当前位置:网站首页>JS --- detailed explanation of JS facing objects (VI)
JS --- detailed explanation of JS facing objects (VI)
2022-07-06 15:22:00 【Cirrod】
1、 object-oriented
Object oriented is closer to our real life , You can use object-oriented to describe things in the real world . But things are divided into concrete things and abstract things
Object oriented thinking characteristics :
extract ( abstract ) Objects share properties and behaviors ( encapsulation ) Into a class ( Templates )
Instantiate the class , Get the object of the class
1.1、 object
stay JavaScript in , An object is an unordered collection of related properties and methods , All things are objects , Like strings 、 The number 、 Array 、 Functions, etc .
Objects are made up of properties and methods
attribute : The characteristics of things , Use attributes to represent... In objects
Method : The behavior of things , Use methods to represent... In objects
1.2、 class
stay ES6 The concept of class is added in , have access to class Keyword declares a class , Then instantiate the object with this class .
Class abstracts the common part of an object , It refers to a general category (class)
Object refers to a particular , Instantiate a specific object through a class
1.2.1、 Create a class
class name {
// class body
}Create examples
var XX = new name();Be careful : Class must use new Instantiate objects
1.2.2、 Constructors
constructor() Method is the constructor of the class ( The default method ), Used to pass parameters , Return instance object , adopt new When the command generates an object instance , Call this method automatically . If no definition is displayed , Class will automatically create a constructor()
<script>
// 1. Create a class class Create a Stars
class Star {
// constructor Constructors or constructors
constructor(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
}
// 2. Using classes to create objects new
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ', 20);
console.log(ldh);
console.log(zxy);
</script>adopt class Keyword to create a class , Class names are usually capitalized
There is a constructor function , You can receive the passed parameters , And return the instance object
constructor Function as long as new When generating an instance , This function will be called automatically , If we don't write this function , Class will also automatically generate this function
Finally, pay attention to grammatical norms
Create a class without parentheses after the class name
Generate instance class name followed by parentheses
Constructors don't need to add function keyword
1.2.3、 Class to add methods
grammar :
class Person {
constructor(name,age) {
// constructor Called constructors or constructors
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
say() {
console.log(this.name + ' Hello ');
}
}
var ldh = new Person(' Lau Andy ', 18);
ldh.say()Be careful : Methods cannot be separated by commas , At the same time, the method does not need to add function keyword .
<script>
// 1. Create a class class Create a Stars
class Star {
// The common properties of a class are placed in constructor Inside
constructor(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
sing(song) {
console.log(this.uname + song);
}
}
// 2. Using classes to create objects new
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ', 20);
console.log(ldh);
console.log(zxy);
// (1) All functions in our class do not need to write function
// (2) There is no need to add a comma between multiple function methods
ldh.sing(' Ice rain ');
zxy.sing(' Li Xianglan ');
</script>The common properties of a class are placed in constructor Inside
The functions in the class don't need to write function keyword
1.3 、 Class inheritance
Inheritance in reality : A son inherits his father's work , For example, we all inherited our father's last name .
Inheritance in programs : Subclasses can inherit some properties and methods of the parent class .
grammar :
// Parent class
class Father {
}
// Subclass inherits parent
class Son extends Father {
}
1
Look at an example :
<script>
// The superclass has an addition method
class Father {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
sum() {
console.log(this.x + this.y);
}
}
// The subclass inherits the addition method of the superclass meanwhile Extended subtraction
class Son extends Father {
constructor(x, y) {
// utilize super Call the constructor of the parent class
// super Must be in subclass this Previous call
super(x, y);
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
subtract() {
console.log(this.x - this.y);
}
}
var son = new Son(5, 3);
son.subtract();
son.sum();
</script>1.4、super keyword
super Keyword is used to access and call functions on the object's parent class , You can call the constructor of the parent class , You can also call the normal function of the parent class
1.4.1、 Call the constructor of the parent class
grammar :
// Parent class
class Person {
constructor(surname){
this.surname = surname;
}
}
// Subclass inherits parent
class Student entends Person {
constructor(surname,firstname) {
super(surname); // Calling the constructor(surname)
this.firstname = firstname; // Define properties unique to subclasses
}
}Be careful : Subclasses use... In constructors super, It must be put in this front ( You must first call the constructor of the parent class , Using subclasses to construct methods )
Case study :
// Parent class
class Father {
constructor(surname){
this.surname = surname;
}
saySurname() {
console.log(' My last name is ' + this.surname);
}
}
// Subclass inherits parent
class Son entends Father {
constructor(surname,firstname) {
super(surname); // Calling the constructor(surname)
this.firstname = firstname; // Define properties unique to subclasses
}
sayFirstname() {
console.log(' My name is :' + this.firstname);
}
}
var damao = new Son(' Liu ',' Dehua ');
damao.saySurname();
damao.sayFirstname();1.4.2、 Call the normal function of the parent class
grammar :
class Father {
say() {
return ' I'm daddy ';
}
}
class Son extends Father {
say(){
// super.say() super Calls a method of the parent class
return super.say() + ' Son ';
}
}
var damao = new Son();
console.log(damao.say());There is no need to add comma separation between multiple methods
Search principles for properties and methods in inheritance : Nearby principle , Look at the subclass first , Look at the parent class
1.4、 Three points for attention
stay ES6 The middle class has no variable promotion , So you have to define the class first , To instantiate an object through a class
The common properties and methods in the class must be added with this Use
The inside of the class this Point to :
constructor Inside this Point to instance object
Method this Point to the caller of this method
<body>
<button> Click on </button>
<script>
var that;
var _that;
class Star {
constructor(uname, age) {
// constructor Inside this Pointing to Create an instance object
that = this;
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
// this.sing();
this.btn = document.querySelector('button');
this.btn.onclick = this.sing;
}
sing() {
// This sing Method this Pointing to btn This button , Because this button calls this function
console.log(that.uname);
// that What's in it is constructor Inside this
}
dance() {
// This dance Inside this It points to the instance object ldh because ldh Called this function
_that = this;
console.log(this);
}
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ');
console.log(that === ldh);
ldh.dance();
console.log(_that === ldh);
// 1. stay ES6 The middle class has no variable promotion , So you have to define the class first , To instantiate an object through a class
// 2. The common properties and methods in the class must be added this Use .
