当前位置:网站首页>Mysql32 lock
Mysql32 lock
2022-07-06 10:23:00 【Protect our party a Yao】
One . summary
Transaction isolation is achieved by locks .
In the database , In addition to traditional computing resources ( Such as CPU、RAM、I/O etc. ) Beyond contention , Data is also a way for many users to share
resources . To ensure data consistency , Need to be right Concurrent operation control , And that's why lock . meanwhile Locking mechanism Also for the realization of MySQL
Each isolation level of provides guarantee . Lock conflict It also affects the database Concurrent access performance An important factor of . So the lock is on the database and
Words are particularly important , It's more complicated .
Two . MySQL Concurrent transactions access the same records
Concurrent transactions accessing the same record can be roughly divided into 3 Kind of :
2.1. read - Read the situation
read - read situation , That is, concurrent transactions occur one after another Read the same record . The read operation itself has no effect on the record , It doesn't cause any problems , So allow this to happen .
2.2. Write - Write about the situation
Write - Write situation , That is, concurrent transactions make changes to the same records one after another .
In this case Dirty write The problem of , No level of isolation allows this to happen . So when multiple uncommitted transactions make changes to a record one after another , Need to make them Queued execution , This queuing process is actually through lock To achieve . This so-called lock is actually a The structure in memory , There was no lock before the transaction was executed , That is to say, at first there was no Lock structure Associated with records , As shown in the figure :
When a transaction wants to make changes to this record , First, we will see if there is any in memory associated with this record Lock structure , When there is no, a... Will be generated in memory Lock structure Associated with it . such as , Business T1 To make changes to this record , You need to generate a The lock structure is associated with it :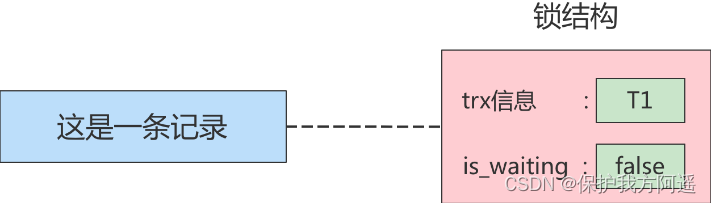
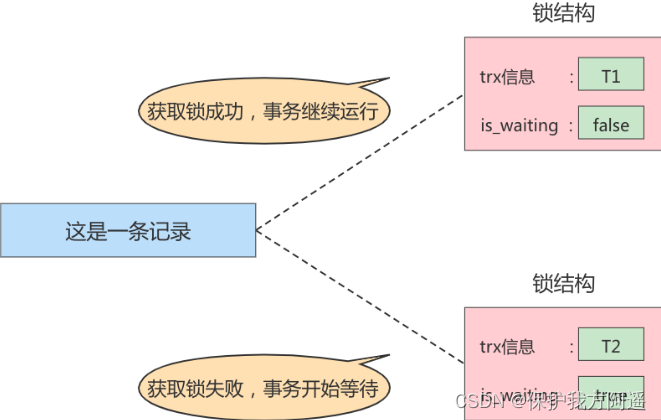
Summarize several statements :
- No locks
It means that there is no need to generate the corresponding... In memory Lock structure , You can perform operations directly . - Lock acquired successfully , Or lock successfully
It means that the corresponding... Is generated in memory Lock structure , And the lock structure is_waiting The attribute is false , That is, the transaction can continue to perform operations . - Lock acquisition failed , Or locking fails , Or the lock is not acquired
It means that the corresponding... Is generated in memory Lock structure , But the lock structure is_waiting The attribute is true , That is, transactions need to wait , The operation cannot be continued .
2.3. read - To write or write - Read the situation
read - Write or Write - read , That is, a transaction is used to read , The other makes changes . In this case it can happen Dirty reading 、 It can't be read repeatedly 、 The problem of unreal reading .
Various database manufacturers SQL standard Your support may be different . such as MySQL stay REPEATABLE READ The problem of unreal reading has been solved at the isolation level .
2.4. Solutions to concurrency problems
How to solve Dirty reading 、 It can't be read repeatedly 、 Fantasy reading These problems ? There are actually two alternative solutions :
- Scheme 1 : Read operations take advantage of multi version concurrency control ( MVCC), Write to lock .
ordinary SELECT Statements in READ COMMITTED and REPEATABLE READ Under the isolation level, you will use MVCC Read records .
1. stay READ COMMITTED Under isolation level , A transaction is executed every time during execution SELECT An... Is generated during operation
individual ReadView,ReadView The very existence of guarantees Transactions cannot read changes made by uncommitted transactions , It's just
Is to avoid the phenomenon of dirty reading ;
2. stay REPEATABLE READ Under isolation level , A transaction has only First execution SELECT operation Will
Generate a ReadView, After that SELECT All operations Reuse This ReadView, This avoids non repeatable reading
And unreal reading .
- Option two : read 、 Write operations all use Lock The way .
- Compared with :
- use MVCC In a way , read - Write Operations do not conflict with each other , Higher performance .
- use Lock In a way , read - Write Operations need each other Queued execution , Affect performance .
In general, we are willing to use MVCC To solve read - Write The problem of concurrent execution of operations , But in some special cases
Next , It is required that Lock By .
3、 ... and . Different angle classification of locks
3.1. From the type of data operation : Read the lock 、 Write lock
- Read the lock : Also known as Shared lock 、 In English S Express . For the same data , The read operation of multiple transactions can be carried out at the same time without affecting each other , They don't block each other .
- Write lock : Also known as Exclusive lock 、 In English X Express . Before the current write operation is completed , It blocks other write and read locks . This ensures that at a given time , Only one transaction can write , And prevent other users from reading the same resource being written .
It should be noted that for InnoDB For the engine , Read and write locks can be added to the table , You can also add it to the line .
3.2. From the granularity of data operation : Table lock 、 Page level lock 、 Row lock
3.2.1. Table locks (Table Lock)
3.2.1.1. Table level S lock 、X lock
Executing on a table SELECT、INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE When the sentence is ,InnoDB The storage engine will not add a table level to this table S lock perhaps X lock Of . Perform some actions on a table, such as ALTER TABLE 、 DROP TABLE This kind of DDL When the sentence is , Other transactions are executed concurrently on this table, such as SELECT、INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE The statement in the table will block . Empathy , Execute... On a table in a transaction SELECT、INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE When the sentence is , Execute... On this table in other sessions DDL Statements can also be blocked . This process is actually through server layer Use one called Metadata lock ( English name : Metadata Locks , abbreviation MDL ) Structure .
