当前位置:网站首页>Interval sum ----- discretization
Interval sum ----- discretization
2022-07-06 16:03:00 【It's Xiao Zhang, ZSY】
discretization
Satisfy the property of discretization : The range of values is large , Sparse number
a[ ] : { 1 , 3 , 100 , 200 , 500000000 } mapping
Subscript :0 1 2 3 4
1.a[] There may be duplicate elements in duplicate removal
2. How to calculate the discrete value Two points ( This question is in order )
Interval and
Suppose there is an infinite number axis , The number on each coordinate on the number axis is 0. Now? , Let's start with n operations , Each operation will a certain position x Add... To the number on c. Next , Conduct m Time to ask , Each query contains two integers l and r, You need to find the interval [l,r] The sum of all numbers between . Input format : The first line contains two integers n and m. Next n That's ok , Each line contains two integers x and c. Next m That's ok , Each line contains two integers l and r. Output format : common m That's ok , Each line outputs a number in the interval and . Data range −1e9≤x≤1e9,1≤n,m≤1e5,−1e9≤l≤r≤1e9,−10000≤c≤10000
sample input :
3 3
1 2
3 6
7 5
1 3
4 6
7 8
sample output :
8
0
5
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,l,r;
int const N=3e5+10; // In the array x,l,c Corresponding to the discretized value , The number is the most 3*1e5
int a[N],s[N];
vector<int> lisan; // Store all discretized values
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
vector<PII> addxc,xunwenlr; // Insert x c; Insert query l r;
int find(int x) // Find the result of discretization
{
int l=0,r=lisan.size()-1;
while(l<r)
{
int mid=l+r >> 1;
if(lisan[mid]>=x) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
return r+1; // Coordinate addition 1, Map to from 1 Start ;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int x,c;
cin>>x>>c;
lisan.push_back(x);
addxc.push_back({
x,c});
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>l>>r;
xunwenlr.push_back({
l,r});
lisan.push_back(l);
lisan.push_back(r);
}
sort(lisan.begin(),lisan.end());
lisan.erase(unique(lisan.begin(),lisan.end()),lisan.end()); // duplicate removal , Inserted x l r Remove the same
for(auto item:addxc) // Insert processing
{
int xx=find(item.first); //xx The subscript corresponding to discretization
a[xx]+=item.second;
}
for(int i=1;i<=lisan.size();i++) // The prefix and
s[i]=s[i-1]+a[i];
for(auto item:xunwenlr) // Deal with inquiries
{
l=find(item.first); // The subscript corresponding to discretization
r=find(item.second);
cout<<s[r]-s[l-1]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
// Remove the weight from the top unique Functions and erase function Source code
vector<int>::iterator unique <vector<int> &a)
{
Int j=0;
For(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)
If( !i || a[i]!=a[i-1] )
a[j++]=a[i];
Return a.begin()+j;
}
unique() function , The following elements replace the previous repeated elements , Generally, it is used after sorting ( The adjacent elements are removed ), The space behind has not been deleted
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]={
2,3,4,4,6};
sort(a,a+5); // Generally in use unique It needs to be sorted before ;
unique(a,a+5); // Use unique The array de duplication function
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<” “; // 2 3 4 6 6
}
cout<<" The length of the non repeating sequence :"<<unique(a,a+5)-a<<endl; // The length of the unrepeated sequence :4
}
边栏推荐
- HDU - 6024 Building Shops(女生赛)
- 【练习-5】(Uva 839)Not so Mobile(天平)
- 7-1 懂的都懂 (20 分)
- [exercise-3] (UVA 442) matrix chain multiplication
- Opencv learning log 16 paperclip count
- Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of geosynthetic clay liner in China
- Information security - security professional name | CVE | rce | POC | Vul | 0day
- 初入Redis
- 信息安全-史诗级漏洞Log4j的漏洞机理和防范措施
- b站 實時彈幕和曆史彈幕 Protobuf 格式解析
猜你喜欢
1010 things that college students majoring in it must do before graduation
Gartner:关于零信任网络访问最佳实践的五个建议
Information security - threat detection - Flink broadcast stream broadcaststate dual stream merging application in filtering security logs
渗透测试 2 --- XSS、CSRF、文件上传、文件包含、反序列化漏洞
快速转 TypeScript 指南

Optimization method of path problem before dynamic planning
Nodejs+vue网上鲜花店销售信息系统express+mysql
![MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’](/img/e6/f4a696179282fe1f4193410c5a493a.png)
MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’
Essai de pénétration (1) - - outils nécessaires, navigation
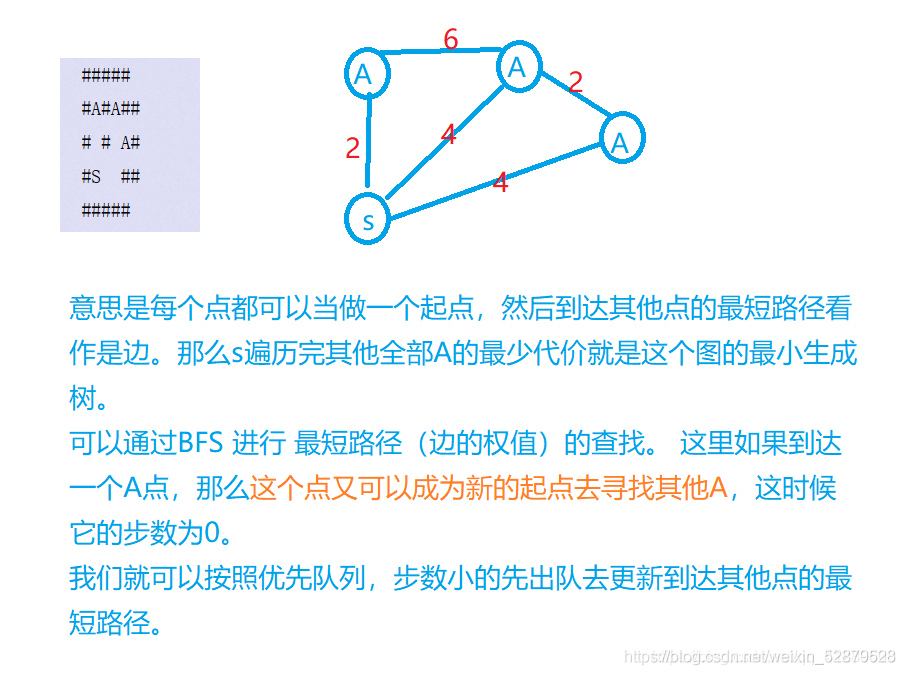
Borg Maze (BFS+最小生成树)(解题报告)
随机推荐
渗透测试 ( 5 ) --- 扫描之王 nmap、渗透测试工具实战技巧合集
socket通讯
Opencv learning log 18 Canny operator
Shell脚本编程
Nodejs+vue网上鲜花店销售信息系统express+mysql
Accounting regulations and professional ethics [5]
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's earth drilling industry
Accounting regulations and professional ethics [3]
Truck History
树莓派CSI/USB摄像头使用mjpg实现网页摄像头监控
C 基本语法
Cost accounting [24]
Opencv learning log 12 binarization of Otsu method
信息安全-威胁检测引擎-常见规则引擎底座性能比较
Truck History
[exercise-7] (UVA 10976) fractions again?! (fraction split)
Cost accounting [23]
Analyse du format protobuf du rideau en temps réel et du rideau historique de la station B
Path problem before dynamic planning
MySQL授予用户指定内容的操作权限