当前位置:网站首页>The concept of C language array
The concept of C language array
2022-07-06 16:04:00 【Programming fish 66】
stay 《C Large summary of language data output and lightweight advanced 》 In this section we give an example , It's the output of a 4×4 The integer matrix of , The code is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a1=20, a2=345, a3=700, a4=22;
int b1=56720, b2=9999, b3=20098, b4=2;
int c1=233, c2=205, c3=1, c4=6666;
int d1=34, d2=0, d3=23, d4=23006783;
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", a1, a2, a3, a4);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", b1, b2, b3, b4);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", c1, c2, c3, c4);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", d1, d2, d3, d4);
system("pause");
return 0;
}Running results :
| 20 | 345 | 700 | 22 |
| 56720 | 999 | 20098 | 2 |
| 233 | 205 | 1 | 6666 |
| 34 | 0 | 23 | 23006783 |
Matrices share 16 It's an integer , We define a variable for each integer , That is to say 16 A variable . that , To reduce the number of variables , Make development more efficient , Can you define a variable for multiple data ? such as , Put the integer of each line in a variable , Or the 16 All integers are put in one variable . The answer, of course, is yes , The way is to use arrays (Array).
The concept and definition of array
We know , To put data into memory , You must allocate memory space first . Put in 4 It's an integer , You have to allocate 4 individual int Type of memory space :
int a[4]; such , Just allocate it in memory 4 individual int Type of memory space , common 4×4=16 Bytes , And gave them a name , It's called a.
We call such a set of data an array (Array), Every piece of data it contains is called an array element (Element), The number of data contained is called array length (Length), for example int a[4]; It defines a length of 4 Integer array , The name is a.
Each element in the array has a sequence number , This number comes from 0 Start , Not from the familiar 1 Start , It's called subscript (Index). When using array elements , Indicate the subscript , In the form of :
arrayName[index]arrayName Is the array name ,index Subscript . for example ,a[0] It means the first one 0 Elements ,a[3] It means the first one 3 Elements .
Next, let's take the first line 4 Put an integer into the array :
a[0]=20;
a[1]=345;
a[2]=700;
a[3]=22; there 0、1、2、3 Is array subscript ,a[0]、a[1]、a[2]、a[3] It's an array element .
In the learning process , We often use circular structures to put data into arrays ( That is, assign values to array elements one by one ), Then use the loop structure to output ( That is, read the values of array elements in turn ), Now let's demonstrate how to 1~10 Put these ten numbers into the array :
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int nums[10];
int i;
// take 1~10 Put it in an array
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
nums[i] = (i+1);
}
// Output the array elements in turn
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
printf("%d ", nums[i]);
}
return 0;
}Running results :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Variable i Is an array subscript , It's also a cyclic condition ; Use array subscripts as loop conditions , When the last element is reached, the loop ends . Array nums The largest subscript of is 9, That is, no more than 10, So we specify that the condition of the cycle is i<10, once i achieve 10 You have to end the cycle .
Change the code above , Let the user type 10 A number and put it into the array :
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int nums[10];
int i;
// Read user input from the console
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
scanf("%d", &nums[i]); // Pay attention to the address character &, Don't forget
}
// Output the array elements in turn
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
printf("%d ", nums[i]);
}
return 0;
}Running results :
22 18 928 5 4 82 30 10 666 888
22 18 928 5 4 82 30 10 666 888 The first 8 Line code ,scanf() An address is required to read data ( Addresses are used to indicate where data is stored ), and nums[i] Represents a specific array element , So we need to add... To the front & To get the address .
Finally, let's summarize how arrays are defined :
dataType arrayName[length];dataType Is the data type ,arrayName Is the array name ,length Is array length . for example :
float m[12]; // Define a length of 12 Floating point array
char ch[9]; // Define a length of 9 Character array of It should be noted that :
1) The data type of each element in the array must be the same , about int a[4];, Each element must be int.