In general , Can't use InnoDB The table level provided by the storage engine S lock and X lock . Only in some special cases , For example Crash recovery Used in the process . such as , In system variable autocommit=0,innodb_table_locks = 1 when , Manual obtain InnoDB The tables provided by the storage engine t Of S lock perhaps X lock It can be written like this :
LOCK TABLES t READ :InnoDB The storage engine will update the table t Plus table level S lock .
OCK TABLES t WRITE :InnoDB The storage engine will update the table t Plus table level X lock .
But try to avoid using InnoDB Use... On the table of the storage engine LOCK TABLES Such manual table locking statements , They do not provide any additional protection , It just reduces concurrency .InnoDB What's more powerful is the implementation of finer grained Row lock .
MySQL There are two modes of table level lock :( With MyISAM Demonstration of table operation )Table share read lock (Table Read Lock)
Table Write Lock (Table Write Lock)
| Lock type | Read for yourself | Write your own | You can operate other tables by yourself | Others can read | Others can write |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read the lock | yes | no | no | yes | no , etc. |
| Write lock | yes | yes | no | no , etc. | no , etc. |
3.2.1.2. Intent locks (intention lock)
InnoDB Support Multi granularity lock (multiple granularity locking) , It allows the Row-level locks And Table lock coexistence , Intention lock is one of them Table locks .
There are two kinds of intention locks :
- Intention sharing lock (intention shared lock, IS): Transaction intends to add shared lock to some rows in the table (S lock )
-- Transaction to get the S lock , You must first obtain the IS lock .
SELECT column FROM table ... LOCK IN SHARE MODE;
- Intention exclusive lock (intention exclusive lock, IX): The transaction intends to lock some rows in the table (X lock )
-- Transaction to get the X lock , You must first obtain the IX lock .
SELECT column FROM table ... FOR UPDATE;
namely : Intent locks are created by the storage engine Self maintained , The user cannot manually operate the intention lock , Add sharing for data rows / Before he locks ,InooDB The data row will be obtained first The corresponding intent lock of the data table .
Concurrency of intent locks :
Intent locks are not shared with row level / Exclusive locks are mutually exclusive ! Because of that , When multiple transactions are locked, it will not affect the row locking .( Otherwise, we can just use the ordinary watch lock ).
- InnoDB Support Multi granularity lock , Under specific scenarios , Row level locks can coexist with table level locks .
- Intention locks are not mutually exclusive , But in addition to IS And S Out of compatibility , Intention lock meeting and Shared lock / Exclusive lock Mutually exclusive .
- IX,IS Is the table level lock , Not at the row level X,S Lock conflict . It'll only work at the table level X,S conflict .
- Intention lock under the premise of ensuring concurrency , Realized Row and table locks coexist And Satisfy transaction isolation The requirements of .
3.2.1.3. Self increasing lock (AUTO-INC lock )
In the use of MySQL In the process , We can add... To a column of the table AUTO_INCREMENT attribute . give an example :
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
Because of the id Field declares AUTO_INCREMENT, It means that there is no need to assign a value to the insert statement when writing it ,SQL The statement is modified as follows .
INSERT INTO teacher (name) VALUES ('zhangsan'), ('lisi');
The above insert statement is not for id Column explicit assignment , So the system will automatically assign an increasing value to it , The results are shown below .
SELECT * FROM teacher;
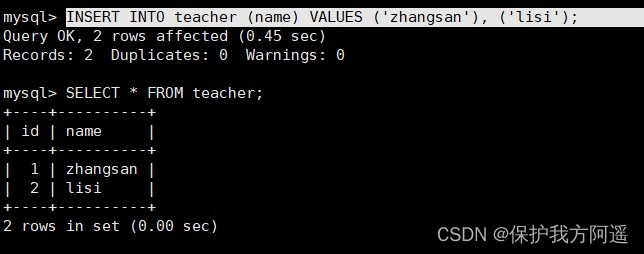
Now we can see that the above insert data is just a simple insert mode , All methods of inserting data are divided into three categories , Namely “ Simple inserts ”,“ Bulk inserts ” and “ Mixed-mode inserts ”.
- “Simple inserts” ( A simple insert )
Sure Predetermine the number of rows to insert ( When the statement is initially processed ) The sentence of . Including single row and multiple rows without nested subqueries INSERT…VALUES() and REPLACE sentence . For example, the example we mentioned above belongs to this class , The number of rows to insert has been determined . - “Bulk inserts” ( Batch insert )
I don't know the number of rows to insert in advance ( And the amount of automatic increment required ) The sentence of . such as INSERT … SELECT , REPLACE… SELECT and LOAD DATA sentence , But not pure INSERT. InnoDB Process each line , by AUTO_INCREMENT Assign a new value to the column . - “Mixed-mode inserts” ( Mixed mode insertion )
These are “Simple inserts” Statement, but specifies the automatic increment of some new lines . for example INSERT INTO teacher (id,name) VALUES (1,‘a’), (NULL,‘b’), (5,‘c’), (NULL,‘d’); It just specifies some id Value . Another type of “ Mixed mode insertion ” yes INSERT … ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE .
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode There are three values , Corresponding to different locking modes :
(1)innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 0(“ Tradition ” Lock mode )
In this lock mode , All types of insert Statement will get a special table level AUTO-INC lock , Used to insert with AUTO_INCREMENT List of columns . This model is actually like our example above , That is, whenever insert When , Will get a table lock (AUTO-INC lock ), Make... Generated in the statement auto_increment For the order , And in binlog During playback , Can guarantee master And slave Secondary data auto_increment It's the same . Because it's a table lock , When multiple transactions are executed at the same time insert When , about AUTO-INC The competition for locks will Limit concurrency Ability .
(2)innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 1(“ continuity ” Lock mode )
stay MySQL 8.0 Before , The continuous locking mode is Default Of .