</script>
</body>2、 Constructors and prototypes
2.1、 summary
In a typical OOP The language of ( Such as Java), There is the concept of class , A class is a template for an object , An object is an instance of a class , But in ES6 Before , JS The concept of introducing classes is not used in .
ES6, Full name ECMAScript 6.0 ,2015.06 release . But the current browser's JavaScript yes ES5 edition , Most advanced browsers also support ES6, But only achieved ES6 Part of the features and functions of .
stay ES6 Before , Object is not created based on class , Instead, a special function called a constructor is used to define objects and their characteristics .
There are three ways to create objects
Object literal
new Object()
Custom constructors
// 1. utilize new Object() Create objects
var obj1 = new Object();
// 2. Create objects with object literals
var obj2 = {};
// 3. Using constructors to create objects
function Star(uname,age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
}
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ',18);Be careful :
Constructor is used to create a class of objects , The first letter should be capitalized
Constructors and new It makes sense to use them together
2.2、 Constructors
A constructor is a special function , It's mainly used to initialize objects ( Assign initial values to object member variables ), It's always related to new Use it together
We can extract some common attributes and methods from objects , Then encapsulate it into this function
new There are four things you can do in execution
Create a new empty object in memory .
Give Way this Point to this new object .
Execute the code in the constructor , Add properties and methods to this new object .
Return to this new object ( So it's not needed in the constructor return ).
2.2.1、 Static members and instance members
JavaScript You can add some members to the constructor of , You can add... To the constructor itself , It can also be inside the constructor this Add . Members added in these two ways , They are called static members and instance members respectively .
Static members : The members added to the constructor itself are static members , Can only be accessed by the constructor itself
Instance members : The object members created inside the constructor are called instance members , Can only be accessed by instantiated objects
// The properties and methods in the constructor are called members , Members can be added
function Star(uname,age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
}
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ',18);
// Instance members are internal to constructors this Added members uname age sing Instance members
// Instance members can only be accessed through instantiated objects
ldh.sing();
Star.uname; // undefined Instance members cannot be accessed through constructors
// Static members are members added to the constructor itself sex Is a static member
// Static members can only be accessed through constructors
Star.sex = ' male ';
Star.sex;
ldh.sex; // undefined Cannot access... Through objects 2.2.2、 Constructor problem
Constructor method is easy to use , But there is a problem of wasting memory .
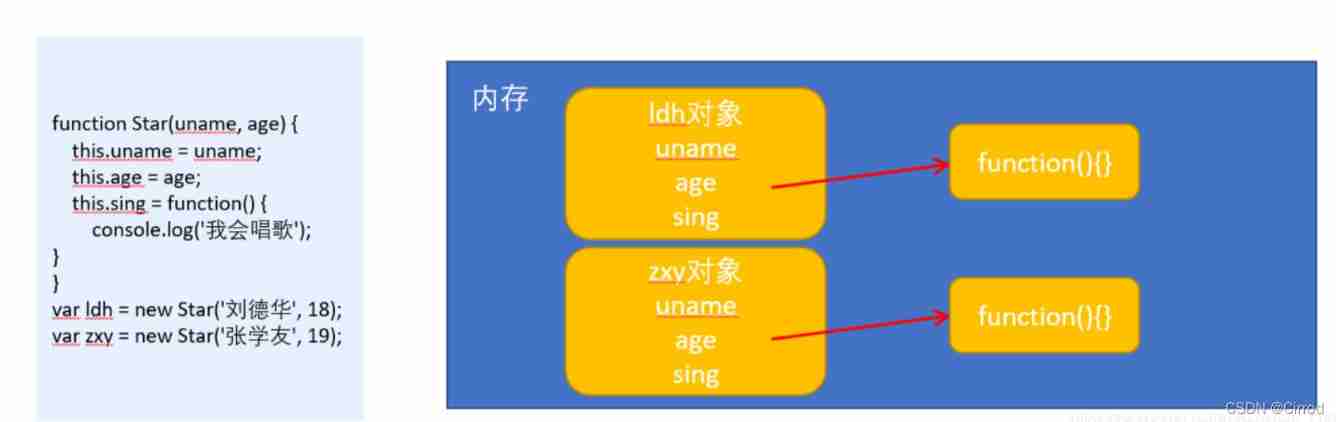
We want all objects to use the same function , This will save more memory
2.3、 Constructor prototype prototype
The function allocated by the constructor through the prototype is shared by all objects , This solves the problem of memory waste
JavaScript Regulations , Each constructor has one prototype attribute , Point to another object , Pay attention to this prototype It's an object , All the properties and methods of this object , Will be owned by constructors
We can take those unchanging methods , Directly defined in prototype On the object , In this way, all instances of objects can share these methods
<body>
<script>
// 1. Constructor problem .
