当前位置:网站首页>C language string function summary
C language string function summary
2022-07-06 10:33:00 【Banse】
<string.h> There are many commonly used string functions in the Library , Cute new bloggers have made some summaries here
Catalog
1.strlen
The function prototype :size_t strlen ( const char * str );
function : Calculate string length .
Parameters :str The string to evaluate
Return value : The length of the returned string does not include '\0'
Example :
int main()
{
char str[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", strlen(str));
// The result is 6
return 0;
}
Simulation Implementation :
// Counter method
int my_strlen1(const char *str)
{
int count = 0;
assert(str);
while (*str++)
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
// Pointer minus pointer
int my_strlen2(const char *str)
{
char *p = str;
assert(str);
while (*str)
str++;
return str - p;
}
// recursive
int my_strlen2(const char *str)
{
assert(str);
if (*str != '\0')
{
return 1 + my_strlen(str + 1);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
2.strcpy
The function prototype :char* strcpy(char * destination, const char * source );
function : Copy a string to another place
Parameters :source The source of the string to be copied ; destination Where the string to be copied will be placed ;
Return value : Return the address of the copied string
Be careful : The space where the string will be placed should be larger than the string to be copied .
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[10] = { 0 };
char str2[] = "abcdef";
printf("%s\n", strcpy(str1, str2));
// The result is abcdef
return 0;
}
Simulation Implementation :
char* my_strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)
{
char *tmp = dest;
assert(dest && src);
while (*src)
{
*dest = *src;
src++;
dest++;
}
return tmp;
}
3.strcat
The function prototype :char * strcat ( char * destination, const char * source );
function : Copy one string to the end of another .
Parameters :source String to be copied ,destination Copy to the end of this string
Return value : Return the address after copying
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[10] = "abc";
char str2[] = "def";
printf("%s\n", strcat(str1, str2));
// result abcdef
return 0;
}
Simulation Implementation :
char* my_strcat(char *dest, const char *src)
{
char *tmp = dest;
assert(dest && src);
while (*dest)// Find the end
dest++;
while (*src)
{
*dest++ = *src++;
}
return tmp;
}
4.strcmp
The function prototype :int strcmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2 );
function : String comparison , Press ASCII Code table comparison characters
Parameters :str1,str2 Two strings to compare
Return value :str1 Greater than str2 Return is greater than the 0 The number of :str1 be equal to str2 return 0;str1 Less than str2 Back to less than 0 The number of
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[] = "abcd";
char str2[] = "acde";
int tmp = strcmp(str1, str2);
if (tmp > 0)
{
printf("str1 > str2\n");
}
else if (tmp < 0)
{
printf("str1 < str2\n");
}
else
{
printf("str1 = str2\n");
}
// result str1 < str2
return 0;
}
Simulation Implementation :
int my_strcmp(const char *dest, const char *src)
{
assert(dest && src);
while (*dest == *src && *dest)
{
dest++;
src++;
}
return *dest - *src;
}
5.strncpy
The function prototype : char * strncpy ( char * destination, const char * source, size_t num );
function : Copy n Characters from the source string to the target space .
Parameters : destination Copy destination source Copy source num Number of copied characters
Return value : Return the address after copying
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[] = "abcdefg";
char str2[10] = { 0 };
printf("%s\n", strncpy(str2, str1, 3));
// result abc
return 0;
}
6.strncat
The function prototype : char * strncat ( char * destination, const char * source, size_t num );
function : The source of n Copy characters to the end of the destination plus '\0'
Parameters : destination Copy destination , sourse Copy source , num Number of copies
Return value : Return the address after copying
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[10] = "abc";
char str2[] = "defgh";
printf("%s\n", strncat(str1, str2, 3));
// result abcdef
return 0;
}7.strncmp
The function prototype : int strncmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2, size_t num );
function : Compare to the occurrence of different characters or the end of a string or n Compare all the characters .