In this mode ,“bulk inserts” Still use AUTO-INC Table lock , And keep it until the end of the statement . This applies to all INSERT …SELECT,REPLACE … SELECT and LOAD DATA sentence . Only one statement can hold at a time AUTO-INC lock .
about “Simple inserts”( The number of rows to insert is known in advance ), Then by mutex( Lightweight lock ) Obtain the required amount of automatic increment under the control of to avoid table level AUTO-INC lock , It is maintained only for the duration of the allocation process , Not until the statement is complete . Do not use table level AUTO-INC lock , Unless AUTO-INC The lock is held by another transaction . If another transaction remains AUTO-INC lock , be “Simple inserts” wait for AUTO-INC lock , As if it were a “bulk inserts”.
(3)innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 2(“ staggered ” Lock mode )
from MySQL 8.0 Start , The interleaving lock mode is Default Set up .
In this lock mode , Automatic increment Guarantee In all concurrent execution of all types of insert In the sentence is only And Monotone increasing Of . however , Because multiple statements can generate numbers at the same time ( namely , Cross numbering across statements ), The value generated for any line inserted into an attributive sentence may not be continuous .
3.2.1.4. Metadata lock (MDL lock )
MySQL5.5 Introduced meta data lock, abbreviation MDL lock , It belongs to the category of watch lock .MDL The role of is , Ensure the correctness of reading and writing . such as , If a query is traversing data in a table , And during execution, another thread is on this Change the table structure , Added a column , Then the result obtained by the query thread does not match the table structure , Surely not .
therefore , When adding, deleting, modifying and querying a table , Add MDL Read the lock ; When you want to make structural changes to a table , Add MDL Write lock .
3.2.2. InnoDB Row lock in
3.2.2.1. Record locks (Record Locks)
Record lock is to lock only one record , The official type name is : LOCK_REC_NOT_GAP . For example, we put id The value is 8 The schematic diagram of adding a record lock to the record is shown in the figure . Just locked id The value is 8 The record of , It has no effect on the surrounding data .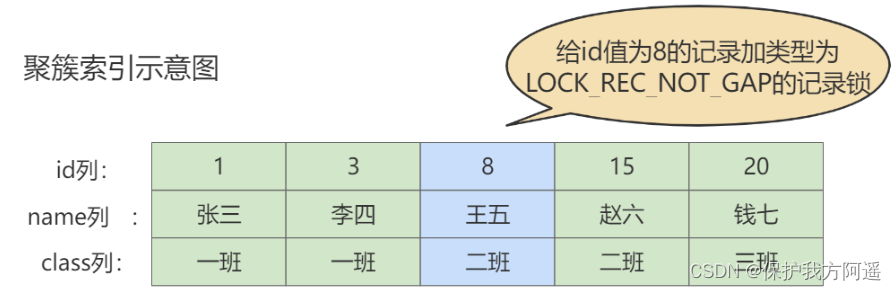
Examples are as follows :
create table student(id int,name varchar(50));
insert into student values (1,' Zhang San '),(2,' Li Si '),(3,' Zhang Fei ');
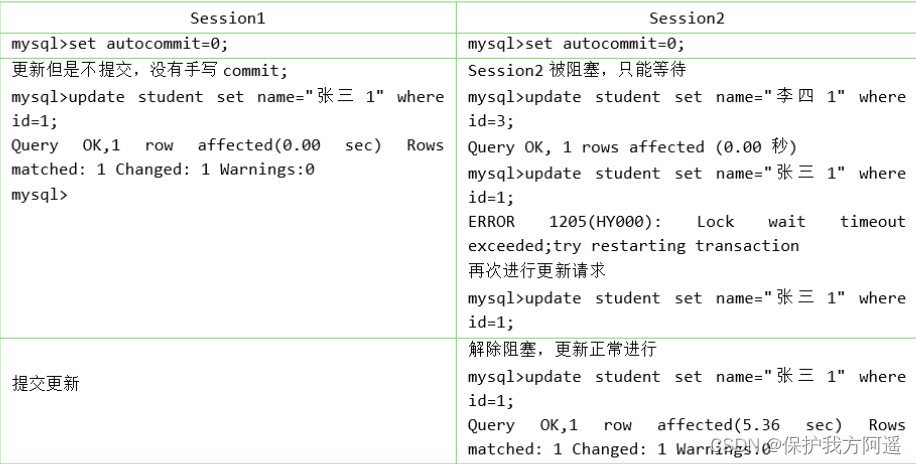
The record lock has S Lock and X It's a lock , be called S Type record lock and X Type record lock .
- When a transaction gets a record S Type record lock , Other transactions can also continue to get the record S Type record lock , But you can't continue to get X Type record lock ;
- When a transaction gets a record X Type record lock , No other transaction can continue to get the record S Type record lock , You can't continue to get X Type record lock .
3.2.2.2. Clearance lock (Gap Locks)
MySQL stay REPEATABLE READ The problem of unreal reading can be solved at the isolation level , There are two solutions , have access to MVCC Solution , You can also use Lock Solution . But there is a big problem when using the locking solution , That is, when the transaction first performs a read operation , Those phantom records don't exist yet , We can't give these Phantom recording add Record locks .InnoDB Put forward a kind of call Gap Locks Lock of , The official type name is : LOCK_GAP , We can abbreviate it to gap lock . such as , hold id The value is 8 Add one to that record gap The schematic diagram of the lock is as follows .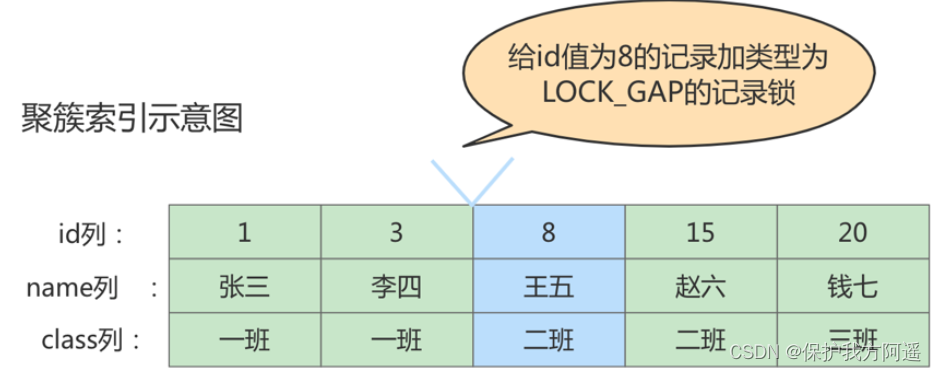
In the figure id The value is 8 My record is added gap lock , signify No other business is allowed in id The value is 8 Insert a new record in the gap in front of the record , In fact, that is id The value of the column (3, 8) New records in this interval are not allowed to be inserted immediately . such as , There is another transaction and I want to insert another one id The value is 4 New record of , It locates to the next record of the new record id The value is 8, And there's another one on this record gap lock , So it will block the insertion operation , Until you have this gap After the lock transaction is committed ,id The value of the column is in the interval (3, 8) New records in can be inserted .
gap The lock is only proposed to prevent the insertion of phantom records .