function Star(uname, age) {
// Public attributes are defined in the constructor
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
// this.sing = function() {
// console.log(' I can sing ');
// }
}
// We put the common method on the prototype object
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ', 19);
console.log(ldh.sing === zxy.sing);
ldh.sing();
zxy.sing();
// 2. In general , Our public properties are defined in the constructor , We put the common method on the prototype object
</script>
</body>In general , Our public properties are defined in the constructor , We put the common method on the prototype object
Question and answer : What is the prototype ?
An object , We also call it prototype For prototype objects
Question and answer : What is the role of archetype ?
Sharing method
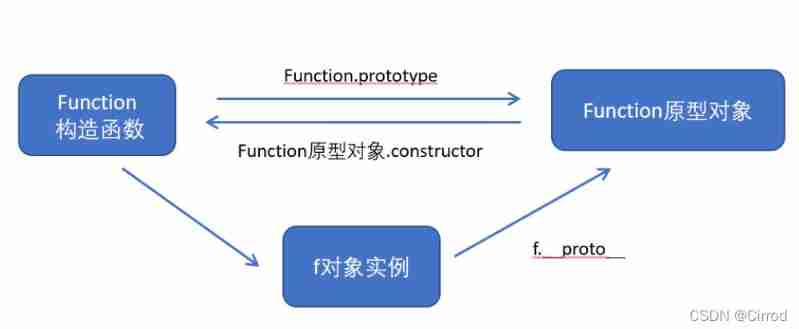
2.4、 Object prototype __ proto __
Objects have a property _proto_ To the constructor prototype Prototype object , The reason why we can use constructors for objects prototype Properties and methods of prototype objects , It's because the object has _proto_ The existence of archetypes .
_proto_ Object prototypes and prototype objects prototype It is equivalent.
_proto_ The significance of the object prototype is to provide a direction for the object search mechanism , Or a route , But it's a nonstandard attribute , So in actual development , You can't use this property , It just points internally to the prototype object prototype
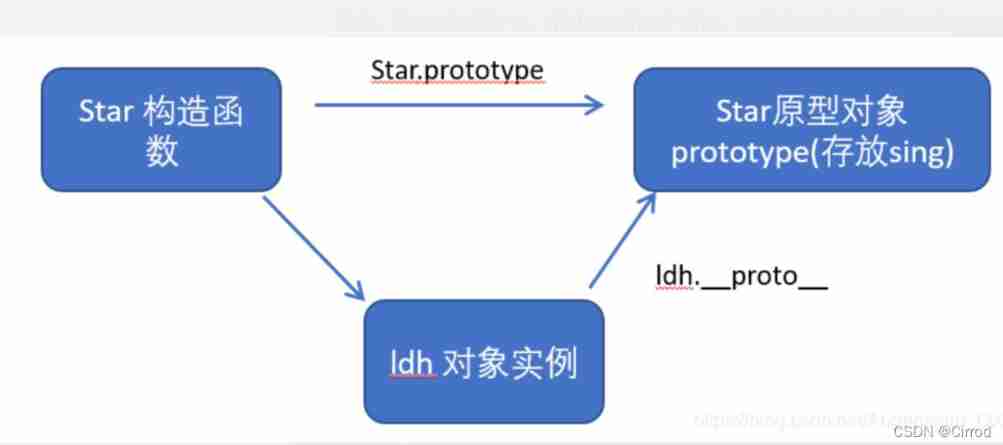
Star.prototype and ldh._proto_ Pointing to the same direction
<body>
<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ', 19);
ldh.sing();
console.log(ldh);
// The system adds one to the object itself __proto__ Point to the prototype object of our constructor prototype
console.log(ldh.__proto__ === Star.prototype);
// Search rules for methods : First look at ldh Does the object have sing Method , If there is, execute the... On this object sing
// without sing This method , Because there is __proto__ The existence of , Go to constructor prototype object prototype Look for sing This method
</script>
</body>2.5、constructor Constructors
Object prototype (__ proto __) And constructor (prototype) Prototype object There is an attribute in it constructor attribute , constructor We call it constructors , Because it points back to the constructor itself .
