当前位置:网站首页>C miscellaneous dynamic linked list operation
C miscellaneous dynamic linked list operation
2022-07-06 09:59:00 【Bright-SKY】
Catalog
Knowledge point 1【 Layout a simple frame 】
Knowledge point 2【 Insertion of linked list 】
1、 Insert... At the end of the linked list
2、 Orderly insertion of linked list ( difficulty )
Knowledge point 2【 The linked list queries a node 】 By name lookup
Knowledge point 3【 Delete the specified node in the linked list 】
Knowledge point 4【 Release of linked list 】
Knowledge point 5【 Take a look back. 】
Insertion of linked list : Insert before the head Tail insertion To insert in order
Deletion of linked list nodes :
Knowledge point 6【 The reverse order of the linked list 】
Knowledge point 7【 Sorting of linked lists 】
Sorting by selection :( Implemented as an array )
Knowledge point 7【 Sorting of linked lists ( Selection method )】
Knowledge point 1【 Layout a simple frame 】
main.c
#include<stdio.h>
void stu_help(void);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
stu_help();
while(1)
{
char cmd[32]="";
printf(" Please input the operation instruction :");
scanf("%s",cmd);
if(strcmp(cmd,"help") == 0)
{
stu_help();
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"insert") == 0)
{
printf("-----insert------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"print") == 0)
{
printf("-----print------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"search") == 0)
{
printf("-----search------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"delete") == 0)
{
printf("-----delete------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"free") == 0)
{
printf("-----free------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
void stu_help(void)
{
printf("################################\n");
printf("#help: Print help #\n");
printf("#insert: Insert linked list node #\n");
printf("#print: Traverse the linked list node information #\n");
printf("#search: Query linked list nodes #\n");
printf("#delete: Delete the linked list node #\n");