3.2.2.3. Temporary key lock (Next-Key Locks)
Sometimes we both want to Lock a record , Think again prevent Other transactions are in front of the record Insert a new record in the gap , therefore InnoDB This paper puts forward a method called Next-Key Locks Lock of , The official type name is : LOCK_ORDINARY , We can also abbreviate it to next-key lock .Next-Key Locks It's in the storage engine innodb 、 The transaction level is Repeatable Database lock used in case of ,innodb The default lock is Next-Key locks.
begin;
select * from student where id <=8 and id > 3 for update;
3.2.2.4. Insert intention lock (Insert Intention Locks)
Let's talk about a business in Insert For a record, you need to judge whether the insertion position is added by other transactions gap lock ( next-key The lock also contains gap lock ), If any , The insert operation needs to wait , Until you have gap lock The transaction submitted by . however InnoDB It is stipulated that a lock structure should also be generated in memory when the transaction is waiting , Indicates that there is a transaction that wants to be in a The gap in Insert New record , But now it's waiting .InnoDB Just name this type of lock Insert Intention Locks , The official type name is :LOCK_INSERT_INTENTION , We call it Insert intention lock . Inserting the intent lock is a kind of Gap lock , It's not the intent lock , stay insert Operation produces .
Insert intent lock is before inserting a record line , from INSERT A clearance lock produced by operation .
In fact, inserting an intent lock does not prevent other transactions from continuing to acquire any type of lock on the record .
3.2.3. Page locks
Page lock is in Page granularity Lock on the , More data resources are locked than row locks , Because a page can have multiple row records . When we use page locks , There will be a waste of data , But most of this waste is data rows on a page . The overhead of page lock is between table lock and row lock , A deadlock occurs . Lock granularity is between table lock and row lock , The concurrency is average .
There is a limit to the number of locks per level , Because locks take up memory space , The size of the lock space is limited . When the number of locks in a level exceeds the threshold of that level , It will Lock escalation . Lock upgrade is to replace multiple smaller granularity locks with larger granularity locks , such as InnoDB Upgrade middle row lock to table lock , The advantage of this is that it takes less lock space , But at the same time, the concurrency of data has also decreased .
3.3. From the attitude towards locks : Optimism lock 、 Pessimistic locking
From the attitude towards the lock, if the lock , Lock can be divided into optimistic lock and pessimistic lock , It can be seen from the name that these two kinds of locks are two ways of thinking about data concurrency . It should be noted that , Optimism and pessimism are not locks , It's locked design idea .
3.3.1. Pessimistic locking (Pessimistic Locking)
Pessimistic lock is a kind of thought , seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Is very pessimistic , Be conservative about data being modified by other transactions , It will be realized through the lock mechanism of the database itself , So as to ensure the exclusivity of data operation .
Pessimistic lock always assumes the worst , Every time I go to get the data, I think others will modify it , So every time I get the data, I will
lock , So that if people want to take this data, they will Blocking Until it gets the lock ( Shared resources are used by only one thread at a time , Other threads are blocking , Transfer resources to other threads after use ). For example, line locks. , Table lock, etc. , Read the lock , Write locks, etc. , It's all locked before the operation , When other threads want to access data , All need to block pending .Java in synchronized and ReentrantLock Waiting for exclusive lock is the realization of pessimistic lock thought .
3.3.2. Optimism lock (Optimistic Locking)
Optimistic locking holds that concurrent operations on the same data will not always occur , It's a small probability event , You don't have to lock the data every time , But in the process of updating, we will judge whether other people have updated this data during this period , That is to say, it does not use the lock mechanism of the database itself , It's a program . On procedure , We can use Version number mechanism perhaps CAS Mechanism Realization . Optimistic lock is suitable for multi read applications , This can improve throughput . stay Java in java.util.concurrent.atomic The atomic variable class under the package uses optimistic lock begin;
select * from student where id <=8 and id > 3 for update; An implementation of :CAS Realized .
3.3.2.1. Optimistic lock version number mechanism
Design a... In the table Version field version , The first time I read it , Will get version Value of field . Then update or delete the data , Will execute UPDATE … SET version=version+1 WHERE version=version . At this time, if a transaction has changed this data , The modification will not succeed .
3.3.2.2. The timestamp mechanism of optimistic lock
Timestamp is the same as the version number mechanism , It's also when the update is submitted , Compare the timestamp of the current data with that obtained before the update , If both are consistent, the update is successful , Otherwise it's a version conflict .
As you can see, optimistic lock is the programmer's permission to control the concurrent operation of data , Basically by adding a stamp to the data row ( Version number or time stamp ), So as to prove whether the current data is up-to-date .
3.3.2.3. Applicable scenarios of two kinds of locks
From the design ideas of these two kinds of locks , Summarize the applicable scenarios of optimistic lock and pessimistic lock :
- Optimism lock fit There are many reading operations Scene , Relatively speaking, there are fewer operations to write . Its advantage lies in Program realization , There is no deadlock problem , But the applicable scenario will also be relatively optimistic , Because it can't stop database operations other than programs .
- Pessimistic locking fit There are many writing operations Scene , Because the write operation has Exclusivity . Adopt pessimistic lock mode , You can prevent other transactions from operating on the data at the database level , prevent read - Write and Write - Write The conflict of .
3.4. According to the way of locking : Explicit lock 、 Implicit lock
3.4.1. Implicit lock
- The situation a : For clustered index records , There is one trx_id Hide columns , The hidden column records the last change to the record Business id . Then, if a new cluster index record is inserted in the current transaction , It should be recorded trx_id The hidden column represents the of the current transaction Business id , If other transactions want to add... To this record at this time S lock perhaps X lock when , First, I'll take a look at the record trx_id Whether the transaction represented by the hidden column is the current active transaction , If so , Then help the current transaction create a X lock ( That is to create a lock structure for the current transaction , is_waiting The attribute is false ), Then he enters the waiting state ( That is to create a lock structure for yourself , is_waiting The attribute is true ).
