当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #771 (Div. 2)
2022-07-06 09:29:00 【狗蛋儿l】
A. Reverse
You are given a permutation p1,p2,…,pn of length n. You have to choose two integers l,r (1≤l≤r≤n) and reverse the subsegment [l,r] of the permutation. The permutation will become p1,p2,…,pl−1,pr,pr−1,…,pl,pr+1,pr+2,…,pn.
Find the lexicographically smallest permutation that can be obtained by performing exactly one reverse operation on the initial permutation.
Note that for two distinct permutations of equal length a and b, a is lexicographically smaller than b if at the first position they differ, a has the smaller element.
A permutation is an array consisting of n distinct integers from 1 to n in arbitrary order. For example, [2,3,1,5,4] is a permutation, but [1,2,2] is not a permutation (2 appears twice in the array) and [1,3,4] is also not a permutation (n=3 but there is 4 in the array).
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤500) — the number of test cases. Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n
(1≤n≤500) — the length of the permutation.
The second line of each test case contains n
integers p1,p2,…,pn (1≤pi≤n) — the elements of the permutation.
Output
For each test case print the lexicographically smallest permutation you can obtain.
Example
Input
4
1
1
3
2 1 3
4
1 4 2 3
5
1 2 3 4 5
Output
1
1 2 3
1 2 4 3
1 2 3 4 5
Note
In the first test case, the permutation has length 1, so the only possible segment is [1,1]. The resulting permutation is [1].
In the second test case, we can obtain the identity permutation by reversing the segment [1,2]. The resulting permutation is [1,2,3].
In the third test case, the best possible segment is [2,3]. The resulting permutation is [1,2,4,3].
In the fourth test case, there is no lexicographically smaller permutation, so we can leave it unchanged by choosing the segment [1,1]. The resulting permutation is [1,2,3,4,5].
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,t,p[510];
int main()
{
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>p[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(p[i]!=i){
int j=i+1;
for(;j<=n;j++)
if(p[j]==i)break;
reverse(p+i,p+j+1);
break;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<p[i]<<' ';
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
B. Odd Swap Sort
You are given an array a1,a2,…,an. You can perform operations on the array. In each operation you can choose an integer i (1≤i<n), and swap elements ai and ai+1 of the array, if ai+ai+1is odd.
Determine whether it can be sorted in non-decreasing order using this operation any number of times.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t
(1≤t≤105) — the number of test cases. Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n
(1≤n≤105) — the length of the array.
The second line of each test case contains n
integers a1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤109) — the elements of the array.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n
over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, print “Yes” or “No” depending on whether you can or can not sort the given array.
You may print each letter in any case (for example, “YES”, “Yes”, “yes”,“yEs” will all be recognized as positive answer).
Example
Input
4
4
1 6 31 14
2
4 2
5
2 9 6 7 10
3
6 6 6
Output
Yes
No
No
Yes
Note
In the first test case, we can simply swap 31
and 14 (31+14=45 which is odd) and obtain the non-decreasing array [1,6,14,31].
In the second test case, the only way we could sort the array is by swapping 4and 2, but this is impossible, since their sum 4+2=6is even.
In the third test case, there is no way to make the array non-decreasing.
In the fourth test case, the array is already non-decreasing.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n, x;
cin >> n;
ll even = 0 , odd = 0;
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
if (x & 1)
{
if (x < odd)flag = false;
odd = max(odd, x);
}
else
{
if (x < even)flag = false;
even = max(x, even);
}
}
if (flag)cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C. Inversion Graph
You are given a permutation p1,p2,…,pn. Then, an undirected graph is constructed in the following way: add an edge between vertices i, j such that ipj. Your task is to count the number of connected components in this graph.
Two vertices uand v belong to the same connected component if and only if there is at least one path along edges connecting u and v.
A permutation is an array consisting of n distinct integers from 1 to n in arbitrary order. For example, [2,3,1,5,4] is a permutation, but [1,2,2] is not a permutation (2 appears twice in the array) and [1,3,4] is also not a permutation (n=3 but there is 4in the array).
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤105) — the number of test cases. Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤105) — the length of the permutation.
The second line of each test case contains n
integers p1,p2,…,pn (1≤pi≤n) — the elements of the permutation.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n
over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, print one integer k — the number of connected components.
Example
Input
6
3
1 2 3
5
2 1 4 3 5
6
6 1 4 2 5 3
1
1
6
3 2 1 6 5 4
5
3 1 5 2 4
Output
3
3
1
1
2
1
Note
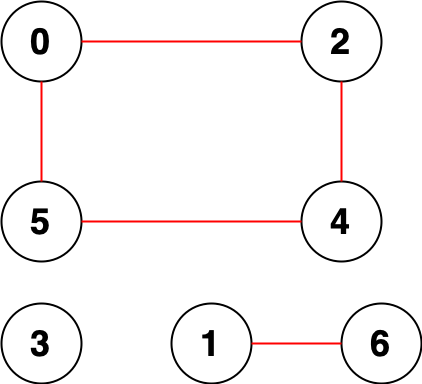
Each separate test case is depicted in the image below. The colored squares represent the elements of the permutation. For one permutation, each color represents some connected component. The number of distinct colors is the answer.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t ;
cin>>t;
while(t -- ) {
int n ;
cin>> n ;
map<int , int> p ;
int res= 0 , maxx = 1 ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
int k ;
cin>>k ;
p[k] = 1 ;
while(p[maxx]) maxx ++ ;
if(maxx > i ) res ++ ;
}
cout<<res <<"\n" ;
}
return 0 ;
}
边栏推荐
- Remove the border when input is focused
- Candy delivery (Mathematics)
- Spark的RDD(弹性分布式数据集)返回大结果集
- Problem - 922D、Robot Vacuum Cleaner - Codeforces
- AcWing——第55场周赛
- Pytorch extract skeleton (differentiable)
- js封装数组反转的方法--冯浩的博客
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's tetraacetylethylenediamine (TAED) industry
- 使用jq实现全选 反选 和全不选-冯浩的博客
- Codeforces Round #797 (Div. 3)无F
猜你喜欢
Codeforces Round #802(Div. 2)A~D
Codeforces Round #801 (Div. 2)A~C