printf("#free: Release list #\n");
printf("#quit: sign out #\n");
printf("################################\n");
return;
}Linked list insertion node And Head Insert before
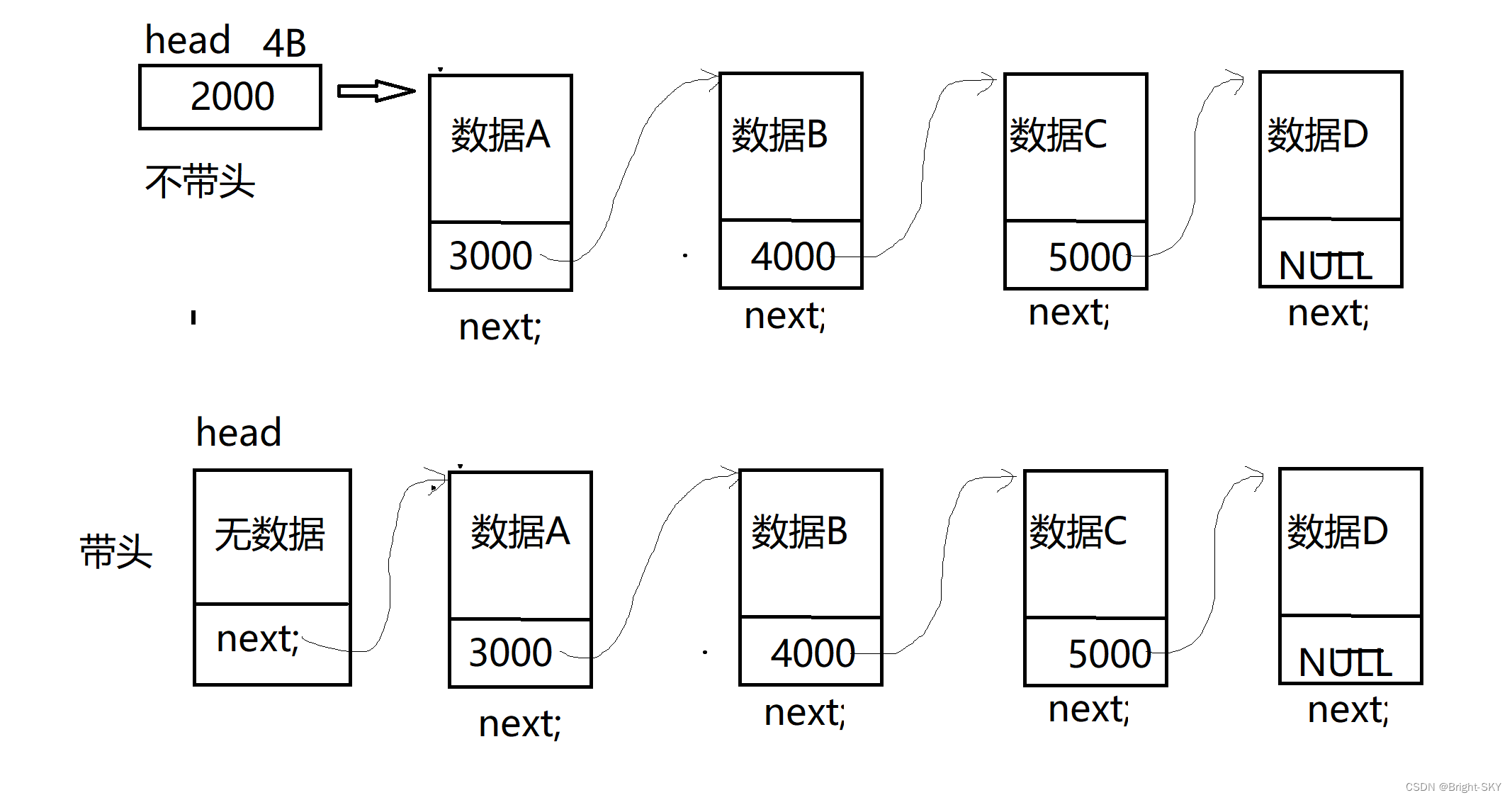
Case study :
main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include "link.h"
void stu_help(void);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
// Define a chain header Be careful Be sure to assign a value of NULL
STU *head=NULL;
stu_help();
while(1)
{
char cmd[32]="";
printf(" Please input the operation instruction :");
scanf("%s",cmd);
if(strcmp(cmd,"help") == 0)
{
stu_help();
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"insert") == 0)
{
STU tmp;
printf(" Please enter the data to be inserted :");
scanf("%d %s %f",&tmp.num, tmp.name, &tmp.score);
// take tmp data Insert into head In the linked list pointed to
head = insert_link(head, tmp);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"print") == 0)
{
print_link(head);
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"search") == 0)
{
printf("-----search------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"delete") == 0)
{
printf("-----delete------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"free") == 0)
{
printf("-----free------\n");
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
void stu_help(void)
{
printf("################################\n");
printf("#help: Print help #\n");
printf("#insert: Insert linked list node #\n");
printf("#print: Traverse the linked list node information #\n");
printf("#search: Query linked list nodes #\n");
printf("#delete: Delete the linked list node #\n");
printf("#free: Release list #\n");
printf("#quit: sign out #\n");
printf("################################\n");
return;
}link.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//calloc
#include"link.h"
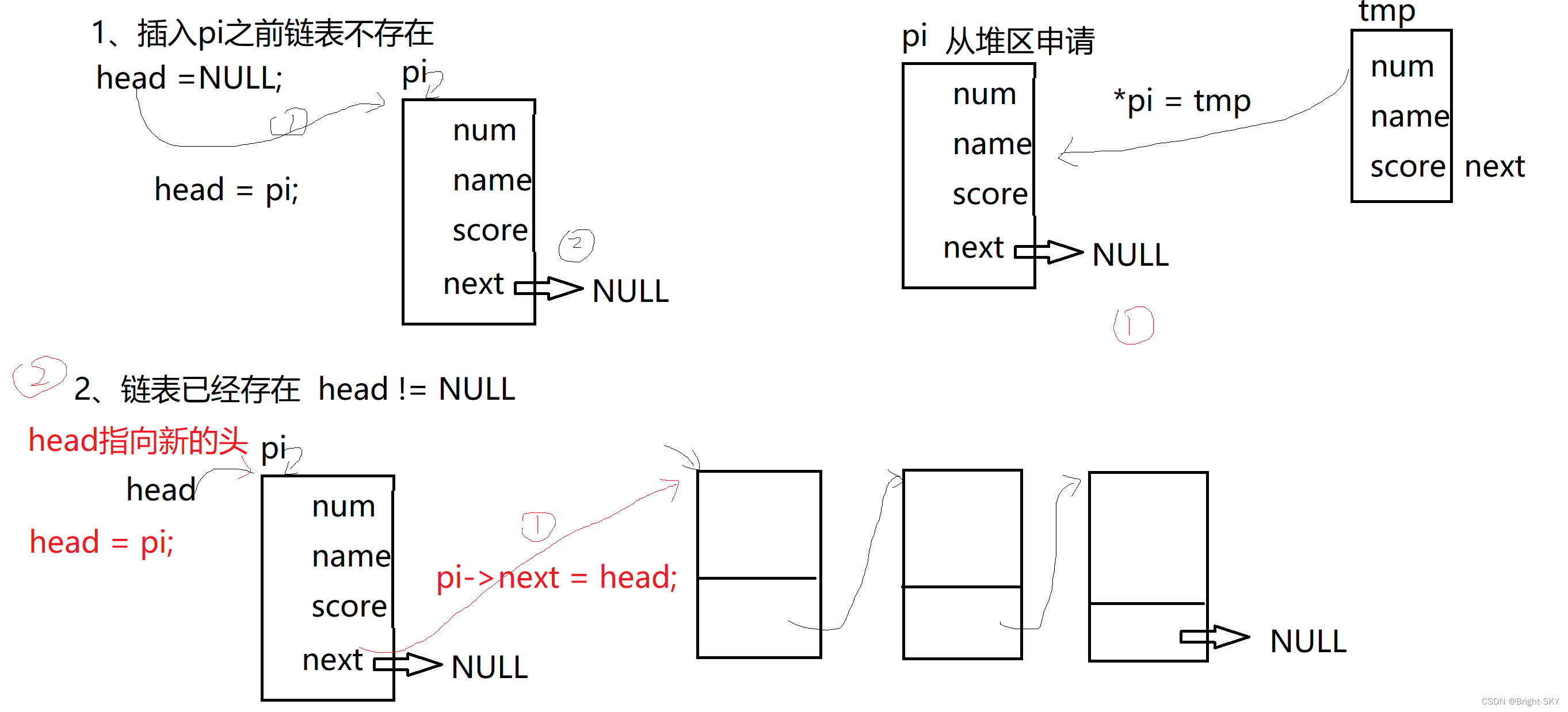
STU* insert_link(STU *head, STU tmp)
{
//1、 Apply for a node space to be inserted from the heap