Parameters : str1,str2 Two strings to compare num The number of characters to compare
Return value : str1 Greater than str2 Return is greater than the 0 The number of :str1 be equal to str2 return 0;str1 Less than str2 Back to less than 0 The number of
Example :
int main()
{
char str[][5] = { "R2D2" , "C3PO" , "R2A6" };
int n;
puts("Looking for R2 astromech droids...");
for (n = 0; n < 3; n++)
if (strncmp(str[n], "R2xx", 2) == 0)
{
printf("found %s\n", str[n]);
}
// result :
//found R2D2
//found R2A6
return 0;
}8.strstr
The function prototype : char * strstr ( const char *str1, const char * str2);
function : String lookup function , In string str1 Find string in str2
Parameters : str1 will By String to find ,str2 The string to find
Return value : Return to the address where you found the same location
Example :
// Example 1
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello whord!";
char str2[] = "ell";
printf("%s", strstr(str1, str2));
// result ello whord!
return 0;
}
// Example 2
int main ()
{
char str[] ="This is a simple string";
char * pch;
pch = strstr (str,"simple");
strncpy (pch,"sample",6);
puts (str);
// result This is a simple string
return 0;
}9.strtok
The function prototype : char * strtok ( char * str, const char * sep );
function : Find the separator flag in the string , And then split
Parameters str The string to be searched ,sep The string of delimiters can be multiple delimiters
Return value : The first call returns the address of the first string , When str Parameter input NULL Return the address of the next string , Returns... At the end of the string NULL
Add :
1.sep The parameter is a string , Defines the set of characters used as separators2. The first parameter specifies a string , It contains 0 One or more by sep A character separated by one or more separators in a string remember .3.strtok Function found str The next mark in , And use it \0 ending , Returns a pointer to the tag .( notes : strtok Function changes the string being manipulated , So it's using strtok The string segmented by function is usually the content of temporary copy And it can be modified .)4.strtok The first argument of the function is not NULL , Function will find str The first mark in ,strtok The function will save it in the string Position in .5.strtok The first argument to the function is NULL , The function will start at the same position in the string that is saved , Find next tag .6. If there are no more tags in the string , Then return to NULL The pointer .
Example :
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hell#o wh$ord";
char str2[] = "#$";
char* pstr = NULL;
for (pstr = strtok(str1, str2); pstr; pstr = strtok(NULL, str2))
{
printf("%s\n", pstr);
}
// result
//hell
//o wh
//ord
return 0;
}
10.strerror
The function prototype : char * strerror ( int errnum );
function : Return error information according to the error code
Parameters : ermun Error code
Return value : The address of the error message
Add :strerror Function with global variables errno Use
errno The header file <errno.h>
printf(" error message : %s", strerror(errno));
11.memcpy
The function prototype : void * memcpy ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );
function : Memory copy
Parameters destination The destination of the copy source Source of copy num Number of bytes copied
Return value : return void* Type of The address of the destination
Example
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 5, 6, 848, 4, 11, 3, 51, 9 };
int b[20] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
memcpy(b, a, sizeof(int) * 8);
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
}
// result 1 5 6 848 4 11 3 51 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
return 0;
}
Simulation Implementation :
void* my_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t n)
{
void* tmp = dest;
assert(dest);
assert(src);
while (n--)
{
*(char*)dest = *(char*)src;
(char*)dest += 1;
(char*)src += 1;
}
return tmp;
}
12.memmove
The function prototype : void * memmove ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );
function : Function and memmove Same but can handle string overlap , Can replace memcpy
Parameters : destination The destination of the copy source Source of copy num Number of bytes copied
Return value : return void* Type of The address of the destination
Simulation Implementation :
void* my_memmove(void* dest, const void* src, size_t n)
{
void* tmp = dest;
assert(dest);
assert(src);
if (dest < src)// Copy from front to back
{
while (n--)
{
*(char*)dest = *(char*)src;
src = (char*)src + 1;
(char*)dest += 1;
}
}
else
{
while (n--)
{
*((char*)dest + n - 1) = *((char*)src + n - 1);
}
}
return tmp;
}
13.memcmp
The function prototype : int memcmp ( const void * ptr1, const void * ptr2, size_t num );
function : Memory compare function , Compare by byte ,
Parameters : ptr1 ptr2 Two memory addresses to be compared num Number of bytes to compare
Return value : ptr1 Greater than ptr2 Return is greater than the 0 The number of :ptr1 be equal to ptr2 return 0;ptr1 Less than ptr2 Back to less than 0 The number of
14.memset
The function prototype : void * memset ( void * ptr, int value, size_t num );
function : Initialize the specified memory
Parameters : ptr Pointer to the memory to be initialized value What to initialize num Number of bytes to initialize
Return value : return void* Type ptr The address of
边栏推荐
- Google login prompt error code 12501
- Solution to the problem of cross domain inaccessibility of Chrome browser
- Good blog good material record link
- MySQL实战优化高手07 生产经验:如何对生产环境中的数据库进行360度无死角压测?
