当前位置:网站首页>JDBC principle
JDBC principle
2022-07-06 11:01:00 【Bolus acidophilus】
List of articles
- Database connection mode
- Mode one :Driver Implement class object to get connection
- Mode two :“ Iteration of mode 1 ”, There is no third-party api Make the program more portable
- Mode three :DriverManager Replace Driver
- Mode 4 : The load driver , Do not display registered drivers .
- Methods five (final edition ): Connect the database to the required 4 The basic information is declared in the configuration file , By reading the configuration file , Get the connection
- PreparedStatement Inquire about
- Aim at Customers Table addition, deletion and modification operations
- encapsulation JDBCUtils
- Aim at Customers Addition, deletion and modification of general table
- Aim at Customers The query operation of the table returns a record
- Aim at Customers General query operations for tables
- The general addition, deletion and modification of database transactions are not considered
- Consider the general addition, deletion and modification after database transactions
- Consider general queries after database transactions
- JDBCUtils( Including connection pool )
- BaseDAO/DAO
- DbUtils
Database connection mode
If yes, if the driver package version is 8.x Words ,properties In the document driverClass The path is com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver, It's not the original com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Mode one :Driver Implement class object to get connection
@Test
public void testConnection1() throws SQLException {
// obtain Driver Implementation class object
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
// url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
// `jdbc:mysql`: agreement
// localhost:ip Address
// 3306: Default mysql Port number
// test:test database
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8";
// Encapsulate the user name and password in Properties in
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty("user", "root");
info.setProperty("password", "abc123");
Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
explain : In the above code, the third-party database's API
Mode two :“ Iteration of mode 1 ”, There is no third-party api Make the program more portable
@Test
public void testConnection2() throws Exception {
// 1. obtain Driver Implementation class object : Using reflection
// call Class Static method to get Class Class :forName(String classPath)
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// call Class Object's newInstance() Method to get the runtime class (new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()) The object of
Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
// 2. Provide the database you want to connect to
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8";
// 3. Provide the user name and password needed to connect
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty("user", "root");
info.setProperty("password", "abc123");
// 4. Get the connection
Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
explain : Compared to mode one , Here we use reflection instantiation Driver, Do not reflect the third-party database in the code API. It embodies the idea of interface oriented programming .
Mode three :DriverManager Replace Driver
@Test
public void testConnection3() throws Exception {
// 1. obtain Driver Objects that implement classes
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
// 2. Provide basic information about the other three connections :
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8";
String user = "root";
String password = "abc123";
// Registration drive
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// Get the connection
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
explain : Use DriverManager Realize the connection of database . Experience getting the connection necessary 4 Basic elements .
Mode 4 : The load driver , Do not display registered drivers .
@Test
public void testConnection4() throws Exception {
// 1. Provide basic information about three connections :
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8";
String user = "root";
String password = "abc123";
// 2. load Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// Compared with mode three , The following operations can be omitted :
// Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
// // Registration drive
// DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// Why can we omit the above operation ?
/* * stay mysql Of Driver In the implementation class , The following operations are declared : * static { try { java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); } catch (SQLException E) { throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!"); } } */
// 3. Get the connection
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
explain : There's no need to explicitly register the driver . Because in DriverManager Static code blocks already exist in the source code of , Realized the driver registration .
Methods five (final edition ): Connect the database to the required 4 The basic information is declared in the configuration file , By reading the configuration file , Get the connection
/* The benefits of this approach ? * 1. The separation of data and code is realized . Achieve decoupling * 2. If you need to modify the profile information , You can avoid repackaging programs .*/
@Test
public void getConnection5() throws Exception{
//1. Read... In the configuration file 4 A basic message
//.class obtain Class Class
//getClassLoader Get the system class loader of the class
//getResourceAsStream Get the input stream of the specified file under the classpath
InputStream is = ConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//2. The load driver -- load Driver
Class.forName(driverClass);
// Registration drive Driver Static code blocks are declared in the implementation class
//3. Get the connection
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(conn);
among , The configuration file is declared in the src Under the table of contents :【jdbc.properties】
user=root
password=abc123
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
explain : Save configuration information in the form of a configuration file , Load the configuration file in the code
The benefits of using profiles :
① The separation of code and data is realized , If you need to modify the configuration information , Modify directly in the configuration file , There's no need to drill down into the code
② If the configuration information is modified , Save the process of recompiling .