STU *pi = (STU *)calloc(1,sizeof(STU));
if(pi == NULL)
{
perror("calloc");
return head;
}
//2、 take tmp Value assignment to *pi
*pi = tmp;
pi->next = NULL;// Be careful
//3、 take pi Insert into the linked list
if(head == NULL)// The list does not exist
{
head = pi;
//return head;
}
else// The linked list exists ( Insert before the head )
{
//1、 Give Way pi Point to your head
pi->next = head;
//2、head Point to the new head node
head = pi;
//return head;
}
return head;
}
void print_link(STU *head)
{
if(head == NULL)// The list does not exist
{
printf("link not find\n");
return;
}
else
{
STU *pb = head;
while(pb != NULL)
{
printf("%d %s %f\n", pb->num, pb->name,pb->score);
//pb Point to next node
pb = pb->next;
}
}
return;
}link.h
// Prevent header files from repeatedly containing
#ifndef __LINK_H__
#define __LINK_H__
// Linked list node type Definition
typedef struct stu
{
// Data fields
int num;
char name[32];
float score;
// Pointer to the domain
struct stu *next;
}STU;
extern STU* insert_link(STU *head, STU tmp);
extern void print_link(STU *head);
#endifKnowledge point 2【 Insertion of linked list 】
1、 Insert... At the end of the linked list
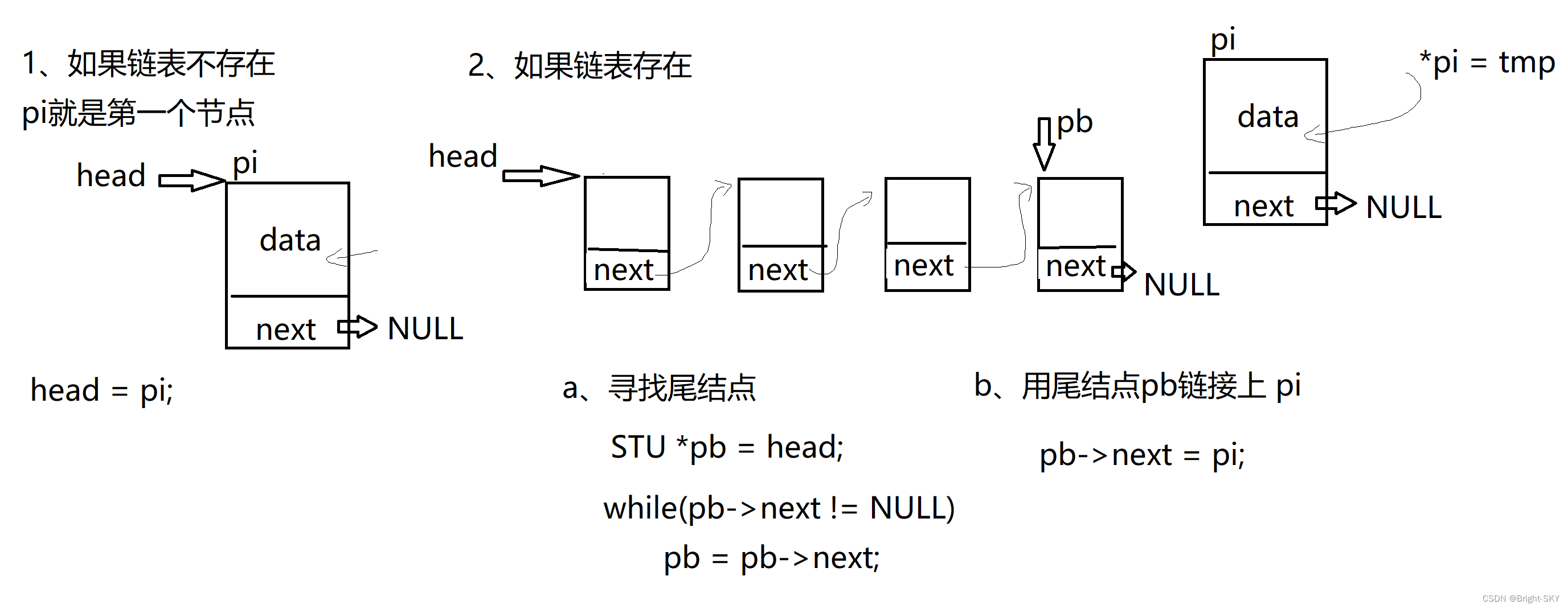
// The tail of the linked list is inserted
STU* insert_link(STU *head, STU tmp)
{
//1、 Apply for the node to be inserted
STU *pi = (STU *)calloc(1,sizeof(STU));
if(pi == NULL)
{
perror(calloc);
return head;
}
//2、 take tmp The data of Assign values to the *pi
*pi = tmp;
pi->next = NULL;
//3、 Insert the node into the end of the linked list
if(head == NULL)// The list does not exist
{
head = pi;
return head;
}
else// The linked list exists
{
//a、 Find the tail node of the linked list
STU *pb = head;
while(pb->next != NULL)// If it's not the tail node
pb = pb->next;//pb Just point to the next node
//b、 Use the tail node pb On link Inserted nodes pi
pb->next = pi;
return head;
}
return head;
}2、 Orderly insertion of linked list ( difficulty )
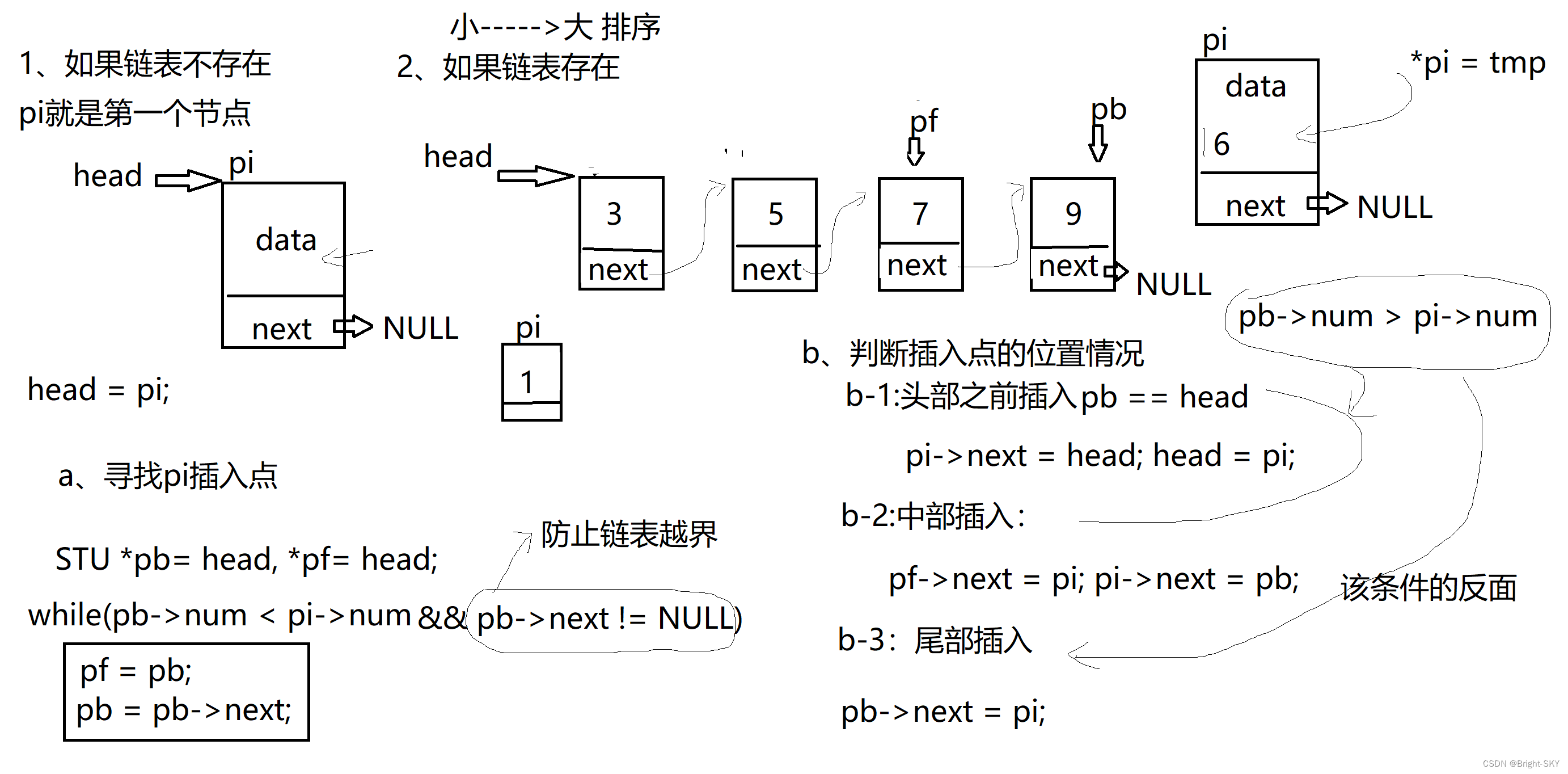
