One 、 Unit Overview
Through the study of this chapter, I can understand MySQL The meaning of grouping query in database , Master the use of common grouping functions , master GROUP BY Rules for using clauses , Master the conditional filtering of data results after grouping , master SELECT Statement execution procedure , Understand the meaning of subquery , Master the use of single line sub query and multi line sub query
Two 、 Key points and difficulties in teaching
a key : Master the use of common grouping functions master GROUP BY Rules for using clauses master HAVING Rules for using clauses Master the usage rules of sub query difficulty : SELECT Statement execution procedure HAVING and WHERE The difference between Single line subquery and multi line subquery
4.1 Why use grouping functions
● Please consider the following questions ?
○ Query the total monthly salary of all employees , Average wage ?
○ Query the maximum and minimum wages ?
○ Check the total number of people in the company ?
○ Query the total number of people with bonuses ?
○ ………..
● Grouping function is to operate on the set of data rows and give a result by group , This result can be output directly , Or used to make judgment conditions
4.2 Overview of grouping functions
4.2.1 Group function
● Grouping function is to operate a group of records in a table , Each group returns only one result , That is, first group the table records , Then the operation summary , Each group returns a result , When grouping, the whole table may be divided into a group , It may also be divided into groups according to conditions .4.2.2 Common grouping functions
● Grouping functions are commonly used in the following five functions :
○ MIN
○ MAX
○ SUM
○ AVG
○ COUNT
● 4.2.2 Syntax of grouping function
SELECT [column,] group_function(column)
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY column]
[HAVING group_function(column)expression
[ORDER BY column | group_function(column)expression];
4.3 Use of grouping functions
4.3.1 MIN Functions and MAX function
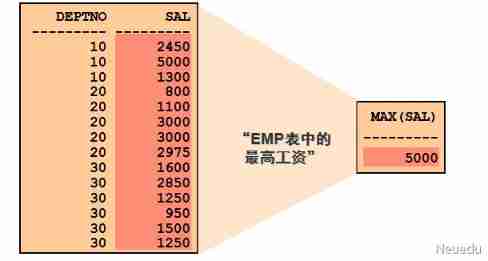
● MIN and MAX The function mainly returns the minimum and maximum values of each group .
○ MIN([DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression)
○ MAX([DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression)
● MIN and MAX Can be used for any data type
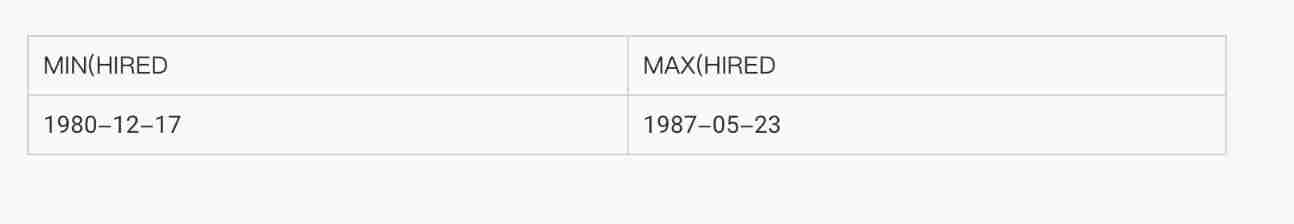
● Query the earliest and latest date of employment
SELECT MIN(hiredate), MAX(hiredate)
FROM emp;
4.3.2 SUM Functions and AVG function
● SUM and AVG Function returns the sum and average of each group .
○ SUM([DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression)
○ AVG([DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression)
● SUM and AVG Functions can only operate on columns or expressions of numeric type .
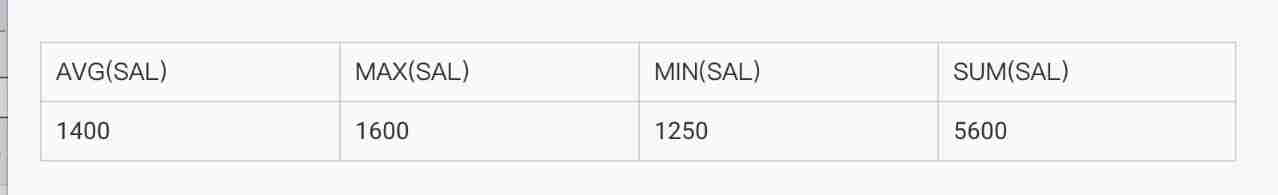
● Query the position with SALES The average salary of all employees at the beginning 、 minimum wage 、 Maximum wage 、 Wages and .
SELECT AVG(sal), MAX(sal),MIN(sal), SUM(sal)
FROM emp
WHERE job LIKE 'SALES%';
4.3.3 COUNT function
1. COUNT Function syntax
● COUNT The main function of the function is to return the number of records in each group that meet the conditions .
COUNT( * | {[DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression})
● COUNT(*): Returns the number of qualified row records in the table
● Inquiry Department 30 How many employees
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM emp
WHERE deptno = 30;

2. count Function USES
● COUNT( [DISTINCT | ALL] column | expression): Return non empty that meets the condition (NULL) The number of lines
● Inquiry Department 30 How many employees receive bonuses
SELECT COUNT(comm)
FROM emp
WHERE deptno = 30;

3. In group functions DISTINCT
● DISTINCT Will eliminate duplicate records before using group functions
● Check the number of departments with employees .