2) The length of the array length Preferably an integer or constant expression , for example 10、20*4 etc. , In this way, it can run under all compilers ; If length Contains variables , for example n、4*m etc. , In some compilers, errors will be reported ,
3) When accessing array elements , The value range of subscript is 0 ≤ index < length, Too big or too small will cross the border , Cause array overflow , Something unpredictable happens , Please pay attention to the big housework .
Array memory is continuous
An array is a whole , Its memory is continuous ; in other words , Array elements are next to each other , There is no gap between each other . The following figure illustrates int a[4]; Storage in memory :

「 Array memory is continuous 」 This is important , So I used a headline to emphasize . Continuous memory for pointer operations ( Access array elements through pointers ) And memory processing ( Copy of whole memory 、 Write, etc ) Provides convenience , This allows the array to act as a cache ( A block of memory that temporarily stores data ) Use . You may not understand what this sentence means for the moment , After learning the pointer and memory, you will naturally understand .
Initialization of an array
The above code defines the array first and then assigns a value to the array , We can also assign values while defining an array , for example :
int a[4] = {20, 345, 700, 22}; The value of the array element is determined by { } Surround , The values are separated by , Separate .
For the initialization of array, we need to pay attention to the following points :
1) You can assign values to just a few elements . When { } When the number of median is less than the number of elements , Assign values to only the preceding elements . for example :
int a[10]={12, 19, 22 , 993, 344}; To give only to a[0]~a[4] 5 Element assignment , And the back 5 Elements are automatically initialized to 0.
When the assigned elements are less than the total elements of the array , The remaining elements are automatically initialized to 0:
- about short、int、long, It's integer. 0;
- about char, It's the characters '\0';
- about float、double, It's a decimal 0.0.
We can initialize all the elements of the array to 0:
int nums[10] = {0};
char str[10] = {0};
float scores[10] = {0.0}; Because the remaining elements are automatically initialized to 0, So just give it to the third party 0 The first element is assigned to 0 that will do .
2) You can only assign values to elements one by one , You can't assign values to an array as a whole . For example, to 10 All elements are assigned to 1, I can only write :
int a[10] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1};Instead of writing :
