal array
We can go through for The circular index traverses each item in the array
// The array index accesses the elements in the array
var arr = ['red','green', 'blue'];
console.log(arr[0]) // red
console.log(arr[1]) // green
console.log(arr[2]) // blue
// for Loop through groups
var arr = ['red','green', 'blue'];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
console.log(arrStus[i]);
}5.4、 Length of array
Use “ Array name .length” The number of array elements that can be accessed ( The length of the array )
var arrStus = [1,2,3];
alert(arrStus.length); // 3Be careful :
Here, the length of the array is the number of array elements , Don't confuse it with the index number of the array
When the number of elements in our array changes , This length Properties change with each other
5.5、 Case study
1. Please put [“ Guan yu ”,“ Zhang Fei ”,“ d ”,“ zhaoyun ”,“ Huang Zhong ”,“ Liu bei ”,“ Jiang Wei ”]; The elements in the array are printed to the console in turn v
ar arr = [" Guan yu "," Zhang Fei "," d "," zhaoyun "," Huang Zhong "," Liu bei "," Jiang Wei "];
// Traverse From the first to the last
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++ ) {
console.log( arr[i] );
}2. Find an array [2,6,1,7, 4] The sum and average of all the elements in it
① Declare a summation variable sum.
① Traverse the array , Add each array element to sum Inside .
① Use summation variables sum Divide by the length of the array to get the average value of the array .
var arr = [2, 6, 1, 7, 4];
var sum = 0;
var average = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
average = sum / i; // here i by 5
// average = sum / arr.length;
console.log(' And for ' + sum);
console.log(' The average value is ' + average);3. Find an array [2,6,1,77,52,25,7] Maximum of
① Declare a variable that holds the largest element max.
② The default maximum value can take the first element in the array .
③ Traverse the array , Put every array element in it and max Comparison .
④ If this array element is larger than max Just save this array element to max Inside , Otherwise, continue with the next round of comparison .
⑤ Finally, output this max.
var arr = [2, 6, 1, 77, 52, 25, 7];
var max = arr[0];
var temp;
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (max < arr[i]) {
temp = max;
max = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
console.log(' The maximum value is ' + max);Method 2 :
var arrNum = [2,6,1,77,52,25,7];
var maxNum = arrNum[0]; // Used to hold the largest element , The default maximum value is the first element in the array
// from 0 Start looping through each element in the array
for(var i = 0;i< arrNum.length; i++){
// If the element of the current loop in the array is greater than maxNum, Save this element and subscript
if(arrNum[i] > maxNum){
maxNum = arrNum[i]; // Save values to variables maxNum
}
}4. Will array [‘red’, ‘green’, ‘blue’, ‘pink’] The elements inside are converted into strings
Ideas : Just add the elements inside , But be sure to add characters
① Need a new variable str Used to store the converted String .
② Traverse the original array , Take out the data inside , Add to string variable str Inside .
var arr = ['red','green','blue','pink'];
var str ='';
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
str += arr[i];
}
console.log(str);
// redgreenbluepink5. Will array [‘red’, ‘green’, ‘blue’, ‘pink’] Convert to string , And use | Or other symbols
① You need a new variable to store the converted String str.
① Traverse the original array , Take out the data inside , Add to the string .
① At the same time, add an additional separator after .
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink'];
var str = '';
var separator = '|';
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
str += arr[i] + separator;
}
console.log(str);
// red|green|blue|pink5.6、 New elements in the array
① By modifying the length Length adds an array element
It can be modified by length Length to achieve the purpose of array expansion
length Properties are readable and writable
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink'];
arr.length = 7;
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr[4]);
console.log(arr[5]);
console.log(arr[6]);Where the index number is 4,5,6 The space is not given a value , Is to declare that the variable is not given a value , The default value is undefined
② Add new array elements by modifying the array index
You can append array elements by modifying the array index
You cannot assign values to array names directly , Otherwise, the previous data will be overwritten
This way is also the most commonly used way
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink'];
arr[4] = 'hotpink';
console.log(arr);5.7、 New elements in the array
1. Create a new array , Inside the store 10 It's an integer ( 1~10), It is required to output by circular addition : [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
① Use a loop to append an array .
② Declare an empty array arr.
③ The counter in the loop i Can be stored as an array element .
Because the index number of the array is from 0 At the beginning , So the counter starts from 0 It's more appropriate to start , The stored array elements should +1.
var arr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++){
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
console.log(arr);2. Will array [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7] Medium greater than or equal to 10 Select the elements of , Put the new array
① Declare a new array for storing new data .
② Traverse the original array , Find a value greater than or equal to 10 The elements of .
③ Append to the new array in turn newArr.
Implementation code 1:
var arr = [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7];
var newArr = [];
// Define a variable To calculate The index number of the new array
var j = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] >= 10) {
// Give the new array
newArr[j] = arr[i];
// Reference no. Keep adding
j++;
}
}
console.log(newArr);Implementation code 2:
var arr = [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7];
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] >= 10) {
// Give the new array
newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
}
}
console.log(newArr);5.8、 Deletes the specified array element
Will array [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7] Medium 0 After removal , Form a form that does not contain 0 New array .
var arr = [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7];
var newArr = [];
for(var i = 0; i <arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] != 0){
newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
}
}
console.log(newArr);// Teacher code
var arr = [2, 0, 6, 1, 77, 0, 52, 0, 25, 7];
var newArr = []; // The default length of an empty array is 0
// Define a variable i Used to calculate the index number of the new array
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// Find out more than 10 Number of numbers
if (arr[i] != 0) {
// Give the new array
// Store one value at a time ,newArr Length will be +1
newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
}
}
console.log(newArr);5.9、 Flip array
Will array [‘red’, ‘green’, ‘blue’, ‘pink’, ‘purple’] The contents of are stored in reverse
// Put the first... Of the index number of the old array 4 Take one (arr.length - 1), Give the index number of the new array 0 Elements (newArr.length)
var arr = ['red','green','blue','pink','purple'];
var newArr = [];
for (var i = arr.length -1; i>=0; i--){
newArr[newArr.length] = arr[i];
}
console.log(newArr);5.10、 Array sorting
Bubble sort
Will array [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] The elements in are sorted from small to large , Output : 1,2,3,4,5
var arr = [5,4,3,2,1];
for (var i = 0; i <= arr.lengtg-1; i++){ // Number of outer circulating pipe trips ,5 The number is exchanged 4 lie
for (var j = 0; j <= arr.length - i - 1; j++){
// The number of times of each exchange of the inner circulating pipe
// Compare the previous and the following array elements
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
var temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
console.log(arr);边栏推荐
- Introduction to safety testing
- How to write the bug report of software test?
- MySQL development - advanced query - take a good look at how it suits you
- Practical cases, hand-in-hand teaching you to build e-commerce user portraits | with code
- Pedestrian re identification (Reid) - data set description market-1501
- Knowledge that you need to know when changing to software testing
- Interface test interview questions and reference answers, easy to grasp the interviewer
- MySQL transactions
- Rearrange spaces between words in leetcode simple questions
- 软件测试行业的未来趋势及规划
猜你喜欢
ucore lab2 物理内存管理 实验报告
How to build a nail robot that can automatically reply