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT deptno)
FROM emp;
4. Group function empty value processing
● except COUNT(*) outside , All other grouping functions ignore null values in columns , And then calculate .
SELECT AVG(comm)
FROM emp;

5. Use... In grouping functions IFNULL function
● IFNULL Function to force a group function to contain records with null values
SELECT AVG(IFNULL(comm,0))
FROM emp;

practice
- Inquiry Department 20 The employees' , The sum and average wage of each month .
- The inquiry work is in CHICAGO Of employees , The maximum wage and the minimum wage .
- There are several job types in the employee table .
4.4 Create data group
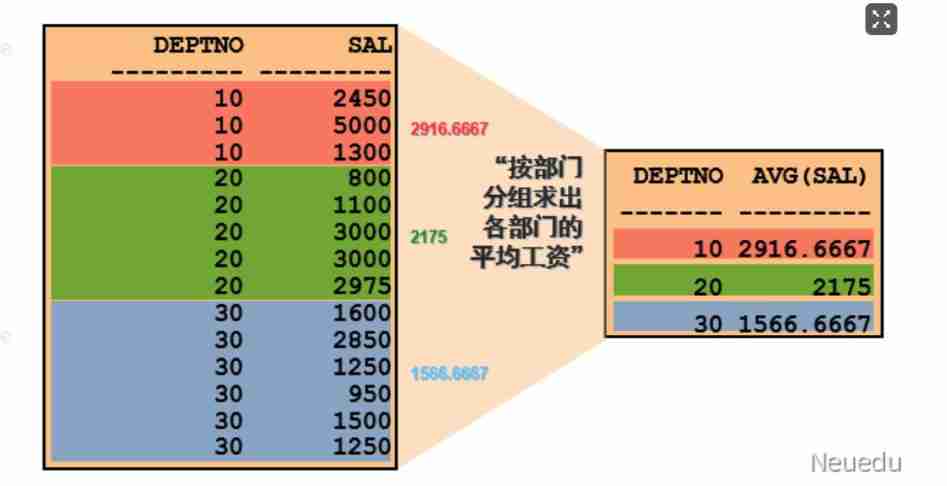
● Find the average salary of each department , Group by Department
4.4.1 use GROUP BY Clause to create a data group
● adopt GROUP BY Clause can satisfy WHERE The records of conditions are divided into several groups according to the specified columns
○ among GROUP BY Clause specifies the columns to group
SELECT column, group_function(column)
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY group_by_expression]
[ORDER BY column];
4.4.2 GROUP BY Use of clauses
● Look up the number of each department , Average wage
SELECT deptno, AVG(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno;
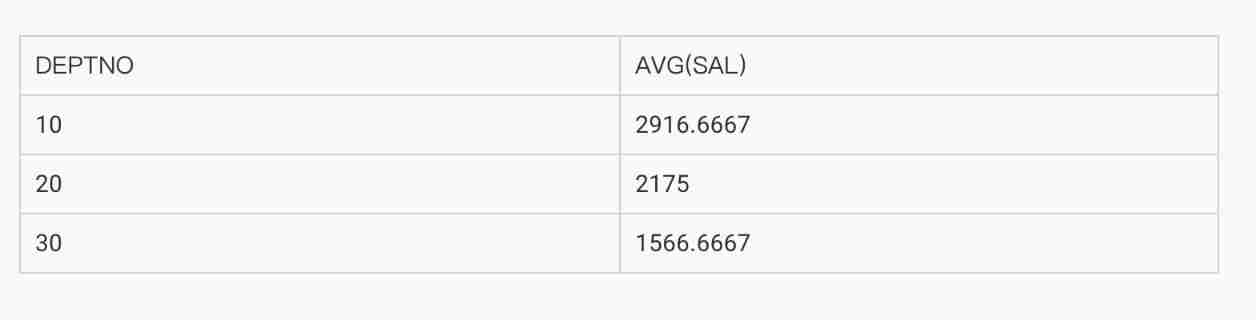
4.4.3 GROUP BY Rules for using clauses
● stay SELECT Except for those items in the grouping function in the list , All columns must be included in GROUP BY clause .
SELECT deptno, AVG(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno;
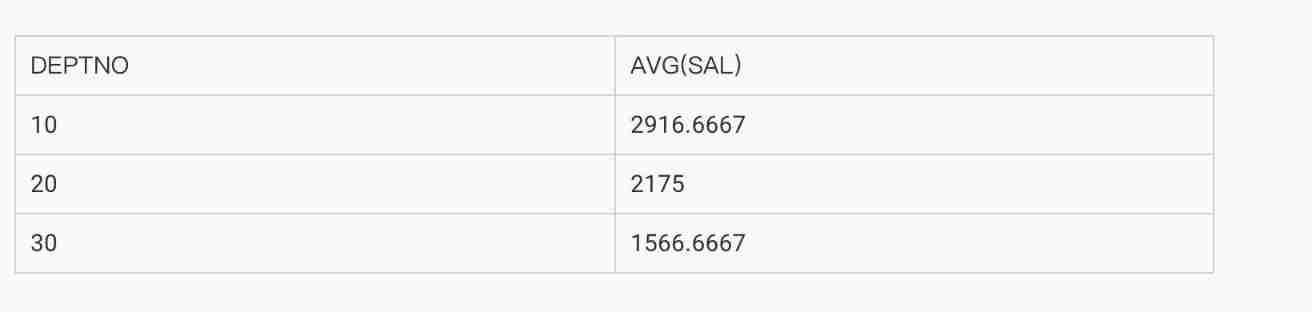
● GROUP BY The specified column does not have to appear in SELECT In the list .