去掉input聚焦时的边框
Problem - 922D、Robot Vacuum Cleaner - Codeforces
VMware Tools和open-vm-tools的安装与使用:解决虚拟机不全屏和无法传输文件的问题

Log statistics (double pointer)
sublime text 代码格式化操作

第三章 MapReduce框架原理

< li> dot style list style type
Li Kou: the 81st biweekly match
随机推荐
Install Jupiter notebook under Anaconda
Educational Codeforces Round 130 (Rated for Div. 2)A~C
业务系统兼容数据库Oracle/PostgreSQL(openGauss)/MySQL的琐事
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of tabletop dishwashers in China
Li Kou - 298th weekly match
浏览器打印边距,默认/无边距,占满1页A4
Problem - 1646C. Factorials and Powers of Two - Codeforces
(POJ - 1458) common subsequence (longest common subsequence)
Codeforces - 1526C1&&C2 - Potions
sublime text 代码格式化操作
Problem - 922D、Robot Vacuum Cleaner - Codeforces
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of double-sided foam tape in China
使用jq实现全选 反选 和全不选-冯浩的博客
Problem - 922D、Robot Vacuum Cleaner - Codeforces
Raspberry pie 4B installation opencv3.4.0
Codeforces Round #798 (Div. 2)A~D
拉取分支失败,fatal: ‘origin/xxx‘ is not a commit and a branch ‘xxx‘ cannot be created from it
js时间函数大全 详细的讲解 -----阿浩博客
1605. Sum the feasible matrix for a given row and column
Classic application of stack -- bracket matching problem