Investment operation steps
Do you know the advantages and disadvantages of several open source automated testing frameworks?
Eigen User Guide (Introduction)
Automated testing problems you must understand, boutique summary

The minimum number of operations to convert strings in leetcode simple problem
Do you know the performance testing terms to be asked in the software testing interview?

Brief introduction to libevent

Threads et pools de threads
随机推荐
Interview answering skills for software testing
Global and Chinese markets of cobalt 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Intensive learning notes: Sutton book Chapter III exercise explanation (ex17~ex29)
The minimum number of operations to convert strings in leetcode simple problem
遇到程序员不修改bug时怎么办?我教你
软件测试方法有哪些?带你看点不一样的东西
ucorelab4
[C language] twenty two steps to understand the function stack frame (pressing the stack, passing parameters, returning, bouncing the stack)
全网最详细的postman接口测试教程,一篇文章满足你
Rearrange spaces between words in leetcode simple questions
Global and Chinese market for antiviral coatings 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
MySQL数据库(五)视 图 、 存 储 过 程 和 触 发 器
LeetCode#412. Fizz Buzz
Take you to use wxpy to create your own chat robot (plus wechat interface basic data visualization)
Lab 8 file system
Contest3145 - the 37th game of 2021 freshman individual training match_ A: Prizes
Global and Chinese markets for GaN on diamond semiconductor substrates 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Leetcode simple question: check whether the numbers in the sentence are increasing
LeetCode#204. Count prime
ucore lab 2