constructor It is mainly used to record which constructor the object refers to , It allows the prototype object to point back to the original constructor
In general , The methods of the object are in the constructor (prototype) Set... In the prototype object of
If there are multiple object methods , We can give prototype objects prototype Assign values in the form of objects , But this will overwrite the original contents of the constructor prototype object , The modified prototype object constructor It no longer points to the current constructor . here , We can in the modified prototype object , Add one constructor Point to the original constructor
For details, please see examples to understand
<body>
<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
// In many cases , We need to use it manually constructor This property refers back to The original constructor
// Star.prototype.sing = function() {
// console.log(' I can sing ');
// };
// Star.prototype.movie = function() {
// console.log(' I'll be in a movie ');
// }
Star.prototype = {
// If we modify the original prototype object , The prototype object is assigned an object , You have to use it manually constructor Point back to the original constructor
constructor: Star,
sing: function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
},
movie: function() {
console.log(' I'll be in a movie ');
}
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
var zxy = new Star(' Jacky Cheung ', 19);
</script>
</body>2.6、 Constructors 、 example 、 The relationship between the prototype object and the three
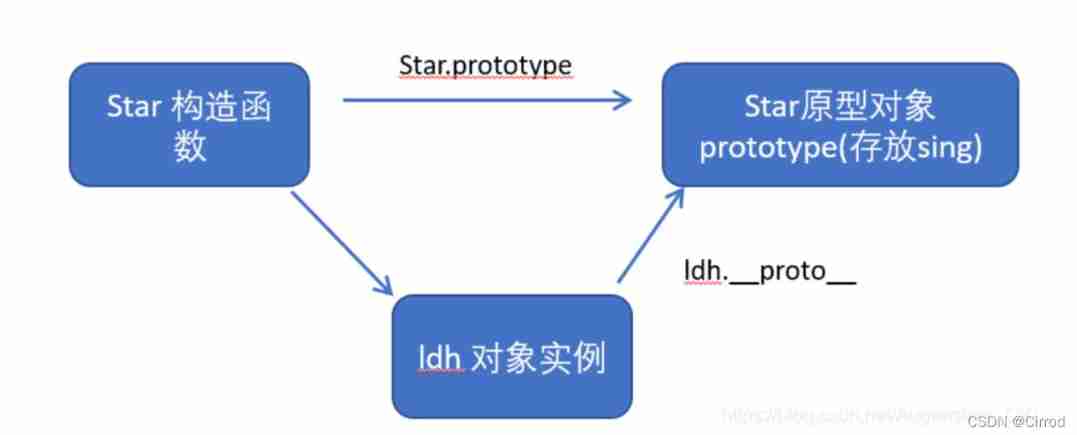
2.7、 Prototype chain lookup rule
When accessing the properties of an object ( Including method ) when , First, find out if the object itself has this property
If not, look for its prototype ( That is to say _proto_ Point to the prototype Prototype object )
If not, find the prototype of the prototype object (Object Prototype object )
And so on until you find Object until (null)
__ proto __ The significance of object prototype is to provide a direction for the search mechanism of object members , Or a route .
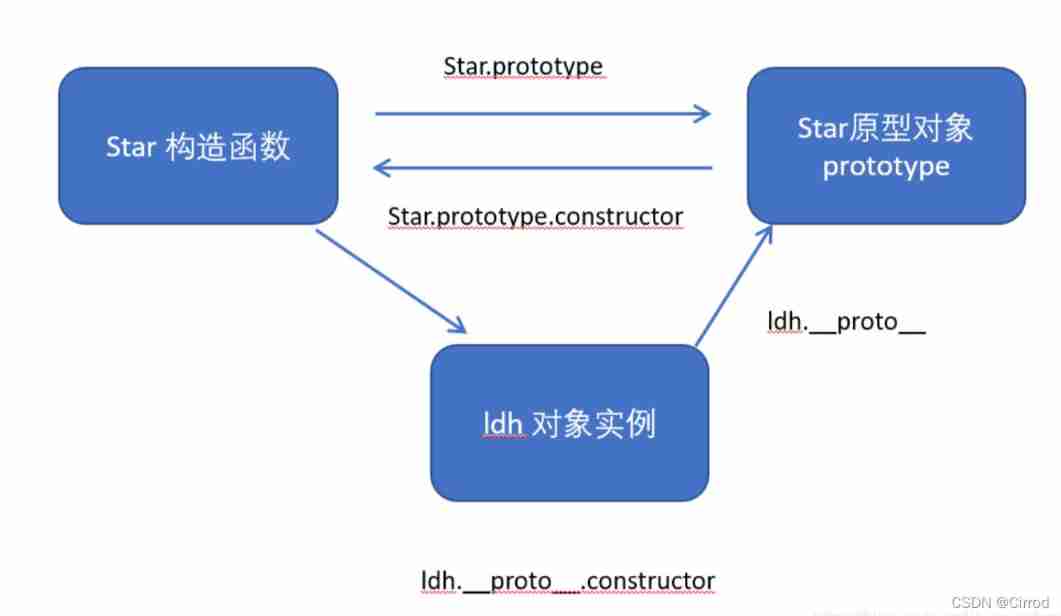
<body>
<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
// 1. As long as it's an object, it has __proto__ Prototype , Point to the prototype object
console.log(Star.prototype);
console.log(Star.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype);
// 2. We Star In the prototype object __proto__ The archetype points to Object.prototype
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__);
// 3. We Object.prototype In the prototype object __proto__ Prototype Pointing to null
</script>
</body>2.8、 Prototype object this Point to
In the constructor this Point to our instance object
Inside the prototype object is the method , In this method this It points to the caller of this method , That is, the instance object
<body>
<script>
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
var that;
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
console.log(' I can sing ');
that = this;
}
var ldh = new Star(' Lau Andy ', 18);
// 1. In the constructor , Inside this It points to an object instance ldh
ldh.sing();
console.log(that === ldh);
// 2. In the prototype object function this Pointing to Instance object ldh
</script>
</body>2.9、 Extend built-in objects
You can use prototype objects , The method of extending and customizing the original built-in object
For example, add a custom even sum function to the array
<body>
<script>
// Application of prototype object Extending built-in object methods
Array.prototype.sum = function() {
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
sum += this[i];
}
return sum;
};
// Array.prototype = {
// sum: function() {
// var sum = 0;
// for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
// sum += this[i];
// }
// return sum;
// }
// }
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.sum());