- 13 医疗挂号系统_【 微信登录】
- Time complexity (see which sentence is executed the most times)
- MySQL实战优化高手02 为了执行SQL语句,你知道MySQL用了什么样的架构设计吗?
- 该不会还有人不懂用C语言写扫雷游戏吧
- A necessary soft skill for Software Test Engineers: structured thinking
- Baidu Encyclopedia data crawling and content classification and recognition
猜你喜欢
ZABBIX introduction and installation

Introduction tutorial of typescript (dark horse programmer of station B)
MySQL 29 other database tuning strategies
Installation de la pagode et déploiement du projet flask
Complete web login process through filter
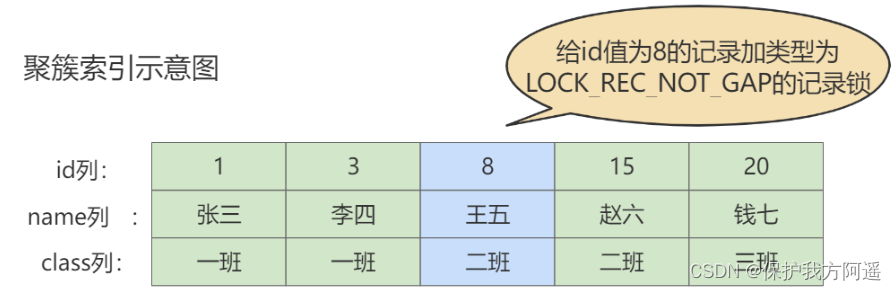
MySQL32-锁
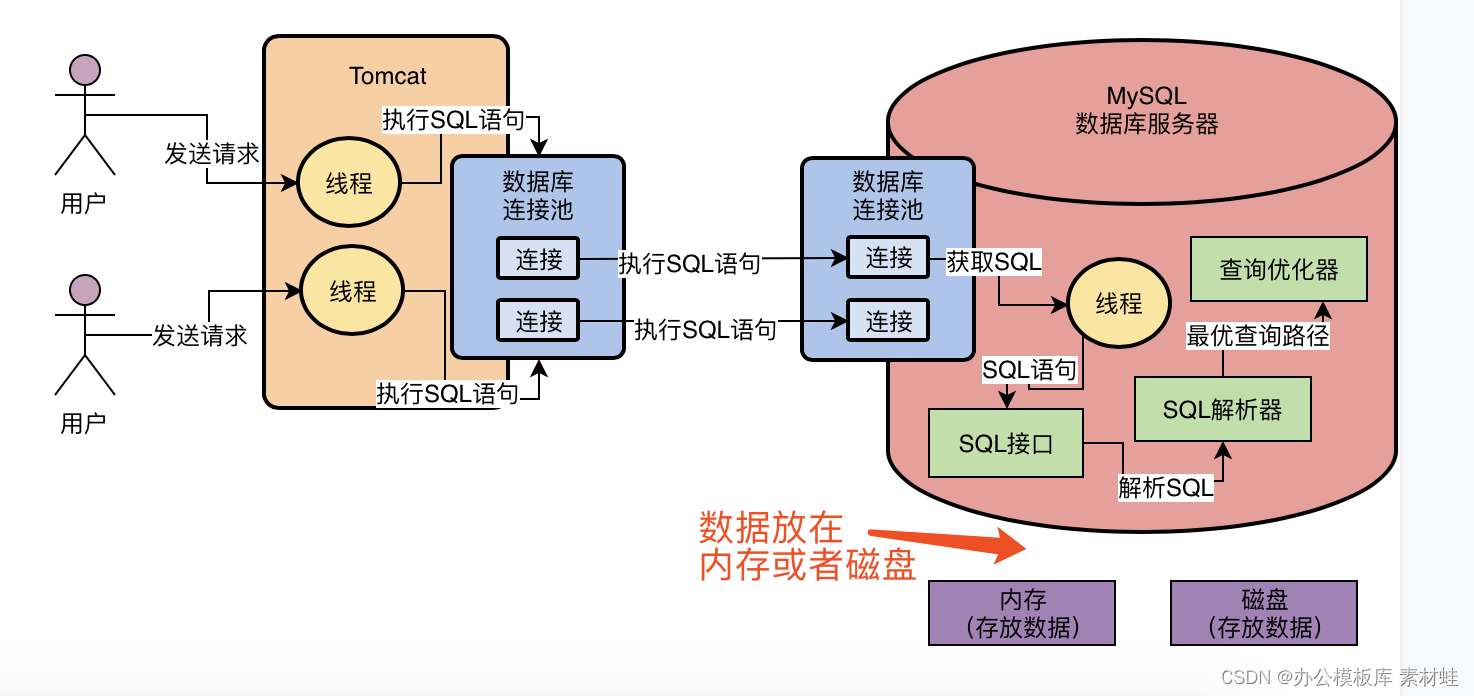
MySQL combat optimization expert 02 in order to execute SQL statements, do you know what kind of architectural design MySQL uses?