// Orderly insertion of linked list With num The order of ( Small ---> Big )
STU* insert_link(STU *head, STU tmp)
{
//1、 To the node to be inserted pi apply Heap space
STU *pi = (STU *)calloc(1,sizeof(STU));
if(pi == NULL)
{
perror("calloc");
return head;
}
//2、 take tmp The content of Assign a value to *pi
*pi = tmp;
pi->next = NULL;
//3、 List nodes pi Insertion
if(head == NULL)// The list does not exist
{
head = pi;
return head;
}
else// There is
{
//a、 Look for the insertion point
STU *pb = head, *pf = head;
while(pb->num < pi->num && pb->next != NULL)
{
pf = pb;
pb = pb->next;
}
//b、 Judgment of insertion point
if(pb->num >= pi->num)// Head Middle insert
{
if(pb == head)// Insert before the head
{
pi->next = head;
head = pi;
return head;
}
else// Middle insert
{
pf->next = pi;
pi->next = pb;
return head;
}
}
else// Tail insertion
{
pb->next = pi;
return head;
}
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 2【 The linked list queries a node 】 By name lookup
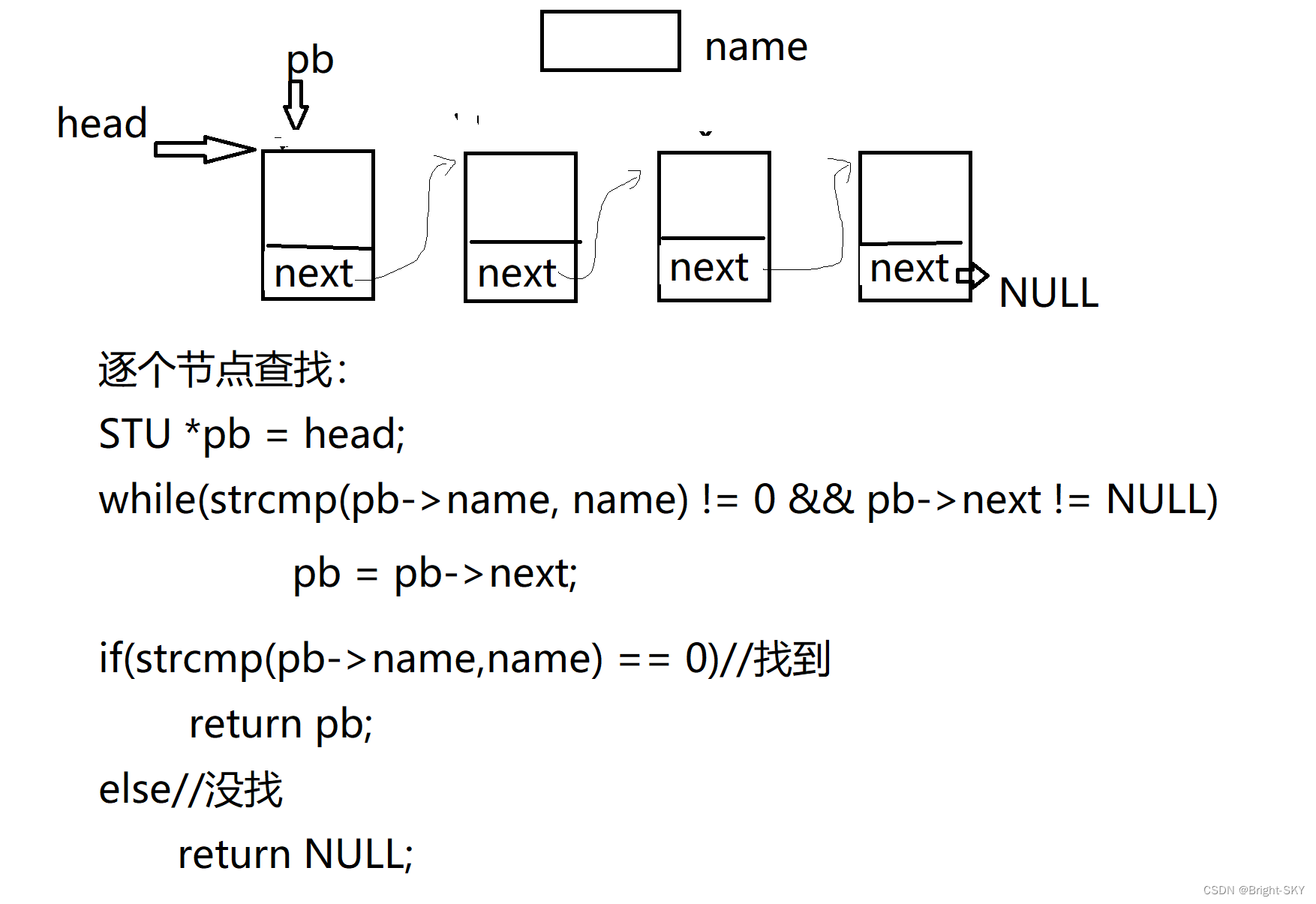
STU* search_link(STU *head, char *name)
{
//1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
if(head == NULL)// non-existent
{
printf("link not found\n");
return NULL;
}
else// The linked list exists
{
STU *pb = head;
// One by one name and name Compare If it's not equal pb=pb->next
while(strcmp(pb->name,name)!=0 && pb->next != NULL)
pb = pb->next;
// Determine if it is found
if(strcmp(pb->name,name)==0)// find
return pb;
else// Did not find
return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}Knowledge point 3【 Delete the specified node in the linked list 】
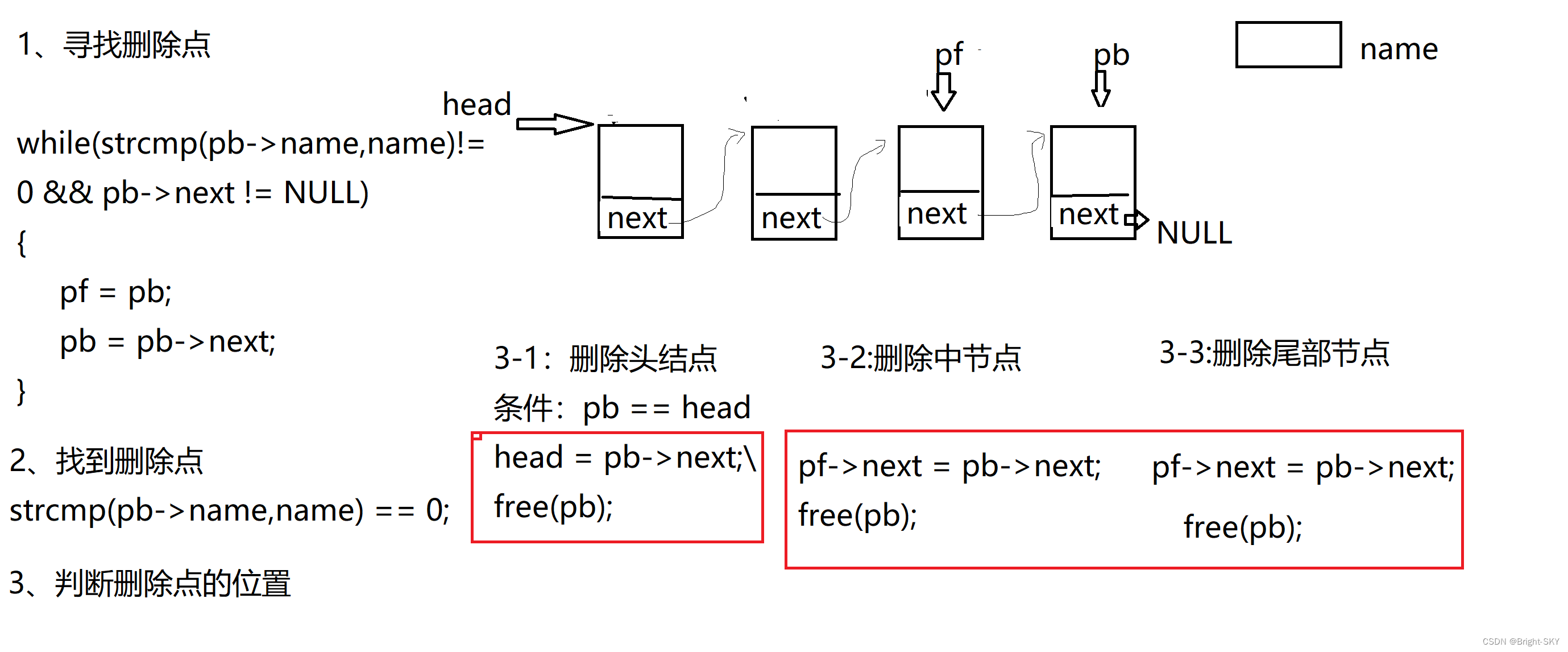
STU* detele_link(STU *head,char *name)
{
//1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
if(head == NULL)// non-existent
{
printf("link not found\n");
return head;
}
else// There is
{
//2、 Look for deletion points
STU *pf=head, *pb = head;
while(strcmp(pb->name,name)!=0 && pb->next != NULL)
{
pf = pb;
pb = pb->next;
}