PreparedStatement Inquire about
jdbc.properties
user=root
password=abc123
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Aim at Customers Table addition, deletion and modification operations
public class PreparedStatementUpdateTest {
// modify customers A record of a table
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//1. Get the connection to the database
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2. precompile sql sentence , return PreparedStatement Example
String sql = "update customers set name = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//3. Fill in placeholders
ps.setObject(1," Mozart ");
ps.setObject(2, 18);
//4. perform
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//5. Closure of resources
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
}
// towards customers Add a record to the table
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 1. Read... In the configuration file 4 A basic message
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
// 2. The load driver
Class.forName(driverClass);
// 3. Get the connection
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//4. precompile sql sentence , return PreparedStatement Example
String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth)values(?,?,?)";//?: Place holder
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5. Fill in placeholders
ps.setString(1, " Which zha ");
ps.setString(2, "[email protected]");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
java.util.Date date = sdf.parse("1000-01-01");
ps.setDate(3, new Date(date.getTime()));
//6. Perform the operation
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//7. Closure of resources
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
encapsulation JDBCUtils
public class JDBCUtils {
/** * @Description Get the connection to the database */
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
// 1. Read... In the configuration file 4 A basic message
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
// 2. The load driver
Class.forName(driverClass);
// 3. Get the connection
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
/** * @Description Close the connection and Statement The operation of */
public static void closeResource(Connection conn,Statement ps){
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/** * @Description Close resource operations */
public static void closeResource(Connection conn,Statement ps,ResultSet rs){
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(rs != null)
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Aim at Customers Addition, deletion and modification of general table
// General addition, deletion and modification operations
public void update(String sql,Object ...args){
//sql The number of placeholders in is the same as the length of the variable parameter !
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//1. Get the connection to the database
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2. precompile sql sentence , return PreparedStatement Example
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//3. Fill in placeholders
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);// Beware of parameter declaration errors !!
}
//4. perform
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//5. Closure of resources
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
}
Aim at Customers The query operation of the table returns a record
public class CustomerForQuery {
@Test
public void testQuery1() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, 1);
// perform , And return the result set
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
// Processing result set
if (resultSet.next()) {
// next(): Determine whether the next item in the result set has data , If there is data returned true, And move the pointer down ; If you return false, The pointer doesn't move down .
// Get the field values of the current data
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String name = resultSet.getString(2);
String email = resultSet.getString(3);
Date birth = resultSet.getDate(4);
// Mode one :
// System.out.println("id = " + id + ",name = " + name + ",email = " + email + ",birth = " + birth);
// Mode two :
// Object[] data = new Object[]{id,name,email,birth};
// Mode three : Encapsulating data as an object ( recommend )
Customer customer = new Customer(id, name, email, birth);
System.out.println(customer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, resultSet);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
Aim at Customers General query operations for tables
public Customer queryForCustomers(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// Get metadata of result set :ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// adopt ResultSetMetaData Get the number of columns in the result set
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
Customer cust = new Customer();
// Process each column in a row of data in the result set
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// Get column values
Object columValue = rs.getObject(i + 1);
// Get the column name of each column
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// to cust Object specified columnName attribute , The assignment is columValue: By reflection
Field field = Customer.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(cust, columValue);
}
return cust;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
@Test
public void testQueryForCustomers() {
String sql = "select id,name,birth,email from customers where id = ?";
Customer customer = queryForCustomers(sql, 13);
System.out.println(customer);
sql = "select name,email from customers where name = ?";
Customer customer1 = queryForCustomers(sql, " Jay Chou ");
System.out.println(customer1);
}
}
The general addition, deletion and modification of database transactions are not considered
// ****************** Transfer operations without considering database transactions **************************
/* * For datasheets user_table Come on : AA User give BB User transfer 100 * * update user_table set balance = balance - 100 where user = 'AA'; update * user_table set balance = balance + 100 where user = 'BB'; */
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
String sql1 = "update user_table set balance = balance - 100 where user = ?";
update(sql1, "AA");
// Simulate network anomalies
System.out.println(10 / 0);
String sql2 = "update user_table set balance = balance + 100 where user = ?";
update(sql2, "BB");
System.out.println(" Transfer succeeded ");
}
// General addition, deletion and modification operations ---version 1.0
public int update(String sql, Object... args) {
// sql The number of placeholders in is the same as the length of the variable parameter !