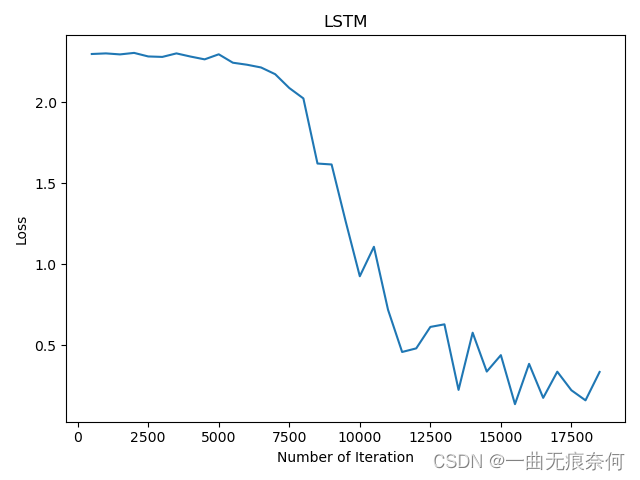
Pytoch LSTM implementation process (visual version)
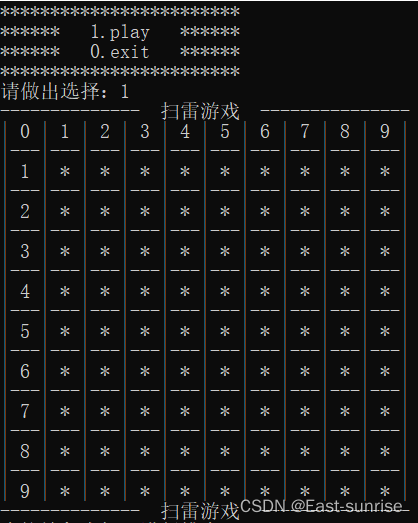
Isn't there anyone who doesn't know how to write mine sweeping games in C language
颜值爆表,推荐两款JSON可视化工具,配合Swagger使用真香
随机推荐
MySQL29-数据库其它调优策略
PyTorch RNN 实战案例_MNIST手写字体识别
① BOKE
第一篇博客
What should the redis cluster solution do? What are the plans?
Download and installation of QT Creator
实现微信公众号H5消息推送的超级详细步骤
Const decorated member function problem
【C语言】深度剖析数据存储的底层原理
MySQL combat optimization expert 06 production experience: how does the production environment database of Internet companies conduct performance testing?
C miscellaneous shallow copy and deep copy
[unity] simulate jelly effect (with collision) -- tutorial on using jellysprites plug-in
The underlying logical architecture of MySQL
Anaconda3 installation CV2
[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage
What is the current situation of the game industry in the Internet world?
MySQL combat optimization expert 07 production experience: how to conduct 360 degree dead angle pressure test on the database in the production environment?
Introduction tutorial of typescript (dark horse programmer of station B)
使用OVF Tool工具从Esxi 6.7中导出虚拟机
[Julia] exit notes - Serial