当前位置:网站首页>[unsolved]7-14 calculation diagram
[unsolved]7-14 calculation diagram
2022-07-06 16:45:00 【HBUcs2020】
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50000+10;
struct Node{
int op,x1,x2;
double v;
}node[maxn];
map<int,map<int,map<int,double>>>save;// The first parameter is node , The second parameter determines whether to take the derivative , The third parameter is to whom to derive
int have[maxn];
double dfs(int id,int key,int x){
if(save[id][key][x]) return save[id][key][x];
else{
switch(node[id].op){
case 0://value
return save[id][key][x]=key==0?node[id].v:(id==x?1:0);
case 1://plus
return save[id][key][x]=dfs(node[id].x1,key,x)+dfs(node[id].x2,key,x);
case 2://minus
return save[id][key][x]=dfs(node[id].x1,key,x)-dfs(node[id].x2,key,x);
case 3://multiply
return save[id][key][x]=key==0?dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)*dfs(node[id].x2,0,x):dfs(node[id].x2,0,x)*dfs(node[id].x1,1,x)+dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)*dfs(node[id].x2,1,x);
case 4://e
return save[id][key][x]=key==0?exp(dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)):exp(dfs(node[id].x1,0,x))*dfs(node[id].x1,1,x);
case 5://ln
return save[id][key][x]=key==0?log(dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)):1/dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)*dfs(node[id].x1,1,x);
case 6://sin
return save[id][key][x]=key==0?sin(dfs(node[id].x1,0,x)):cos(dfs(node[id].x1,0,x))*dfs(node[id].x1,1,x);
}
}
}
int main(){
int n,root=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&node[i].op);
if(node[i].op==0) scanf("%lf",&node[i].v);
else if(node[i].op<=3){
scanf("%d%d",&node[i].x1,&node[i].x2);
have[node[i].x1]=have[node[i].x2]=1;
}
else{
scanf("%d",&node[i].x1);
have[node[i].x1]=1;
}
}
while(have[root]==1) root++;
printf("%.3f\n",dfs(root,0,-1));
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(node[i].op==0){
if(flag) printf(" ");
printf("%.3f",dfs(root,1,i));
flag=true;
}
}
return 0;
}
Calculation chart ”(computational graph) It is the basic execution engine of modern deep learning system , It provides a way to express any mathematical expression , For example, neural networks represented by directed acyclic graphs . The nodes in the graph represent basic operations or input variables , Edges represent the dependency of intermediate values between nodes . for example , The following figure is a function f(x1,x2)=lnx1+x1x2−sinx2 The calculation chart of .

Now let's give a calculation diagram , Please calculate the function value and its partial derivative according to all input variables ( That's gradient ). for example , A given input x1=2,x2=5, The function value obtained from the above calculation diagram f(2,5)=ln(2)+2×5−sin(5)=11.652; And according to the differential chain rule , The gradient obtained from the above figure ∇f=[∂f/∂x1,∂f/∂x2]=[1/x1+x2,x1−cosx2]=[5.500,1.716].
I know you've forgotten calculus , So here you are only required to deal with a few simple operators : Add 、 Subtraction 、 Multiplication 、 Index (ex, In programming language exp(x) function )、 logarithm (lnx, In programming language log(x) function ) And sine function (sinx, In programming language sin(x) function ).
A friendly reminder :
- The derivative of a constant is 0;x The derivative of is 1;ex The derivative of is still ex;lnx The derivative of is 1/x;sinx The derivative of is cosx.
- Review what is Partial derivative : In mathematics , The partial derivative of a multivariable function , It's about the derivative of one variable and keeping the other constant . In the example above , When we are right x1 Find the partial derivative ∂f/∂x1 when , will x2 As a constant , So get lnx1 The derivative of is 1/x1,x1x2 The derivative of is x2,sinx2 The derivative of is 0.
- Take a look back. The chain rule : The derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivatives of the finite functions at the corresponding points , If so u=f(y),y=g(x), be du/dx=du/dy⋅dy/dx. For example sin(lnx) Derivation , You get cos(lnx)⋅(1/x).
If you pay attention to observation , It can be found in the calculation diagram , Calculating the function value is a calculation from left to right , The calculation of partial derivatives is just the opposite .
Input format :
The input gives a positive integer on the first line N(≤5×104), To calculate the number of vertices in the graph .
following N That's ok , The first i Line gives i Information about a vertex , among i=0,1,⋯,N−1. The first value is the type number of the vertex , Respectively :
- 0 Represents the input variable
- 1 For addition , Corresponding x1+x2
- 2 For subtraction , Corresponding x1−x2
- 3 Represents multiplication , Corresponding x1×x2
- 4 For index , Corresponding ex
- 5 Represents logarithm , Corresponding lnx
- 6 Represents a sine function , Corresponding sinx
For input variables , It will be followed by its double precision floating-point value ; For monocular operators , It will be followed by the vertex number of its corresponding single variable ( Number from 0 Start ); For binocular operators , It will be followed by the vertex number of its corresponding two variables .
The problem is guaranteed to have only one output vertex ( That is, vertices without edges , For example, the one on the far right in the figure above -), And the calculation process will not exceed the calculation accuracy range of double precision floating-point numbers .
Output format :
First, output the function value of the given calculation graph on the first line . In the second line, output the value of the partial derivative of the function for each variable in sequence , Separated by a space , There must be no extra space at the beginning and end of the line . The output order of partial derivatives is the same as that of input variables . Output after decimal point 3 position .
sample input :
7
0 2.0
0 5.0
5 0
3 0 1
6 1
1 2 3
2 5 4
sample output :
11.652
5.500 1.716
边栏推荐
- Codeforces Round #803 (Div. 2)A~C
- Discussion on QWidget code setting style sheet
- QT simulates mouse events and realizes clicking, double clicking, moving and dragging
- 解决Intel12代酷睿CPU单线程只给小核运行的问题
- Simply try the new amp model of deepfacelab (deepfake)
- LeetCode 1641. Count the number of Lexicographic vowel strings
- 图像处理一百题(11-20)
- Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of Chinese table lamp industry
- Chapter 5 detailed explanation of consumer groups
- Educational Codeforces Round 122 (Rated for Div. 2)
猜你喜欢