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 1. Get the connection to the database
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 2. precompile sql sentence , return PreparedStatement Example
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3. Fill in placeholders
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);// Beware of parameter declaration errors !!
}
// 4. perform
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Change it to auto submit data
// Mainly for the use of database connection pool
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 5. Closure of resources
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
return 0;
}
Consider the general addition, deletion and modification after database transactions
@Test
public void testUpdateWithTx() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn.getAutoCommit());// true
// 1. Cancel automatic submission of data
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql1 = "update user_table set balance = balance - 100 where user = ?";
update(conn, sql1, "AA");
// Simulate network anomalies
System.out.println(10 / 0);
String sql2 = "update user_table set balance = balance + 100 where user = ?";
update(conn, sql2, "BB");
System.out.println(" Transfer succeeded ");
// 2. Submit data
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 3. Undo Data
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// General addition, deletion and modification operations ---version 2.0 ( Think about business )
public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
// sql The number of placeholders in is the same as the length of the variable parameter !
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 1. precompile sql sentence , return PreparedStatement Example
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 2. Fill in placeholders
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);// Beware of parameter declaration errors !!
}
// 3. perform
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. Closure of resources
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps);
}
return 0;
}
Consider general queries after database transactions
public <T> T getInstance(Connection conn, Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// Get metadata of result set :ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// adopt ResultSetMetaData Get the number of columns in the result set
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.newInstance();
// Process each column in a row of data in the result set
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// Get column values
Object columValue = rs.getObject(i + 1);
// Get the column name of each column
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// to t Object specified columnName attribute , The assignment is columValue: By reflection
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columValue);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
JDBCUtils( Including connection pool )
public class JDBCUtils {
/** * @Description Get the connection to the database */
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
// 1. Read... In the configuration file 4 A basic message
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
// 2. The load driver
Class.forName(driverClass);
// 3. Get the connection
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
/** * Use Druid Database connection pool technology */
private static DataSource source;
static{
try {
Properties pros = new Properties();
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pros.load(is);
source = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pros);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection1() throws SQLException{
Connection conn = source.getConnection();
return conn;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
/** * @Description Use DBCP Database connection pool technology obtains database connection */
// Create a DBCP Database connection pool
private static DataSource source1;
static{
try {
Properties pros = new Properties();
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("src/dbcp.properties"));
pros.load(is);
source1 = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pros);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection2() throws Exception{
Connection conn = source1.getConnection();
return conn;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
/** * @Description Use C3P0 Database connection pool technology of */
// The database connection pool only needs to provide one .
private static ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource("hellc3p0");
public static Connection getConnection4() throws SQLException{
Connection conn = cpds.getConnection();
return conn;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
/** * @Description Close the connection and Statement The operation of */
public static void closeResource(Connection conn,Statement ps){
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/** * @Description close ResultSet Result set resource operation */
public static void closeResource(Connection conn,Statement ps,ResultSet rs){
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(rs != null)
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
/** * @Description Use dbutils.jar Provided in DbUtils Tool class , Close the resource */
public static void closeResource1(Connection conn,Statement ps,ResultSet rs){
// try {
// DbUtils.close(conn);
// } catch (SQLException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// try {
// DbUtils.close(ps);
// } catch (SQLException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// try {
// DbUtils.close(rs);
// } catch (SQLException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
DbUtils.closeQuietly(conn);
DbUtils.closeQuietly(ps);
DbUtils.closeQuietly(rs);
}
}
BaseDAO/DAO
DAO: data(base) access object
/** * It encapsulates the general basic operations for the database */
public abstract class BaseDAO<T> {
// Get generics T Of Class object , Get the type of the generic , Generics are determined when they are inherited by subclasses
private Class<T> clazz ;
// public BaseDAO(){
//
// }
{
// adopt this Get the class and then get the parent class of the class , In strong conversion to a generic parent , Getting generic arrays , Take the first generic type
// Because this class is an abstract class, which is inherited by subclasses , When the subclass object is created, it will call the static method or constructor method when the parent constructor is called
// At this time, the transmitted this Value is the value of the calling class, that is, the value of the inherited class or the value of the subclass of the inherited parent class )
// this.getClass() Get the subclass type of the calling parent class
// getGenericSuperclass() The type used to get the parent of the current class
// Get current BaseDAO The subclass of inherits the generics in the parent class
Type genericSuperclass = this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
// ParameterizedType Represents a type with generics
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
// Get the generic parameters of the parent class
// getActualTypeArguments Get the type of a specific generic type
// This method will return a Type Generic array of type
Type[] typeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();
// Get the type of a specific generic type · The first parameter of generics
clazz = (Class<T>) typeArguments[0];
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// General addition, deletion and modification operations ---version 2.0 ( Think about business )
public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
// sql The number of placeholders in is the same as the length of the variable parameter !