- Scenario two : For secondary index records , Not in itself trx_id Hide columns , But on the secondary index page Page Header Part of it has a PAGE_MAX_TRX_ID attribute , This attribute represents the largest number of changes made to the page Business id , If PAGE_MAX_TRX_ID The property value is less than the current minimum active value Business id , Then it means that the transactions that modify the page have been committed , Otherwise, you need to locate the corresponding secondary index record in the page , Then go back to the table and find its corresponding cluster index record , Then repeat The situation a How to do it .
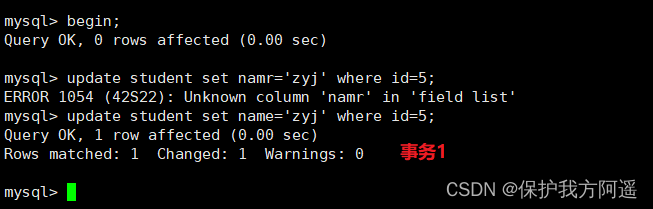
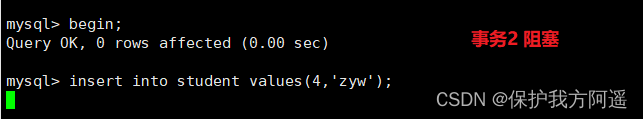
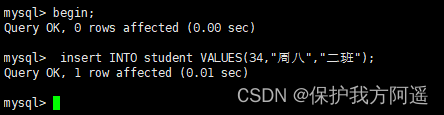
create table student(id int,name varchar(50),className varchar(50));
session 1:
begin;
insert INTO student VALUES(34," Tuesday "," Class two ");
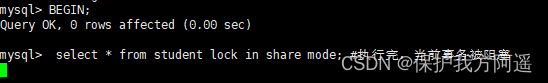
session 2:
begin;
select * from student lock in share mode; # After execution , The current transaction is blocked
Execute the following statement , Output results :
SELECT * FROM performance_schema.data_lock_waits\G;
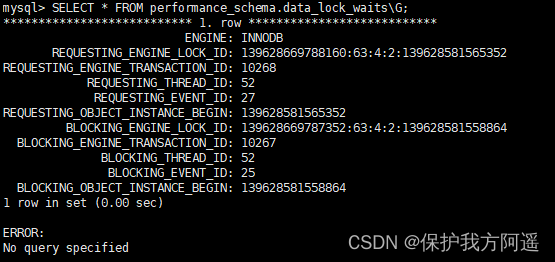
The logical process of implicit locking is as follows :
- InnoDB There is an implied in every record of trx_id Field , This field exists in the cluster index B+Tree in .
- Before operating a record , First, according to the record trx_id Check whether the transaction is active ( Not committed or rolled back ). If it's an active transaction , First of all, will Implicit lock Convert to Explicit lock ( Is to add a lock to the transaction ).
- Check for lock conflicts , If there is a conflict , Create a lock , And set to waiting state . If there is no conflict, do not lock , Jump to the 5.
- Wait for the lock to succeed , Awakened , Or a timeout .
- Writing data , And put your own trx_id write in trx_id Field .
3.4.2. Explicit lock
Lock through specific statements , We generally call it display locking , for example :
Display with shared lock :
select .... lock in share mode;
Show the addition and exclusion lock :
select .... for update;
3.5. Other locks : Global lock
The global lock is right The entire database instance Lock . When you need to keep the whole library in Read only status When , You can use this command , After that, the following statements of other threads will be blocked : Data update statement ( Data addition, deletion and modification )、 Data definition statement ( Including building tables 、 Modify table structure, etc ) Commit statements for and update class transactions . Typical use of global locks scene yes : do Full library logical backup .
Global lock command :
Flush tables with read lock;
3.6. Other locks : Deadlock
Deadlock means that two or more transactions occupy each other on the same resource , And request to lock the resources occupied by the other party , Which leads to a vicious circle . Deadlock example :
| project | Business 1 | Business 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | start transaction;update account set money=10 where id=1; | start transaction; |
| 2 | update account set money=10 where id=2; | |
| 3 | update account set money=20 where id=2; | |
| 4 | update account set money=20 where id=1; |
Now , Business 1 Waiting for business 2 Release id=2 The row lock , And the business 2 Waiting for business 1 Release id=1 The row lock . Business 1 And transaction 2 Waiting for each other's resources to be released , Is to enter the deadlock state . When there's a deadlock , Yes Two strategies :
- One strategy is , Direct entry waiting , Until timeout . This timeout can be set by the parameter innodb_lock_wait_timeout To set up .
- Another strategy is , Initiate deadlock detection , After deadlock is found , Actively roll back a transaction in the deadlock chain ( Rollback the transaction with the least row level exclusive lock ), Allow other business to continue . The parameter innodb_deadlock_detect Set to on , Indicates that the logic is turned on .
Cost analysis of the second strategy :
Method 1: If you can make sure that there is no deadlock in this business , Can temporarily turn off deadlock detection . But there is a certain risk in this operation , Because business design generally does not regard deadlock as a serious error , After all, there's a deadlock , Just roll back , Then it's OK to retry through business , This is a Business lossless Of . Turning off deadlock detection means that there may be a lot of timeouts , This is business damaging Of .
Method 2: Control concurrency . If concurrency can be controlled , For example, there is only one line at a time 10 Threads updating , So the cost of deadlock detection is very low , That's not going to happen .
This concurrency control should be done in Database server . If you have Middleware , You can consider Middleware implementation ; Even have the ability to modify MySQL Source person , It can also be done in MySQL Inside . The basic idea is , For peer updates , Queue up before getting into the engine , In this way InnoDB There won't be a lot of deadlock detection work inside .