SELECT AVG(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno;

4.4.4 Group by multiple columns
● Query the total salary of each position in each department .
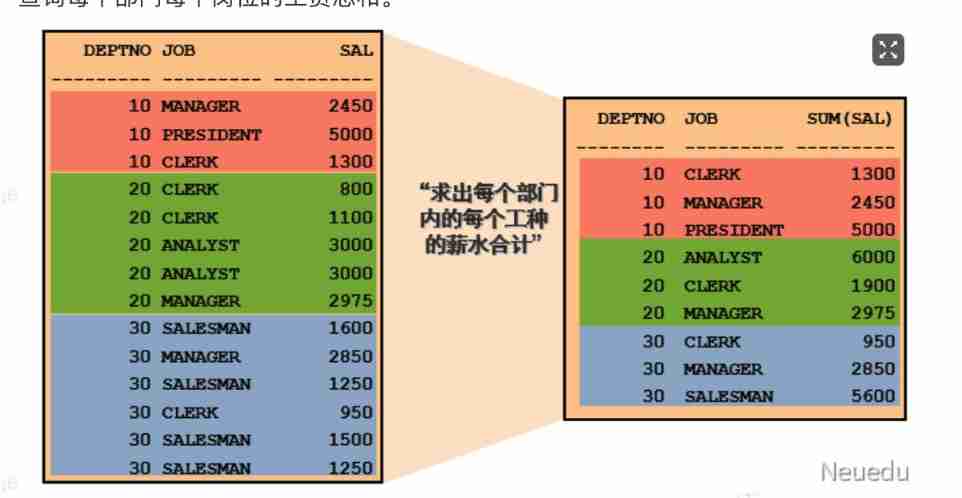
● Query the total salary of each position in each department
SELECT deptno, job, sum(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno, job;
practice
- Query the department number of each department , Department name , Number of departments , Maximum wage , minimum wage , The sum of wages , Average wage .
- Check every department , Department number of each position , Department name , Job title , Number of departments , Maximum wage , minimum wage , The sum of wages , Average wage .
- Check the number of people managed by each manager , Manager number , Name of manager , Requirements include information about people who do not have a manager .
4.5 Exclude group results
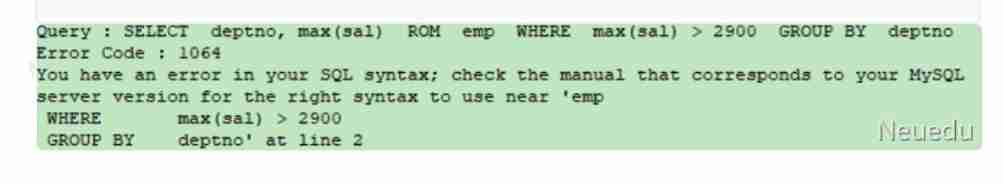
4.5.1 Illegal queries using group functions
● Can't be in WHERE Restrict group in clause
● Can pass HAVING Clause restriction group
SELECT deptno, max(sal)
FROM emp
WHERE max(sal) > 2900
GROUP BY deptno;
4.5.2 use HAVING Clause excludes group results
● Use HAVING Clause restriction group
○ The records have been grouped .
○ Used group functions .
○ And HAVING The result of clause matching is output
SELECT column, group_function
FROM table
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY group_by_expression]
[HAVING group_condition]
[ORDER BY column];
4.5.3 HAVING Use of clauses
● Query the maximum salary of each department greater than 2900 Department number of , Maximum wage
SELECT deptno, max(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno
HAVING max(sal)>2900;
DEPTNO MAX(SAL)
10 5000
20 3000
SELECT job, SUM(sal) PAYROLL
FROM emp
WHERE job NOT LIKE 'SALES%'
GROUP BY job
HAVING SUM(sal)>5000
ORDER BY SUM(sal);
JOB PAYROLL
ANALYST 6000
MANAGER 8275
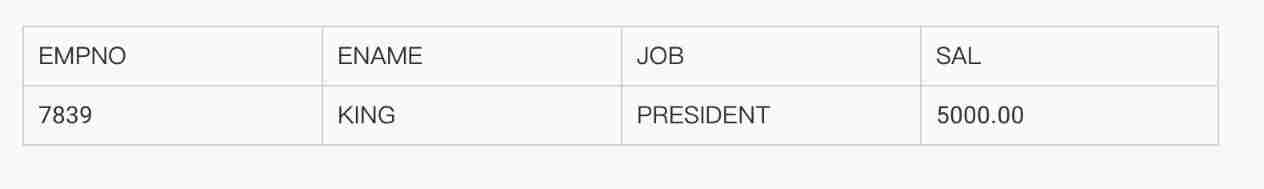
4.5.4 SELECT Statement execution procedure
● Explain through cases SELECT Statement execution .