int a[10] = 1;3) Such as assigning values to all elements , So when defining an array, you can not give the length of the array . for example :
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};Equivalent to
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};Last , We use arrays to output a 4×4 Matrix :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[4] = {20, 345, 700, 22};
int b[4] = {56720, 9999, 20098, 2};
int c[4] = {233, 205, 1, 6666};
int d[4] = {34, 0, 23, 23006783};
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", b[0], b[1], b[2], b[3]);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3]);
printf("%-9d %-9d %-9d %-9d\n", d[0], d[1], d[2], d[3]);
return 0;
}Like to share games UP Lord Remember to pay attention to me ! Source code and material into the group to obtain ~:828339809 Remember to connect three times with one button ! One key, three links ! One key, three links !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
b站 實時彈幕和曆史彈幕 Protobuf 格式解析
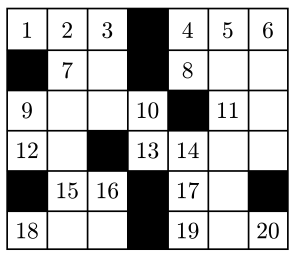
【练习-7】Crossword Answers
![[analysis of teacher Gao's software needs] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class](/img/3b/dc43564a36f82e73826b08f39c935e.png)
[analysis of teacher Gao's software needs] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class

C语言数组的概念
渗透测试 ( 7 ) --- 漏洞扫描工具 Nessus

Analysis of protobuf format of real-time barrage and historical barrage at station B
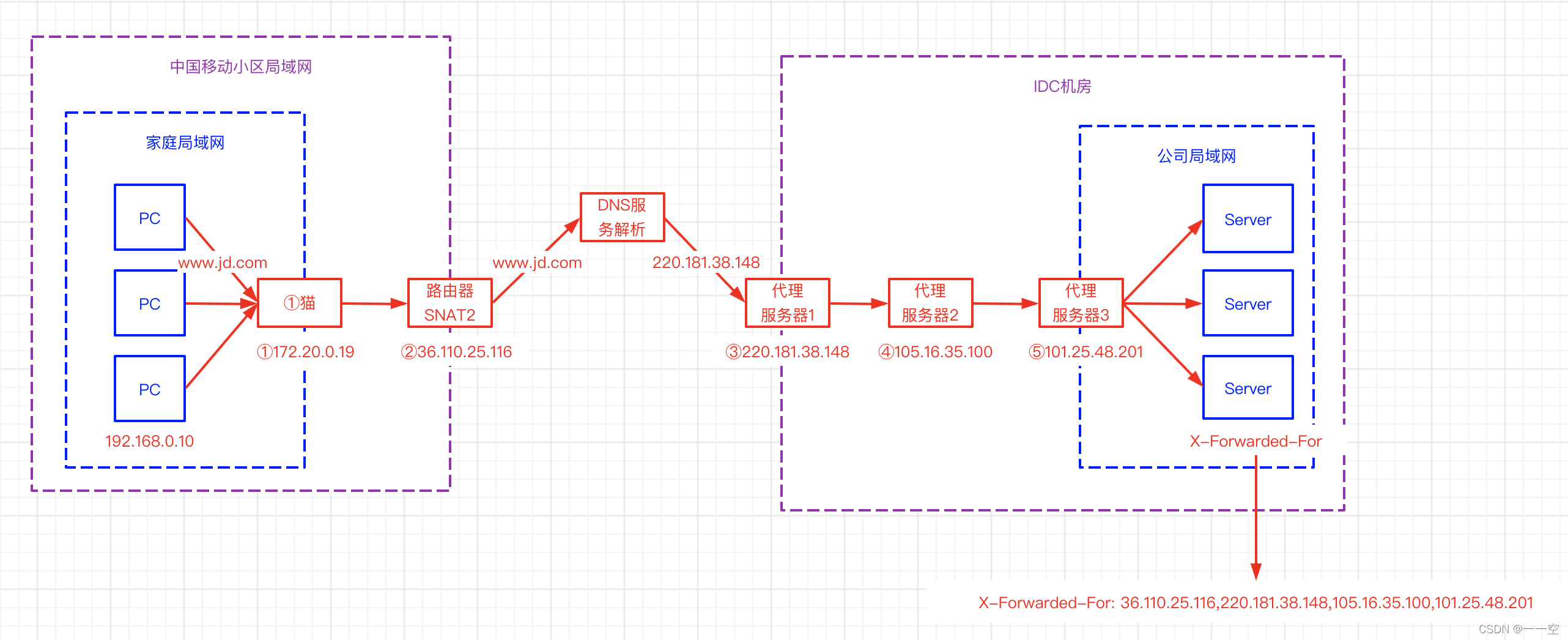
X-Forwarded-For详解、如何获取到客户端IP
7-1 understand everything (20 points)
![[exercise-4] (UVA 11988) broken keyboard = = (linked list)](/img/59/78ca7170ab1fd364ec44cfbcdc7ab5.png)
[exercise-4] (UVA 11988) broken keyboard = = (linked list)

信息安全-威胁检测引擎-常见规则引擎底座性能比较
随机推荐
C语言数组的概念
Find 3-friendly Integers
编程到底难在哪里?
Frida hook so layer, protobuf data analysis
Matlab comprehensive exercise: application in signal and system
Borg maze (bfs+ minimum spanning tree) (problem solving report)
最全编程语言在线 API 文档
树莓派CSI/USB摄像头使用mjpg实现网页摄像头监控
JS call camera
Penetration test (2) -- penetration test system, target, GoogleHacking, Kali tool
Penetration test (8) -- official document of burp Suite Pro
China potato slicer market trend report, technical dynamic innovation and market forecast
信息安全-安全专业名称|CVE|RCE|POC|VUL|0DAY
Path problem before dynamic planning
差分(一维,二维,三维) 蓝桥杯三体攻击
[exercise-9] Zombie's Treasury test
Information security - threat detection - Flink broadcast stream broadcaststate dual stream merging application in filtering security logs
Gartner: five suggestions on best practices for zero trust network access
Information security - security professional name | CVE | rce | POC | Vul | 0day
想应聘程序员,您的简历就该这样写【精华总结】