//3、 Find the deletion point
if(strcmp(pb->name,name)==0)// Find the deletion point
{
//4、 Determine the location of deletion
if(pb == head)// Delete header node
{
head = pb->next;
free(pb);
}
else// In the middle or The tail node
{
pf->next = pb->next;
free(pb);
}
printf(" Successfully deleted %s Related nodes of \n",name);
return head;
}
else// No deletion point found
{
printf(" Not in the linked list %s Relevant data node information \n",name);
}
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 4【 Release of linked list 】
STU* free_link(STU *head)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("link not found\n");
return head;
}
else// The linked list exists
{
STU *pb = head;
// Release... Node by node
while(pb != NULL)
{
//head Save the location of the next node
head = pb->next;
// Release pb Node to
free(pb);
//pb Point to head
pb = head;
}
printf(" The linked list has been released \n");
return head;
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 5【 Take a look back. 】
Insertion of linked list : Insert before the head Tail insertion To insert in order
1、 For the inserted node pi To apply for space
2、 take tmp The value of is assigned to *pi *pi = tmp
3、 Determine whether the linked list There is
3-1: non-existent head = pi
3-2: There is ( Tail insertion To insert in order ) Look for the insertion point Specific installation location Insert node
Traversal of the list :
1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
1-1: non-existent Do nothing
1-2: There is Traverse node by node Be careful Don't cross the line .
Query of linked list :
1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
1-1: non-existent Do nothing
1-2: There is Compare node by node Return to the location successfully Be careful Don't cross the line .
Deletion of linked list nodes :
1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
1-1: non-existent Do nothing
1-2: There is Compare node by node Delete the specified node Be careful Don't cross the line .