SELECT deptno,job,avg(sal)
FROM emp
WHERE job in ('SALESMAN','MANAGER','CLERK')
GROUP BY deptno,job
HAVING avg(sal)>1000
ORDER BY 3 DESC;
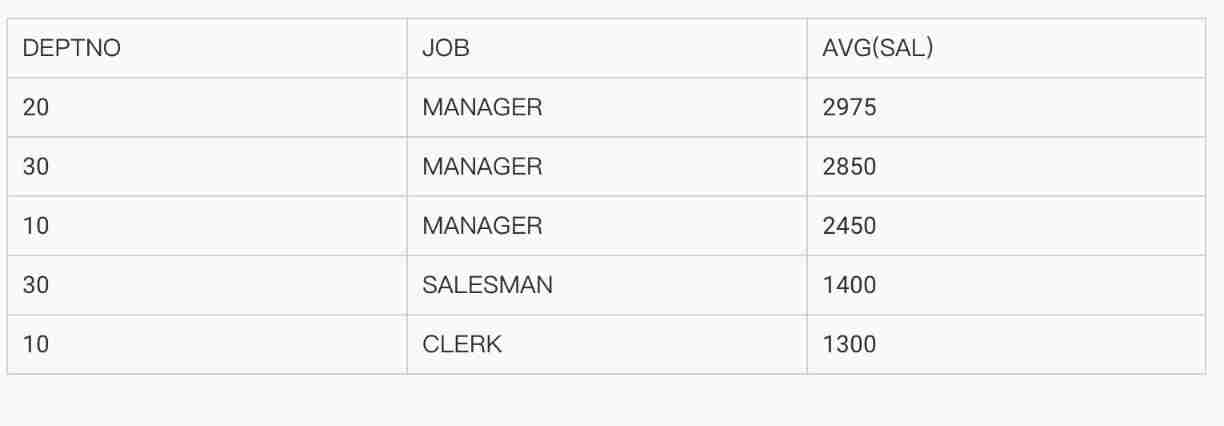
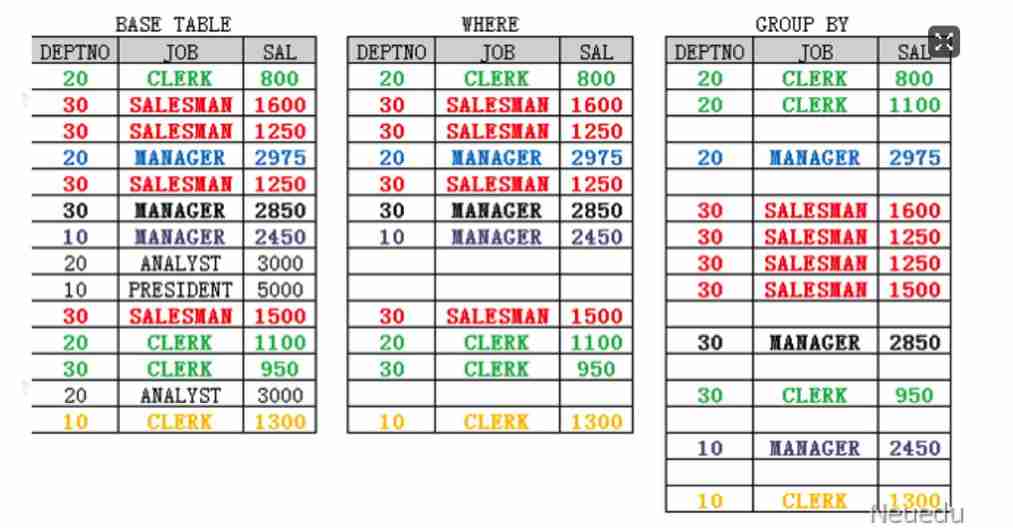
● SELECT Statement execution procedure :
- adopt FROM Clause to find the table to query ;
- adopt WHERE Clause to make non grouping function filtering judgment ;
- adopt GROUP BY Clause complete grouping operation ;
- adopt HAVING Clause complete group function filter judgment ;
- adopt SELECT Clause select the displayed column or expression and group function ;
- adopt ORDER BY Clause to sort .
practice
- The number of people in the query department is greater than 2 Department number of , Department name , Number of departments .
- Query Department average wage greater than 2000, And the number of people is greater than 2 Department number of , Department name , Number of departments , Department average wage , And sort them in ascending order according to the number of people in the Department .
4.6 Overview of subquery
4.6.1 Why use subqueries
● Think about the following ?
○ Check the wage ratio Jones High paid employee information ?
○ Check the name of the lowest paid employee ?
