当前位置:网站首页>Pedestrian re identification (Reid) - Overview
Pedestrian re identification (Reid) - Overview
2022-07-06 15:09:00 【gmHappy】
What is? Re-ID?
- Pedestrian recognition (Person re-identification, abbreviation Re-ID) Also known as pedestrian recognition , Is the use of computer vision technology to determine whether there is a specific pedestrian in the image or video sequence . It is widely regarded as a sub problem of image retrieval . Given a monitored pedestrian image , Retrieve the pedestrian image under the cross device . It aims to make up for the visual limitations of the current fixed camera , And can detect with pedestrians / Combination of pedestrian tracking technology , It can be widely used in intelligent video surveillance 、 Intelligent security and other fields .
- As shown in the figure below : There are multiple cameras shooting video sequences in an area ,ReID The requirements of a camera under the interest of pedestrians , Retrieve all pictures of the pedestrian under other cameras .
Why Re-ID?
In surveillance video , Due to the camera resolution and shooting angle , Very high quality face images are usually not available . When face recognition fails ,ReID It has become a very important alternative technology .
Research forms
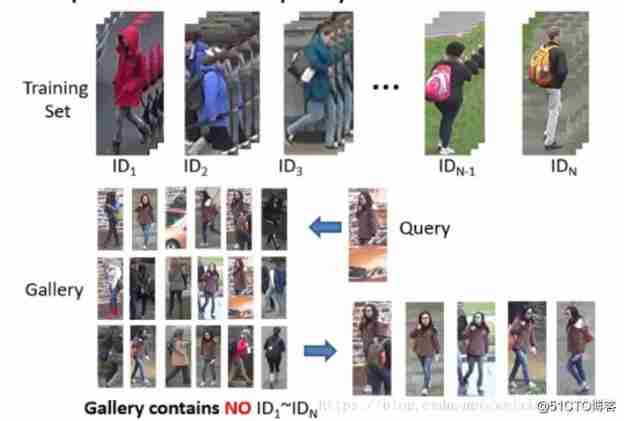
- Data sets are usually pedestrian images obtained by manual annotation or detection algorithms , At present, it is independent of detection , Pay attention to identification
- Data sets are divided into training sets 、 Verification set 、Query、Gallery
- Train the model on the training set , After getting the model, right Query And Gallery Image feature extraction and similarity calculation in , For each Query stay Gallery Find out before N A similar picture
- Training 、 The identity of the person in the test is not repeated

Two directions
- feature extraction : Learn to be able to cope with the characteristics of people changing under different cameras
- Measure learning : Mapping the learned features to a new space makes the same people closer and different people farther
There are challenges
- Different cameras cause great changes in the appearance of pedestrians ;
- Target occlusion (Occlusion) Some features are lost ;
- Different View,Illumination Differences in characteristics that lead to the same goal ;
- Different target clothes have similar colors 、 Feature approximation leads to a decrease in discrimination ;
Common data set
CUHK03
Market1501
DukeMTMC-reID
MSMT17
Only commonly used data sets are listed here , A more complete data set can be referred to : Person Re-identification Datasets
Commonly used evaluation index
- rank-k: The sorting list returned by the algorithm , front k If the bit is an existing search target, it is called rank-k hit .eg:rank1: The first is the search target rank-1 hit .
- Cumulative Match Characteristic (CMC)
Take a very simple example , Suppose in face recognition , There are 100 personal , Now comes 1 A face to be recognized ( If label by m1), After comparing with the faces in the bottom database, the faces in the bottom database are sorted from high to low , We found that :
If the recognition result is m1、m2、m3、m4、m5……, Now rank-1 The accuracy of is 100%;rank-2 The correct rate of is 100%;rank-5 The correct rate of is 100%;
If the recognition result is m2、m1、m3、m4、m5……, Now rank-1 The accuracy of is 0%;rank-2 The accuracy of is 100%;rank-5 The correct rate of is 100%;
If the recognition result is m2、m3、m4、m5、m1……, Now rank-1 The accuracy of is 0%;rank-2 The accuracy of is 0%;rank-5 The accuracy of is 100%;
Empathy , When there are many faces to be recognized , Take the average . For example, the face to be recognized has 3 individual ( If label by m1,m2,m3), Similarly, there is a score from high to low for everyone's face ,
such as :
Face 1 The result is m1、m2、m3、m4、m5……,
Face 2 The result is m2、m1、m3、m4、m5……,
Face 3 result m3、m1、m2、m4、m5……,
Now rank-1 The accuracy of is (1+1+1)/3=100%;
rank-2 The correct rate of is (1+1+1)/3=100%;
rank-5 The correct rate of is (1+1+1)/3=100%;
such as :
Face 1 The result is m4、m2、m3、m5、m6……,
Face 2 The result is m1、m2、m3、m4、m5……,
Face 3 result m3、m1、m2、m4、m5……,
Now rank-1 The accuracy of is (0+0+1)/3=33.33%;
rank-2 The accuracy of is (0+1+1)/3=66.66%;
rank-5 The correct rate of is (0+1+1)/3=66.66%;
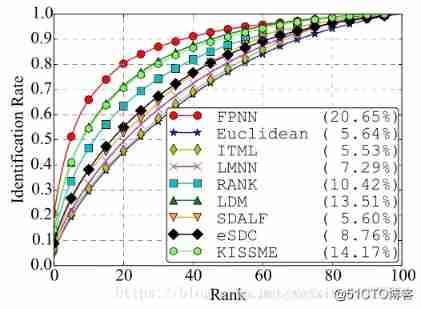
curve: Calculation rank-k Hit rate of , formation rank-acc The curve of , Here's the picture :
- mAP(mean average precision): Reflect the extent to which all the correct pictures in the database of the person who searched are in front of the sorted list , It can be measured more comprehensively ReID Performance of the algorithm . Here's the picture , Suppose the search pedestrian is gallery There is 10 A picture , In the list Middle position (rank) Respectively 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9, be ap by (1/ 1 + 2 / 2 + 3 / 3 + 4 / 4 + 5 / 5 + 6 / 6 + 7 / 7 + 8 / 8 + 9 / 9) / 10 = 0.90;ap large , The search results of this pedestrian are relatively high , For all query Of ap Take the average value to mAP