console.log(Array.prototype);
var arr1 = new Array(11, 22, 33);
console.log(arr1.sum());
</script>
</body>Be careful :
Array and string built-in objects cannot override operations on prototype objects Array.prototype = {}, Can only be Array.prototype.xxx = function(){} The way
3、 Inherit
ES6 We have not been provided with extends Inherit
We can use constructors + Prototype object simulation implementation inheritance , It's called combinatorial inheritance
3.1、call()
Call this function , And modify the function runtime this Point to
fun.call(thisArg,arg1,arg2,......)thisArg: The current call function this Point to object of
arg1,arg2: Other parameters passed
Example
<body>
<script>
// call Method
function fn(x, y) {
console.log(' I hope my hope has hope ');
console.log(this); // Object{...}
console.log(x + y); // 3
}
var o = {
name: 'andy'
};
// fn();
// 1. call() You can call functions
// fn.call();
// 2. call() You can change the of this function this Point to At this point, the of this function this It points to o This object
fn.call(o, 1, 2);
</script>
</body>3.2、 Borrow constructor to inherit parent type properties
The core principle : adopt call() Put the parent type of this Pointing to a subtype this, In this way, the child type can inherit the properties of the parent type
<body>
<script>
// Inheriting properties from a parent constructor
// 1. Parent constructor
function Father(uname, age) {
// this Object instance pointing to the parent constructor
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
// 2 . Child constructors
function Son(uname, age, score) {
// this Object instance pointing to the child constructor
Father.call(this, uname, age);
this.score = score;
}
var son = new Son(' Lau Andy ', 18, 100);
console.log(son);
</script>
</body>19
3.3、 Inheriting parent type methods from prototype objects
In general , The methods of the object are set in the prototype object of the constructor , Cannot inherit parent class method through constructor
The core principle :
Extract the methods shared by subclasses , Let subclass's prototype Prototype object = new Parent class ()
The essence : A subclass prototype object is an instantiated parent class , Because after the parent class is instantiated, another space is opened up , It will not affect the original parent prototype object
Subclass constructor Re point to the constructor of the subclass
<body>
<script>
// Inheriting properties from a parent constructor
// 1. Parent constructor
function Father(uname, age) {
// this Object instance pointing to the parent constructor
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
}
Father.prototype.money = function() {
console.log(100000);
};
// 2 . Child constructors
function Son(uname, age, score) {
// this Object instance pointing to the child constructor
Father.call(this, uname, age);
this.score = score;
}
// Son.prototype = Father.prototype; There will be problems with direct assignment , If you modify the child prototype object , The parent prototype object changes with it
Son.prototype = new Father();
// If you modify the prototype object in the form of an object , Don't forget to use constructor Point back to the original constructor
Son.prototype.constructor = Son;
// This is a special method for sub constructors
Son.prototype.exam = function() {
console.log(' Children have exams ');
}
var son = new Son(' Lau Andy ', 18, 100);
console.log(son);
console.log(Father.prototype);
console.log(Son.prototype.constructor);
</script>
</body>3.3 The essence of class
class In essence function
All methods of a class are defined in the prototype Attribute
Instance created by class , There are also _proto_ Pointing to the class prototype Prototype object
therefore ES6 Most of its functions ,ES5 Can do it , new class The writing method is just to make the writing method of the object prototype clearer 、 It's more like the syntax of object-oriented programming .