● “ Whose salary is better than Jones It's still high ?”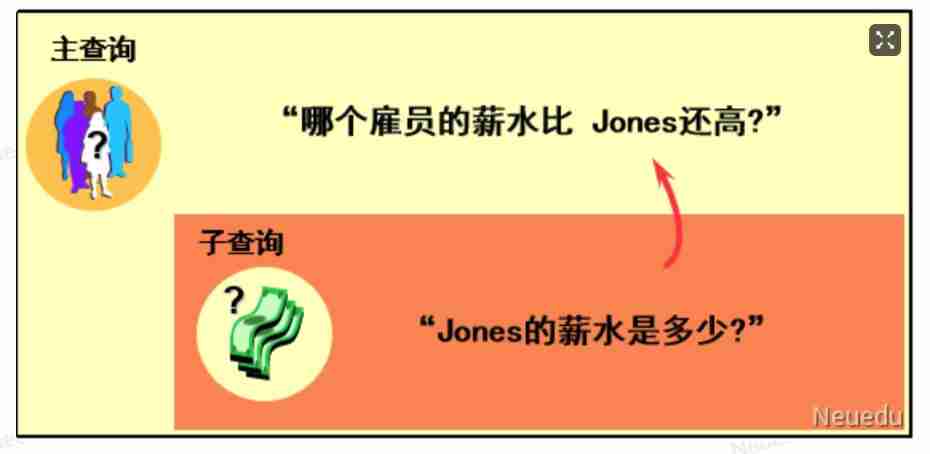
● Subquery Syntax
SELECT select_list
FROM table
WHERE expr operator
(SELECT select_list
FROM table);
● Queries in parentheses are called subqueries , Also called internal query , Execute before the main query .
● The results of the sub query are by the main query ( External query ) Use
● expr operator Including comparison operators
○ Single line operators :>、=、>=、<、<>、<=
○ Multiline operator : IN、ANY、ALL
● Subqueries can be embedded in the following SQL clause :
○ WHERE Clause
○ HAVING Clause
○ FROM Clause
4.6.2 Use subquery
● Find out more than JONES For other employees with high wages
SELECT ename
FROM emp
WHERE sal >
(SELECT sal
FROM emp
WHERE ename='JONES');

4.6.3 Subquery type
According to the number of rows and columns returned by the sub query , It is divided into :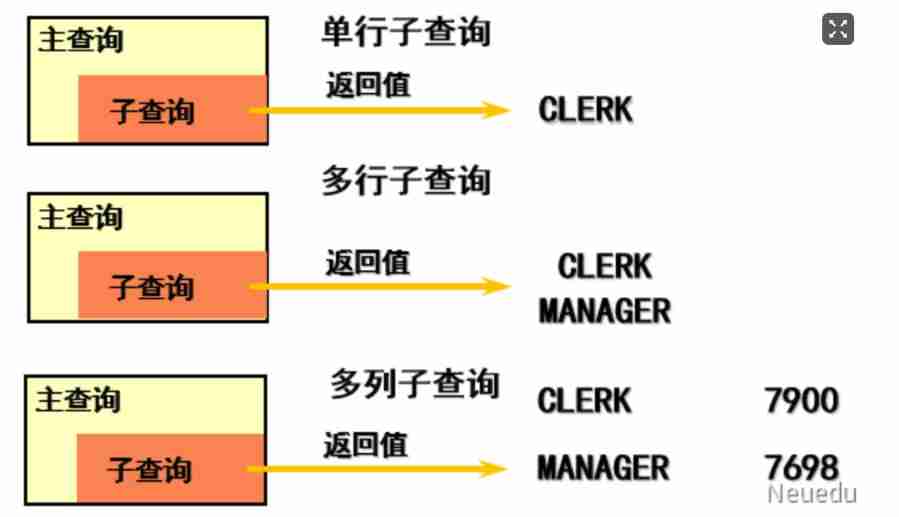
4.6.4 Subquery instructions
● Subqueries should be enclosed in brackets
● Place the subquery to the right of the comparison operator
● For single line subqueries, use single line operators
● For multi row subqueries, use multi row operators
4.7 Single line sub query
4.7.1 Overview of single line sub query
● Subquery only returns one row and one column
● Use the single line operator | Operator | meaning | | ---- | ----- | | = | be equal to | | > | Greater than | | >= | Greater than or equal to | | < | Less than | | <= | Less than or equal to | | <> | It's not equal to |
4.7.2 Single row subquery statement
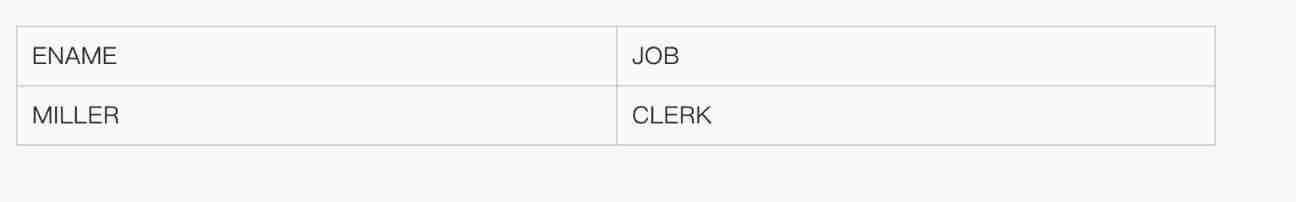
● Display and employees 7369 Engaged in the same job and paid more than employees 7876 The name and job of the employee .
