当前位置:网站首页>【练习-2】(Uva 712) S-Trees (S树)
【练习-2】(Uva 712) S-Trees (S树)
2022-07-06 09:26:00 【火焰车】
不想看这么长的题干就直接跳过,后面有翻译……实际上这个题说白了就几句话,搞这么长就是为了脏你哈哈哈。
S-Trees
Description
A Strange Tree (S-tree) over the variable set Xn={x1,x2,…,xn} is a binary tree representing a Boolean function f:{0,1}n→{0,1}. Each path of the S-tree begins at the root node and consists of n+1 nodes. Each of the S-tree’s nodes has a depth, which is the amount of nodes between itself and the root (so the root has depth 0). The nodes with depth less than n are called non-terminal nodes. All non-terminal nodes have two children: the right child and the left child. Each non-terminal node is marked with some variable xi from the variable set Xn. All non-terminal nodes with the same depth are marked with the same variable, and non-terminal nodes with different depth are marked with different variables. So, there is a unique variable xi1 corresponding to the root, a unique variable xi2 corresponding to the nodes with depth 1, and so on. The sequence of the variables xi1,xi2,…,xin is called the variable ordering. The nodes having depth n are called terminal nodes. They have no children and are marked with either 0 or 1. Note that the variable ordering and the distribution of 0’s and 1’s on terminal nodes are sufficient to completely describe an S-tree.
As stated earlier, each S-tree represents a Boolean function f. If you have an S-tree and values for the variables x1,x2,…,xn, then it is quite simple to find out what f(x1,x2,…,xn) is: start with the root. Now repeat the following: if the node you are at is labelled with a variable xi, then depending on whether the value of the variable is 1 or 0, you go its right or left child, respectively. Once you reach a terminal node, its label gives the value of the function.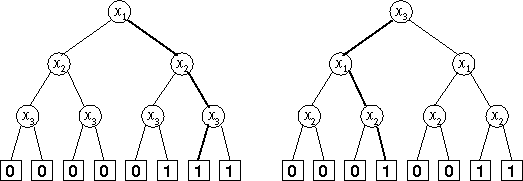
Figure 1: S-trees for the x1 and (x2 or x3) function
On the picture, two S-trees representing the same Boolean function,f(x1,x2,x3)=x1 and (x2 or x3), are shown. For the left tree, the variable ordering is x1,x2,x3, and for the right tree it is x3,x1,x2.
The values of the variables x1,x2,…,xn, are given as a Variable Values Assignment (VVA)
(x1=b1,x2=b2,…,xn=bn)
with b1,b2,…,bn in {0,1}. For instance, ( x1=1,x2=1,x3=0) would be a valid VVA for n=3, resulting for the sample function above in the value f(1,1,0)=1 and (1 or 0) = 1. The corresponding paths are shown bold in the picture.
Your task is to write a program which takes an S-tree and some VVAs and computes f(x1,x2,…,xn) as described above.
Input
The input contains the description of several S-trees with associated VVAs which you have to process. Each description begins with a line containing a single integer n, 1≤n≤7, the depth of the S-tree. This is followed by a line describing the variable ordering of the S-tree. The format of that line is xi1xi2…xin. (There will be exactly n different space-separated strings). So, for n=3 and the variable ordering x3,x1,x2, this line would look as follows:
x3x1x2
In the next line the distribution of 0’s and 1’s over the terminal nodes is given. There will be exactly 2n characters (each of which can be 0 or 1), followed by the new-line character. The characters are given in the order in which they appear in the S-tree, the first character corresponds to the leftmost terminal node of the S-tree, the last one to its rightmost terminal node.
The next line contains a single integer m, the number of VVAs, followed by m lines describing them. Each of the m lines contains exactly n characters (each of which can be 0 or 1), followed by a new-line character. Regardless of the variable ordering of the S-tree, the first character always describes the value of x1, the second character describes the value of x2, and so on. So, the line
110
corresponds to the VVA ( x1=1,x2=1,x3=0).