therefore ES6 It's a kind of grammar sugar
Grammatical sugar : Grammar sugar is a convenient way to write , Simple understanding
4、ES5 The new method
ES5 Added some methods to us , Can be very convenient operation array or string
Array methods
String method
Object methods
4.1、 Array methods
iteration ( Traverse ) Method :foreach() ,map(),filter(),some() ,every() ;
4.1.1、forEach()
array.forEach(function(currentValue,index,arr))currentValue : Array the values of the current item
index: Array the index of the current item
arr: Array object itself
<body>
<script>
// forEach iteration ( Traverse ) Array
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
var sum = 0;
arr.forEach(function(value, index, array) {
console.log(' Every array element ' + value);
console.log(' Index number of each array element ' + index);
console.log(' The array itself ' + array);
sum += value;
})
console.log(sum);
</script>
</body>4.1.2、filter() Filter array
array.filter(function(currentValue,index,arr))filter() Method to create a new array , The elements in the new array are checked by checking all the eligible elements in the specified array , It is mainly used to filter arrays
Notice that it directly returns a new array
<body>
<script>
// filter Filter array
var arr = [12, 66, 4, 88, 3, 7];
var newArr = arr.filter(function(value, index) {
// return value >= 20;
return value % 2 === 0;
});
console.log(newArr);
</script>
</body>4.1.3、some()
some() Method is used to detect whether the elements in the array meet the specified conditions ( Find whether there are elements in the array that meet the conditions )
Notice that it returns a Boolean value , If you find this element , Just go back to true, If you can't find it, return false
If you find the first element that satisfies the condition , Then stop the cycle , Don't continue to find
<body>
<script>
// some Find whether there are elements in the array that meet the conditions
var arr1 = ['red', 'pink', 'blue'];
var flag1 = arr1.some(function(value) {
return value == 'pink';
});
console.log(flag1);
// 1. filter It is also to find the elements that meet the conditions It returns an array And it's to return all the elements that meet the conditions
// 2. some It is also to find whether the element that meets the condition exists It returns a Boolean value If the first element satisfying the condition is found, the loop is terminated
</script>
</body>4.2、 String method
trim() Method to remove white space characters from both ends of a string
trim() Method does not affect the original string itself , It returns a new string
<body>
<input type="text"> <button> Click on </button>
<div></div>
<script>
// trim Method to remove spaces on both sides of a string
var str = ' an dy ';
console.log(str);
var str1 = str.trim();
console.log(str1);
var input = document.querySelector('input');
var btn = document.querySelector('button');
var div = document.querySelector('div');
btn.onclick = function() {
var str = input.value.trim();
if (str === '') {
alert(' Please enter the content ');
} else {
console.log(str);
console.log(str.length);
div.innerHTML = str;
}
}
</script>
</body>4.3、 Object methods
4.3.1、Object.keys()
Object.keys() Used to get all the properties of the object itself
The effect is similar to for...in
Returns an array of property names
<body>
<script>
// Used to get all the properties of the object itself
var obj = {
id: 1,
pname: ' millet ',
price: 1999,
num: 2000
};
var arr = Object.keys(obj);
console.log(arr);
arr.forEach(function(value) {
console.log(value);
// id
// pname
// price
// num
})
</script>
</body>4.3.2、Object.defineProperty()
Object.defineProperty() Define new properties in the object or modify the existing properties ( understand )
Object.defineProperty(obj,prop,descriptor)obj : Target audience
prop : The name of the property to be defined or modified
descriptor : Properties owned by the target property
<body>
<script>
// Object.defineProperty() Define new attributes or modify existing attributes
var obj = {
id: 1,
pname: ' millet ',
price: 1999
};
// 1. How previous objects add and modify properties
// obj.num = 1000;
// obj.price = 99;
// console.log(obj);
// 2. Object.defineProperty() Define new attributes or modify existing attributes
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'num', {
value: 1000,
enumerable: true
});
console.log(obj);
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'price', {
value: 9.9
});
console.log(obj);
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'id', {
// If the value is false It is not allowed to modify this property value The default value is also false
writable: false,
});
obj.id = 2;
console.log(obj);
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'address', {
value: ' Shandong Lanxiang technical school, China xx unit ',
// If only for false It is not allowed to modify this property value The default value is also false
writable: false,
// enumerable If the value is false Traversal is not allowed , The default value is false
enumerable: false,
// configurable If false You are not allowed to delete this property It is not allowed to modify the properties in the third parameter The default is false
configurable: false
});
console.log(obj);
console.log(Object.keys(obj));
delete obj.address;
console.log(obj);
delete obj.pname;
console.log(obj);
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'address', {
value: ' Shandong Lanxiang technical school, China xx unit ',
// If the value is false It is not allowed to modify this property value The default value is also false
writable: true,
// enumerable If the value is false Traversal is not allowed , The default value is false
enumerable: true,
// configurable If false You are not allowed to delete this property The default is false
configurable: true
});
console.log(obj.address);
</script>
</body>The third parameter descriptor explain : In the form of objects { } Writing
value: Set the value of the property , The default is undefined
writeable: Whether the value can be overridden true | false The default is false
enumerable: Whether the target property can be enumerated true | false The default is false
configurable: Whether the target attribute can be deleted or the attribute can be modified again true | false The default is false
5、 Function advanced