SELECT ename, job
FROM emp
WHERE job =
(SELECT job FROM emp WHERE empno = 7369)
AND sal >
(SELECT sal FROM emp WHERE empno = 7876);
4.7.3 Group functions are used in subqueries
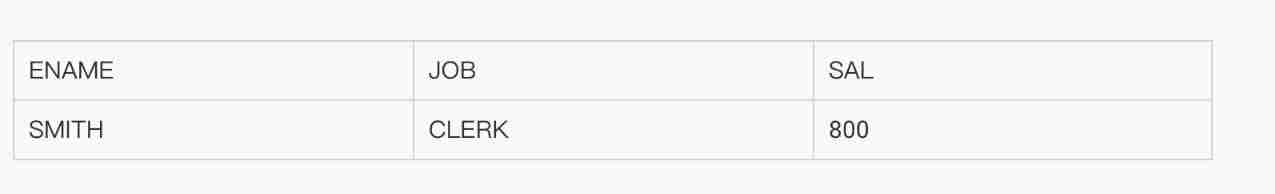
● Check the name of the lowest paid employee , Position and salary
SELECT ename, job, sal
FROM emp
WHERE sal =
(SELECT MIN(sal) FROM emp);
4.7.4 HAVING Clause using subqueries
● Check the minimum wage ratio of the Department 20 Department number with high minimum wage and minimum wage
SELECT deptno, MIN(sal)
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno
HAVING MIN(sal) >
(SELECT MIN(sal)
FROM emp
WHERE deptno = 20);
practice
- Query the name of the employee with the earliest entry date , Date of entry
- Check the wage ratio SMITH The salary is high and the place of work is CHICAGO Of employees , Wages , Department name
- Query the employment date ratio 20 The name of the employee with the earliest entry date in the Department , Date of entry
4.8 Multi line sub query
4.8.1 Overview of multiline subqueries
● The number of records returned by the sub query It can be one or more .
● When comparing with multi row subqueries , You need to use multiline operators , Multiline operators include :
○ IN
○ ANY
○ ALL
● IN The function of the operator is the same as that described before , Determine whether it is the same as any return value of the sub query .
4.8.2 IN Use
SELECT ename, sal
FROM emp
WHERE empno IN (SELECT mgr
FROM emp);
4.8.3 ANY Use
● ANY: Represents a comparison with any row result of a subquery , There is a condition to be satisfied .
○ < ANY: Indicates that it is smaller than any one in the sub query result set , That is, less than the maximum value .
○ > ANY: Indicates that it is larger than any one in the sub query result set , That is, if it is greater than the minimum value .
○ = ANY: Indicates that it is equal to any one of the sub query results , That is, anyone can , amount to IN.
● Case study 1 The query is the name of the manager's employee , Wages .
SELECT ename, sal
FROM emp
WHERE empno = ANY (SELECT mgr
FROM emp);
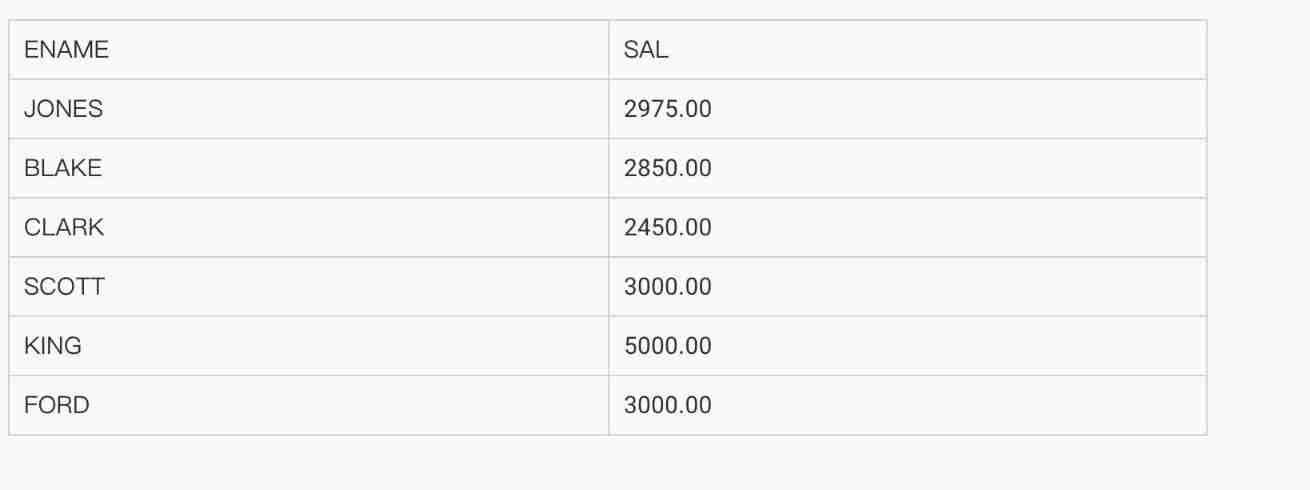
● Case study 2 The query department number is not 10, And the wage ratio 10 The employee number of any employee in the Department with high salary , full name , Position , Wages .