Release list :
1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
1-1: non-existent Do nothing
1-2: There is Release node by node Be careful Don't cross the line
Knowledge point 6【 The reverse order of the linked list 】
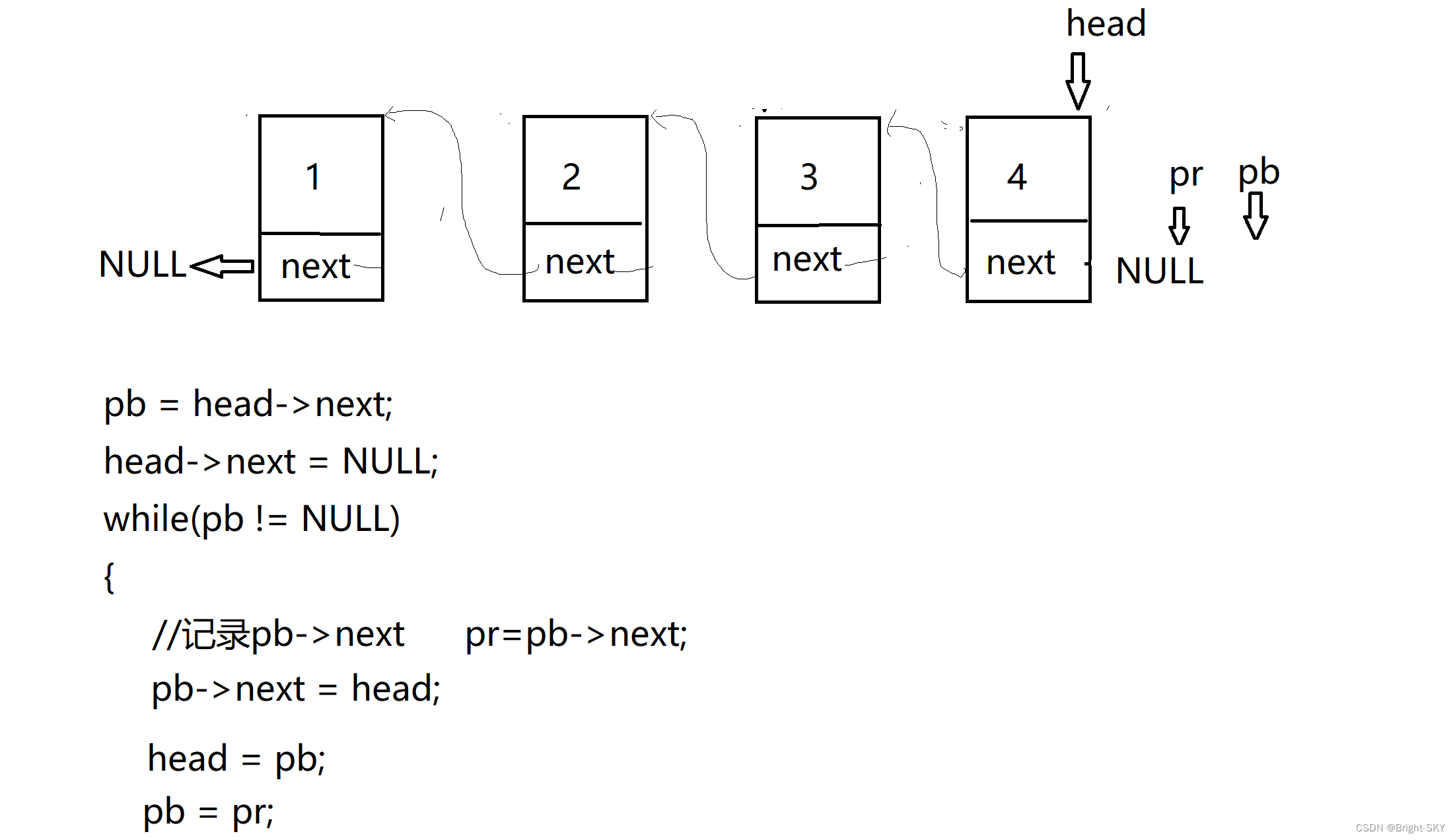
STU* reverse_link(STU *head)
{
// Determine whether the linked list exists
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("link not founf\n");
return head;
}
else// The linked list exists
{
//int *p,num;//p by int * , num by int
STU *pb,*pr;//pb by STU * , pr by STU *
//pb preservation head->next( reason head->next I'll set NULL)
pb = head->next;
// take head->next Set up NULL ( reason : Head node becomes tail node )
head->next = NULL;
while(pb != NULL)
{
//pr preservation pb->next ( reason :pb->next Will point to head)
pr = pb->next;
//pb->next Point to head ( reason : reverse direction )
pb->next = head;
// preservation Reverse the direction of the code Can be repeated perform
head = pb;
pb = pr;
}
return head;
}
return head;
}Knowledge point 7【 Sorting of linked lists 】
Sorting by selection :( Implemented as an array )

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10]={0};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int i=0,j=0,min=0;
printf(" Please enter %d individual int data \n",n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",arr+i);
}
// Sorting by selection
for(i=0;i<n-1; i++)
{
for(min=i,j=min+1; j<n;j++)
{
if(arr[min] > arr[j])
min = j;
}
if(min != i)
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[min];
arr[min]=tmp;
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}Running results :

Knowledge point 7【 Sorting of linked lists ( Selection method )】