The input is terminated by a test case starting with n=0. This test case should not be processed.
Output
For each S-tree, output the line “S-Tree #j:”, where j is the number of the S-tree. Then print a line that contains the value of f(x1,x2,…,xn) for each of the given m VVAs, where f is the function defined by the S-tree.
Output a blank line after each test case.
Samples
Input
3
x1 x2 x3
00000111
4
000
010
111
110
3
x3 x1 x2
00010011
4
000
010
111
110
0
Output
S-Tree #1:
0011
S-Tree #2:
0011
翻译:
给出一颗满二叉树,每一层代表一个01变量,取0时往左走,取1时往右走。
例如,上面左右两个图都对应表达式 x1∧(x2∨x3)。
给出所有叶子的值以及一些查询(即每个变量),求每个查询到达的叶子的值。例如,有四个查询:000、010、111、110,则输出应为0011。
解释一下:
①上面的表达式就是说 x2和x3至少有一个是1,并且x1是1的时候才能让查询到达的叶子结点的值是1(这个可能是某种高级做法的思路吧,虽然知道他的意思但是没想到怎么用合取和析取来实现 )
②直接按照样例解释:
a.先输入一个值n表示有几层是x。
b.输入x?,x?,x?,顺序表示在第几层,比如x3 x1 x2 表示x3是第一层,x1是第二层,x2是第三层。
c.输入最终查询叶子结点的01值(共有2的n次方个数)。
d.输入查询次数t。
e.输入查询的方法,顺序代表的是x的下标,比如110,是指x1向右,x2向右,x3向左。(注意不是按照层数顺序)
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5+5;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
int main()
{
int n,T=0;
while(cin>>n && n)
{
int qq = pow(2,n);
char c;
int x[10]={
0};//记录访问顺序
int k[10]={
0}; //记录每个位置向左还是向右。
int w[1000]={
0};//记录最末端的数值0/1
int ans[10]={
0};//答案
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>c>>x[i];
for(int i=0;i<qq;i++)
{
cin>>c;
w[i+qq] = c-'0';
}
int t;
cin>>t;
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
cin>>c;
k[j] = c-'0';
}
int tmp=1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(k[x[j]]==1)
tmp = tmp*2+1;
else
tmp = tmp*2;
}
ans[i] = w[tmp];
}
cout<<"S-Tree #"<<++T<<":"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++)
cout<<ans[i];
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
}
思路:
①根节点是1,向左走×2,向右走×2+1。
②用数组保存最后的结点的01数值。
③记录下层数顺序。
④记录下x1,x2,x3的01方法,然后按照层数顺序逐个操作。
⑤得到的tmp就是叶子的坐标 从数组中取出这个数存进 答案ans数组中
边栏推荐
- ucore lab 6
- JS --- detailed explanation of JS DOM (IV)
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's medical chair industry
- Cost accounting [16]
- Truck History
- MySQL授予用户指定内容的操作权限
- Research Report on surgical fluid treatment industry - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
- China's peripheral catheter market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast
- VS2019初步使用
- mysql导入数据库报错 [Err] 1273 – Unknown collation: ‘utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci’
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Printing quality inspection and verification system Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
Matlab comprehensive exercise: application in signal and system
学习记录:USART—串口通讯
C语言必背代码大全
JS --- detailed explanation of JS facing objects (VI)
Learning record: understand systick system timer and write delay function
Accounting regulations and professional ethics [1]
ucore lab 2
学习记录:理解 SysTick系统定时器,编写延时函数
Report on the market trend, technological innovation and market forecast of printing and decorative paper in China
Research Report of exterior wall insulation system (ewis) industry - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
Cost accounting [13]
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's Medical Automation Industry
Research Report on printed circuit board (PCB) connector industry - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
Interesting drink
Truck History
信息安全-安全编排自动化与响应 (SOAR) 技术解析
Opencv learning log 13 corrosion, expansion, opening and closing operations
Learning record: use STM32 external input interrupt
Learning record: STM32F103 clock system overview working principle