SELECT empno, ename, job, sal
FROM emp
WHERE sal > ANY (SELECT sal
FROM emp
WHERE deptno = 10)
AND deptno <> 10;
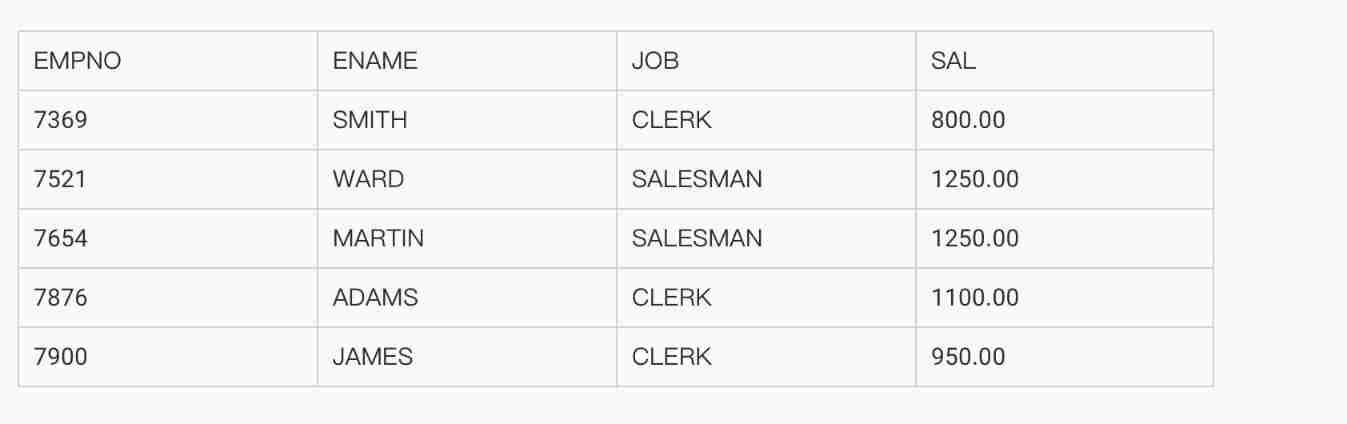
| EMPNO | ENAME | JOB | SAL | | 7499 | ALLEN | SALESMAN | 1600.00 | | 7566 | JONES | MANAGER | 2975.00 | | 7698 | BLAKE | MANAGER | 2850.00 | | 7788 | SCOTT | ANALYST | 3000.00 | | 7844 | TURNER | SALESMAN | 1500.00 | | 7902 | FORD | ANALYST | 3000.00 |
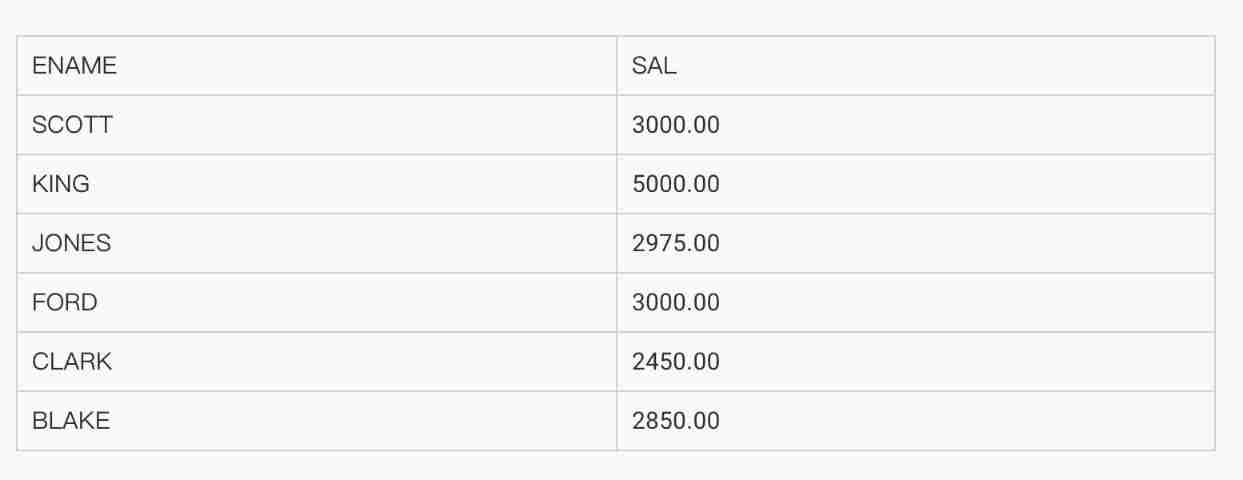
4.8.4 ALL Use
● ALL: Represents a comparison with all row results of a subquery , Each line must meet the conditions .
○ < ALL: Represents all rows smaller than the sub query result set , That is, less than the minimum value .
○ >ALL: Represents all rows larger than the sub query result set , I.e. greater than the maximum .
○ = ALL : Indicates that it is equal to all rows in the sub query result set , Equal to all values , Usually meaningless .
● Case study 1 The query department number is not 20, And the wage ratio 20 The employee number of all employees in the Department with high salary , full name , Position , Wages .
SELECT empno, ename,job, sal
FROM emp
WHERE sal > ALL (SELECT sal
FROM emp
WHERE deptno= 20)
AND deptno <> 20;
● Case study 2 The query department number is not 10, And the wage ratio 10 The employee number of all employees in the Department with low salary , full name , Position , Wages .