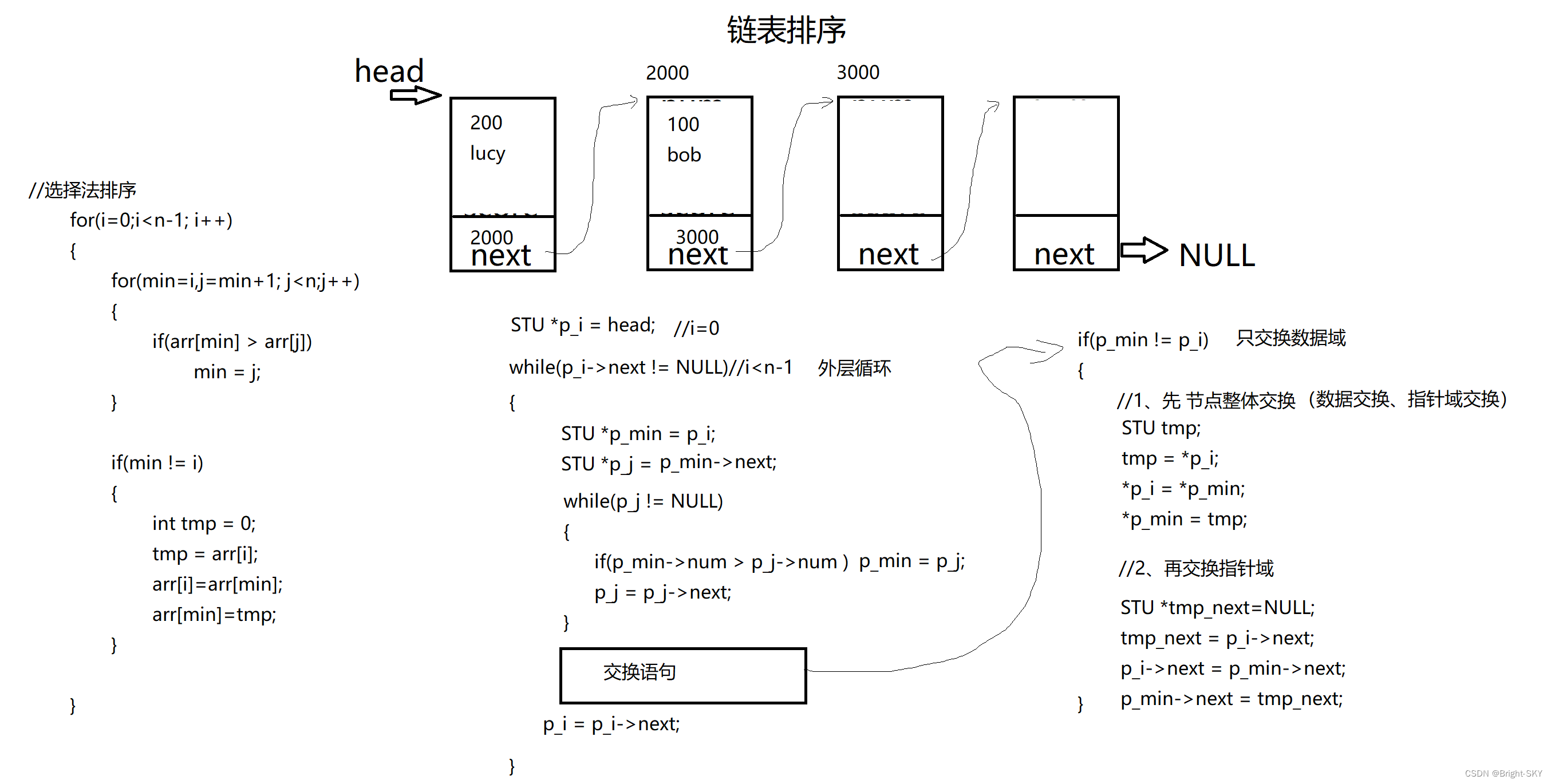
void sort_link(STU *head)
{
//1、 Determine whether the linked list exists
if(NULL == head)
{
printf("link not found\n");
return;
}
else
{
STU *p_i = head;//i=0
while(p_i->next != NULL)//i<n-1 The outer loop
{
STU *p_min = p_i;//min = i;
STU *p_j = p_min->next;//j = min+1
while(p_j != NULL)//j<n Inner circulation
{
// Looking for members num The minimum node
if(p_min->num > p_j->num)//if(arr[min] > arr[j])
p_min = p_j;//min = j
p_j = p_j->next;//j++
}
if(p_min != p_i)//min != i
{
// Exchange only data fields (1、 Overall exchange of node content 2、 Only exchange pointer fields )
//1、 Overall exchange of node content ( Data domain exchange 1 Time Pointer field Exchange 1 Time )
STU tmp;
tmp = *p_i;
*p_i = *p_min;
*p_min = tmp;
//2、 Only exchange pointer fields ( Pointer field Exchange 2 Time )
tmp.next = p_i->next;
p_i->next = p_min->next;
p_min->next = tmp.next;
}
p_i = p_i->next;//i++
}
}
}边栏推荐
- 宝塔的安装和flask项目部署
- Configure system environment variables through bat script
- 15 医疗挂号系统_【预约挂号】
- 018. Valid palindromes
- Take you back to spark ecosystem!
- Contrôle de l'exécution du module d'essai par panneau dans Canoe (primaire)
- Some thoughts on the study of 51 single chip microcomputer
- The 32 year old programmer left and was admitted by pinduoduo and foreign enterprises. After drying out his annual salary, he sighed: it's hard to choose
- There are software load balancing and hardware load balancing. Which one to choose?
- Some thoughts on the study of 51 single chip microcomputer
猜你喜欢
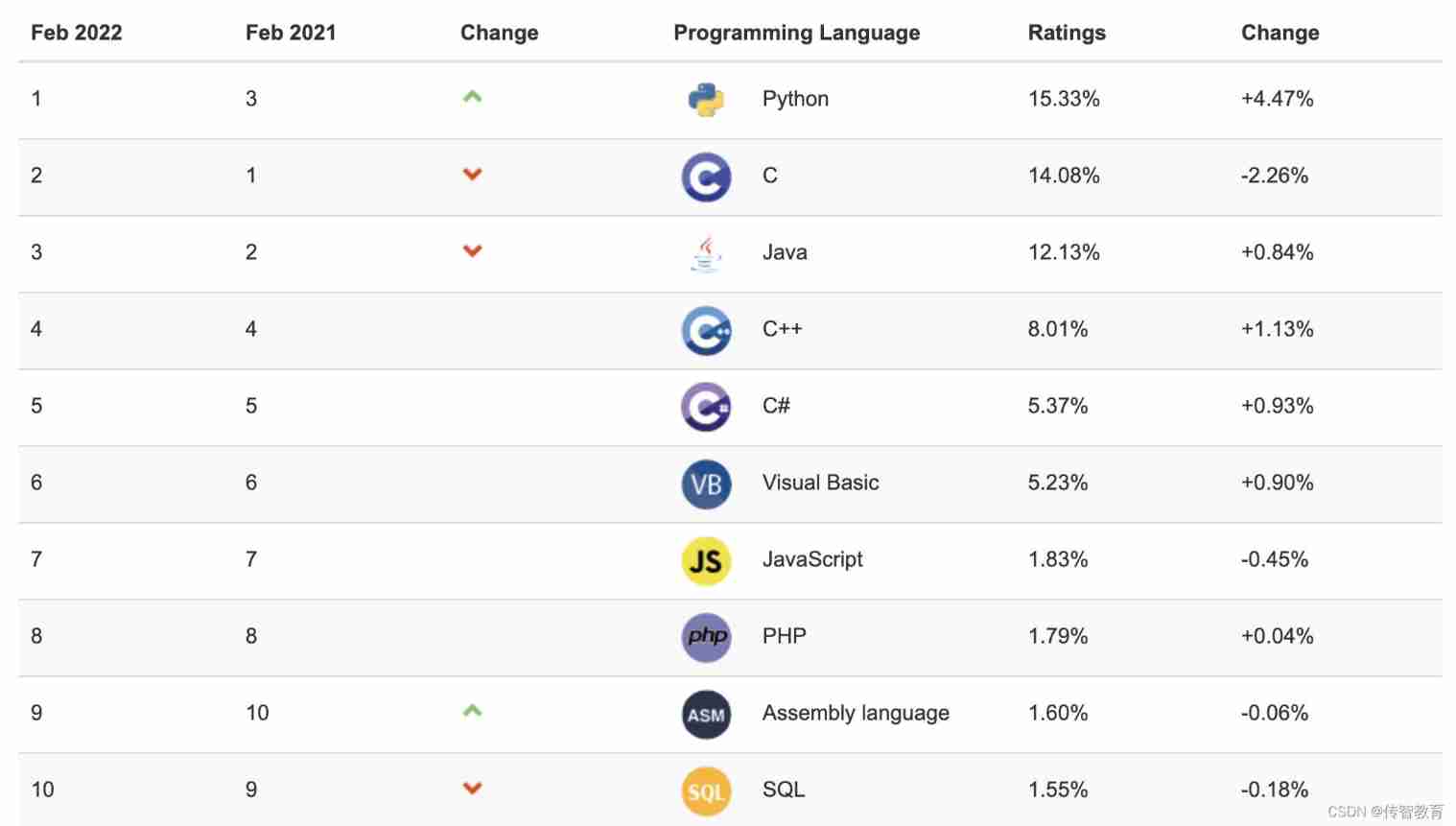
The programming ranking list came out in February. Is the result as you expected?