Chapter III principles of MapReduce framework
Pull branch failed, fatal: 'origin/xxx' is not a commit and a branch 'xxx' cannot be created from it
Spark independent cluster dynamic online and offline worker node
Spark独立集群Worker和Executor的概念
视频压缩编码和音频压缩编码基本原理

< li> dot style list style type
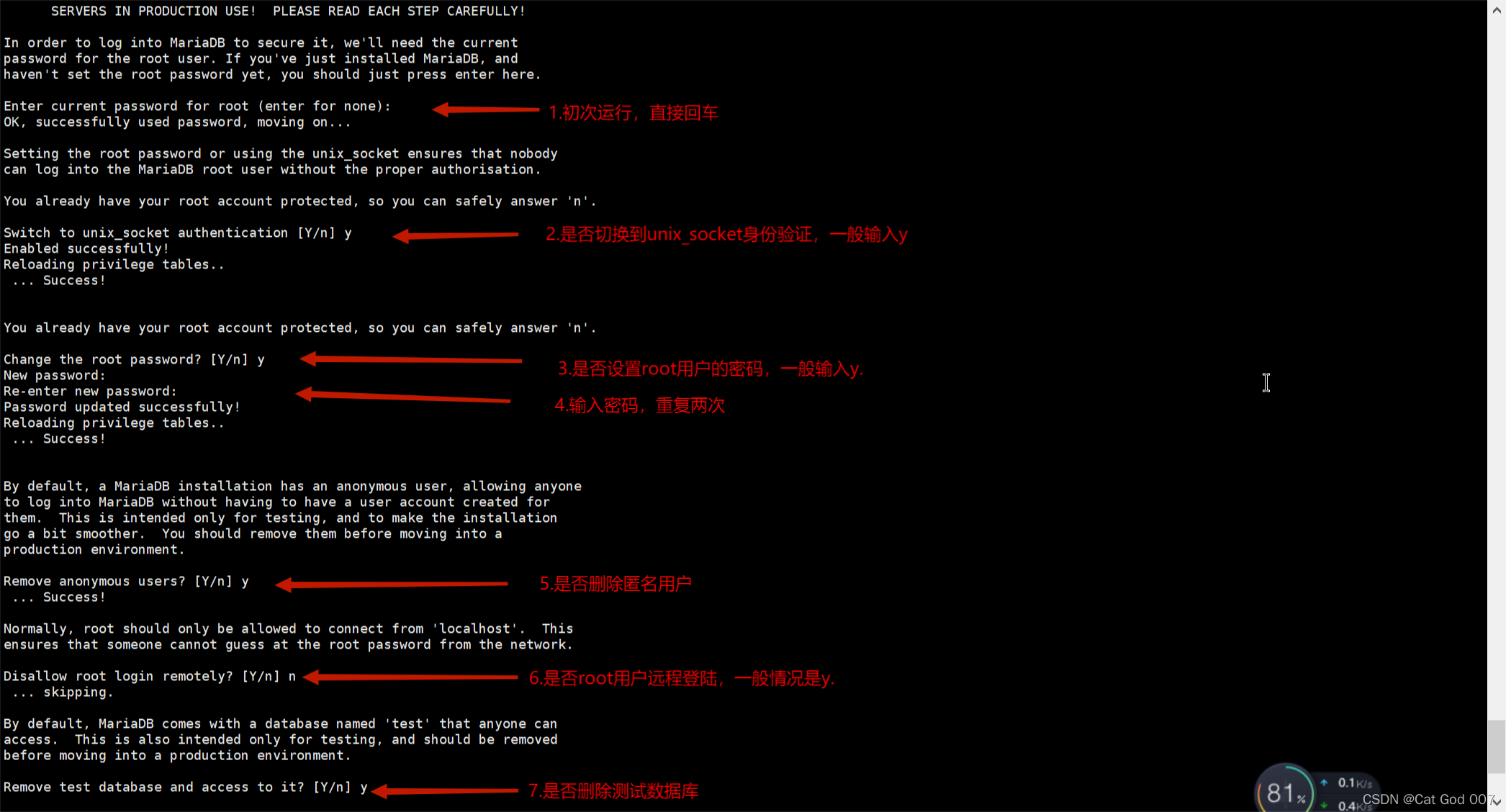
Installation and configuration of MariaDB
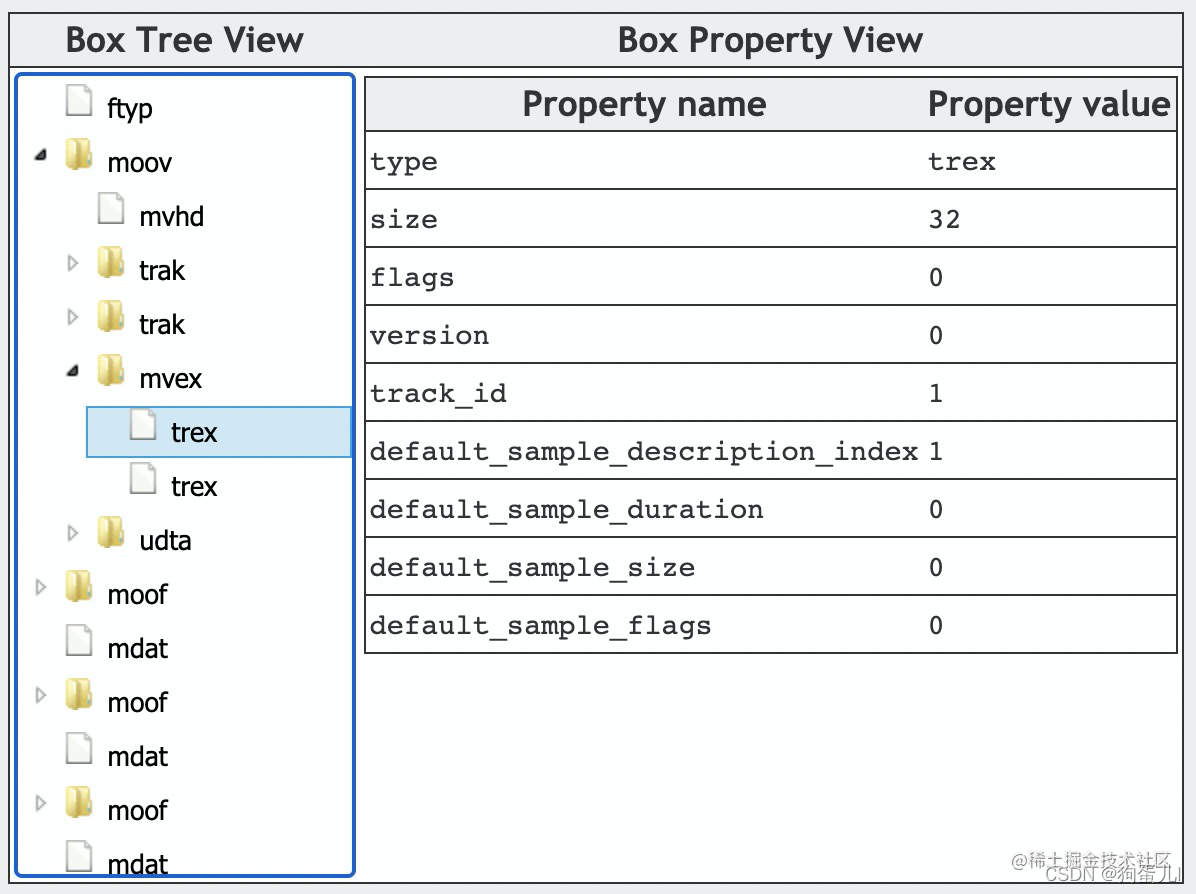
MP4格式详解

Log statistics (double pointer)

(lightoj - 1323) billiard balls (thinking)
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of FLV format
(lightoj - 1369) answering queries (thinking)
音视频开发面试题
业务系统兼容数据库Oracle/PostgreSQL(openGauss)/MySQL的琐事
Double specific tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect prediction
业务系统从Oracle迁移到openGauss数据库的简单记录
本地可视化工具连接阿里云centOS服务器的redis
Acwing: Game 58 of the week
LeetCode 1560. The sector with the most passes on the circular track
Business system compatible database oracle/postgresql (opengauss) /mysql Trivia
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of Chinese table lamp industry
ffmpeg命令行使用
7-5 blessing arrived
Simply try the new amp model of deepfacelab (deepfake)
Spark独立集群动态上线下线Worker节点
LeetCode 1640. Can I connect to form an array
解决Intel12代酷睿CPU单线程调度问题(二)
Kubernetes集群部署
Remove the border when input is focused
I'm "fixing movies" in ByteDance