Four . Memory structure of lock
InnoDB In the storage engine Lock structure as follows :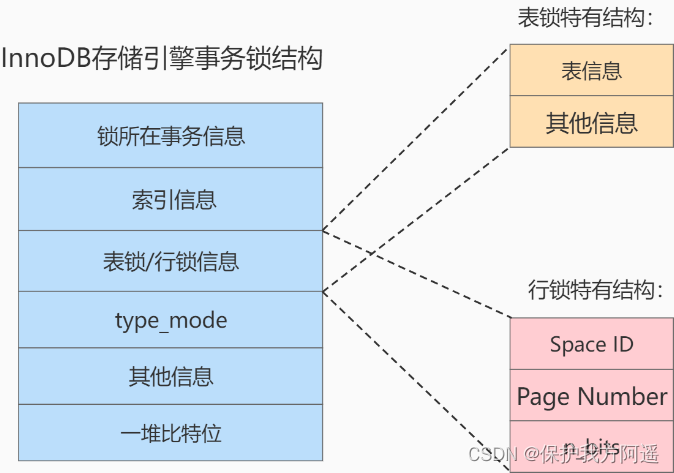
Structural analysis :
- The transaction information where the lock is located :
Whether it's Table locks still Row lock , Are generated during the execution of the transaction , Which transaction generated this Lock structure , Here is the information of this transaction .
this The transaction information where the lock is located It's just a pointer in the memory structure , More information about the transaction in memory can be found through the pointer , Let's say business id etc. .
- Index information :
about Row lock Come on , You need to record which index the locked record belongs to . Here is also a pointer . - Table locks / Row lock information :
Watch lock structure and Row lock structure The content in this position is different :
- Table locks :
It records which watch was locked , There's some other information . - Row lock :
Three important messages are recorded :
a. Space ID : The table space where the record is located .
b. Page Number : Record page number .
c. n_bits : For row locks , A record corresponds to a bit , A page contains many records , Use different
To distinguish which record is locked . To do this, a bunch of bits are placed at the end of the row lock structure , This
n_bits Attribute represents how many bits are used
n_bits The value of is usually more than the number of records in the page . The main purpose is to avoid reassigning the lock structure after inserting new records into the page .
- type_mode :
This is a 32 The number of bits , Divided into lock_mode 、 lock_type and rec_lock_type Three parts , As shown in the figure :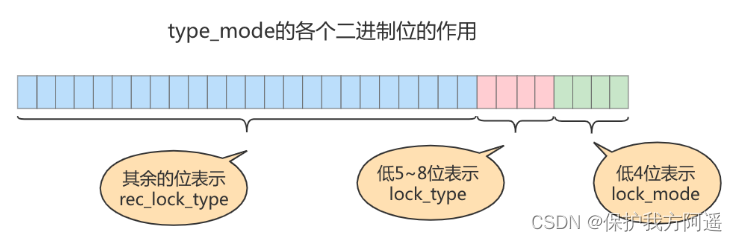
4.1. Lock mode ( lock_mode ), Low occupancy 4 position , The optional values are as follows :
- LOCK_IS ( Decimal 0 ): Indicates the sharing intention lock , That is to say IS lock .
- LOCK_IX ( Decimal 1 ): Indicates an exclusive intent lock , That is to say IX lock .
- LOCK_S ( Decimal 2 ): Represents a shared lock , That is to say S lock .
- LOCK_X ( Decimal 3 ): Represents an exclusive lock , That is to say X lock .
- LOCK_AUTO_INC ( Decimal 4 ): Express AUTO-INC lock .
4.2. stay InnoDB In the storage engine ,LOCK_IS,LOCK_IX,LOCK_AUTO_INC They are all table lock modes ,LOCK_S and LOCK_X It can be regarded as the mode of table level lock , It can also be the mode of row level lock .
The type of lock ( lock_type ), Occupy No 5~8 position , But at this stage, there's only one 5 Position and number 6 Bits are used : - LOCK_TABLE ( Decimal 16 ), That is to say, when the first 5 One bit position is 1 when , Represents a table level lock .
- LOCK_REC ( Decimal 32 ), That is to say, when the first 6 One bit position is 1 when , Represents a row level lock .
4.3. Specific types of row locks ( rec_lock_type ), Use the rest of the bits to represent . Only in lock_type The value of is LOCK_REC when , That is, only when the lock is a row level lock , Will be subdivided into more types : - LOCK_ORDINARY ( Decimal 0 ): Express next-key lock .
- LOCK_GAP ( Decimal 512 ): That is to say, when the first 10 One bit position is 1 when , Express gap lock .
- LOCK_REC_NOT_GAP ( Decimal 1024 ): That is to say, when the first 11 One bit position is 1 when , Mean serious Record locks .
- LOCK_INSERT_INTENTION ( Decimal 2048 ): That is to say, when the first 12 One bit position is 1 when , It means insert intention lock . Other types : There are also some types that are not commonly used. We won't talk more about them .
4.4. is_waiting Attribute? ? Based on memory space savings , So the is_waiting The attributes are placed in type_mode This 32 In a number of digits : - LOCK_WAIT ( Decimal 256 ) : When the first 9 One bit position is 1 when , Express is_waiting by true , That is, the current transaction has not yet acquired the lock , In a waiting state ; When this bit is 0 when , Express is_waiting by false , That is, the current transaction has successfully obtained the lock .
- Other information :
In order to better manage the various lock structures generated during the operation of the system, various hash tables and linked lists are designed . - A bunch of bits :
If it is Row lock structure Words , A pile of bits is also placed at the end of the structure , The number of bits is mentioned above n_bits Property means .InnoDB Each record in the data page is in Record header information All of them contain a heap_no attribute , A false record Infimum heap_no The attribute value is 0 , Supremum Of heap_no The value is 1 , After that, every record inserted , heap_no The value increases 1. Lock structure The last pile of bits corresponds to the record in a page , One bit maps one heap_no , That is, a bit is mapped to a record in the page .
5、 ... and . Lock monitoring
About MySQL Lock monitoring , We can usually check InnoDB_row_lock And other state variables to analyze the contention of row locks on the system :
show status like '%innodb_row_lock%';
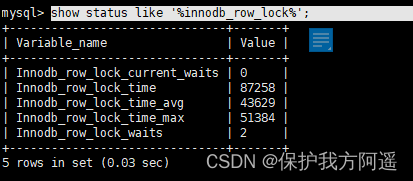
The description of each state quantity is as follows :
- Innodb_row_lock_current_waits: The number of currently waiting locks ;
- Innodb_row_lock_time : The total length of time from system startup to lock up ;( The total waiting time );
- Innodb_row_lock_time_avg : The average time it takes to wait ;( Average waiting time );
- Innodb_row_lock_time_max: Time spent waiting for the most frequent time from system startup to now ;
- Innodb_row_lock_waits : The total number of times the system has been waiting since it was started ;( Total waiting times );
For this 5 Two state variables , More important 3 See above ( Darker color ).