SELECT empno, ename,job, sal
FROM emp
WHERE sal < ALL (SELECT sal
FROM emp
WHERE deptno= 10)
AND deptno <> 10;
practice
- Query the employment date ratio 10 Name of any employee in the Department 、 Date of entry , barring 10 Department staff
- Query the employment date ratio 10 Name of all employees in the Department 、 Date of entry , barring 10 Department staff
- Query position and 10 Name of any employee with the same position in the Department , Position , barring 10 Department staff
4.9 Null value in subquery
● Query the names of employees who are not managers .
SELECT ename
FROM emp
WHERE empno NOT IN
(SELECT mgr
FROM emp);

● The result returned by subquery contains null value
● above SQL Statement attempts to find employees who have no subordinates , logically , This SQL The statement should return 8 Bar record , But none of them came back ,why?
● Because there is a null value in the result of the subquery , This null value causes the main query to return no records . This is because all conditions and null value comparison results are null . Therefore, whenever a null value is used, it may become a part of the sub query result set , You can't use it NOT IN Operator
4.10 stay FROM Clause using subqueries
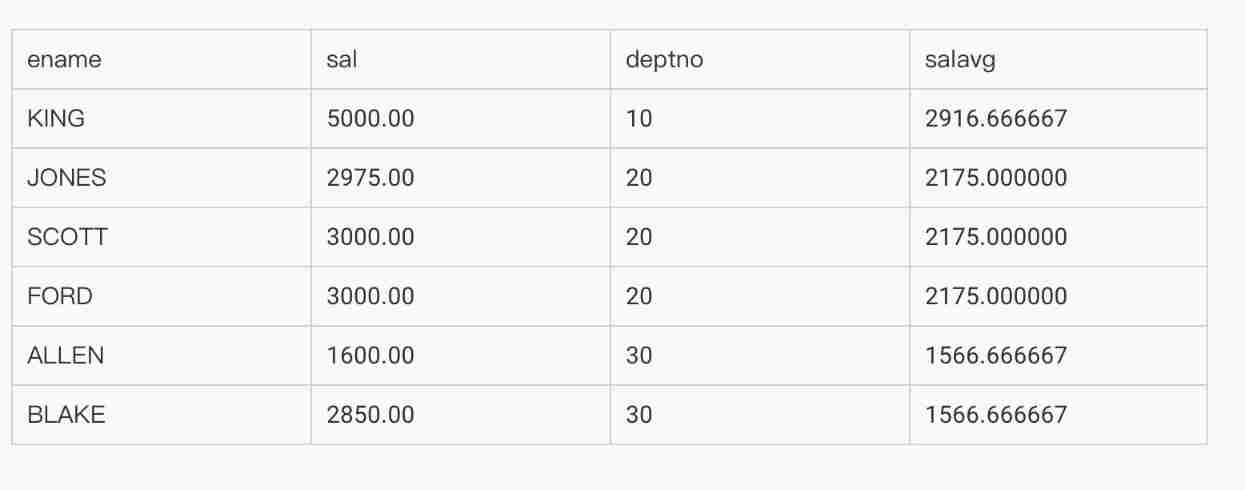
● Query the names of employees with higher average salary than their own department , Wages , Department number , Department average wage
SELECT a.ename, a.sal, a.deptno, b.salavg
FROM emp a, (SELECT deptno, AVG(sal) salavg
FROM emp
GROUP BY deptno) b
WHERE a.deptno = b.deptno AND a.sal > b.salavg;
4.11 Summary of this chapter
● MIN Functions and MAX function
● SUM Functions and AVG function
● COUNT function
● Group function null value processing
● adopt GROUP BY Clause to group and summarize
● HAVING Use of clauses
● Single line sub query
● Multi line sub query
● Subquery null value problem
4.12 Homework after class
- The average salary of the inquiry department is 2500 Department name and average salary above yuan .
- The query of employee position is not based on “SA” At the beginning, and the average salary is 2500 Positions above RMB yuan and average salary , And in descending order of average wage .
- The number of people in the inquiry department is 2 Department name with more than people 、 minimum wage 、 Maximum wage .
- The query position is not SALESMAN, The sum of wages is greater than or equal to 2500 And the salary and .
- Show manager number and manager name , The minimum wage of the staff managed by this manager , There is no manager KING Also show , Excluding minimum wage less than 3000 Of , Sort the minimum wage from high to low
- The inquiry salary is higher than the number 7782 The salary of our employees , and 7369 Employee No. the number of the employee who is engaged in the same work 、 Name and salary .
- Check the name and salary of the highest paid employee .
- The minimum wage of the inquiry department is higher than 10 Department No. the number of the minimum wage Department 、 Name and department minimum wage .
- Query the number, name and salary of the employee whose salary is the minimum wage of his department .
- Show manager is KING Of employees , Wages .
- Show employees SMITH Names of employees who work late , Wages , Working hours .



![Transplant hummingbird e203 core to Da Vinci pro35t [Jichuang xinlai risc-v Cup] (I)](/img/85/d6b196f22b60ad5003f73eb8d8a908.png)