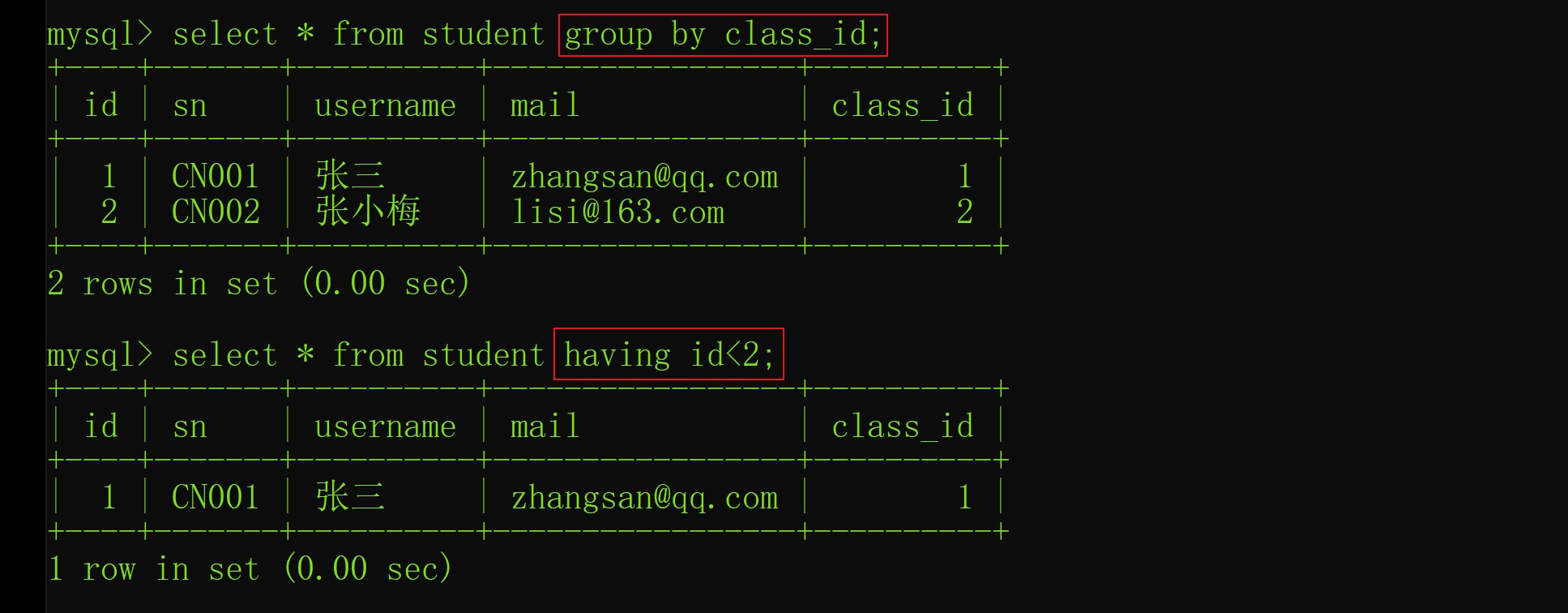
Interview shock 62: what are the precautions for group by?
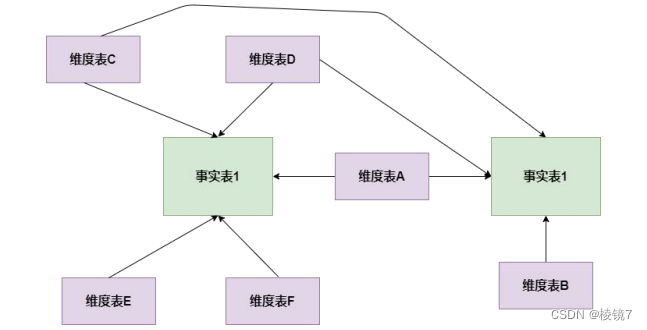
What are the models of data modeling
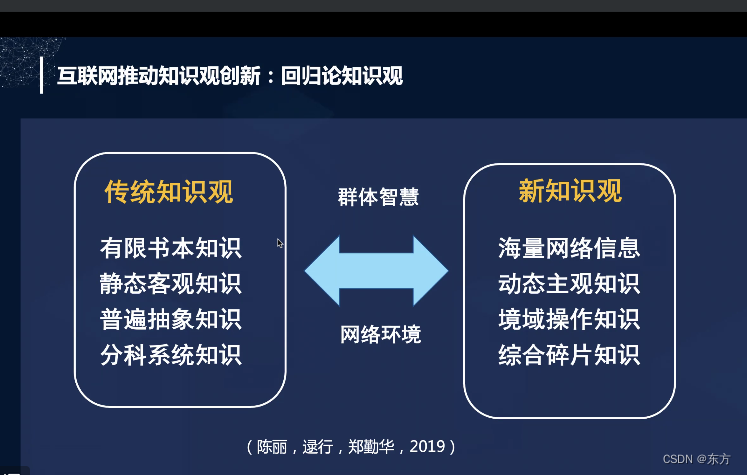
cmooc互联网+教育

51单片机进修的一些感悟

MapReduce instance (VIII): Map end join

MapReduce instance (x): chainmapreduce

C杂讲 动态链表操作 再讲
寶塔的安裝和flask項目部署

Programmation défensive en langage C dans le développement intégré
随机推荐
There are software load balancing and hardware load balancing. Which one to choose?
068. Find the insertion position -- binary search
CANoe的数据回放(Replay Block),还是要结合CAPL脚本才能说的明白
flask运维脚本(长时间运行)
Yarn organizational structure
Hero League rotation chart manual rotation
Canoe cannot automatically identify serial port number? Then encapsulate a DLL so that it must work
C杂讲 文件 续讲
Contest3145 - the 37th game of 2021 freshman individual training match_ B: Password
五月刷题01——数组
Tianmu MVC audit I
Southwest University: Hu hang - Analysis on learning behavior and learning effect
Function description of shell command parser
机械工程师和电气工程师方向哪个前景比较好?
The replay block of canoe still needs to be combined with CAPL script to make it clear
Zsh configuration file
Cap theory
Control the operation of the test module through the panel in canoe (Advanced)
C杂讲 动态链表操作 再讲
硬件工程师的真实前途我说出来可能你们不信