5.1、 How to define a function
Function declaration mode function keyword ( Name the function )
Function expression ( Anonymous functions )
new Function()
var fn = new Function(' Parameters 1',' Parameters 2',.....,' The body of the function ');Function The parameters must be in string format
The third way is inefficient , It's not easy to write , Therefore, it is less used
All functions are Function Example ( object )
Functions also belong to objects
<body>
<script>
// How to define a function
// 1. Custom function ( Name the function )
function fn() {};
// 2. Function expression ( Anonymous functions )
var fun = function() {};
// 3. utilize new Function(' Parameters 1',' Parameters 2', ' The body of the function ');
// Function The parameters must be in string format , Inefficient execution , Write less
var f = new Function('a', 'b', 'console.log(a + b)');
f(1, 2);
// 4. All functions are Function Example ( object )
console.dir(f);
// 5. Functions also belong to objects
console.log(f instanceof Object);
</script>
</body>5.2、 How to call function
Ordinary function
Object method
Constructors
Binding event functions
Timer Functions
Immediate execution function
<body>
<script>
// How to call function
// 1. Ordinary function
function fn() {
console.log(' The peak of life ');
}
// fn(); fn.call()
// 2. Object method
var o = {
sayHi: function() {
console.log(' The peak of life ');
}
}
o.sayHi();
// 3. Constructors
function Star() {};
new Star();
// 4. Binding event functions
// btn.onclick = function() {}; // Click the button to call this function
// 5. Timer Functions
// setInterval(function() {}, 1000); This function is timer Auto 1 Call once per second
// 6. Immediate execution function
(function() {
console.log(' The peak of life ');
})();
// The immediate function is called automatically
</script>
</body>5.3、 Within the function this The direction of
this Point to , It's determined when we call the function , The different calling methods determine this The direction of is different , Usually we point to our caller
| Call mode | this Point to |
| Ordinary function call | window |
| Constructor call | Instance object , Methods in prototype objects also point to instance objects |
| Object method call | The object of this method |
| Event binding method | Bind event object |
| Timer Functions | window |
| Immediate execution function | window |
<body>
<button> Click on </button>
<script>
// The different ways of calling function determine this The direction of is different
// 1. Ordinary function this Point to window
function fn() {
console.log(' Of a normal function this' + this);
}
window.fn();
// 2. Object method this Point to the object o
var o = {
sayHi: function() {
console.log(' Object method this:' + this);
}
}
o.sayHi();
// 3. Constructors this Point to ldh This instance object In the prototype object this It also points to ldh This instance object
function Star() {};
Star.prototype.sing = function() {
}
var ldh = new Star();
// 4. Binding event functions this Point to the caller of the function btn This button object
var btn = document.querySelector('button');
btn.onclick = function() {
console.log(' Binding time function this:' + this);
};
// 5. Timer Functions this It also points to window
window.setTimeout(function() {
console.log(' Timer this:' + this);
}, 1000);
// 6. Immediate execution function this Or point to window
(function() {
console.log(' Execute the function immediately this' + this);
})();
</script>
</body>5.4、 Change function interior this Point to
JavaScript It provides us with some function methods to help us deal with the internal of the function this Direction problem of , Commonly used bind(),call(),apply() Three methods
5.4.1、call() Method
call() Method calls an object , Simply understood as the way to call a function , But it can change the function this Point to
fun.call(thisArg,arg1,arg2,.....)
thisArg: stay fun Specified by function runtime this value
arg1,arg2: Other parameters passed
The return value is the return value of the function , Because it's the calling function
So when we want to change this Point to , When you want to call this function at the same time , have access to call, Like inheritance
<body>
<script>
// Change the function inside this Point to js There are three ways call() apply() bind()
// 1. call()
var o = {
name: 'andy'
}
function fn(a, b) {
console.log(this);
console.log(a + b);
};
fn.call(o, 1, 2);
// call The first one can call the function The second one can change the... In the function this Point to
// call The main role of inheritance can be achieved
function Father(uname, age, sex) {
this.uname = uname;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
function Son(uname, age, sex) {
Father.call(this, uname, age, sex);
}
var son = new Son(' Lau Andy ', 18, ' male ');
console.log(son);
</script>
</body>5.4.2、apply() Method
apply() Method to call a function , Simply understood as the way to call a function , But it can change the function this Point to
fun.apply(thisArg,[argsArray])
thisArg: stay fun Specified by function runtime this value
argsArray : Value delivered , Must be included in the array
The return value is the return value of the function , Because it's the calling function
therefore apply Mainly related to arrays , For example, use Math.max() Find the maximum value of the array
<body>
<script>
// Change the function inside this Point to js There are three ways call() apply() bind()
// 2. apply() application It means to use
var o = {
name: 'andy'
};
function fn(arr) {
console.log(this);
console.log(arr); // 'pink'
};
fn.apply(o, ['pink']);
// 1. It's also a call function The second one can change the inside of the function this Point to
// 2. But its arguments have to be arrays ( Pseudo array )
// 3. apply The main application of For example, we can use apply With the help of mathematical built-in object to find the maximum value of the array
// Math.max();
var arr = [1, 66, 3, 99, 4];
var arr1 = ['red', 'pink'];
// var max = Math.max.apply(null, arr);
var max = Math.max.apply(Math, arr);
var min = Math.min.apply(Math, arr);
console.log(max, min);
</script>
</body>5.4.3、bind() Method
bind() Methods do not call functions . But it can change the inside of the function this Point to
fun.bind(thisArg,arg1,arg2,....)