Other monitoring methods :
MySQL Record the transaction and lock information in information_schema In the library , The three tables involved are INNODB_TRX 、 INNODB_LOCKS and INNODB_LOCK_WAITS .
MySQL5.7 And before , Can pass information_schema.INNODB_LOCKS Check the lock status of the transaction , But you can only see the locks that block transactions ; If the transaction is not blocked , Then the lock of the transaction cannot be seen in the table .
MySQL8.0 Deleted information_schema.INNODB_LOCKS, Added performance_schema.data_locks , Can pass performance_schema.data_locks Check the lock status of the transaction , and MySQL5.7 The same as before ,performance_schema.data_locks Not only can you see the lock blocking the transaction , You can also see the locks held by the transaction .
meanwhile ,information_schema.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS Also by performance_schema.data_lock_waits Instead of .
We simulate a lock waiting scenario , The following is the information collected from these three tables :
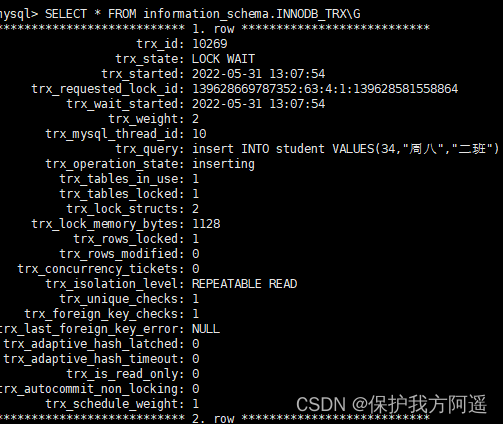
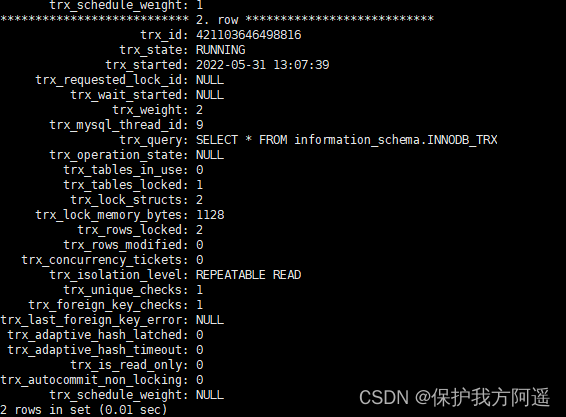
Lock waiting scenario , We still use the case in the record lock , When a transaction 2 While waiting , The inquiry is as follows :
(1) Query is blocked by lock sql sentence .
SELECT * FROM information_schema.INNODB_TRX\G
(2) Query lock waiting status
SELECT * FROM data_lock_waits\G;
(3) Query the lock
SELECT * from performance_schema.data_locks\G;
It can be seen from the lock , The two transactions get IX lock , We can know from the intention lock chapter ,IX When the locks are compatible with each other . So there's no waiting here , But the business 1 Also hold X lock , At this point, the transaction 2 Also go to the same line of records to get X lock , They are incompatible , A situation that leads to waiting .
边栏推荐
- The programming ranking list came out in February. Is the result as you expected?
- 颜值爆表,推荐两款JSON可视化工具,配合Swagger使用真香
- Preliminary introduction to C miscellaneous lecture document
- Software test engineer development planning route
- Use JUnit unit test & transaction usage
- MySQL combat optimization expert 02 in order to execute SQL statements, do you know what kind of architectural design MySQL uses?
- Several errors encountered when installing opencv