Generally speaking ,Precision It's the retrieved items ( such as : file 、 Web page, etc ) How much is accurate ,Recall It's how many of the exact entries have been retrieved .
Accuracy rate = The number of positive samples detected / Total number detected
Recall rate = The number of positive samples detected / Number of all positive samples
Let's take a new example .
Suppose there is a search engine , According to search engines , The results are as follows :
Search for 1 The total number of relevant samples is 5 individual : just , just , just , just , just
Rank1 | just | negative | just | negative | negative | just | negative | negative | just | just |
Recall | 1/5=0.2 | 1/5=0.2 | 2/5=0.4 | 2/5=0.4 | 2/5=0.4 | 3/5=0.6 | 3/5=0.6 | 3/5=0.6 | 4/5=0.8 | 5/5=1.0 |
Precision | 1/1=1.0 | 1/2=0.5 | 2/3=0.66 | 2/4=0.5 | 2/5=0.4 | 3/6=0.5 | 3/7=0.42 | 3/8=0.38 | 4/9=0.44 | 7/10=0.5 |
Precision From left to right 1/1, 1/2, 2/3, 2/4… And so on
Search for 2 There are a total of 3 individual , The following are the results returned by the search engine
Rank1 | just | negative | negative | just | just | negative | negative |
Recall | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Precision | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.33 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.43 |
We put each positive sample corresponding to Precision Averaging
Search for 1 Of mAP:mAP = (1/1 + 2/3 + 3/6 + 4/9+ 5/10) / 5 = 0.72
Search for 2 Of mAP: mAP = (1/1 + 2/4 + 3/5) / 3 = 0.63
Holistic mAP = (0.72 + 0.63) /2 = 0.675
边栏推荐
- Zhejiang University Edition "C language programming experiment and exercise guide (3rd Edition)" topic set
- Global and Chinese market of portable and handheld TVs 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- What are the business processes and differences of the three basic business modes of Vos: direct dial, callback and semi direct dial?
- The latest query tracks the express logistics and analyzes the method of delivery timeliness
- Face and eye recognition based on OpenCV's own model
- Which version of MySQL does php7 work best with?
- The number of reversing twice in leetcode simple question
- Quaternion -- basic concepts (Reprint)
- C language learning summary (I) (under update)
- 如何成为一个好的软件测试员?绝大多数人都不知道的秘密
猜你喜欢

Capitalize the title of leetcode simple question

数字电路基础(三)编码器和译码器
Software testing interview summary - common interview questions
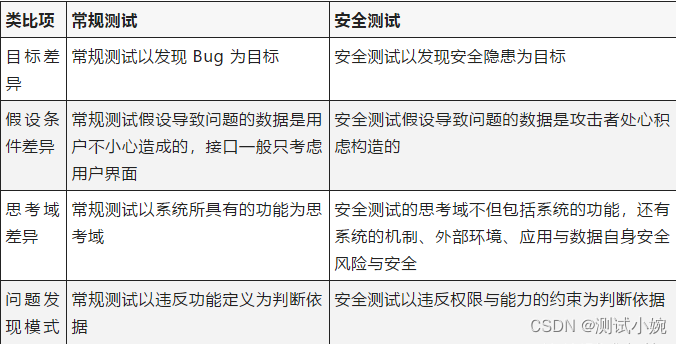
安全测试入门介绍
Soft exam information system project manager_ Project set project portfolio management --- Senior Information System Project Manager of soft exam 025
Cc36 different subsequences
想跳槽?面试软件测试需要掌握的7个技能你知道吗
软件测试工作太忙没时间学习怎么办?
STC-B学习板蜂鸣器播放音乐
Practical cases, hand-in-hand teaching you to build e-commerce user portraits | with code
随机推荐
CSAPP家庭作业答案7 8 9章
CSAPP Shell Lab 实验报告
How to learn automated testing in 2022? This article tells you
数字电路基础(五)算术运算电路
Practical cases, hand-in-hand teaching you to build e-commerce user portraits | with code
HackTheBox-Emdee five for life
数字电路基础(二)逻辑代数
150 common interview questions for software testing in large factories. Serious thinking is very valuable for your interview
UCORE lab7 synchronous mutual exclusion experiment report
ucore lab2 物理内存管理 实验报告
1. Payment system
Opencv recognition of face in image
DVWA exercise 05 file upload file upload
Quaternion -- basic concepts (Reprint)
[pointer] find the value of the largest element in the two-dimensional array
UCORE lab2 physical memory management experiment report
Fundamentals of digital circuits (II) logic algebra
Sorting odd and even subscripts respectively for leetcode simple problem
Dlib detects blink times based on video stream
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (I)