Returns the specified by this Values and initialization parameters Original function copy
So when we just want to change this Point to , And when you don't want to call this function , have access to bind
<body>
<button> Click on </button>
<button> Click on </button>
<button> Click on </button>
<script>
// Change the function inside this Point to js There are three ways call() apply() bind()
// 3. bind() binding Binding means
var o = {
name: 'andy'
};
function fn(a, b) {
console.log(this);
console.log(a + b);
};
var f = fn.bind(o, 1, 2);
f();
// 1. Will not call the original function You can change the inside of the original function this Point to
// 2. Return is the original function change this And the new functions that come out of it
// 3. If there are functions we don't need to call immediately , But I want to change the internal of this function this Point to this time with bind
// 4. We have a button , When we click , Just disable this button ,3 Turn on this button in seconds
// var btn1 = document.querySelector('button');
// btn1.onclick = function() {
// this.disabled = true; // This this Pointing to btn This button
// // var that = this;
// setTimeout(function() {
// // that.disabled = false; // In the timer function this Pointing to window
// this.disabled = false; // At this point, in the timer function this Pointing to btn
// }.bind(this), 3000); // This this Pointing to btn This object
// }
var btns = document.querySelectorAll('button');
for (var i = 0; i < btns.length; i++) {
btns[i].onclick = function() {
this.disabled = true;
setTimeout(function() {
this.disabled = false;
}.bind(this), 2000);
}
}
</script>
</body>5.4.4、 summary
call apply bind summary :
The same thing :
Can change the function of the internal this Point to
Difference point :
call and apply Will call functions , And change the inside of the function this Point to
call and apply The parameters passed are different ,call Pass parameters ,apply Must be in array form
bind Does not call function , You can change the inside of the function this Point to
Main application scenarios
call Often do inheritance
apply It's often related to arrays , For example, with the help of mathematical alignment, the maximum and minimum values of the array are realized
bind Don't call functions , But also want to change this Point to , For example, change the internal timer this Point to
边栏推荐
- LeetCode#19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- 转行软件测试必需要知道的知识
- Servlet
- LeetCode#53. Maximum subarray sum
- Example 071 simulates a vending machine, designs a program of the vending machine, runs the program, prompts the user, enters the options to be selected, and prompts the selected content after the use
- [C language] twenty two steps to understand the function stack frame (pressing the stack, passing parameters, returning, bouncing the stack)
- FSM和i2c实验报告
- Scoring system based on 485 bus
- Report on the double computer experiment of scoring system based on 485 bus
- Portapack application development tutorial (XVII) nRF24L01 launch B
猜你喜欢

The minimum number of operations to convert strings in leetcode simple problem
What is "test paper test" in software testing requirements analysis
Scoring system based on 485 bus
Word macro operation: convert the automatic number in the document into editable text type
软件测试面试要问的性能测试术语你知道吗?
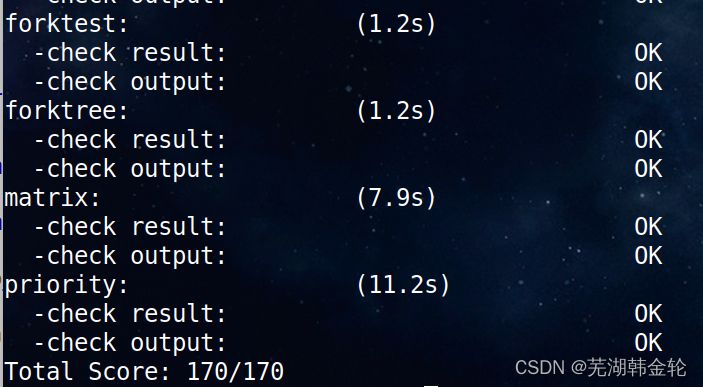
ucore lab5

51 lines of code, self-made TX to MySQL software!
UCORE LaB6 scheduler experiment report
Take you to use wxpy to create your own chat robot (plus wechat interface basic data visualization)

The number of reversing twice in leetcode simple question
随机推荐
ucore Lab 1 系统软件启动过程
C4D quick start tutorial - creating models
Investment should be calm
Your wechat nickname may be betraying you
Nest and merge new videos, and preset new video titles
ucore lab5
Global and Chinese markets for GaN on diamond semiconductor substrates 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese markets for complex programmable logic devices 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
如何成为一个好的软件测试员?绝大多数人都不知道的秘密
Mysql database (V) views, stored procedures and triggers
UCORE lab1 system software startup process experimental report
JDBC introduction
软件测试Bug报告怎么写?
Mysql database (II) DML data operation statements and basic DQL statements
几款开源自动化测试框架优缺点对比你知道吗?
Emqtt distribution cluster and node bridge construction
LeetCode#19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
CSAPP homework answers chapter 789
How to become a good software tester? A secret that most people don't know
Capitalize the title of leetcode simple question