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 1. obtain PreparedStatement Example , precompile sql sentence
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 2. Fill in placeholders
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);//Object Prevent parameter declaration errors
}
// 3. perform executeUpdate Returns the number of rows of operations
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. Closure of resources
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps);
}
return 0;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// General query operations , Used to return a record in a data table (version 2.0: Think about business )
public T getInstance(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
//
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 1. obtain PreparedStatement() Example , precompile sql sentence
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 2. Fill in placeholders
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
// 3. perform executeQuery() return ResultSet Result set object
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// getMetaData() Get metadata of result set :ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// Through metadata getColumnCount() Get the number of columns in the result set
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
// 4. Processing result set row data , Determine whether the next item in the result set has data , If there is data returned true, And move the pointer down ; If you return false, The pointer doesn't move down .
if (rs.next()) {
// Create return value T Object of type
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 5. Process each column in a row of data in the result set
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// Get column values
Object columValue = rs.getObject(i + 1);
// Get the column name of each column
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// to t Object specified columnLabel attribute , The assignment is columValue: By reflection
// At present clazz The value of is that the subclass inherits the value of the generic defined in the parent class ( See the code header in detail )
//getDeclaredField() Call private properties , Gets the property of the specified variable name in the runtime class
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columValue);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// General query operations , Used to return a collection of multiple records in a data table (version 2.0: Think about business )
public List<T> getForList(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// Get metadata of result set :ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// adopt ResultSetMetaData Get the number of columns in the result set
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
// Create a collection object
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
while (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// Process each column in a row of data in the result set : to t Property assignment specified by the object
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// Get column values
Object columValue = rs.getObject(i + 1);
// Get the column name of each column
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// to t Object specified columnName attribute , The assignment is columValue: By reflection
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columValue);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// A general method for querying special values
public <E> E getValue(Connection conn,String sql,Object...args){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
return (E) rs.getObject(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
}
DbUtils
/* * commons-dbutils yes Apache An open source provided by the organization JDBC Tool library , It encapsulates the operation of adding, deleting, modifying and querying the database * */
public class QueryRunnerTest {
// Test insert
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth)values(?,?,?)";
int insertCount = runner.update(conn, sql, " Cai Xukun: A boy devoted to music in "More than Forever" ","[email protected]","1997-09-08");
System.out.println(" Added " + insertCount + " Bar record ");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
// Test the query
/* * BeanHander: yes ResultSetHandler Implementation class of interface , Used to encapsulate a record in a table . */
@Test
public void testQuery1(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
BeanHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanHandler<>(Customer.class);
Customer customer = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
System.out.println(customer);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
/* * BeanListHandler: yes ResultSetHandler Implementation class of interface , It is used to encapsulate a set composed of multiple records in a table . */