- MySQL实战优化高手04 借着更新语句在InnoDB存储引擎中的执行流程,聊聊binlog是什么?
- 西南大学:胡航-关于学习行为和学习效果分析
- A necessary soft skill for Software Test Engineers: structured thinking
猜你喜欢
![15 medical registration system_ [appointment registration]](/img/c1/27c7a5aae82783535e5467583bb176.png)
15 medical registration system_ [appointment registration]
Ueeditor internationalization configuration, supporting Chinese and English switching

实现微信公众号H5消息推送的超级详细步骤
![13 medical registration system_ [wechat login]](/img/c9/05ad1fc86e02cf51a37c9331938b0a.jpg)
13 medical registration system_ [wechat login]
Mexican SQL manual injection vulnerability test (mongodb database) problem solution
Carolyn Rosé博士的社交互通演讲记录
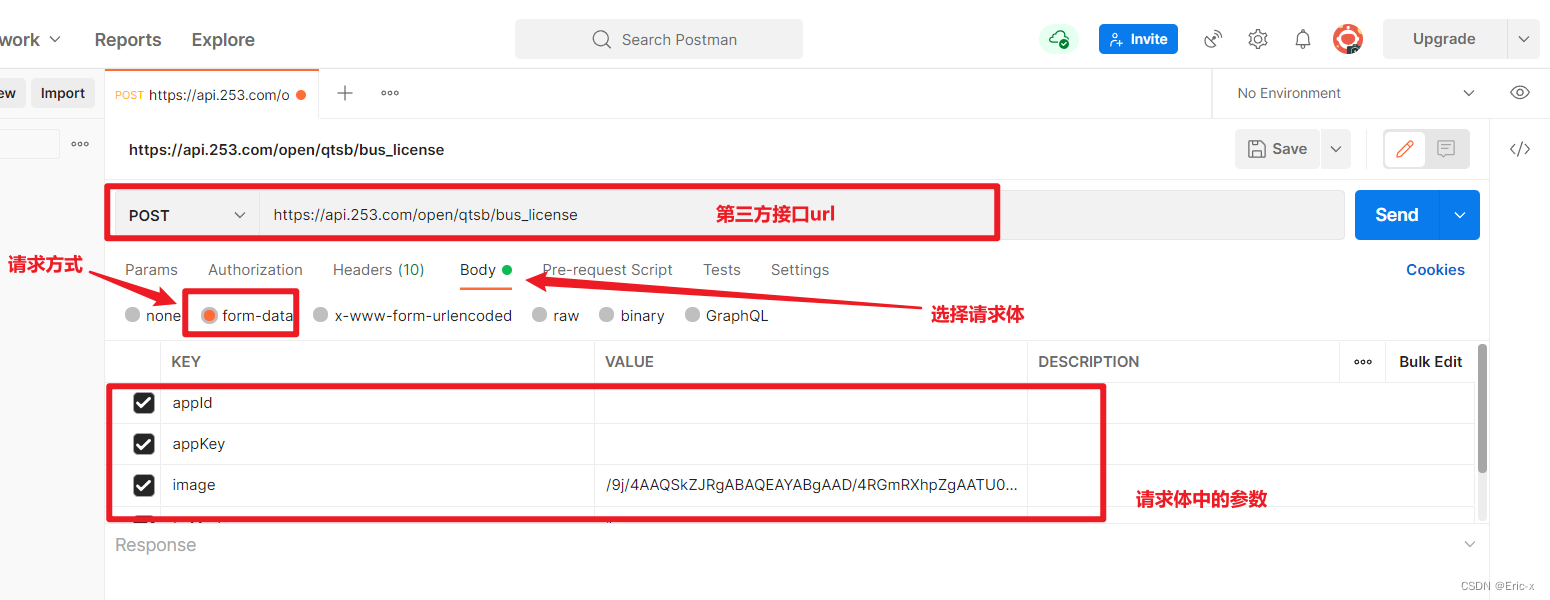
实现以form-data参数发送post请求
Solve the problem of remote connection to MySQL under Linux in Windows
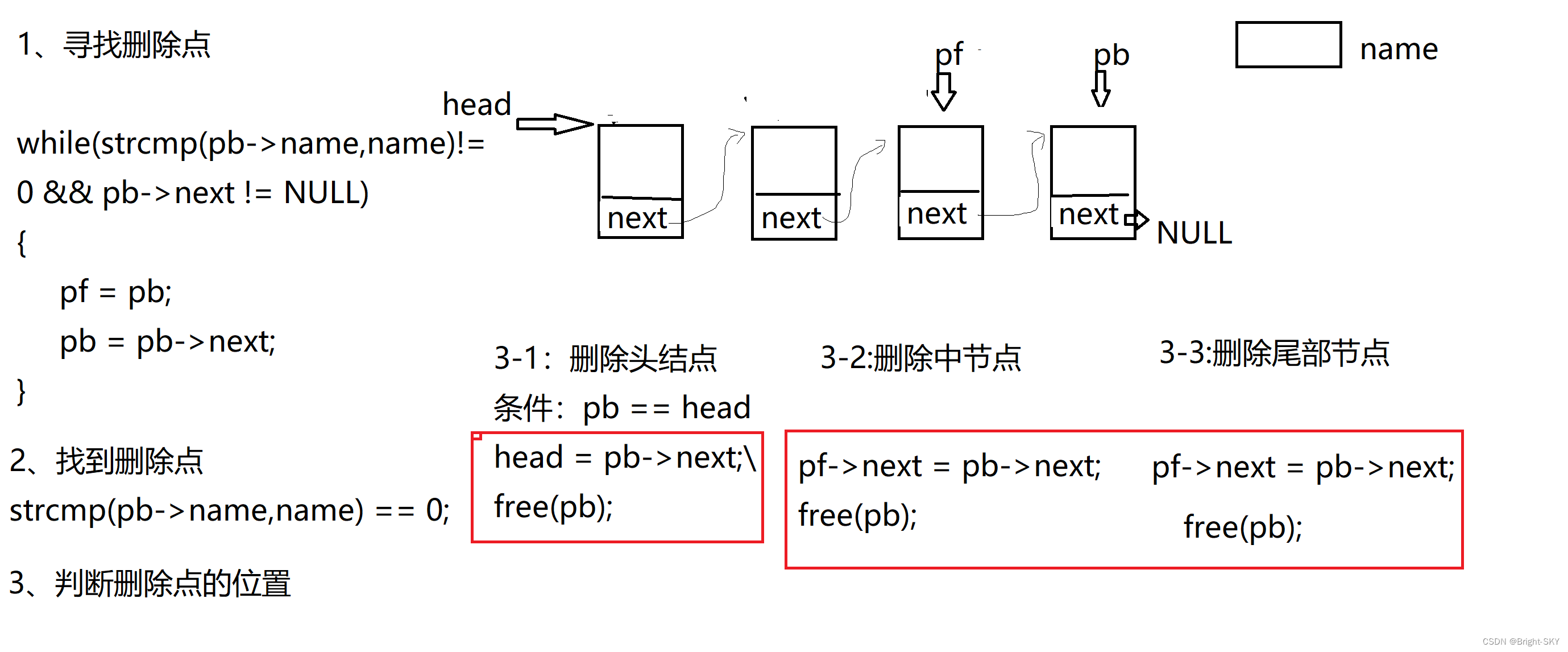
C杂讲 动态链表操作 再讲
MySQL real battle optimization expert 11 starts with the addition, deletion and modification of data. Review the status of buffer pool in the database
随机推荐
Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties, marked(@ConfigurationProperties的使用)
Technology | diverse substrate formats
MySQL Real Time Optimization Master 04 discute de ce qu'est binlog en mettant à jour le processus d'exécution des déclarations dans le moteur de stockage InnoDB.
Windchill配置远程Oracle数据库连接
Contest3145 - the 37th game of 2021 freshman individual training match_ C: Tour guide
Southwest University: Hu hang - Analysis on learning behavior and learning effect
[after reading the series] how to realize app automation without programming (automatically start Kwai APP)
How to make shell script executable
17 medical registration system_ [wechat Payment]
美疾控中心:美国李斯特菌疫情暴发与冰激凌产品有关
Jar runs with error no main manifest attribute
Canoe CAPL file operation directory collection
13 medical registration system_ [wechat login]
pytorch的Dataset的使用
Constants and pointers
Upload vulnerability
MySQL实战优化高手04 借着更新语句在InnoDB存储引擎中的执行流程,聊聊binlog是什么?
Simple solution to phpjm encryption problem free phpjm decryption tool
MySQL combat optimization expert 06 production experience: how does the production environment database of Internet companies conduct performance testing?
In fact, the implementation of current limiting is not complicated