@Test
public void testQuery2() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?";
BeanListHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class);
List<Customer> list = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
/* * MapHander: yes ResultSetHandler Implementation class of interface , Corresponding to a record in the table . * Take the field and the value of the corresponding field as map Medium key and value */
@Test
public void testQuery3(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
MapHandler handler = new MapHandler();
Map<String, Object> map = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
System.out.println(map);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
/* * MapListHander: yes ResultSetHandler Implementation class of interface , Corresponding to multiple records in the table . * Take the field and the value of the corresponding field as map Medium key and value. Will these map Add to List in */
@Test
public void testQuery4(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?";
MapListHandler handler = new MapListHandler();
List<Map<String, Object>> list = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
/* * ScalarHandler: Used to query special values */
@Test
public void testQuery5(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select count(*) from customers";
ScalarHandler handler = new ScalarHandler();
Long count = (Long) runner.query(conn, sql, handler);
System.out.println(count);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
@Test
public void testQuery6(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select max(birth) from customers";
ScalarHandler handler = new ScalarHandler();
Date maxBirth = (Date) runner.query(conn, sql, handler);
System.out.println(maxBirth);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
/* * Customize ResultSetHandler Implementation class of */
@Test
public void testQuery7(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
ResultSetHandler<Customer> handler = new ResultSetHandler<Customer>(){
@Override
public Customer handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
// System.out.println("handle");
// return null;
// return new Customer(12, " Jackie Chan ", "[email protected]", new Date(234324234324L));
if(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String email = rs.getString("email");
Date birth = rs.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(id, name, email, birth);
return customer;
}
return null;
}
};
Customer customer = runner.query(conn, sql, handler,23);
System.out.println(customer);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- CSDN Q & a tag skill tree (V) -- cloud native skill tree
- MySQL30-事务基础知识
- Detailed reading of stereo r-cnn paper -- Experiment: detailed explanation and result analysis
- LeetCode #461 汉明距离
- MySQL28-数据库的设计规范
- [ahoi2009]chess Chinese chess - combination number optimization shape pressure DP
- [leectode 2022.2.13] maximum number of "balloons"
- MySQL23-存儲引擎
- 【博主推荐】asp.net WebService 后台数据API JSON(附源码)
- MySQL master-slave replication, read-write separation
猜你喜欢
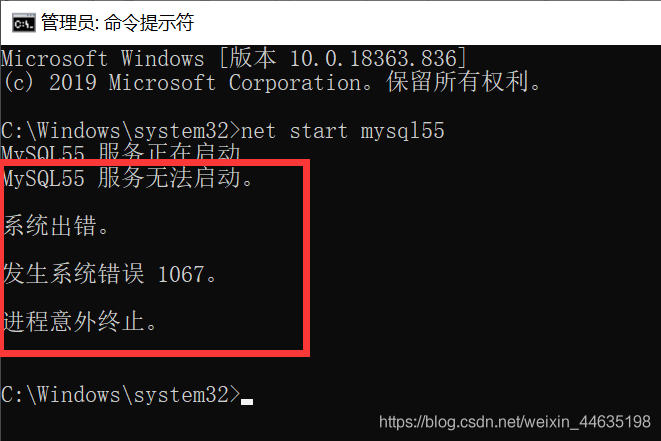
windows无法启动MYSQL服务(位于本地计算机)错误1067进程意外终止
Mysql24 index data structure
![[C language foundation] 04 judgment and circulation](/img/59/4100971f15a1a9bf3527cbe181d868.jpg)
[C language foundation] 04 judgment and circulation
Mysql28 database design specification
Copie maître - esclave MySQL, séparation lecture - écriture
CSDN问答模块标题推荐任务(一) —— 基本框架的搭建
![[recommended by bloggers] C WinForm regularly sends email (with source code)](/img/5d/57f8599a4f02c569c6c3f4bcb8b739.png)
[recommended by bloggers] C WinForm regularly sends email (with source code)
1. Mx6u learning notes (VII): bare metal development (4) -- master frequency and clock configuration

Solution: log4j:warn please initialize the log4j system properly

Mysql33 multi version concurrency control
随机推荐
[untitled]
Csdn-nlp: difficulty level classification of blog posts based on skill tree and weak supervised learning (I)
MySQL master-slave replication, read-write separation
JDBC原理
MySQL主從複制、讀寫分離
[Li Kou 387] the first unique character in the string
[leectode 2022.2.13] maximum number of "balloons"
CSDN-NLP:基于技能树和弱监督学习的博文难度等级分类 (一)
MySQL 29 other database tuning strategies
Mysql30 transaction Basics
Case identification based on pytoch pulmonary infection (using RESNET network structure)
Global and Chinese markets of static transfer switches (STS) 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
虚拟机Ping通主机,主机Ping不通虚拟机
Moteur de stockage mysql23
Global and Chinese markets for aprotic solvents 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
项目实战-后台员工信息管理(增删改查登录与退出)
[recommended by bloggers] C # generate a good-looking QR code (with source code)
Mysql25 index creation and design principles
Have you mastered the correct posture of golden three silver four job hopping?
[BMZCTF-pwn] 11-pwn111111